网络中的注意力机制-CNN attention
网络中的注意力机制-CNN attention
- 前言
- 网络结构
- SEnet
- CBAM
- GSoP-Net
- AA-Net
- ECA-Net
前言
Attention机制就是加权,目前实现形式主要包括三个方面:CNN-Attention(图像)、RNN-Attention(NLP)、self-Attention(机器翻译)。下面对CNN-Attention进行记录。
注意模块的开发大致可以分为两个方向:(1)增强特征聚合;(2)通道与空间注意相结合
记录常用的CNN-Attention主要包括以下:
SEnet(Squeeze-and-Excitation Network) 在特征通道之间加入注意力机制,论文
CBAM(Convolutional Block Attention Module) 在特征通道和特征空间两个维度上加入注意力机制,论文
GSOP-Net(Global Second-order Pooling Convolutional Networks) 在特征通道之间加入注意力机制,论文
AA-Net(Attention-Augmented-Conv2d Network) 在空间和特征子空间中同时加入注意机制,论文
ECA-Net(Efficient Channel Attention Network) 在局部特征通道之间加入注意力机制,论文
网络结构
SEnet
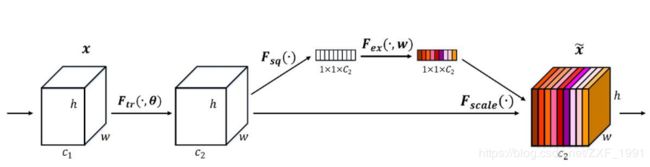
总体结构:
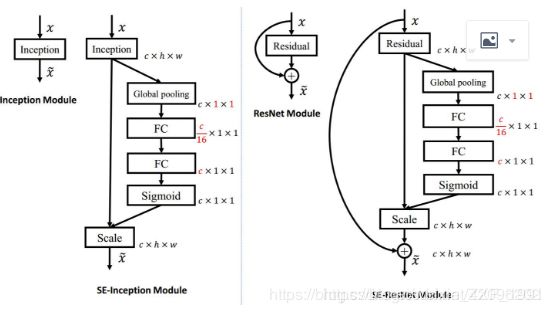
 在inception、resnet中的使用:
在inception、resnet中的使用:
 SEnet通过学习的方式自动获取每个特征通道的重要程度,目的是自动提升有用特征并抑制不重要的特征。SEnet通过Squeeze模块和Exciation模块实现所述功能。
SEnet通过学习的方式自动获取每个特征通道的重要程度,目的是自动提升有用特征并抑制不重要的特征。SEnet通过Squeeze模块和Exciation模块实现所述功能。
squeeze操作:对空间维度进行压缩,直白的说就是对每个特征图做全局池化,平均成一个实数值。该实数从某种程度上来说具有全局感受野。
excitaton操作:由于经过squeeze操作后,网络输出了11C大小的特征图,作者利用权重w来学习C个通道直接的相关性。在实际应用时有的框架使用全连接,有的框架使用11的卷积实现。推荐使用11的卷积,先对通道进行降维然后在升维到C,好处就是一方面降低了网络计算量,一方面增加了网络的非线性能力。
最后一个操作时将exciation的输出看作是经过特征选择后的每个通道的重要性,通过乘法加权的方式将excitaton的输出乘到先前的特征上,从事实现提升重要特征,抑制不重要特征这个功能。
pytorch code:
#https://github.com/Amanbhandula/AlphaPose/blob/master/train_sppe/src/models/layers/SE_module.py
class SELayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=1):
super(SELayer, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(channel, channel // reduction),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(channel // reduction, channel),
nn.Sigmoid())
self.fc2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(channel , channel // reduction, 1, bias=False),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(channel , channel // reduction, 1, bias=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
y = self.avg_pool(x).view(b, c)
y = self.fc1(y).view(b, c, 1, 1)
return x * y
keras code:
class SELayer():
"""
SE layer contains Squeeze and excitaton operations
"""
def __init__(self,input_tensor,ratio):
"""
:param input_tensor: input_tensor.shape=[h,w,c]
:param ratio:Number of output channels for excitation intermediate operation
"""
self.in_tensor=input_tensor
self.in_channels=keras.backend.in_shape(input_tensor)[-1]
self.ratio=ratio
def squeeze(self, input):
return GlobalAveragePooling2D()(input)
def excitation_dense(self,input):
out=Dense(units=self.in_channels//self.ratio)(input)
out=Activation("relu")(out)
out=Dense(units=self.in_channels)(out)
out=Activation("sigmoid")(out)
out=Reshape((1,1,self.in_channels))(out)
return out
def excitation_conv(self,input):
out=Conv2D(filters=self.in_channels//self.ratio,kernel_size=(1,1))(input)
out=Activation("relu")(out)
out=Conv2D(filters=self.in_channels,kernel_size=(1,1))(out)
out=Activation('sigmoid')(out)
out = Reshape((1, 1, self.in_channels))(out)
return out
def forward(self):
"""
Use conv by default
:param self:
:return:
"""
out=self.squeeze(self.in_tensor)
out=self.excitation_conv(out)
scale=multiply([self.in_tensor,out])
return scale
#或者
def se_layer(inputs_tensor=None,ratio=None,num=None,**kwargs):
"""
SE-NET
:param inputs_tensor:input_tensor.shape=[batchsize,h,w,channels]
:param ratio:
:param num:
:return:
"""
channels = K.int_shape(inputs_tensor)[-1]
x = KL.GlobalAveragePooling2D()(inputs_tensor)
x = KL.Reshape((1, 1, channels))(x)
x = KL.Conv2D(channels//ratio, (1, 1), strides=1, name="se_conv1_"+str(num), padding="valid")(x)
x = KL.Activation('relu', name='se_conv1_relu_'+str(num))(x)
x = KL.Conv2D(channels, (1, 1), strides=1, name="se_conv2_"+str(num), padding="valid")(x)
x = KL.Activation('sigmoid', name='se_conv2_relu_'+str(num))(x)
output = KL.multiply([inputs_tensor, x])
return output
CBAM
总体结构:
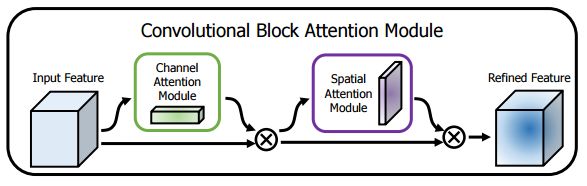
Channel Attention Module
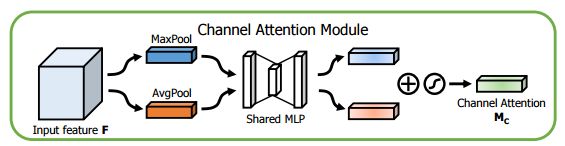
Spatial Attention Module

CBAM在特征通道和特征空间两个维度加入注意力机制。
特征通道中加入注意力机制,和SE思想类似不过是加入了一个max pooling操作,而且共享了一个MLP op,具体操作:
将输入的featuremap,分别经过基于width和height的global max pooling 和global average pooling,然后分别经过共享的MLP(注意这里的MLP是共享的,不是分别建立的)。将MLP输出的特征进行基于elementwise的加和操作,再经过sigmoid激活操作,生成最终的channel attention featuremap。将该channel attention featuremap和input featuremap做elementwise乘法操作,生成Spatial attention模块需要的输入特征。
特征空间中加入注意力机制,具体操作:
将Channel attention模块输出的特征图作为本模块的输入,首先对输入做一个基于channel的global max pooling 和global average pooling,然后将这2个结果基于channel 做concat操作。然后经过一个卷积操作,降维为1个channel。再经过sigmoid生成spatial attention feature。最后将该feature和该模块的输入feature做乘法,得到最终生成的特征。
pytorch code:
#https://github.com/luuuyi/CBAM.PyTorch/blob/master/model/resnet_cbam.py
class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, ratio=16):
super(ChannelAttention, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.max_pool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d(1)
self.fc1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, in_planes / 16, 1, bias=False)
self.relu1 = nn.ReLU()
self.fc2 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes / 16, in_planes, 1, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
avg_out = self.fc2(self.relu1(self.fc1(self.avg_pool(x))))
max_out = self.fc2(self.relu1(self.fc1(self.max_pool(x))))
out = avg_out + max_out
return self.sigmoid(out)
class SpatialAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, kernel_size=7):
super(SpatialAttention, self).__init__()
assert kernel_size in (3, 7), 'kernel size must be 3 or 7'
padding = 3 if kernel_size == 7 else 1
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(2, 1, kernel_size, padding=padding, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
avg_out = torch.mean(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
max_out, _ = torch.max(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat([avg_out, max_out], dim=1)
x = self.conv1(x)
return self.sigmoid(x)
keras code:
def cbam_layer(inputs_tensor=None,ratio=None,num=None,**kwargs):
"""
CBAM-NET
:param inputs_tensor: input_tensor.shape=[batchsize,h,w,channels]
:param ratio:
:param num:
:return:
"""
channels = K.int_shape(inputs_tensor)[-1]
H_ = K.int_shape(inputs_tensor)[1]
W_ = K.int_shape(inputs_tensor)[2]
def share_layer(inputs=None):
# x_ = KL.Conv2D(channels // ratio, (1, 1), strides=1, name="cbam_conv1_" + str(num), padding="valid")(inputs)
x_ = KL.Conv2D(channels // ratio, (1, 1), strides=1, padding="valid")(inputs)
# x_ = KL.Activation('relu', name='cbam_conv1_relu_' + str(num))(x_)
x_ = KL.Activation('relu')(x_)
# output_share = KL.Conv2D(channels, (1, 1), strides=1, name="cbam_conv2_" + str(num), padding="valid")(x_)
output_share = KL.Conv2D(channels, (1, 1), strides=1, padding="valid")(x_)
return output_share
x_global_avg_pool = KL.GlobalAveragePooling2D()(inputs_tensor)
x_global_avg_pool = KL.Reshape((1, 1, channels))(x_global_avg_pool)
x_global_max_pool = KL.GlobalMaxPool2D()(inputs_tensor)
x_global_max_pool = KL.Reshape((1, 1, channels))(x_global_max_pool)
x_global_avg_pool = share_layer(x_global_avg_pool)
x_global_max_pool = share_layer(x_global_max_pool)
x = KL.Add()([x_global_avg_pool,x_global_max_pool])
x = KL.Activation('sigmoid', name='cbam_conv2_relu_'+str(num))(x)
# x = KL.Reshape((-1,1,1,channels))(x)
CAM = KL.multiply([inputs_tensor, x]) #ChannelAttention
x_mean = K.mean(CAM,axis=-1,keepdims=True)
x_max = K.max(CAM,axis=-1,keepdims=True)
x_cat = KL.Concatenate(axis=-1)([x_mean,x_max])
x = KL.Conv2D(1, (3, 3), strides=1, name="cbam_conv3_" + str(num), padding="same")(x_cat)
x = KL.Activation('sigmoid', name='cbam_conv3_relu_' + str(num))(x)
output = KL.multiply([CAM, x]) # ChannelAttention
return output
GSoP-Net
总体结构:

具体操作过程:
输入张量先经过卷积进行降维后,然后GSoP块进行协方差矩阵计算,然后进行线性卷积和非线性激活的两个连续运算,得到输出张量,输出张量沿通道维数对原始输入进行缩放,一定程度上也是一种通道注意力的体现,但与SEnet不同的是该模块提出了2维平均池化,通过协方差的形式体现了通道与通道之间的关系。
torch code:
#https://github.com/ZilinGao/Global-Second-order-Pooling-Convolutional-Networks
class Covpool(Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input):
x = input
batchSize = x.data.shape[0]
dim = x.data.shape[1]
h = x.data.shape[2]
w = x.data.shape[3]
M = h*w
x = x.reshape(batchSize,dim,M)
I_hat = (-1./M/M)*torch.ones(M,M,device = x.device) + (1./M)*torch.eye(M,M,device = x.device)
I_hat = I_hat.view(1,M,M).repeat(batchSize,1,1).type(x.dtype)
y = x.bmm(I_hat).bmm(x.transpose(1,2))
ctx.save_for_backward(input,I_hat)
return y
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
input,I_hat = ctx.saved_tensors
x = input
batchSize = x.data.shape[0]
dim = x.data.shape[1]
h = x.data.shape[2]
w = x.data.shape[3]
M = h*w
x = x.reshape(batchSize,dim,M)
grad_input = grad_output + grad_output.transpose(1,2)
grad_input = grad_input.bmm(x).bmm(I_hat)
grad_input = grad_input.reshape(batchSize,dim,h,w)
return grad_input
class Sqrtm(Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input, iterN):
x = input
batchSize = x.data.shape[0]
dim = x.data.shape[1]
dtype = x.dtype
I3 = 3.0*torch.eye(dim,dim,device = x.device).view(1, dim, dim).repeat(batchSize,1,1).type(dtype)
normA = (1.0/3.0)*x.mul(I3).sum(dim=1).sum(dim=1)
A = x.div(normA.view(batchSize,1,1).expand_as(x))
Y = torch.zeros(batchSize, iterN, dim, dim, requires_grad = False, device = x.device)
Z = torch.eye(dim,dim,device = x.device).view(1,dim,dim).repeat(batchSize,iterN,1,1)
if iterN < 2:
ZY = 0.5*(I3 - A)
Y[:,0,:,:] = A.bmm(ZY)
else:
ZY = 0.5*(I3 - A)
Y[:,0,:,:] = A.bmm(ZY)
Z[:,0,:,:] = ZY
for i in range(1, iterN-1):
ZY = 0.5*(I3 - Z[:,i-1,:,:].bmm(Y[:,i-1,:,:]))
Y[:,i,:,:] = Y[:,i-1,:,:].bmm(ZY)
Z[:,i,:,:] = ZY.bmm(Z[:,i-1,:,:])
ZY = 0.5*Y[:,iterN-2,:,:].bmm(I3 - Z[:,iterN-2,:,:].bmm(Y[:,iterN-2,:,:]))
y = ZY*torch.sqrt(normA).view(batchSize, 1, 1).expand_as(x)
ctx.save_for_backward(input, A, ZY, normA, Y, Z)
ctx.iterN = iterN
return y
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
input, A, ZY, normA, Y, Z = ctx.saved_tensors
iterN = ctx.iterN
x = input
batchSize = x.data.shape[0]
dim = x.data.shape[1]
dtype = x.dtype
der_postCom = grad_output*torch.sqrt(normA).view(batchSize, 1, 1).expand_as(x)
der_postComAux = (grad_output*ZY).sum(dim=1).sum(dim=1).div(2*torch.sqrt(normA))
I3 = 3.0*torch.eye(dim,dim,device = x.device).view(1, dim, dim).repeat(batchSize,1,1).type(dtype)
if iterN < 2:
der_NSiter = 0.5*(der_postCom.bmm(I3 - A) - A.bmm(der_sacleTrace))
else:
dldY = 0.5*(der_postCom.bmm(I3 - Y[:,iterN-2,:,:].bmm(Z[:,iterN-2,:,:])) -
Z[:,iterN-2,:,:].bmm(Y[:,iterN-2,:,:]).bmm(der_postCom))
dldZ = -0.5*Y[:,iterN-2,:,:].bmm(der_postCom).bmm(Y[:,iterN-2,:,:])
for i in range(iterN-3, -1, -1):
YZ = I3 - Y[:,i,:,:].bmm(Z[:,i,:,:])
ZY = Z[:,i,:,:].bmm(Y[:,i,:,:])
dldY_ = 0.5*(dldY.bmm(YZ) -
Z[:,i,:,:].bmm(dldZ).bmm(Z[:,i,:,:]) -
ZY.bmm(dldY))
dldZ_ = 0.5*(YZ.bmm(dldZ) -
Y[:,i,:,:].bmm(dldY).bmm(Y[:,i,:,:]) -
dldZ.bmm(ZY))
dldY = dldY_
dldZ = dldZ_
der_NSiter = 0.5*(dldY.bmm(I3 - A) - dldZ - A.bmm(dldY))
grad_input = der_NSiter.div(normA.view(batchSize,1,1).expand_as(x))
grad_aux = der_NSiter.mul(x).sum(dim=1).sum(dim=1)
for i in range(batchSize):
grad_input[i,:,:] += (der_postComAux[i] \
- grad_aux[i] / (normA[i] * normA[i])) \
*torch.ones(dim,device = x.device).diag()
return grad_input, None
class Triuvec(Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input):
x = input
batchSize = x.data.shape[0]
dim = x.data.shape[1]
dtype = x.dtype
x = x.reshape(batchSize, dim*dim)
I = torch.ones(dim,dim).triu().t().reshape(dim*dim)
index = I.nonzero()
y = torch.zeros(batchSize,int(dim*(dim+1)/2),device = x.device)
for i in range(batchSize):
y[i, :] = x[i, index].t()
ctx.save_for_backward(input,index)
return y
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
input,index = ctx.saved_tensors
x = input
batchSize = x.data.shape[0]
dim = x.data.shape[1]
dtype = x.dtype
grad_input = torch.zeros(batchSize,dim,dim,device = x.device,requires_grad=False)
grad_input = grad_input.reshape(batchSize,dim*dim)
for i in range(batchSize):
grad_input[i,index] = grad_output[i,:].reshape(index.size(),1)
grad_input = grad_input.reshape(batchSize,dim,dim)
return grad_input
def CovpoolLayer(var):
return Covpool.apply(var)
def SqrtmLayer(var, iterN):
return Sqrtm.apply(var, iterN)
def TriuvecLayer(var):
return Triuvec.apply(var)
#use
if GSoP_mode == 1:
self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(14, stride=1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
print("GSoP-Net1 generating...")
else :
self.isqrt_dim = 256
self.layer_reduce = nn.Conv2d(512 * block.expansion, self.isqrt_dim, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False)
self.layer_reduce_bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.isqrt_dim)
self.layer_reduce_relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.fc = nn.Linear(int(self.isqrt_dim * (self.isqrt_dim + 1) / 2), num_classes)
print("GSoP-Net2 generating...")
if self.GSoP_mode == 1:
x = self.avgpool(x)
else :
x = self.layer_reduce(x)
x = self.layer_reduce_bn(x)
x = self.layer_reduce_relu(x)
x = MPNCOV.CovpoolLayer(x)
x = MPNCOV.SqrtmLayer(x, 3)
x = MPNCOV.TriuvecLayer(x)
AA-Net
总体结构:
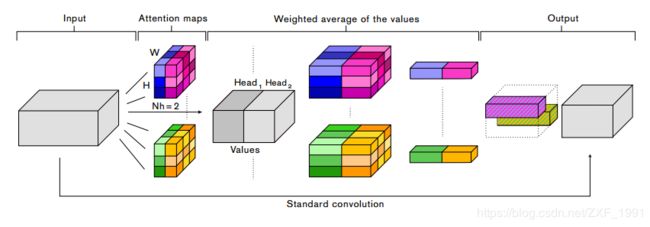 AA-Net使用可以共同参与空间和特征子空间的注意机制(每个头对应于特征子空间),引入额外的特征映射而不是精炼它们。核心思想是使用自注意力机制,首先通过矩阵运算获得注意力权重图,通过多Head操作赋值多个空间,在多个空间内进行注意力点乘,实现自注意力机制。参考
AA-Net使用可以共同参与空间和特征子空间的注意机制(每个头对应于特征子空间),引入额外的特征映射而不是精炼它们。核心思想是使用自注意力机制,首先通过矩阵运算获得注意力权重图,通过多Head操作赋值多个空间,在多个空间内进行注意力点乘,实现自注意力机制。参考
pytorch:
# https://github.com/leaderj1001/Attention-Augmented-Conv2d/
class AugmentedConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, dk, dv, Nh, relative):
super(AugmentedConv, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.kernel_size = kernel_size
self.dk = dk
self.dv = dv
self.Nh = Nh
self.relative = relative
self.conv_out = nn.Conv2d(self.in_channels, self.out_channels - self.dv, self.kernel_size, padding=1)
self.qkv_conv = nn.Conv2d(self.in_channels, 2 * self.dk + self.dv, kernel_size=1)
self.attn_out = nn.Conv2d(self.dv, self.dv, 1)
def forward(self, x):
# Input x
# (batch_size, channels, height, width)
batch, _, height, width = x.size(
# conv_out
# (batch_size, out_channels, height, width)
conv_out = self.conv_out(x)
# flat_q, flat_k, flat_v
# (batch_size, Nh, height * width, dvh or dkh)
# dvh = dv / Nh, dkh = dk / Nh
# q, k, v
# (batch_size, Nh, height, width, dv or dk)
flat_q, flat_k, flat_v, q, k, v = self.compute_flat_qkv(x, self.dk, self.dv, self.Nh)
logits = torch.matmul(flat_q.transpose(2, 3), flat_k)
if self.relative:
h_rel_logits, w_rel_logits = self.relative_logits(q)
logits += h_rel_logits
logits += w_rel_logits
weights = F.softmax(logits, dim=-1)
# attn_out
# (batch, Nh, height * width, dvh)
attn_out = torch.matmul(weights, flat_v.transpose(2, 3))
attn_out = torch.reshape(attn_out, (batch, self.Nh, self.dv / self.Nh, height, width))
# combine_heads_2d
# (batch, out_channels, height, width)
attn_out = self.combine_heads_2d(attn_out)
attn_out = self.attn_out(attn_out)
return torch.cat((conv_out, attn_out), dim=1)
ECA-Net
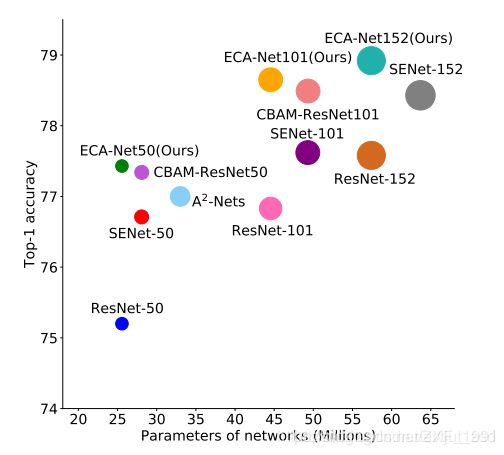
总体结构:
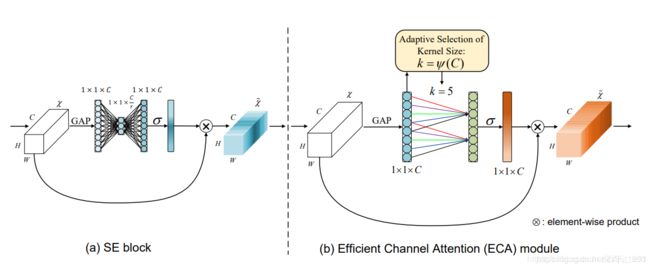 目前市面上最高效的注意力机制,能以更有效的方式学习有效的注意力渠道,其它的一些研究通过捕获更复杂的通道依赖来改进SE块或者结合额外的空间注意力。这些方法虽然取得了较高的精度,但往往带来较高的模型复杂度和较大的计算量。
目前市面上最高效的注意力机制,能以更有效的方式学习有效的注意力渠道,其它的一些研究通过捕获更复杂的通道依赖来改进SE块或者结合额外的空间注意力。这些方法虽然取得了较高的精度,但往往带来较高的模型复杂度和较大的计算量。
SE块首先对每个通道独立使用全局平均池,然后使用两个非线性的全连接(FC)层和一个s形函数生成每个通道的权值。这两个FC层的设计是为了捕获非线性的跨通道交互作用,其中包括降维以避免过高的模型复杂度。虽然该策略被广泛应用于后续的通道注意模块,但是实证分析表明降维会对渠道关注度的预测产生副作用,而且对所有渠道的相关性进行捕获是低效且不必要的。
SE块使用两个FC层计算权重。与之不同的是,ECA通过执行大小为k的快速一维卷积来生成通道权值,其中k通过通道维C的函数自适应地确定,考虑到了跨通道交互影响,是一种为轻量级CNN架构设计的。
pytorch code:
class ECA_layer(nn.Module):
"""Constructs a ECA module.
Args:
channel: Number of channels of the input feature map
k_size: Adaptive selection of kernel size
"""
def __init__(self, x,gamma=2,bias=1):
super(eca_layer, self).__init__()
# x: input features with shape [b, c, h, w]
self.x=x
self.gamma=gamma
self.bias=bias
b, c, h, w = x.size()
t=int(abs((math.log(c,2)+self.bias)/self.gamma))
k_size= t if t%2 else t+1
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.conv = nn.Conv1d(1, 1, kernel_size=k_size, padding=(k_size - 1) // 2, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self):
# feature descriptor on the global spatial information
y = self.avg_pool(self.x)
# Two different branches of ECA module
y = self.conv(y.squeeze(-1).transpose(-1, -2))
y = y.transpose(-1, -2).unsqueeze(-1)
# Multi-scale information fusion
y = self.sigmoid(y)
return self.x * y.expand_as(self.x)
keras code:
class ECALayer():
"""
ECA layer
"""
def __init__(self,input_tensor,gamma=2,b=1):
"""
:param input_tensor: input_tensor.shape=[batchsize,channels,h,w]
:param gamma:
:param b:
"""
self.in_tensor = input_tensor
self.gamma=gamma
self.b=b
self.channels=keras.backend.in_shape(self.in_tensor)[1]
def forward(self,input):
t=int(abs((math.log(self.channels,2)+self.b)/self.gamma))
k= t if t%2 else t+1
out=GlobalAveragePooling2D(data_format='channels_first')(input)
out=Reshape((-1,self.channels,1))(out)
out=Conv1D(1,kernel_size=k,padding='same')(out)
out = Activation('sigmoid')(out)
out=tf.expand_dims(out,-1) #shape=[batchsize,channels,h,w]
scale = multiply([self.in_tensor, out])
return scale
#或者
def eca_layer(inputs_tensor=None,num=None,gamma=2,b=1,**kwargs):
"""
ECA-NET
:param inputs_tensor: input_tensor.shape=[batchsize,h,w,channels]
:param num:
:param gamma:
:param b:
:return:
"""
channels = K.int_shape(inputs_tensor)[-1]
t = int(abs((math.log(channels,2)+b)/gamma))
k = t if t%2 else t+1
x_global_avg_pool = KL.GlobalAveragePooling2D()(inputs_tensor)
x = KL.Reshape((channels,1))(x_global_avg_pool)
x = KL.Conv1D(1,kernel_size=k,padding="same",name="eca_conv1_" + str(num))(x)
x = KL.Activation('sigmoid', name='eca_conv1_relu_' + str(num))(x) #shape=[batch,chnnels,1]
x = tf.expand_dims(x,-1) #shape=[batch,chnnels,1,1]
x = tf.transpose(x,(0,2,3,1))
output = KL.multiply([inputs_tensor,x])
return output