python scipy库基础学习(图片消噪, 求解圆周率, Scipy文件输入/输出, scipy矩阵)
文章目录
- 1、登月图片消噪
- 1.1、导入图片
- 1.2、查看图片信息
- 1.3、进行傅里叶变换
- 1.4、计算平均值并过滤大的值
- 1.5、反转变换
- 1.6、显示该图片
- 1.7、把图片变白
- 2、数值积分,求解圆周率
- 2.1、首先画一个圆
- 2.2、求圆的面积
- 3、Scipy文件输入/输出
- 3.1、使用io.savemat保存数据
- 3.2、使用io.loadmat()读取数据
- 3.3、读写图片
- 3.4、图片处理
- 3.5、图片进行过滤
- 4、scipy矩阵
- 4.1、创建矩阵
- 4.2、保存到本地
- 4.3、稀松矩阵
操作平台: win10,python37, jupyter
(1)导入包
import numpy as np
import scipy as sp
(2)查看版本
sp.__version__
'1.4.1'
1、登月图片消噪
- scipy 和numpy类似的高端的科学计算库
- 傅里叶变换:
- 物理世界中,所有东西,无论形态如何都是由基本粒子组成
- 数学世界中,所有公式,数据,无论形态如何,都是由基本的方程组成,正弦波
- 音乐,谱,数据,非常多歌曲------------->基本谱调组成
- 时域-------------->频域
- 人看到数据样子----------->真实样子,基本样子
- 时域是现象,频域是本质,将数据由表及里,来进行分析
- scipy.fftpack模块用来计算快速傅里叶变换
- 速度比传统傅里叶变换更快,是对之前算法的改进
- 图片是二维数据,注意使用fftpack的二维转变方法
# fft2处理二维数据;ifft2 inverse 反转
from scipy.fftpack import fft2,ifft2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
1.1、导入图片
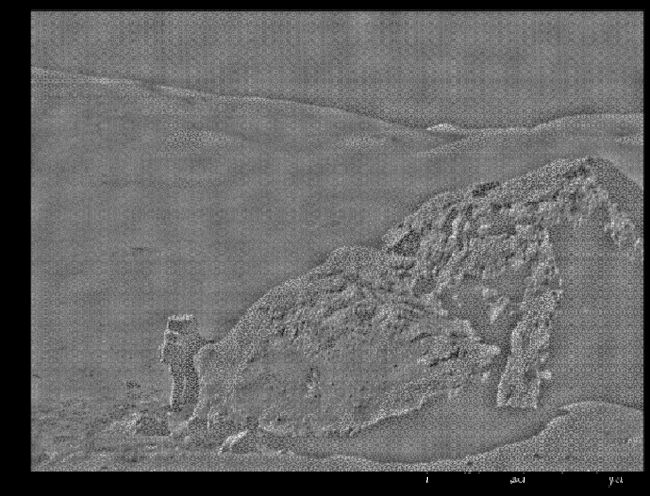
cmap = plt.cm.gray展示时对应的图片颜色,plt.cm.Blues,plt.cm.Reds- 登月不平滑:
- ‘噪声’------>白色圆环
- 数据不平滑---->不协调----->波动比较大
- 傅里叶变换,时域----->频域(波动)
- 将波动大的数据过滤掉,保留下的数据自然,平滑
- 傅里叶变化,高等算法,处理数据
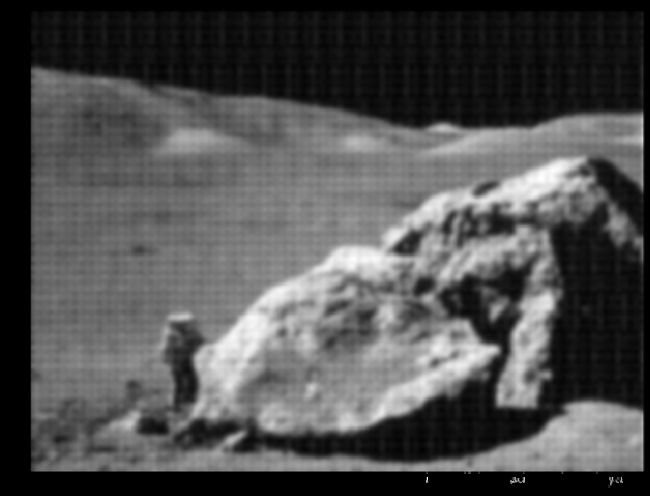
moon = plt.imread('./moonlanding.png')
plt.figure(figsize=(12,9))
plt.imshow(moon,cmap = plt.cm.gray)
plt.show()
1.2、查看图片信息
moon.shape #结果为(474, 630)
moon
array([[0.04705882, 0. , 0.23921569, ..., 0. , 0.00392157,
0.53333336],
[0. , 0. , 0.6784314 , ..., 0.10196079, 0.2901961 ,
0. ],
[0.72156864, 0.10980392, 0.6039216 , ..., 0. , 0.21568628,
1. ],
...,
[0.00392157, 0. , 1. , ..., 1. , 1. ,
0.95686275],
[0. , 0. , 0.15686275, ..., 0. , 0. ,
0.3529412 ],
[1. , 0.52156866, 0.04705882, ..., 0. , 0. ,
1. ]], dtype=float32)
1.3、进行傅里叶变换
moon_fft = fft2(moon)
moon_fft.shape #结果为(474, 630),形状没有变化
moon_fft
array([[126598.46 -0.j , -4608.579 -1892.4691j ,
-322.0927 -20.277735j, ..., -906.1584 +1539.3083j ,
-322.0927 +20.277735j, -4608.579 +1892.4691j ],
[ -9421.1 +5242.114j , 5224.017 -3171.743j ,
1607.9927 +1269.4243j , ..., -677.345 -936.16174j ,
354.62457-1003.8347j , 1965.366 -2188.0593j ],
[ -2928.3508 +7280.916j , -1116.4069 +1338.3181j ,
-474.20056 +385.40207j , ..., 239.77225 -977.2128j ,
1582.9283 -261.9535j , 2641.927 -292.0936j ],
...,
[ 1850.5717 -2451.1785j , -781.0807 +13.744507j,
377.90704 +12.66983j , ..., -1526.7867 +1271.2621j ,
-2705.5718 -3488.5286j , 1897.4039 -2281.9092j ],
[ -2928.3508 -7280.916j , 2641.927 +292.0936j ,
1582.9283 +261.9535j , ..., -2208.43 +81.80743j ,
-474.20056 -385.40207j , -1116.4069 -1338.3181j ],
[ -9421.1 -5242.114j , 1965.366 +2188.0593j ,
354.62457+1003.8347j , ..., 1190.5853 -1431.9934j ,
1607.9927 -1269.4243j , 5224.017 +3171.743j ]],
dtype=complex64)
1.4、计算平均值并过滤大的值
(1)计算所有数据波动频率平均值
np.abs(moon_fft).mean()
51.193375
(2)大于10倍平均值波动,波动比较大,过滤掉
cond = np.abs(moon_fft) > 500
cond
array([[ True, True, False, ..., True, False, True],
[ True, True, True, ..., True, True, True],
[ True, True, True, ..., True, True, True],
...,
[ True, True, False, ..., True, True, True],
[ True, True, True, ..., True, True, True],
[ True, True, True, ..., True, True, True]])
(3)过滤重新赋值,超过500的变成常量0
moon_fft[cond] = 0
1.5、反转变换
(1)将频域变为时域
# 将频域--------->时域(肉眼可见的图片)
moon_result = ifft2(moon_fft)
moon_result
array([[-0.21588416-2.06498307e-09j, 0.08547959-2.22494068e-09j,
-0.1734157 -6.48814069e-09j, ..., 0.00313994+2.01924011e-09j,
-0.12628847+1.93838989e-09j, -0.12006476-1.46896051e-09j],
...,
[-0.06233133-9.71054970e-09j, 0.06238186-7.02620895e-09j,
-0.05904225-1.34424294e-09j, ..., -0.05108551-1.63348766e-08j,
-0.01733965+1.31372992e-08j, -0.04830755+2.72279710e-09j]],
dtype=complex64)
(2)去掉虚数
moon2 = np.real(moon_result)
moon2
array([[-0.21588416, 0.08547959, -0.1734157 , ..., 0.00313994,
-0.12628847, -0.12006476],
[-0.07464704, 0.02630263, -0.05795978, ..., -0.10645279,
-0.10607976, -0.06213437],
...,
[-0.02365951, -0.21761245, -0.04112263, ..., -0.03240316,
-0.03881304, 0.18942524],
[-0.06233133, 0.06238186, -0.05904225, ..., -0.05108551,
-0.01733965, -0.04830755]], dtype=float32)
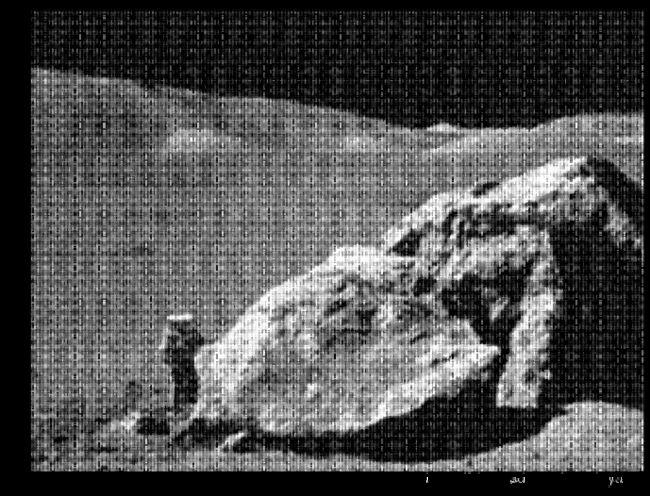
1.6、显示该图片
plt.figure(figsize=(12,9))
plt.imshow(moon2, cmap = plt.cm.gray)
1.7、把图片变白
(1)绝对值
moon3 = np.abs(moon2)
moon3
array([[0.21588416, 0.08547959, 0.1734157 , ..., 0.00313994, 0.12628847,
0.12006476],
[0.07464704, 0.02630263, 0.05795978, ..., 0.10645279, 0.10607976,
0.06213437],
[0.01300091, 0.04392406, 0.03069698, ..., 0.09355523, 0.09281518,
0.0542772 ],
...,
[0.00554967, 0.06839291, 0.11348298, ..., 0.05521009, 0.02254211,
0.17004329],
[0.02365951, 0.21761245, 0.04112263, ..., 0.03240316, 0.03881304,
0.18942524],
[0.06233133, 0.06238186, 0.05904225, ..., 0.05108551, 0.01733965,
0.04830755]], dtype=float32)
(2)数值增大
- 数值越大,图片亮度越高
moon4 = (moon3*255).astype(np.uint8) #数值变大并转换类型
moon4
array([[55, 21, 44, ..., 0, 32, 30],
[19, 6, 14, ..., 27, 27, 15],
[ 3, 11, 7, ..., 23, 23, 13],
...,
[ 1, 17, 28, ..., 14, 5, 43],
[ 6, 55, 10, ..., 8, 9, 48],
[15, 15, 15, ..., 13, 4, 12]], dtype=uint8)
(3)绘制图片
plt.figure(figsize=(12,9))
plt.imshow(moon4 + 100,cmap = plt.cm.gray)
2、数值积分,求解圆周率
- 求解圆周率
- integrate 对函数(1 - x2)0.5进行积分
- X2 + Y2 = 1,半径是1
- pi×r**2,只要求得面积—>pi
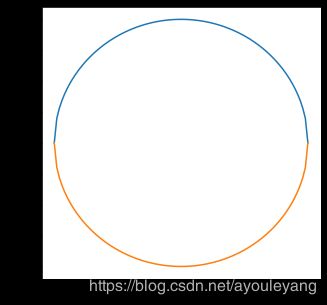
2.1、首先画一个圆
# X**2 + Y**2 = 1
# Y = (1 - X**2)**0.5
c = lambda x : (1-x**2)**0.5
x = np.linspace(-1,1,100)
y = c(x)
plt.figure(figsize=(5,5))
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.plot(x,-y)
2.2、求圆的面积
- 圆的面积等于:
s = pi * r ** 2 - 圆周率等于:
pi = s / (r**2) - 假设我们不知道圆周率,就可以使用积分的方式求上面个半圆的面积,然后乘以2,得到整个圆的面积。
- 求积分
- 使用scipy.integrate进行积分,调用quad()方法
from scipy import integrate
# 半圆面积,圆周率一半
integrate.quad(c,-1,1)
(1.5707963267948983, 1.0002354500215915e-09) #(结果,误差)
整个圆的面积:
1.5707963267948983 * 2
3.1415926535897967
当年祖冲之把 pi 精确到 3.1415926,我们的结果完全正确!
3、Scipy文件输入/输出
- 随机生成数组,使用scipy中的io.savemat()保存
- 文件格式是.mat,标准的二进制文件
from scipy import io
3.1、使用io.savemat保存数据
#将上面的moon2写入moon.mat
io.savemat('moon.mat',mdict = {'moon':moon2})
3.2、使用io.loadmat()读取数据
io.loadmat('./moon.mat')
{'__header__': b'MATLAB 5.0 MAT-file Platform: nt, Created on: Mon Apr 15 10:45:32 2019',
'__version__': '1.0',
'__globals__': [],
'moon': array([[-0.2158841 , 0.08547963, -0.17341562, ..., 0.00313992,
-0.1262884 , -0.12006474],
[-0.07464715, 0.02630262, -0.05795981, ..., -0.10645279,
-0.10607974, -0.06213436],
[ 0.01300102, -0.04392404, -0.03069701, ..., -0.09355526,
-0.09281505, 0.0542773 ],
...,
[ 0.00554965, -0.06839301, -0.11348293, ..., 0.05521014,
-0.02254207, 0.17004317],
[-0.0236596 , -0.21761242, -0.04112267, ..., -0.03240317,
-0.03881308, 0.18942517],
[-0.06233123, 0.06238206, -0.05904231, ..., -0.05108529,
-0.01733968, -0.04830741]], dtype=float32)}
3.3、读写图片
- 读写图片使用scipy中misc.imread()/imsave()
备注: 我上面用的的版本 1.4.1 出现了错误,AttributeError: module 'scipy.misc' has no attribute 'imread' ,于是我就降低了版本为 1.2.1 ,才运行成功的!
- 卸载以前的版本
pip uninstall scipy - 安装指定版本
pip install scipy==1.2.1
from scipy import misc
cat = misc.imread('./cat.jpg')
cat
array([[[231, 186, 131],
[232, 187, 132],
[233, 188, 133],
...,
[ 99, 54, 51],
[ 91, 47, 48],
[ 83, 41, 42]],
...,
[188, 98, 64],
[188, 95, 62],
[188, 95, 62]]], dtype=uint8)
(1)展示图片:
plt.imshow(cat)
(2)旋转60°
cat2 = misc.imrotate(cat,60) #旋转60度
plt.imshow(cat2)
(3)大小变换
''' size : int, float or tuple
* int - Percentage of current size.
* float - Fraction of current size.
* tuple - Size of the output image (height, width).'''
cat3 = misc.imresize(cat, 0.1) #10, 50, (100,100)
plt.imshow(cat3)
(4)滤波操作
# 滤波操作
''' ftype : str
The filter that has to be applied. Legal values are:
'blur', 'contour', 'detail', 'edge_enhance', 'edge_enhance_more',
'emboss', 'find_edges', 'smooth', 'smooth_more', 'sharpen'.'''
cat4 = misc.imfilter(cat,'smooth')
plt.imshow(cat4)
3.4、图片处理
- 使用scipy.misc.face(gray=True)获取图片,使用ndimage移动坐标、旋转图片、切割图片、缩放图片
(1)导包,读取图片显示图片
from scipy import ndimage
# scipy自带的一张图片,练习
# 使用任何图片都可以
face = misc.face()
plt.imshow(face)
(2)shift移动坐标
# 0 纯黑,255纯白
face2 = ndimage.shift(face,shift = [0,-500,0],cval = 255)
plt.imshow(face2)
(3)照镜子
face2 = ndimage.shift(face,shift = [0,-500,0],mode = 'mirror') # mode = {'reflect', 'constant', 'nearest', 'mirror', 'wrap'}
plt.imshow(face2)
(4)rotate旋转图片
face3 = ndimage.rotate(face,angle = 60)
plt.imshow(face3)
(5)zoom缩放图片
face4 = ndimage.zoom(face,zoom = [0.5,0.5,1/3],mode = 'mirror')
plt.imshow(face4.reshape(384,512),cmap = plt.cm.gray) #1/3为黑白图片,必须要降维二维才能显示
(6)透明度
face4 = ndimage.zoom(face,zoom = [0.5,0.5,4/3],mode = 'mirror')
face4.shape #结果为(384, 512, 4) #grb+透明
plt.imshow(face4,cmap = plt.cm.gray)
3.5、图片进行过滤
- 添加噪声,对噪声图片使用ndimage中的高斯滤波、中值滤波、signal中维纳滤波进行处理,使图片变清楚。
(1)高斯滤波sigma:高斯核的标准偏差
# 高斯分布,正太分布,概率不一样
# misc.imfilter(moon,'smooth')
moon5 = ndimage.gaussian_filter(moon,sigma = 3)
plt.figure(figsize=(12,9))
plt.imshow(moon5,cmap = plt.cm.gray)
(2)中值滤波
- 中值滤波参数size:给出在每个元素上从输入数组中取出的形状位置,定义过滤器功能的输入
moon6 = ndimage.median_filter(moon,size=5)
plt.figure(figsize=(12,9))
plt.imshow(moon6,cmap = plt.cm.gray)
4、scipy矩阵
- matrix,scipy将矩阵进行了封装,对象matrix
- sparse稀松矩阵:大部分是0,小部分是非零数据
优点:节省内存
from scipy import matrix
4.1、创建矩阵
(1)举证A
A = matrix(np.random.randint(0,10,size = (4,5)))
A
matrix([[5, 8, 8, 4, 6],
[3, 7, 5, 9, 5],
[1, 2, 1, 4, 0],
[8, 8, 1, 3, 7]])
(2)矩阵B
B = matrix(np.random.randint(0,10,size= (5,4)))
B
matrix([[3, 6, 5, 5],
[3, 0, 6, 2],
[5, 7, 2, 0],
[4, 8, 4, 0],
[3, 5, 8, 9]])
(3)乘积运算
A.dot(B)
matrix([[113, 148, 153, 95],
[106, 150, 143, 74],
[ 30, 45, 35, 9],
[ 86, 114, 158, 119]])
(4)创建一个10000 * 10000的矩阵
S = np.random.randint(0,100,size = (10000,10000))
S
array([[46, 19, 63, ..., 81, 92, 48],
[90, 35, 48, ..., 37, 23, 90],
[25, 42, 38, ..., 99, 25, 7],
...,
[76, 16, 30, ..., 82, 62, 83],
[39, 98, 94, ..., 61, 1, 6],
[62, 7, 99, ..., 47, 54, 91]])
4.2、保存到本地
(1)保存数据
np.save('./S.npy',S)
S[S < 98] = 0 #用0填充小于98的数据
S
array([[ 0, 0, 0, ..., 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, ..., 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 0, ..., 99, 0, 0],
...,
[ 0, 0, 0, ..., 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 98, 0, ..., 0, 0, 0],
[ 0, 0, 99, ..., 0, 0, 0]])
(3)重新保存数据
np.save('S2.npy',S)
文件结果的大小并没有被改变
(4)文件大小计算
10000 * 10000 * 32 / 8 / 1024 / 1024
381.4697265625
4.3、稀松矩阵
(1)转为稀松矩阵
# 稀松矩阵,大部分是0,小部分是非零数据
from scipy import sparse
S1 = sparse.csc_matrix(S)
print (S1)
(44, 0) 99
(51, 0) 99
(102, 0) 99
(156, 0) 99
: :
(9721, 9999) 98
(9801, 9999) 99
(9845, 9999) 99
(9945, 9999) 99
(2)保存数据
sparse.save_npz('./sparse.npz',S1)
- 几乎把它的大小降了100倍