在之前的文章我们介绍了一下 Java 中的 集合框架中的Collection 的泛型,本章我们来看一下 Java 集合框架中的Collection 的子接口 List。
Collection 接口有 3 种子类型,List、Set 和 Queue,其中 List 和 Set 的区别是 Set 中不能存放相同的元素,而 List 中可以,本章我们就来介绍一下 List。
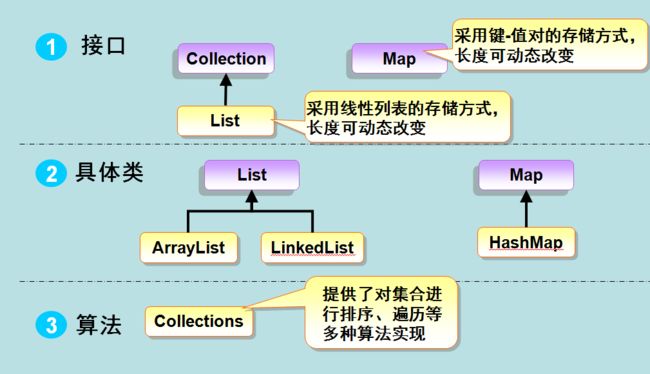
从上图我们可以知道 List 有两个实例类,ArrayList 和 LinkedList,
ArrayList 是数组实现,查找快,增上慢,由于是数组实现,在增和删的时候牵扯到数组的增容,以及靠背元素,所以慢,数组是可以直接按索引查找,所以查找时较快。
LinkedList 是链表实现,增删快,查找慢,由于链表实现,增加时只要让前一个元素记住自己就可以了,删除时让前一个元素记住后一个元素,后一个元素记住前一个元素,这样的增删效率高但查询时需要一个一个遍历,所以效率低。
LinkedList 我们可以形象的比作老式手表的链子,一节扣一节,增删时只需要打开两个之间的节扣即可,不需要牵扯到其他节扣。
ArrayList 和 LinkedList 都有各自的优缺点,在用的时候可以根据需求自行选择,避免性能消耗。在现在计算机计算能力越来越强,做的也不是大型项目的时候,这两个之间的性能差异我们其实是可以忽略的。
接下来我们就来看一下 List 接口的一些基础用法,如下:
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.List; 3 4 /** 5 * java.util.List 6 * 可重复集合,并且有序 7 * 特点是可以根据下表操作元素 8 * ArrayList:使用数组实现,查询更快 9 * LinkedList:使用链表实现,增删更快(收尾增删效果更明显) 10 */ 11 12 public class Main { 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 Listlist = new ArrayList (); 15 list.add("one"); 16 list.add("two"); 17 list.add("three"); 18 list.add("four"); 19 /** 20 * E set(int index, E e) 21 * 将给定元素设置到制定位置上,返回原位置的元素 22 * 所以是替换元素操作 23 * 如果超出了元素的长度,则使用 add 添加,否则编译错误 24 * */ 25 String old = list.set(1, "2"); // 将下标为 1 的元素改为 2,返回值则是被替换的元素 26 System.out.println(old); // two 27 System.out.println(list); // [one, 2, three, four] 28 29 /** 30 * E get(int index) 31 * 获取给定下标对应的元素 32 * */ 33 String two = list.get(1); // 获取第二个元素 34 System.out.println(two); // 2 35 36 /** 37 * 可以通过传统的循环遍历 List 集合 38 * */ 39 for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { 40 System.out.println(list.get(i)); // one 2 three four 41 } 42 } 43 }
在上面的代码中,我们通过 set 和 get 方法来设置和获取我们想要的下标的元素,当然还有其他方法,如下:
1 /** 2 * List 集合提供了一对重载的 add,remove 方法 3 * void add(int index, E e) 4 * 将给定元素插入到指定位置, 5 * 如果不指定下标,则插入到末尾 6 *7 * E remove(int index) 8 * 从集合中删除指定位置的元素,并将其返回 9 */ 10 11 public class Main { 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 List
list = new ArrayList (); 14 list.add("one"); 15 list.add("two"); 16 list.add("three"); 17 list.add("four"); 18 19 list.add(1, "2"); // 将下标为 1 的元素插入 2 20 System.out.println(list); // [one, 2, two, three, four] 21 22 String string = list.remove(1); // 将下标为 1 的元素删除,返回值为该元素 23 System.out.println(string); // 2 24 System.out.println(list); // [one, two, three, four] 25 } 26 }
我们在将 Collection 的时候讲过 add 和 remove 方法,在 List 中这两个方法被重载了,可以根据需求插入和删除想要删除的下标的元素,那如果我们想要获取两个下标之间的元素和删除两个下标之间的元素该怎么办呢,如下:
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.List; 3 4 public class Main { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 Listlist = new ArrayList (); 7 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 8 list.add(i); 9 } 10 System.out.println(list); // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] 11 List subList = list.subList(2, 5); // 获取下标从 2 到 5 的元素,含 2 不含 5 12 System.out.println(subList); // [2, 3, 4] 13 // 将 subList 中每个元素扩大 10 倍 14 for (int i = 0; i < subList.size(); i++) { 15 subList.set(i, subList.get(i) * 10); 16 } 17 System.out.println(subList); // [20, 30, 40] 18 /** 19 * 对子集的修改,就是修改原集合相应内容 20 * */ 21 System.out.println(list); // [0, 1, 20, 30, 40, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] 22 /** 23 * 删除集合中 2-5 的元素 24 * */ 25 list.subList(2, 5).clear(); 26 System.out.println(list); // [0, 1, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] 27 } 28 }
我们说集合和数组有很多相似的地方,那课可以进行相互转换呢,当然是可以的,如下:
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.Collection; 3 4 public class Main { 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 Collectioncollection = new ArrayList (); 7 collection.add("one"); 8 collection.add("two"); 9 collection.add("three"); 10 collection.add("four"); 11 System.out.println(collection); // [one, two, three, four] 12 /** 13 * 集合提供了一个 toArray,可以将当前集合转换为数组 14 * */ 15 // Object[] array = collection.toArray(); // 不常用 16 /** 17 * collection.size() 表示要转换的数组的 length 18 * 如果大于给定的 collection 的 size,则自动填充完整 array 19 * 如果小于给定的 collection 的 size,则自动创建给你一样长度的 size 20 * */ 21 String[] array = collection.toArray(new String[collection.size()]); 22 System.out.println(array.length); // 4 23 for (String string : array) { 24 System.out.println(string); // one two three four 25 } 26 27 String[] array1 = collection.toArray(new String[6]); 28 System.out.println(array.length); // 4 29 for (String string : array1) { 30 System.out.println(string); // one two three four null null 31 } 32 33 String[] array2 = collection.toArray(new String[1]); 34 System.out.println(array.length); // 4 35 for (String string : array2) { 36 System.out.println(string); // one two three four 37 } 38 } 39 }
在上面的代码中我们实现了集合转换为数组的方法,接下来我们再看一下数组转换为集合的方法:
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.Arrays; 3 import java.util.List; 4 5 /** 6 * 数组转换为集合 7 * 需要注意,转换只能转换为 List 集合 8 * 使用的是数组的工具类 Arrays 的静态方法 asList 9 * 只能转换为 List 集合的主要原因是:Set 不能存放重复元素 10 * 所以若转换为 Set 集合可能会出现丢失元素的情况 11 */ 12 public class Main { 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 String[] array = {"one", "two", "three", "four"}; 15 Listlist = Arrays.asList(array); 16 System.out.println(list); // [one, two, three, four] 17 18 /** 19 * 向集合中添加元素,会出现编译错误 20 * 相当于在原数组添加元素 21 * 该集合时由数组转换过来的,那么该集合就表示原来的数组 22 * 所以对集合的操作就是对数组的操作 23 * 那么添加元素会导致原数组扩容 24 * 那么久不能表示原来的数组了 25 * 所以不允许向该集合添加元素 26 */ 27 // list.add("five"); // 编译错误 Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException 28 29 /** 30 * 若希望增删元素,需要另外创建一个集合 31 * */ 32 /** 33 * 所有的集合都提供了一个带有 Collection 类型参数的构造方法 34 * 该构造方法称为:复制构造器 35 * 作用是在创建当前集合的同时, 36 * 集合中包含给定集合中的所有元素 37 * */ 38 // List list1 = new ArrayList // 复制构造器,一步到位 39 List(list); list1 = new ArrayList (); 40 list1.addAll(list); 41 list1.add("five"); 42 System.out.println(list1); // [one, 2, three, four, five] 43 44 /** 45 * 修改集合元素,数组元素也会改变 46 * */ 47 list.set(1, "2"); 48 System.out.println(list); // [one, 2, three, four] 49 for (String string : array) { 50 System.out.println(string); // one 2 three four 51 } 52 } 53 }