lwIP TCP/IP 协议栈笔记之十九: JPerf 工具测试网速
目录
1. iPerf 与JPerf
2. 测试网络速度
2.1 获取JPerf 网络测速工具
2.2 测试开发板接收速度(NETCONN API)
2.3 测试开发板接收速度(Socket API)
2.4 测试开发板发送速度(NETCONN API)
2.5 测试开发板发送速度(Socket API)
2.6. 测试开发板收发速度(apps\lwiperf)
3. 提高LwIP 网络传输的速度
1. iPerf 与JPerf
iPerf 是一个跨平台的网络性能测试工具,它支持Win/Linux/Mac/Android/iOS 等平台,iPerf 可以测试TCP 和UDP(我们一般不对UDP 进行测速)带宽质量,iPerf 可以测量最大TCP 带宽,可以具有多种参数进行测试,同时iPerf 还可以报告带宽,延迟抖动和数据包丢失的情况,我们可以利用iPerf的这些特性来测试一些网络设备如路由器,防火墙,交换机等的性能。
iper3的使用可以见之前的文章:https://blog.csdn.net/XieWinter/article/details/91422595
虽然iPerf 很好用,但是它却是命令行格式的软件,对使用测试的人员并不友好,使用者需要记下他繁琐的命令,不过它还有一个图形界面程序叫做JPerf,使用JPerf 程序能简化了复杂命令行参数的构造,而且 它还保存测试结果,并且将测试结果实时图形化出来,更加一目了然,当然,JPerf 也肯定拥有iPerf 的所有功能,本质执行的iperf的功能。
2. 测试网络速度
2.1 获取JPerf 网络测速工具
获取工具,
参考下载链接:https://sourceforge.net/projects/jperf/
http://www.firebbs.cn/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=26274&fromuid=37393
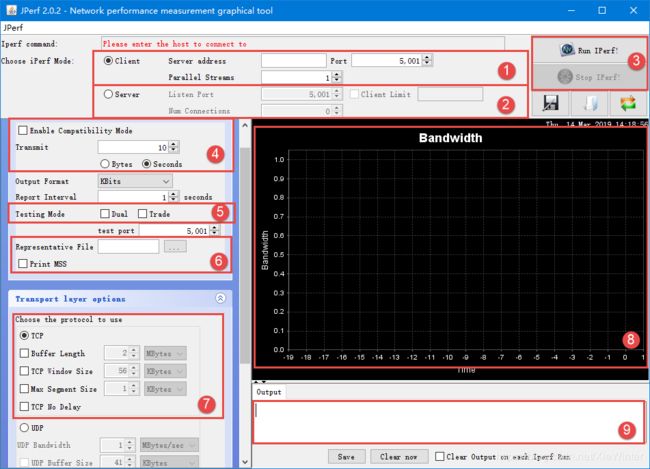
下载后解压,双击jperf.bat 运行,稍等一会就出现JPerf 的界面,工具依赖JAVA 运行环境(Java Runtime Environment),需要提前下载安装好(可百度搜索,或参考链接:https://java-runtime-environment.en.softonic.com/)
(1):客户端设置,电脑作为客户端,连接到服务器中(即我们的开发板作为服务器),服务器地址需要填写正确,端口号默认是5001,并发流默认是1 个。
(2):服务器设置,电脑作为服务器,我们的开发板作为客户端,client limit 选项表示仅允许指定客户端连接,Num Connections 指定最大允许连接的数量,为0 不限制。
(3):开始和停止JPerf 的运行。
(4):兼容旧版本(当server 端和client 端版本不一样时使用),默认不勾选,Transmit 设置测试模式,我们一般指定发送的时间,以秒为单位,当然也可以指定发送的数据大小,以字节为单位。
(5):如果勾选Dual 表示同时进行双向传输测试,如果勾选Trade 表示单独进行双向传输测试,默认不勾选。
(6):指定需要传输的文件以及显示最大TCP 报文段。
(7):传输层设置,我们一般用来测试TCP 连接的速度,Buffer Length 选项用于设置缓冲区大小,TCP Window Size 用于指定TCP 窗口大小,Max Segment Size 用于设定最大MTU 值,TCP No Delay 用于设定TCP 不延时。
(8):网速显示窗口,以折线图的形式显示出来。
(9):网速相关数据输出窗口,以文本的形式。
2.2 测试开发板接收速度(NETCONN API)
/* FreeRTOSÍ·Îļþ */
#include "FreeRTOS.h"
#include "task.h"
#include "queue.h"
#include "semphr.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include "iperf.h"
#include "lwip/opt.h"
#include "lwip/sys.h"
#include "lwip/api.h"
#define IPERF_PORT 5001
#define IPERF_BUFSZ (4 * 1024)
void iperf_server(void *thread_param)
{
struct netconn *conn, *newconn;
err_t err;
void* recv_data;
recv_data = (void *)pvPortMalloc(IPERF_BUFSZ);
if (recv_data == NULL)
{
printf("No memory\n");
}
conn = netconn_new(NETCONN_TCP);
netconn_bind(conn, IP_ADDR_ANY, 5001);
LWIP_ERROR("tcpecho: invalid conn", (conn != NULL), return;);
/* Tell connection to go into listening mode. */
netconn_listen(conn);
while (1) {
/* Grab new connection. */
err = netconn_accept(conn, &newconn);
/*printf("accepted new connection %p\n", newconn);*/
/* Process the new connection. */
if (err == ERR_OK) {
struct netbuf *buf;
// void *data;
u16_t len;
while ((err = netconn_recv(newconn, &buf)) == ERR_OK) {
/*printf("Recved\n");*/
do {
netbuf_data(buf, &recv_data, &len);
// err = netconn_write(newconn, data, len, NETCONN_COPY);
} while (netbuf_next(buf) >= 0);
netbuf_delete(buf);
}
/*printf("Got EOF, looping\n");*/
/* Close connection and discard connection identifier. */
netconn_close(newconn);
netconn_delete(newconn);
}
}
}
void
iperf_server_init(void)
{
sys_thread_new("iperf_server", iperf_server, NULL, 2048, 4);
}
2.3 测试开发板接收速度(Socket API)
/* FreeRTOSÍ·Îļþ */
#include "FreeRTOS.h"
#include "task.h"
#include "queue.h"
#include "semphr.h"
#include
#include
//#include
#include
//#include
//#include "netdb.h"
#include "iperf.h"
#include "lwip/opt.h"
#include "lwip/sys.h"
#include "lwip/api.h"
#define IPERF_PORT 5001
#define IPERF_BUFSZ (4 * 1024)
void iperf_server(void *thread_param)
{
uint8_t *recv_data;
socklen_t sin_size;
uint32_t tick1, tick2;
int sock = -1, connected, bytes_received;
uint64_t recvlen;
struct sockaddr_in server_addr, client_addr;
char speed[32] = { 0 };
fd_set readset;
struct timeval timeout;
recv_data = (uint8_t *)pvPortMalloc(IPERF_BUFSZ);
if (recv_data == NULL)
{
printf("No memory\n");
goto __exit;
}
sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (sock < 0)
{
printf("Socket error\n");
goto __exit;
}
server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
server_addr.sin_port = htons(IPERF_PORT);
memset(&(server_addr.sin_zero), 0x0, sizeof(server_addr.sin_zero));
if (bind(sock, (struct sockaddr *)&server_addr, sizeof(struct sockaddr)) == -1)
{
printf("Unable to bind\n");
goto __exit;
}
if (listen(sock, 5) == -1)
{
printf("Listen error\n");
goto __exit;
}
timeout.tv_sec = 3;
timeout.tv_usec = 0;
printf("iperf_server\n");
while (1)
{
FD_ZERO(&readset);
FD_SET(sock, &readset);
if (select(sock + 1, &readset, NULL, NULL, &timeout) == 0)
continue;
printf("iperf_server\n");
sin_size = sizeof(struct sockaddr_in);
connected = accept(sock, (struct sockaddr *)&client_addr, &sin_size);
printf("new client connected from (%s, %d)\n",
inet_ntoa(client_addr.sin_addr), ntohs(client_addr.sin_port));
{
int flag = 1;
setsockopt(connected,
IPPROTO_TCP, /* set option at TCP level */
TCP_NODELAY, /* name of option */
(void *) &flag, /* the cast is historical cruft */
sizeof(int)); /* length of option value */
}
recvlen = 0;
tick1 = xTaskGetTickCount();
while (1)
{
bytes_received = recv(connected, recv_data, IPERF_BUFSZ, 0);
if (bytes_received <= 0) break;
recvlen += bytes_received;
tick2 = xTaskGetTickCount();
if (tick2 - tick1 >= configTICK_RATE_HZ * 5)
{
float f;
f = (float)(recvlen * configTICK_RATE_HZ / 125 / (tick2 - tick1));
f /= 1000.0f;
// snprintf(speed, sizeof(speed), "%.4f Mbps!\n", f);
// printf("%s", speed);
tick1 = tick2;
recvlen = 0;
}
}
if (connected >= 0) closesocket(connected);
connected = -1;
}
__exit:
if (sock >= 0) closesocket(sock);
if (recv_data) free(recv_data);
}
void
iperf_server_init(void)
{
sys_thread_new("iperf_server", iperf_server, NULL, 2048, 4);
}
2.4 测试开发板发送速度(NETCONN API)
#include "iperf_client.h"
#include "lwip/opt.h"
#include "lwip/sys.h"
#include "lwip/api.h"
#define IPERF_PORT 5001
#define IPERF_BUFSZ (4 * 1024)
static void iperf_client(void *thread_param)
{
struct netconn *conn;
int i;
int ret;
uint8_t *send_buf;
uint64_t sentlen;
u32_t tick1, tick2;
ip4_addr_t ipaddr;
send_buf = (uint8_t *) pvPortMalloc(IPERF_BUFSZ);
if (!send_buf) return ;
for (i = 0; i < IPERF_BUFSZ; i ++)
send_buf[i] = i & 0xff;
while(1)
{
conn = netconn_new(NETCONN_TCP);
if (conn == NULL)
{
printf("create conn failed!\n");
vTaskDelay(10);
continue;
}
IP4_ADDR(&ipaddr,192,168,0,181);
ret = netconn_connect(conn,&ipaddr,5001);
if (ret == -1)
{
printf("Connect failed!\n");
netconn_close(conn);
vTaskDelay(10);
continue;
}
printf("Connect to iperf server successful!\n");
tick1 = sys_now();
while (1)
{
tick2 = sys_now();
if(tick2 - tick1 >= configTICK_RATE_HZ * 5)
{
float f;
f = (float)(sentlen*configTICK_RATE_HZ/125/(tick2 - tick1));
f /= 1000.0f;
printf("send speed = %.4f Mbps!\n", f);
tick1 = tick2;
sentlen = 0;
}
ret = netconn_write(conn,send_buf,IPERF_BUFSZ,0);
if (ret == ERR_OK)
{
sentlen += IPERF_BUFSZ;
}
}
// netconn_close(conn);
// netconn_delete(conn);
}
}
void
iperf_client_init(void)
{
sys_thread_new("iperf_client", iperf_client, NULL, 2048, 4);
}2.5 测试开发板发送速度(Socket API)
#include "iperf_client.h"
#include "lwip/opt.h"
#include "lwip/sys.h"
#include "lwip/api.h"
#include
#define PORT 5001
#define IP_ADDR "192.168.0.181"
#define IPERF_BUFSZ (4 * 1024)
static void iperf_client(void *thread_param)
{
int sock = -1,i;
struct sockaddr_in client_addr;
uint8_t* send_buf;
u32_t tick1, tick2;
uint64_t sentlen;
send_buf = (uint8_t *) pvPortMalloc(IPERF_BUFSZ);
if (!send_buf)
return ;
for(i = 0; i < IPERF_BUFSZ; i ++)
send_buf[i] = i & 0xff;
while(1)
{
sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (sock < 0)
{
printf("Socket error\n");
vTaskDelay(10);
continue;
}
client_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
client_addr.sin_port = htons(PORT);
client_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(IP_ADDR);
memset(&(client_addr.sin_zero), 0, sizeof(client_addr.sin_zero));
if (connect(sock,
(struct sockaddr *)&client_addr,
sizeof(struct sockaddr)) == -1)
{
printf("Connect failed!\n");
closesocket(sock);
vTaskDelay(10);
continue;
}
printf("Connect to iperf server successful!\n");
tick1 = sys_now();
while (1)
{
tick2 = sys_now();
if(tick2 - tick1 >= configTICK_RATE_HZ * 5)
{
float f;
f = (float)(sentlen*configTICK_RATE_HZ/125/(tick2 - tick1));
f /= 1000.0f;
printf("send speed = %.4f Mbps!\n", f);
tick1 = tick2;
sentlen = 0;
}
if(write(sock,send_buf,IPERF_BUFSZ) < 0)
break;
else
{
sentlen += IPERF_BUFSZ;
}
}
closesocket(sock);
}
}
void
iperf_client_init(void)
{
sys_thread_new("iperf_client", iperf_client, NULL, 2048, 8);
} 2.6. 测试开发板收发速度(apps\lwiperf)
直接使用官方应用代码API
// 初始化配置一次就可以
void lwiperf_example_init(void);#include "lwip/apps/lwiperf.h"
#include "lwiperf_example.h"
#if LWIP_TCP
static void
lwiperf_report(void *arg, enum lwiperf_report_type report_type,
const ip_addr_t* local_addr, u16_t local_port, const ip_addr_t* remote_addr, u16_t remote_port,
u32_t bytes_transferred, u32_t ms_duration, u32_t bandwidth_kbitpsec)
{
LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(arg);
LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(local_addr);
LWIP_UNUSED_ARG(local_port);
printf("IPERF report: type=%d, remote: %s:%d, total bytes: %"U32_F", duration in ms: %"U32_F", kbits/s: %"U32_F"\n",
(int)report_type, ipaddr_ntoa(remote_addr), (int)remote_port, bytes_transferred, ms_duration, bandwidth_kbitpsec);
}
#endif /* LWIP_TCP */
void
lwiperf_example_init(void)
{
#if LWIP_TCP
ip4_addr_t ipaddr;
lwiperf_start_tcp_server_default(lwiperf_report, NULL);
// IP4_ADDR(&ipaddr,192,168,0,181);
// lwiperf_start_tcp_client_default(&ipaddr, lwiperf_report, NULL);
#endif
}3. 提高LwIP 网络传输的速度
- 如果按照LwIP 默认的配置,是远不可能达到我们实验所显示的速度的,因为还没优化,那肯定也是不稳定的,下面我们来看看优化的参数,首先,网速必然受限于硬件,只有硬件是很好的,那么软件才能优化的更好,网卡肯定要选择好一点的网卡,然后在工程中的stm32f4xx_hal_config.h 文件中配置以太网发送和接收的缓冲区大小,默认是4,我们可以稍微改大一点。
stm32f4xx_hal_config.h
#define ETH_RXBUFNB ((uint32_t)8U) /* 4 Rx buffers of size ETH_RX_BUF_SIZE */
#define ETH_TXBUFNB ((uint32_t)8U) /* 4 Tx buffers of size ETH_TX_BUF_SIZE */
- 此外,还需在lwipopts.h 文件中配置LwIP 的参数
首先,我们对LwIP 管理的内存肯定要分配的大一些,而对于发送数据是存储在ROM或者静态存储区的时候,还要将MEMP_NUM_PBUF 宏定义改的大一点,当然发送缓冲区大小和发送缓冲区队列长度决定了发送速度的大小,根据不同需求进行配置,并且需要不断调试,而对于接收数据的配置,应该配置TCP 缓冲队列中的报文段数量与TCP 接收窗口大小,特别是接收窗口的大小,这直接可以影响数据的接收速度。
/* MEM_SIZE: the size of the heap memory. If the application will send
a lot of data that needs to be copied, this should be set high. */
#define MEM_SIZE (25*1024)
/* MEMP_NUM_PBUF: the number of memp struct pbufs. If the application
sends a lot of data out of ROM (or other static memory), this
should be set high. */
#define MEMP_NUM_PBUF 25
/* ---------- Pbuf options ---------- */
/* PBUF_POOL_SIZE: the number of buffers in the pbuf pool. */
#define PBUF_POOL_SIZE 65
/* PBUF_POOL_BUFSIZE: the size of each pbuf in the pbuf pool. */
#define PBUF_POOL_BUFSIZE LWIP_MEM_ALIGN_SIZE(TCP_MSS+40+PBUF_LINK_ENCAPSULATION_HLEN+PBUF_LINK_HLEN)
/* TCP Maximum segment size. */
#define TCP_MSS (1500 - 40) /* TCP_MSS = (Ethernet MTU - IP header size - TCP header size) */
/* TCP sender buffer space (bytes). */
#define TCP_SND_BUF (11*TCP_MSS)
/* TCP_SND_QUEUELEN: TCP sender buffer space (pbufs). This must be at least
as much as (2 * TCP_SND_BUF/TCP_MSS) for things to work. */
#define TCP_SND_QUEUELEN (8* TCP_SND_BUF/TCP_MSS)
/* TCP receive window. */
#define TCP_WND (11*TCP_MSS)
当然,除此之外,想要整个LwIP 能高速平稳运行,只配置这些是不够的,比如我们应该使用中断的方式接收数据,这就省去了CPU 查询数据,而且,我们应该将内核邮箱的容量增大,这样子在接收到数据之后,投递给内核就不会因为无法投递而阻塞,同时内核线程的优先级应该设置得更高一点,这样子就能及时去处理这些数据,当然,我们也可以独立使用一个新的发送线程,这样子内核就无需调用底层网卡函数,它可以专心处理数据,发送数据的事情就交由发送线程去处理,