WPF学习之路(十一)布局(续)
布局实际上是一个Slot模型,其中每个父对象分配给子对象一个Slot,子对象可以自由占用Slot中的空间,通过Margin\VerticalAlignment\HorizontalAlignment控制
实例
<Border Background="LightBlue" BorderBrush="Black" BorderThickness="2" CornerRadius="45" Padding="25"> <StackPanel Name="SP1" Background="White"> <TextBlock FontSize="15" HorizontalAlignment="Center" Margin="0,0,0,15" Text="StackPanel1"></TextBlock> <Border BorderThickness="1" BorderBrush="Black"> <Button Margin="5,10,15,20">Normal</Button> </Border> <Border BorderThickness="1" BorderBrush="Black"> <Button Margin="5,10,15,20" HorizontalAlignment="Left"> <Button.LayoutTransform> <RotateTransform Angle="15" /> </Button.LayoutTransform> Left</Button> </Border> <Border BorderThickness="1" BorderBrush="Black"> <Button Margin="5,10,15,20" HorizontalAlignment="Right"> <Button.LayoutTransform> <RotateTransform Angle="45" /> </Button.LayoutTransform> Right</Button> </Border> <Border BorderThickness="1" BorderBrush="Black"> <Button Margin="5,10,15,20" HorizontalAlignment="Center"> <Button.LayoutTransform> <RotateTransform Angle="75" /> </Button.LayoutTransform> Center</Button> </Border> <Border BorderThickness="1" BorderBrush="Black"> <Button Margin="5,10,15,20" > <Button.LayoutTransform> <RotateTransform Angle="15" /> </Button.LayoutTransform> LayoutTransform </Button> </Border> <Border BorderThickness="1" BorderBrush="Black"> <Button Margin="5,10,15,20" > <Button.RenderTransform> <RotateTransform Angle="15" /> </Button.RenderTransform> RenderTransform </Button> </Border> </StackPanel> </Border>
注意LayoutTransform和RenderTransform的区别
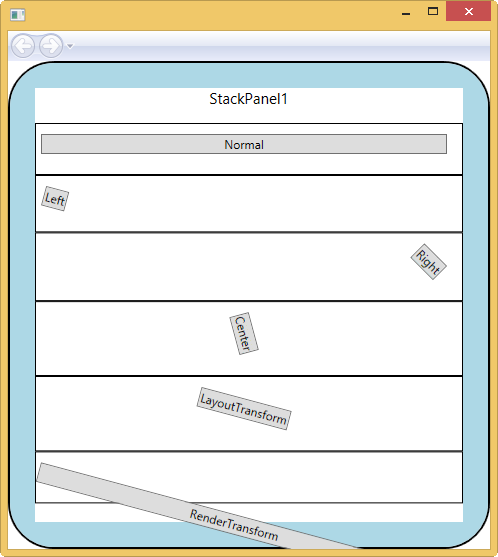
自定义布局
确定空间最佳尺寸经历两个阶段,1.测量,父元素询问子元素期望的尺寸,来确定自身尺寸 2.布置,父元素告知子元素的位置
具体实现为以下两个重载函数
protected override Size ArrangeOverride(Size arrangeBounds);
protected override Size MeasureOverride(Size constraint);
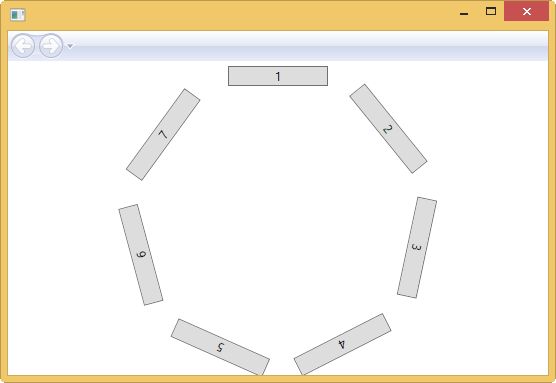
自定义CustomPanel
public class CustomPanel : Panel { public CustomPanel() : base() { } protected override Size MeasureOverride(Size availableSize) { double maxChildWidth = 0.0; double maxChildHeight = 0.0; foreach (UIElement child in InternalChildren) { child.Measure(availableSize); maxChildWidth = Math.Max(child.DesiredSize.Width, maxChildWidth); maxChildHeight = Math.Max(child.DesiredSize.Height, maxChildHeight); } double idealCircumference = maxChildWidth * InternalChildren.Count; double idealRadius = idealCircumference / (Math.PI * 2) + maxChildHeight; Size desired = new Size(idealRadius * 2, idealRadius * 2); if (!double.IsInfinity(availableSize.Width)) { if (availableSize.Width < desired.Width) desired.Width = availableSize.Width; } if (!double.IsInfinity(availableSize.Height)) { if (availableSize.Height < desired.Height) desired.Height = availableSize.Height; } return desired; } protected override Size ArrangeOverride(Size finalSize) { Rect layoutRect; if (finalSize.Width > finalSize.Height) { layoutRect = new Rect((finalSize.Width - finalSize.Height) / 2, 0, finalSize.Height, finalSize.Height); } else { layoutRect = new Rect((finalSize.Height - finalSize.Width) / 2, 0, finalSize.Width, finalSize.Width); } double angleInc = 360 / InternalChildren.Count; double angle = 0; foreach (UIElement child in InternalChildren) { Point childLocation = new Point(layoutRect.Left + (layoutRect.Width - child.DesiredSize.Width) / 2, layoutRect.Top); child.RenderTransform = new RotateTransform(angle, child.DesiredSize.Width / 2, finalSize.Height / 2 - layoutRect.Top); angle += angleInc; child.Arrange(new Rect(childLocation, child.DesiredSize)); } return finalSize; } }
<Page x:Class="Alex_WPFAPPDemo09.DemoPage" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006" xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008" xmlns:local="clr-namespace:Alex_WPFAPPDemo09" mc:Ignorable="d" d:DesignHeight="300" d:DesignWidth="300" Title="DemoPage"> <Grid Margin="5"> <local:CustomPanel> <Button Content="1" MinWidth="100" /> <Button Content="2" MinWidth="100" /> <Button Content="3" MinWidth="100" /> <Button Content="4" MinWidth="100" /> <Button Content="5" MinWidth="100" /> <Button Content="6" MinWidth="100" /> <Button Content="7" MinWidth="100" /> </local:CustomPanel> </Grid> </Page>
To be continue...