一.剧情
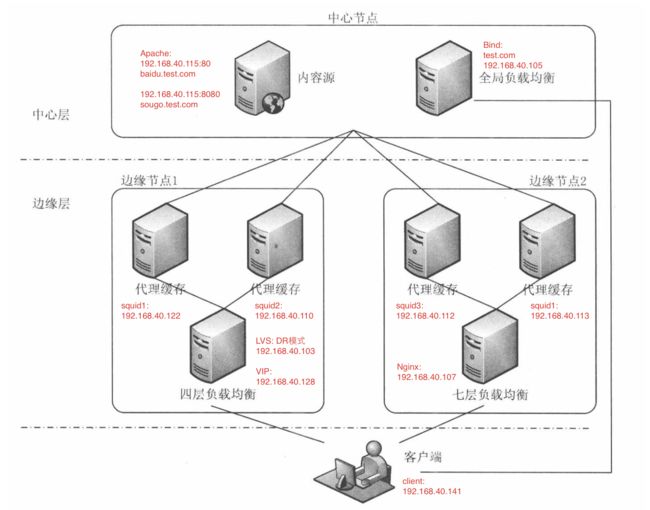
剧情是这样的,本次的多边缘节点负载均衡实验,1个LVS四层负载均衡集群和1个Nginx为反向代理的七层负载均衡集群,由Bind dns解析作为 主负载均衡服务器,调度两个集群,中间层有一台Web服务器。前端是一台客户端。如下图所示:
二.基础环境
1.硬件信息
4G内存、50G硬盘、2核
8台虚拟机系统为Centos 6.5,1台client系统为 windows server 2008。
2.网络信息:
IP地址按上图的标明。(其中每台机器的dns设置,可以在所有软件联网安装完成后,修改成环境中的192.168.40.105)
3.系统内环境配置,所有linux系统内都安装了开发工具,并关闭每台机器的防火墙。主机名已更改为图上所示:
1 1 wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-6.repo (替换yum源为 阿里源) 2 (备用源,如果阿里源不能使用,请更换为网易源:http://mirrors.163.com/.help/CentOS6-Base-163.repo) 3 2 yum -y groupinstall "development tools" 4 3 service iptables stop
三.软件部署
此次实验,我们可以分为两部分,先做通LVS+squid+web四层负载架构。再做Nginx+Bind+Squid+web七层负载。最后将两个集群结合在一起。
LVS四层负载均衡:
1.安装LVS服务器
1 yum install ipvsadm
2.由于我们采用DR的工作方式,DR工作方式要求真实服务器的IP地址和虚拟IP地址(VIP)必须属于同一网段。具体工作原理可参考LVS三种实现技术。这一步我们修改内核参数 /etc/sysctl.conf,在文件最后追加以下三句内容,
1 vim /etc/sysctl.conf 2 net.ipv4.ip_forwarf = 0 (此句,默认是为0) 3 net.ipv4.conf.all.send_redirects = 1 4 net.ipv4.conf.default.send_redirects = 1 5 net.ipv4.conf.eth0.send_redirects = 1
修改完成后,立即生效:
1 sysctl -p
3.配置LVS服务器的VIP即虚拟IP,后续的的两台squid也要配置这个虚拟IP。并增加路由记录
1 ifconfig eth0:0 192.168.40.128 netmask 255.25.255.255 broadcast 192.168.40.128 up 2 route add -host 192.168.40.128 dev eth0:0
创建负载均衡服务器的虚拟服务及相应端口,指令rr 参数表示应用的调度算法为轮询算法(Round Robin)
1 ipvsadm -A -t 192.168.40.128:80 -s rr
建立虚拟服务与后台真实服务器squid1和squid2提供的http服务的链接,并使用DR的工作方式
1 ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.40.128:80 -r 192.168.40.122 -g 2 ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.40.128:80 -r 192.168.40.110 -g
LVS服务器的配置就到这,下一步去配置squid1和squid2缓存代理。
4.在squid1安装squid软件(squid2做同样的设置,除了visible_hostname例外。)
1 yum install squid
安装后,我们先去编辑一下squid的配置文件 /etc/squid/squid.conf
1 vim /etc/squid/squid.conf 2 3 cache_dir ufs /var/spool/squid 100 16 256 4 visible_hostname squid 5 http_port 80 accel vhost vport 6 cache_peer 192.168.40.115 parent 80 0 7 http_access allow all 8 cache_mem 32 MB
简单的讲下各参数的意思,cache_dir 是缓存的目录,后面 100 代表的是这个目录最多能存放100MB数据,visible_hostname 必须得设置一个主机名,http_port 80 本机开放的80端口,cache_peer 是表示当我本机没有客户端请求的资源时,将去这个上一级去取,在这里即是40.115的80端口去获取。最后一个是cache_mem 表示在内存的缓存为32MB.
改完上述文件后,我们用命令检查一下squid
1 squid -z 初始化后启动 2 squid -k parse 3 squid -k reconfigure 修改配置后,重新加载
接着,我们去配置squid的内核参数,使其不再转发IP数据包和处理ARP协议包
1 vim /etc/sysctl.conf 2 net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_ignore = 1 3 net.ipv4.conf.lo.arp_announce = 2 4 net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore = 1 5 net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce = 2
更行内核参数,执行以下命令:
1 sysctl -p
配置虚拟IP(VIP),和LVS服务器配置同一个IP
1 ifconfig lo:0 192.168.40.128 netmask 255.255.255.255 broadcast 192.168.40.128 up 2 route add -host 192.168.40.128 dev lo:0
OK,四层负载均衡服务器将VIP(192.168.40.128)提供给用户访问,并将用户的访问请求以轮询的方式分发给后台的真实服务器,而由真实的服务器去响应客户端,此时的返回给客户这一步,将不再经过lvs。
5.web服务器的安装,使用apache来提供web服务,按照架构图所示,我们登陆40.115这台机器,安装LAMP环境,并创建两个虚拟主机。
1 yum -y install httpd mysql mysql-server mysql-devel 2 yum -y install php php-mysql 3 cd /var/www/html/ 4 mkdir -pv {baidu.test.com,sougo.test.com} 5 cd baidu.test.com 6 wget www.baidu.com 7 cd ../sougo.test.com 8 wget sogou.com
软件安装完成后,我们去配置apache,编辑/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf 文件,修改或者追加以下内容。
1 vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf 2 3 Listen 80 4 ServerName 192.168.40.115 5 NameVirtualHost 192.168.40.115:80 6192.168.40.115:80> 7 ServerName baidu.test.com 8 DocumentRoot /var/www/html/baidu.test.com 9 (其实单做这个实验时,无须使用虚拟主机,因为整体环境需要,所以这里提前修改好了。)
修改完成,检查配置有无错误后,重新启动httpd
1 apachectl -t 2 service httpd restart
验证,客户端40.114去访问192.168.40.128(四层负载的VIP地址。)打开浏览器,输入http://192.168.40.128
1 [root@squid2 ~]# tail -f /var/log/squid/access.log 2 1443079520.674 94 192.168.40.141 TCP_MISS/404 579 GET http://192.168.40.128/content-search.xml - FIRST_UP_PARENT/192.168.40.115 text/html 3 1443079520.776 99 192.168.40.141 TCP_MISS/404 572 GET http://192.168.40.128/favicon.ico - FIRST_UP_PARENT/192.168.40.115 text/html
通过squid1的日志,我们可以看到,客户端的请求,被分配到squid2这台代理服务器上。说明我们的四层负载均衡已经配置成功。如果实验中出现打不开网址现象,或者其它异常的问题,首先去检查一下各个防火墙有无关闭。(对防火墙熟悉的人可以单独打开各服务端口)
Nginx七层负载均衡:
1.七层负载均衡中的环境搭建,利用之前已经安装好的apache的网站服务器,再有两台Squid代理缓存服务器(主机名为squid3和squid4),一台windows 2008 的主机,一台Nginx服务器(猪脚),还有一台Bind域名服务器用于网站的解析指向nginx(sougo.test.com,对应为nginx的ip:192.168.40.107)。
2.安装Bind dns 软件
1 yum -y install bind*
关于bind软件安装完成后的配置,这里说一下,默认安装后,各配置文件都存放在 /var/named/chroot/目录下的子目录中。该目录下的etc/named.conf 是主配置文件,etc/named.rfc1912.zones 文件是添加域的。var/named/目录下 存放的是域名正向解析文件和反向解析文件存放的位置。
先cp一些文件到/var/named/chroot/var/named/目录下,(后续会用的到,不然启动会报错。)
1 cp /var/named/named.*
编辑named.rfc1912.zones文件,添加test.com.域(只添加标红的)
1 [root@bind ~]# vim /var/named/chroot/etc/named.rfc1912.zones 2 // named.rfc1912.zones: 3 // 4 // Provided by Red Hat caching-nameserver package 5 // 6 // ISC BIND named zone configuration for zones recommended by 7 // RFC 1912 section 4.1 : localhost TLDs and address zones 8 // and http://www.ietf.org/internet-drafts/draft-ietf-dnsop-default-local-zones-02.txt 9 // (c)2007 R W Franks 10 // 11 // See /usr/share/doc/bind*/sample/ for example named configuration files. 12 // 13 14 zone "localhost.localdomain" IN { 15 type master; 16 file "named.localhost"; 17 allow-update { none; }; 18 }; 19 20 zone "localhost" IN { 21 type master; 22 file "named.localhost"; 23 allow-update { none; }; 24 }; 25 26 zone "1.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0.ip6.arpa" IN { 27 type master; 28 file "named.loopback"; 29 allow-update { none; }; 30 }; 31 32 zone "1.0.0.127.in-addr.arpa" IN { 33 type master; 34 file "named.loopback"; 35 allow-update { none; }; 36 }; 37 38 zone "0.in-addr.arpa" IN { 39 type master; 40 file "named.empty"; 41 allow-update { none; }; 42 }; 43 44 zone "test.com" IN { //正向解析 45 type master; 46 file "named.test.com"; 47 }; 48 49 50 zone "40.168.192.in-addr.arpa" IN { //反向解析 51 type master; 52 file "named.192.168.40"; 53 };
添加域后,我们去编辑正向解析文件 named.test.com,内容为下:
1 [root@bind ~]# vim /var/named/chroot/var/named/named.test.com 2 $TTL 1D 3 @ IN SOA @ root.test.com. ( 4 0 ; serial 5 1D ; refresh 6 1H ; retry 7 1W ; expire 8 3H ) ; minimum 9 NS @ 10 A 127.0.0.1 11 AAAA ::1 12 bind IN A 192.168.40.105 13 www IN A 192.168.40.115 14 sougo IN A 192.168.40.107
编辑反向解析文件named.192.168.40(反向解析在整个实验中,不是必须的需要。只是为了更完整一些)
1 [root@bind ~]# vim /var/named/chroot/var/named/named.192.168.40 2 $TTL 1D 3 @ IN SOA 40.168.192.in-addr.arpa. root.test.com. ( 4 0 ; serial 5 1D ; refresh 6 1H ; retry 7 1W ; expire 8 3H ) ; minimum 9 @ IN NS bind.test.com. 10 107 IN PTR sougo.test.com. 11 115 IN PTR www.test.com.
编辑完成后,我们检查一下配置文件
1 [root@bind ~]# named-checkconf 2 [root@bind ~]# named-checkzone
检查无误后,重启named守护进程。
1 [root@bind ~]# service named restart
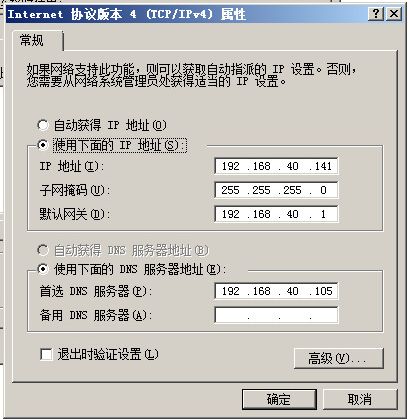
可以在客户端40.114上,修改网络配置,将dns修改成40.115
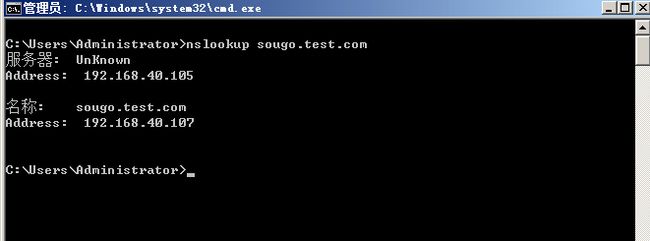
测试一下。cmd内执行nslookup 解析一下,如下图所示,BINd服务器已经提供了域名解析服务,如果无法解析,请检查bind 主机的iptables是否关闭。
3.Nginx服务器的搭建,在40.107上安装nginx软件。
1 yum install nginx
修改nginx配置文件,有的需要追加进去,有的内容可能已经存在,这点需要自己判断一下,进行修改。
1 [root@nginx ~]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf 2 3 upstream webservers { #此处是后台squid代理服务器集群的地址,端口是80,后面我们将对squid3 和squid4 服务器进行修改内核参数及squid服务配置 4 server 192.168.40.112:80; # upstream将按照默认的轮询方式 5 server 192.168.40.113:80; 6 } 7 8 server { 9 listen 80; 10 server_name sougo.test.com; 11 12 #charset koi8-r; 13 #access_log /var/log/nginx/log/host.access.log main; 14 15 location ~/ { 16 proxy_pass http://webservers; 17 proxy_redirect off; 18 proxy_set_header Host $host; 19 proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; 20 proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; 21 } 22 23 #error_page 404 /404.html; 24 25 # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html 26 # 27 error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; 28 location = /50x.html { 29 root /usr/share/nginx/html; 30 } 31 32 # proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80 33 # 34 #location ~ \.php$ { 35 # proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1; 36 #} 37 38 # pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000 39 # 40 #location ~ \.php$ { 41 # root html; 42 # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; 43 # fastcgi_index index.php; 44 # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; 45 # include fastcgi_params; 46 #} 47 48 # deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root 49 # concurs with nginx's one 50 # 51 #location ~ /\.ht { 52 # deny all; 53 #} 54 }
编辑主配置文件/etc/nginx,添加或者修改以下参数:
1 [root@nginx ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf 2 3 events { 4 worker_connections 1024; 5 use epoll; 6 }
修改以上两个文件后,测试检查并重启nginx服务器
1 [root@nginx ~]# nginx -t 2 [root@nginx ~]# /etc/init.d/nginx restart
4.后台Squid两台服务器的配置(squid3 和 squid4 配置一样。)此处,以squid3为例:
1 [root@squid3 ~]# vim /etc/squid/squid.conf 2 3 cache_dir ufs /var/spool/squid 100 16 256 4 visible_hostname squid3 5 http_port 80 accel vhost vport 6 cache_peer 192.168.40.115 parent 80 0 7 http_access allow all 8 cache_mem 32 MB
上述的配置就可以将squid3 和squid4 配置为 web站点 (sougo.test.com)代理缓存服务器。配置完成后记得重启服务器
[root@squid3 ~]# /etc/init.d/squid restart
现在dns解析 sougo.test.com 为nginx服务器ip 40.107后,我们去客户端验证一下。如下图所示。
去squid3上查看一下日志,本机没有资源,去上一级即40.115上去下载资源。然后由squid响应给客户端
[root@squid3 ~]# tail -f /var/log/squid/access.log 1443020309.684 1 192.168.40.107 TCP_MISS/404 579 GET http://sougo.test.com/web/js/addbanner.min.js - FIRST_UP_PARENT/192.168.40.115 text/html 1443020309.893 1 192.168.40.107 TCP_MISS/404 578 GET http://sougo.test.com/images/index/spy_h.png - FIRST_UP_PARENT/192.168.40.115 text/html 1443020309.907 1 192.168.40.107 TCP_MISS/404 567 GET http://sougo.test.com/favicon.ico - FIRST_UP_PARENT/192.168.40.115 text/html 1443077070.478 673 192.168.40.107 TCP_MISS/404 567 GET http://sougo.test.com/favicon.ico - FIRST_UP_PARENT/192.168.40.115 text/html 1443080793.374 88 192.168.40.107 TCP_MISS/404 567 GET http://sougo.test.com/favicon.ico - FIRST_UP_PARENT/192.168.40.115 text/html 1443091064.977 6 192.168.40.107 TCP_MEM_HIT/200 12904 GET http://sougo.test.com/ - NONE/- text/html
现在,七层负载均衡的实验也得到了成功响应。那么下一步,我们就将两个负载集群融合在一块。。。
多边缘节点负载均衡:
1.这次,我们将两个集群变成多边缘。先说web,apache 有两个 虚拟主机,分别是 baidu.test.com(对应端口 192.168.40.115:80) 和 sougo.test.com(对应端口 192.168.40.115:8080),通过Bind DNS的解析,当用户访问 baidu.test.com域名时,dns解析的地址是192.168.40.128(VIP地址),跳转到四层负载集群;当用户访问sougo.test.com域名时,dns解析到192.168.40.107(nginx),跳转到七层负载集群。在此,Bind 担任的是主负载均衡服务器。下面先进行dns的配置:
2.Bind 的配置,其实只需添加一条主机记录,编辑 /var/named/chroot/var/named/named.test.com 正向解析文件
1 [root@bind ~]# vim /var/named/chroot/var/named/named.test.com 2 3 $TTL 1D 4 @ IN SOA @ root.test.com. ( 5 0 ; serial 6 1D ; refresh 7 1H ; retry 8 1W ; expire 9 3H ) ; minimum 10 NS @ 11 A 127.0.0.1 12 AAAA ::1 13 bind IN A 192.168.40.105 14 www IN A 192.168.40.115 15 baidu IN A 192.168.40.128 #(baidu.test.com 与边缘节点1的LVS服务器VIP绑定) 16 sougo IN A 192.168.40.107 #(sougo.test.com 与边缘节点2的nginx服务器绑定)
编辑后,重启域名named服务
1 [root@bind ~]# service named restart
3.Web服务器的配置,编辑 /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf,在最后添加或者修改成下面这样。
1 [root@www ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf 2 3 Listen 80 4 Listen 8080 5 NameVirtualHost 192.168.40.115:80 6 NameVirtualHost 192.168.40.115:8080 7 8192.168.40.115:80> 9 ServerName baidu.test.com 10 DocumentRoot /var/www/html/baidu.test.com (虚拟主机baidu 网页存放路径) 11 12 13192.168.40.115:8080> 14 ServerName sougo.test.com 15 DocumentRoot /var/www/html/sougo.test.com (虚拟主机sougo网页存放路径) 16
开启两个端口,80提供给baidu.test.com,8080提供给sougo.test.com。 编辑完成后,测试并重启httpd服务:
1 [root@www ~]# apachectl -t 2 [root@www ~]# /etc/init.d/httpd restart
4.现在修改七层负载集群中的代理服务器,因为它们要代理访问的是sogou.test.com,所以现在修改squid3 和 squid4 服务器。(两台都要同样设置)以squid3为例:
1 [root@squid3 ~]# vim /etc/squid/squid.conf 2 3 visible_hostname squid3 4 http_port 80 accel vhost vport 5 cache_peer 192.168.40.115 parent 8080 0 (主要修改这个端口为8080即可,其它的,可按上个实验环境中的配置。) 6 http_access allow all 7 cache_mem 32 MB
修改cache_peer 字段,当squid服务器的本地缓存内容不能满足80端口上的http内容请求时,将向其的上一级节点 192.168.40.115的8080端口上去请求并接收数据。从而建立了web站点8080端口的连接,及缓存关系。
修改完成后,重新启动squid服务
[root@squid3 ~]# service squid restart
5.四层的两台squid服务器集群,由于squid.conf 文件中默认80指向的是baidu.test.com,所以我们保持默认即可。至此,8台linux服务器的配置都已ok,现在就是在客户端的测试了。下面看下访问的效果。
当访问baidu.test.com域名时:
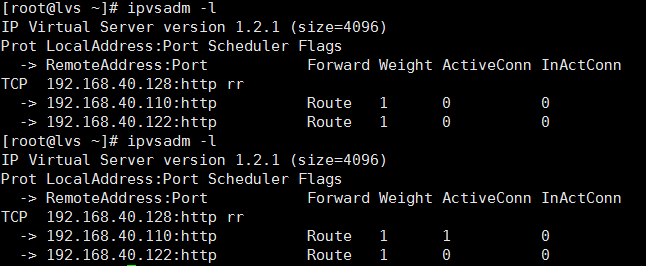
运行ipvsadm -l 命令,可以看到,在没访问之前,运行时,连接时为0 的,但我们访问后,在运行命令,便变成了1,此时,可以多次刷新网页,查看调度情况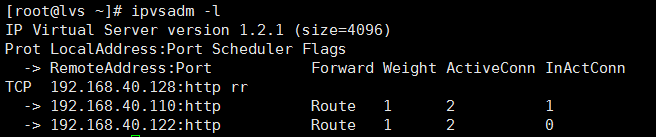
同样的道理,当用户访问sougo.test.com域名时,请求将被Bind全局负载解析调度到Nginx服务器上,再由七层中的集群缓存代理处理网页浏览请求。
三.总结
本次记录,主要利用了Bind作为全局负载,调度以LVS四层负载 + Nginx七层负载的集群,去访问web。在整个环节中,注意的几点:修改内核参数后,立即生效命令:sysctl -p 会打开防火墙,所以在每个环节中如果遇到问题,先排查一下iptables是否关闭。还有一点在dns配置时,也需要谨慎,因为正向或者反向,有时少一个. 可能就会造成解析失败。至于其中利用的技术原理,可以去百度补补。有的我也不是特别的完全明白。\(•ω•`)o