ELK集群搭建(二)
ELK集群部署(二)
ELK 是 elastic 公司旗下三款产品ElasticSearch、Logstash、Kibana的首字母组合,也即Elastic Stack包含ElasticSearch、Logstash、Kibana、Beats。ELK提供了一整套解决方案,并且都是开源软件,之间互相配合使用,完美衔接,高效的满足了很多场合的应用,是目前主流的一种日志系统。
ElasticSearch 一个基于 JSON 的分布式的搜索和分析引擎,作为 ELK 的核心,它集中存储数据,
用来搜索、分析、存储日志。它是分布式的,可以横向扩容,可以自动发现,索引自动分片
Logstash 一个动态数据收集管道,支持以 TCP/UDP/HTTP 多种方式收集数据(也可以接受 Beats 传输来的数据),
并对数据做进一步丰富或提取字段处理。用来采集日志,把日志解析为json格式交给ElasticSearch
Kibana 一个数据可视化组件,将收集的数据进行可视化展示(各种报表、图形化数据),并提供配置、管理 ELK 的界面
Beats 一个轻量型日志采集器,单一用途的数据传输平台,可以将多台机器的数据发送到 Logstash 或 ElasticSearch
X-Pack 一个对Elastic Stack提供了安全、警报、监控、报表、图表于一身的扩展包,不过收费
官网:https://www.elastic.co/cn/ ,中文文档:https://elkguide.elasticsearch.cn/
下载elk各组件的旧版本:
https://www.elastic.co/downloads/past-releases
环境准备
- 角色划分:
系统:CentOS 7
es主节点/es数据节点/kibana/head 192.168.30.128
es主节点/es数据节点/logstash 192.168.30.129
es主节点/es数据节点/filebeat 192.168.30.130
- 全部关闭防火墙和selinux:
# systemctl stop firewalld && systemctl disable firewalld
# sed -i 's/=enforcing/=disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config && setenforce 0
- 全部配置系统环境:
# vim /etc/security/limits.conf
* soft nofile 65536
* hard nofile 131072
* soft nproc 2048
* hard nproc 4096
# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
vm.max_map_count=655360
# sysctl -p
- 全部安装Java环境:
# tar zxf jdk-8u191-linux-x64.tar.gz && mv jdk1.8.0_191/ /usr/local/jdk
# vim /etc/profile
JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk
PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin:$JAVA_HOME/jre/bin
CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar:$JAVA_HOME/jre/lib
export JAVA_HOME PATH CLASSPATH
# source !$
# java -version
# ln -s /usr/local/jdk/bin/java /usr/local/bin/java
x-pack
- 安装x-pack:
# /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-plugin install x-pack
ERROR: this distribution of Elasticsearch contains X-Pack by default
ELK 6.3及更新版本已经默认安装x-pack,我们需要做的就是开启x-pack配置。
- 查看是否有x-pack:
# ls /usr/local/elasticsearch/modules/x-pack-core/x-pack-core-6.7.1.jar
/usr/local/elasticsearch/modules/x-pack-core/x-pack-core-6.7.1.jar
- 创建LicenseVerifier.java文件:
# vim LicenseVerifier.java
package org.elasticsearch.license;
import java.nio.*;
import org.elasticsearch.common.bytes.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.security.*;
import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.*;
import org.apache.lucene.util.*;
import org.elasticsearch.core.internal.io.*;
import java.io.*;
public class LicenseVerifier
{
public static boolean verifyLicense(final License license, final byte[] encryptedPublicKeyData) {
return true;
}
public static boolean verifyLicense(final License license) {
return true;
}
}
- 创建XPackBuild.java文件:
# vim XPackBuild.java
package org.elasticsearch.xpack.core;
import org.elasticsearch.common.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import org.elasticsearch.common.*;
import java.nio.file.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.jar.*;
public class XPackBuild
{
public static final XPackBuild CURRENT;
private String shortHash;
private String date;
@SuppressForbidden(reason = "looks up path of xpack.jar directly")
static Path getElasticsearchCodebase() {
final URL url = XPackBuild.class.getProtectionDomain().getCodeSource().getLocation();
try {
return PathUtils.get(url.toURI());
}
catch (URISyntaxException bogus) {
throw new RuntimeException(bogus);
}
}
XPackBuild(final String shortHash, final String date) {
this.shortHash = shortHash;
this.date = date;
}
public String shortHash() {
return this.shortHash;
}
public String date() {
return this.date;
}
static {
final Path path = getElasticsearchCodebase();
String shortHash = null;
String date = null;
Label_0157: {
shortHash = "Unknown";
date = "Unknown";
}
CURRENT = new XPackBuild(shortHash, date);
}
}
- 编译这两个文件:
# javac -cp "/usr/local/elasticsearch/lib/*:/usr/local/elasticsearch/modules/x-pack-core/x-pack-core-6.7.1.jar" LicenseVerifier.java
# javac -cp "/usr/local/elasticsearch/lib/*:/usr/local/elasticsearch/modules/x-pack-core/x-pack-core-6.7.1.jar" XPackBuild.java
会发现多出来两个class文件:LicenseVerifier.class,XPackBuild.class
- 覆盖这两个class文件:
# mkdir jar && cd jar/
# cp /usr/local/elasticsearch/modules/x-pack-core/x-pack-core-6.7.1.jar .
# jar xf x-pack-core-6.7.1.jar
# ls
logstash-index-template.json monitoring-es.json public.key triggered-watches.json
META-INF monitoring-kibana.json rollup-dynamic-template.json watches.json
monitoring-alerts.json monitoring-logstash.json security_audit_log.json watch-history.json
monitoring-beats.json org security-index-template.json x-pack-core-6.7.1.jar
# find ./ -name LicenseVerifier.class
./org/elasticsearch/license/LicenseVerifier.class
# find ./ -name XPackBuild.class
./org/elasticsearch/xpack/core/XPackBuild.class
# cp ../LicenseVerifier.class ./org/elasticsearch/license/LicenseVerifier.class
# cp ../XPackBuild.class ./org/elasticsearch/xpack/core/XPackBuild.class
- 重新打包,并替换原来的jar包:
# jar cf x-pack-core-6.7.1.jar ./*
# systemctl stop elasticsearch
# cp x-pack-core-6.7.1.jar /usr/local/elasticsearch/modules/x-pack-core/x-pack-core-6.7.1.jar
集群中所有elasticsearch节点都要替换x-pack的jar包,这一步需要注意elasticsearch启动问题。
- 导入授权文件:
先从官网申请basic授权文件,地址,填入邮箱地址,会发邮件给我们进行下载。
将下载的文件重命名为license.json,并做下面修改:
# vim license.json
"type":"platinum" #白金版
"expiry_date_in_millis":2524579200999 #截止日期2050年
# vim /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml #添加
xpack.security.enabled: false #关闭x-pack安全验证
# systemctl start elasticsearch
# curl -XPUT -u elastic 'http://192.168.30.128:9200/_xpack/license' -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d @license.json
Enter host password for user 'elastic': #默认密码是changeme
{"acknowledged":true,"license_status":"valid"}
# curl -XPUT -u elastic 'http://192.168.30.129:9200/_xpack/license' -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d @license.json
# curl -XPUT -u elastic 'http://192.168.30.130:9200/_xpack/license' -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d @license.json
集群所有节点全部替换license。另外,license.json 也可以通过kibana上传。
- 检验是否成功导入license:
# curl -XGET -u elastic:changeme "http://192.168.30.128:9200/_license"
{
"license" : {
"status" : "active",
"uid" : "5676803e-607b-40ee-809b-86edc32d6645",
"type" : "platinum",
"issue_date" : "2019-04-22T00:00:00.000Z",
"issue_date_in_millis" : 1555891200000,
"expiry_date" : "2049-12-31T16:00:00.999Z",
"expiry_date_in_millis" : 2524579200999,
"max_nodes" : 100,
"issued_to" : "l zx (111)",
"issuer" : "Web Form",
"start_date_in_millis" : 1555891200000
}
}
- 生成ssl证书:
# /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-certgen
Please enter the desired output file [certificate-bundle.zip]: elk.zip #保存证书的文件名
Enter instance name: elk #集群名
Enter name for directories and files [elk]: elk #创建证书的文件夹及文件名
Enter IP Addresses for instance (comma-separated if more than one) []: 192.168.30.128,192.168.30.129,192.168.30.130 #集群节点ip,逗号分隔
Enter DNS names for instance (comma-separated if more than one) []: elk-128,elk-129,elk-130 #集群节点名,逗号分隔
Would you like to specify another instance? Press 'y' to continue entering instance information: n #是否有其它实例
Certificates written to /software/elk.zip #证书文件路径
#为es集群创建证书颁发机构
# /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-certutil ca #直接回车
#为集群中节点生成证书和私钥
# /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-certutil cert --ca elastic-stack-ca.p12 #直接回车
# mkdir /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs
# cp *.p12 !$
#将证书拷贝到所有es节点
# scp -r !$ 192.168.30.129:!$ ;scp -r !$ 192.168.30.130:!$
如果生成证书设置了密码,需要将密码添加到elasticsearch秘钥库:
# /usr/local/elasticsearch-keystore add xpack.security.transport.ssl.keystore.secure_password
# /usr/local/elasticsearch-keystore add xpack.security.transport.ssl.truststore.secure_password
# unzip elk.zip
Archive: elk.zip
creating: ca/
inflating: ca/ca.crt
inflating: ca/ca.key
creating: elk/
inflating: elk/elk.crt
inflating: elk/elk.key
# mkdir /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/certs
# mv ca/* !$ && mv elk/* !$
# scp -r !$ 192.168.30.129:/usr/local/elasticsearch/config/; scp -r !$ 192.168.30.130:/usr/local/elasticsearch/config/
- 全部修改配置:
集群内所有elasticsearch机器
# vim /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml
xpack.security.enabled: true #打开x-pack安全验证
http.cors.allow-headers: Authorization,X-Requested-With,Content-Length,Content-Type #增加head
#开启ssl支持
xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled: true
xpack.ssl.key: certs/elk.key
xpack.ssl.certificate: certs/elk.crt
xpack.ssl.certificate_authorities: certs/ca.crt
# chown -R elk:elk /usr/local/elasticsearch
# systemctl restart elasticsearch
- 生成用户名和密码:
# /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-setup-passwords auto #自动生成(二选一)
# /usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-setup-passwords interactive #手动生成(二选一)
#自定义各个密码
Enter password for [elastic]: elk-2019
Reenter password for [elastic]: elk-2019
Enter password for [apm_system]: elk-2019
Reenter password for [apm_system]: elk-2019
Enter password for [kibana]: elk-2019
Reenter password for [kibana]: elk-2019
Enter password for [logstash_system]: elk-2019
Reenter password for [logstash_system]: elk-2019
Enter password for [beats_system]: elk-2019
Reenter password for [beats_system]: elk-2019
Enter password for [remote_monitoring_user]: elk-2019
Reenter password for [remote_monitoring_user]: elk-2019
- 修改kibana配置:
192.168.30.128
# vim /usr/local/kibana/config/kibana.yml
#elasticsearch账户和密码
elasticsearch.username: elastic
elasticsearch.password: elk-2019
# systemctl restart kibana
刷新kibana网页,可以看到需要登录账号及密码
输入前面配置的账号:elastic、密码:elk-2019,登录
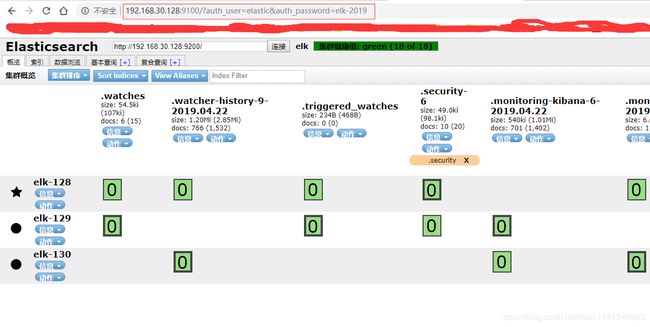
开启x-pack后访问head需要注意加上账号及密码,例如:
http://192.168.30.128:9100/?auth_user=elastic&auth_password=elk-2019
- 修改logstash配置:
192.168.30.129
# vim /usr/local/logstash/config/logstash.yml
xpack.monitoring.enabled: true
xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.username: logstash_system
xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.password: elk-2019
xpack.monitoring.elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://192.168.30.128:9200","http://192.168.30.129:9200","http://192.168.30.130:9200"]
xpack.monitoring.collection.interval: 10s
# systemctl restart logstash
另外,logstash收集日志时需要在output部分设定账号密码,否则无法登陆elasticsearch。
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://192.168.30.129:9200"]
user => "elastic"
password => "elk-2019"
}
- 修改filebeat配置:
192.168.30.130
# vim /usr/local/filebeat/filebeat.yml
setup.kibana:
host: "192.168.30.128:5601"
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["192.168.30.130:9200"] #可以是集群中其它es节点ip
username: "elastic"
password: "elk-2019"
# systemctl restart filebeat
metricbeat
- 安装metricbeat:
metricbeat用来监控系统资源,如CPU、内存、network等。
# wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/metricbeat/metricbeat-6.7.1-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
# tar zxf metricbeat-6.7.1-linux-x86_64.tar.gz && mv metricbeat-6.7.1-linux-x86_64 /usr/local/metricbeat
# vim /usr/local/metricbeat/metricbeat.yml
setup.kibana:
host: "192.168.30.128:5601"
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["192.168.30.128:9200"] #可以是集群中其它es节点ip
username: "elastic"
password: "elk-2019"
# cd /usr/local/metricbeat
# ./metricbeat modules enable system
# ./metricbeat setup
# nohup ./metricbeat -e &
- 配置metricbeat服务:
metricbeat服务文件
# vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/metricbeat.service
[Unit]
Description=Metricbeat is a lightweight shipper for metrics.
Documentation=https://www.elastic.co/products/beats/metricbeat
Wants=network-online.target
After=network-online.target
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/local/metricbeat/metricbeat -c /usr/local/metricbeat/metricbeat.yml -path.home /usr/local/metricbeat -path.config /usr/local/metricbeat -path.data /usr/local/metricbeat/data -path.logs /usr/local/metricbeat/logs
Restart=always
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
- 管理服务:
# systemctl daemon-reload
# systemctl enable metricbeat
# systemctl start metricbeat
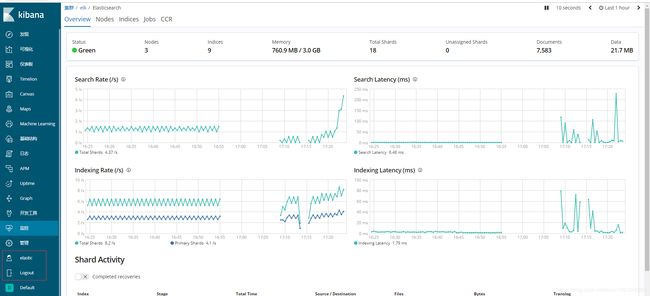
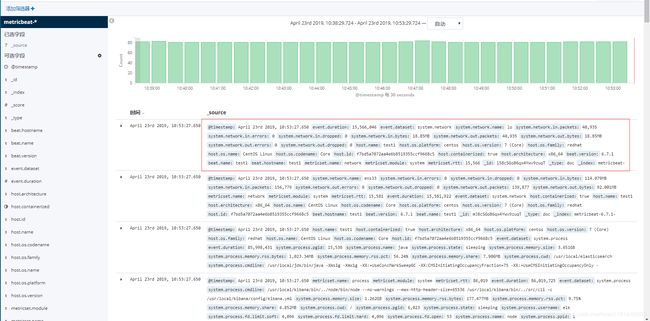
到kibana页面查看
logstash收集nginx日志
192.168.30.129
logstash收集nginx访问日志
- 示例1:
logstash收集nginx访问日志,以json格式。
配置nginx
# yum install -y nginx
# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
log_format json '{"@timestamp":"$time_iso8601",'
'"@version":"1",'
'"client":"$remote_addr",'
'"url":"$uri",'
'"status":"$status",'
'"domain":"$host",'
'"host":"$server_addr",'
'"size":"$body_bytes_sent",'
'"responsentime":"$request_time",'
'"referer":"$http_referer",'
'"useragent":"$http_user_agent"'
'}';
# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/elk.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name elk.test.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://192.168.30.128:5601;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
access_log /var/log/nginx/elk_access_json.log json;
}
配置logstash
# vim /usr/local/logstash/conf.d/nginx_access.conf
input {
file {
path => "/var/log/nginx/elk_access_json.log"
codec => "json"
start_position => "beginning"
type => "nginx_access"
}
}
filter {
json {
source => "message"
skip_on_invalid_json => true
}
}
output {
if [type] == "nginx_access" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.30.129:9200"]
user => "elastic"
password => "elk-2019"
index => "nginx-access.log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
}
启动logstash
# systemctl start nginx
# systemctl restart logstash
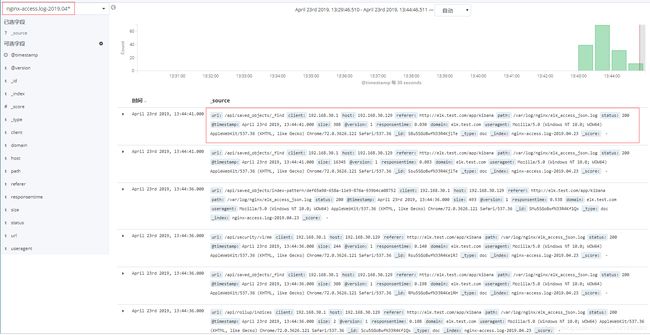
在kibana页面创建索引规则nginx-access.log-2019.04*
可以看到nginx-access.log-2019.04*日志内容是json格式的,继续在head上查看
logstash收集nginx错误日志
- 示例2:
logstash收集nginx错误日志。
配置nginx
# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log error;
# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/test.conf
erver { #将server改为erver
listen 80;
server_name elk.test.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://192.168.30.128:5601;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
access_log /var/log/nginx/elk_access_json.log json;
}
配置logstash
# vim /usr/local/logstash/conf.d/nginx_error.conf
input {
file {
path => "/var/log/nginx/error.log"
type => "nginx_error"
}
}
filter {
grok {
match => [ "message" , "(?%{YEAR}[./-]%{MONTHNUM}[./-]%{MONTHDAY}[- ]%{TIME}) \[%{LOGLEVEL:severity}\] %{POSINT:pid}#%{NUMBER}: (?:, client: (?%{IP}|%{HOSTNAME}))(?:, server: %{IPORHOST:server}?)(?:, request: %{QS:request})?(?:, upstream: (?\"%{URI}\"|%{QS}))?(?:, host: %{QS:request_host})?(?:, referrer: \"%{URI:referrer}\")?" ]
}
}
output {
if [type] == "nginx_error" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.30.129:9200"]
user => "elastic"
password => "elk-2019"
index => "nginx-error.log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
}
启动logstash
# /usr/sbin/nginx -t #生成error日志
nginx: [emerg] unknown directive "erver" in /etc/nginx/conf.d/test.conf:1
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test failed
# /usr/sbin/nginx -s reload
nginx: [emerg] unknown directive "erver" in /etc/nginx/conf.d/test.conf:1
# systemctl restart logstash
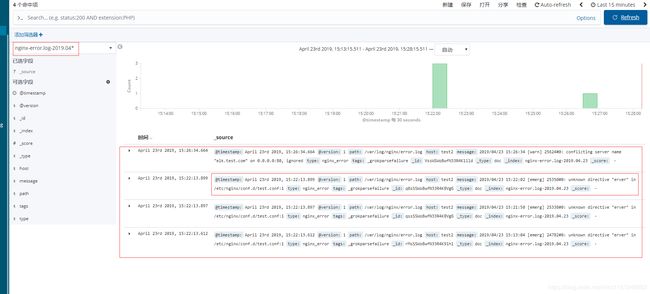
在kibana页面创建索引规则nginx-error.log-2019.04*
在head上查看
通过上面两个例子,就可以很方便的将nginx访问日志和错误日志收集起来,在kibana中展示并做过滤分析,或者在head中进行查询分析。
其实可以将上面logstash关于nginx的日志配置文件写成一个,用type作区分,使用if条件判断分别过滤收集nginx的日志。
logstash收集tomcat日志
192.168.30.129
* catalina开头的日志为Tomcat的综合日志,它记录Tomcat服务相关信息,也会记录错误日志
* host-manager和manager为管理相关的日志,其中host-manager为虚拟主机的管理日志
* localhost和localhost_access为虚拟主机相关日志,其中带access字样的为访问日志,
不带access字样的为默认主机的错误日志(访问日志默认不会生成,需要在server.xml中配置一下)
错误日志会统一记录到catalina.out中,出现问题应该首先查看它
logstash收集catalina日志和localhost_access_log日志(json格式)。
先手动安装tomcat:https://blog.csdn.net/miss1181248983/article/details/81080091 ,不建议yum安装。
- 配置tomcat:
# vim /usr/local/tomcat/conf/server.xml
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve" directory="logs"
prefix="localhost_access_log." suffix=".txt"
pattern="%h %l %u %t "%r" %s %b" />
改为
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve" directory="logs"
prefix="localhost_access_log" suffix=".log"
pattern="{"client":"%h", "client user":"%l", "authenticated":"%u", "access time":"%t", "method":"%r", "status":"%s", "send bytes":"%b", "Query?string":"%q", "partner":"%{Referer}i", "Agent version":"%{User-Agent}i"}" />
- 配置logstash:
# vim /usr/local/logstash/conf.d/tomcat.conf
input {
file {
path => "/usr/local/tomcat/logs/catalina.out"
start_position => "beginning"
sincedb_path => "/dev/null"
type => "catalina.out"
}
file {
path => "/usr/local/tomcat/logs/localhost_access_log*.log"
start_position => "beginning"
codec => "json"
sincedb_path => "/dev/null"
type => "localhost_access_log"
}
}
filter {
if [type] == "catalina.out" {
grok {
match => { "message" => "(\[\s?%{LOGLEVEL:level}\] %{DATA:class} %{DATA:logtime} - )?%{GREEDYDATA:message}" }
}
geoip {
source => "clientip"
}
}
if [type] == "localhost_access_log" {
grok {
match => { "message" => "(\[\s?%{LOGLEVEL:level}\] %{DATA:class} %{DATA:logtime} - )?%{GREEDYDATA:message}" }
}
json {
source => "message"
skip_on_invalid_json => true
}
}
}
output {
if [type] == "catalina.out" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.30.129:9200"]
user => "elastic"
password => "elk-2019"
index => "catalina.out-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
if [type] == "localhost_access_log" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.30.129:9200"]
user => "elastic"
password => "elk-2019"
index => "localhost_access_log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
}
- 启动logstash:
# /usr/local/tomcat/bin/startup.sh
# systemctl restart logstash
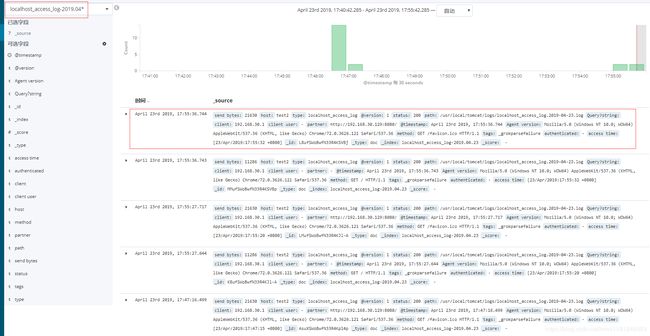
在kibana页面创建索引规则catalina.out-2019.04*和localhost_access_log-2019.04*
可以看到localhost_access_log-2019.04*日志内容是json格式的,继续在head上查看
生产环境下,可以将catalina.out日志级别设置为WARN或ERROR,也可以在logstash配置文件中设置关键字过滤出报错日志,从而得到tomcat运行过程中的报错信息。
logstash收集mysql日志
192.168.30.129
logstash收集mysql慢查询日志及错误日志。
先手动安装mysql:https://blog.csdn.net/miss1181248983/article/details/86621439 ,不建议yum安装。
- 配置mysql:
如果是按照上面方式安装的mysql,默认没有密码
#临时生效
# mysql
mysql> show variables like '%slow_query_log%';
+---------------------+----------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------------+----------------------------+
| slow_query_log | OFF | #默认慢查询日志是禁用的
| slow_query_log_file | /data/mysql/test2-slow.log |
+---------------------+----------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.08 sec)
mysql> set global slow_query_log=1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.34 sec)
mysql> show variables like '%slow_query_log%';
+---------------------+----------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------------+----------------------------+
| slow_query_log | ON |
| slow_query_log_file | /data/mysql/test2-slow.log |
+---------------------+----------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
#永久生效
# vim /etc/my.cnf
slow_query_log =1
slow_query_log_file=/data/mysql/test2-slow.log
long_query_time=3 #指定SQL语句最大执行时间,超过这个时间将被记录
#log_queries_not_using_indexes=1 #记录没有使用索引的查询语句到慢查询日志中
# systemctl restart mysqld.service
mysql> show variables like '%log_output%';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| log_output | FILE | #log_output='FILE'表示将日志存入文件,默认值是'FILE'。log_output='TABLE'表示将日志存入数据库
+---------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.02 sec)
mysql> show global status like '%slow_queries%';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| Slow_queries | 0 | #查询当前有多少条慢查询记录
+---------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.47 sec)
- 配置logstash:
# vim /usr/local/logstash/conf.d/mysql.conf
input {
file {
path => "/data/mysql/test2-slow.log"
start_position => "beginning"
type => "mysql_slow_file"
sincedb_path => "/dev/null"
codec => multiline {
pattern => "^# User@Host:"
negate => true
what => previous
}
}
file {
path => "/usr/local/mysql/log/error.log"
start_position => "beginning"
type => "mysql_error"
sincedb_path => "/dev/null"
}
}
filter {
if [type] == "mysql_slow_file" {
grok {
match => { "message" => "SELECT SLEEP" }
add_tag => [ "sleep_drop" ]
tag_on_failure => [] # prevent default _grokparsefailure tag on real records
}
if "sleep_drop" in [tags] {
drop {}
}
grok {
match => [ "message", "(?m)^# User@Host: %{USER:user}\[[^\]]+\] @ (?:(?\S*) )?\[(?:%{IP:clientip})?\]\s*# Query_time: %{NUMBER:query_time:float}\s+Lock_time: %{NUMBER:lock_time:float}\s+Rows_sent: %{NUMBER:rows_sent:int}\s+Rows_examined: %{NUMBER:rows_examined:int}\s*(?:use %{DATA:database};\s*)?SET timestamp=%{NUMBER:timestamp};\s*(?(?\w+)\s+.*)\n# Time:.*$" ]
}
date {
match => [ "timestamp", "UNIX" ]
remove_field => [ "timestamp" ]
}
}
if [type] == "mysql_error" {
grok {
match => [ 'message', "(?m)^%{NUMBER:date} *%{NOTSPACE:time} %{NUMBER:bytes} %{GREEDYDATA:message}" ]
overwrite => [ 'message' ]
add_field => { "timestamp" => "%{date}%{time}" }
}
}
}
output {
if [type] == "mysql_slow_file" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.30.129:9200"]
user => "elastic"
password => "elk-2019"
index => "mysql_slow.log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
if [type] == "mysql_error" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.30.129:9200"]
user => "elastic"
password => "elk-2019"
index => "mysql_error.log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
}
- 启动logstash:
# systemctl restart mysqld.service
# systemctl restart logstash
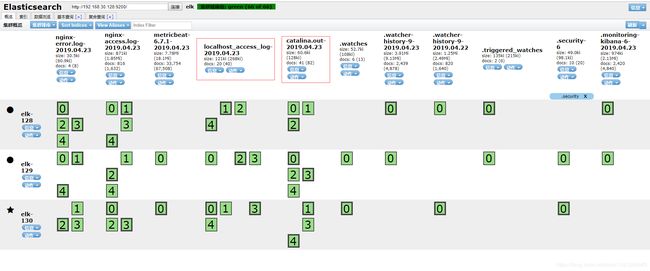
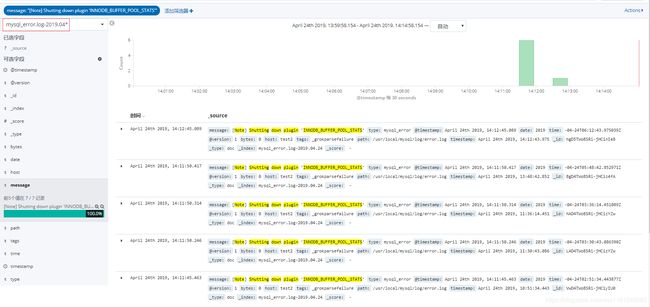
在kibana页面创建索引规则mysql_slow.log-2019.04*和mysql_error.log-2019.04*
# cat /data/mysql/test2-slow.log
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqld, Version: 5.7.25-log (MySQL Community Server (GPL)). started with:
Tcp port: 0 Unix socket: /usr/local/mysql/tmp/mysql.sock
Time Id Command Argument
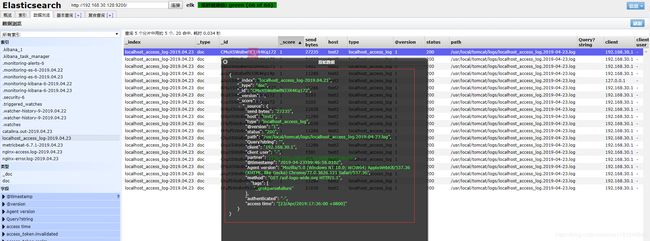
可以看到当前慢查询日志为空,继续在head上查看
通过上面几个例子,我们可以去收集常用应用的相关日志。当然,直接使用logstash是比较耗费资源的,更合适的方法是通过filebeat替代logstash-agent收集日志。下一步需要做的就是,将日志输出到Zabbix,实现错误日志告警。