基于VGG的猫狗识别
由于猫和狗的数据在这里,所以就做了一下分类的神经网络
1、首先进行图像处理:
import csv
import glob
import os
import random
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers
import numpy as np
gpus = tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices(device_type='GPU')
for gpu in gpus:
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(device=gpu, enable=True)
# 加载处理数据集
def load_csv(root, filename, name2label):
# 从csv文件返回images,labels列表
# root:数据集根目录,filename:csv文件名, name2label:类别名编码表
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(root, filename)):
# 如果csv文件不存在,则创建
images = []
for name in name2label.keys(): # 遍历所有子目录,获得所有的图片
# 只考虑后缀为png,jpg,jpeg的图片:'pokemon\\mewtwo\\00001.png
images += glob.glob(os.path.join(root, name, '*png')) # glob.glob()字符串匹配
images += glob.glob(os.path.join(root, name, '*.jpg'))
images += glob.glob(os.path.join(root, name, '*.jpeg'))
# 打印数据集信息:1167, 'pokemon\\bulbasaur\\00000000.png'
print(len(images), images)
random.shuffle(images) # 随机打散顺序
# 创建csv文件,并存储图片路径及其label信息
with open(os.path.join(root, filename), mode='w', newline='') as f:
writer = csv.writer(f)
for img in images:
name = img.split(os.sep)[-2] # 倒数第二个元素(就是name)
label = name2label[name]
writer.writerow([img, label])
print('written into csv file:', filename)
# 此时已经有csv文件,直接读取
images, labels = [], []
with open(os.path.join(root, filename)) as f:
reader = csv.reader(f)
for row in reader:
# 'pokemon\\bulbasaur\\00000000.png', 0
img, label = row
label = int(label)
images.append(img)
labels.append(label)
# 返回图片路径list和标签list
return images, labels
def load_train(root, mode='train'):
# 创建数字编码表
name2label = {} # 'sq...':0
# 遍历根目录下的子文件夹,并排序,保证映射关系固定
for name in sorted(os.listdir(os.path.join(root))):
# 跳过非文件夹
if not os.path.isdir(os.path.join(root, name)):
continue
# 给每个类别编码一个数字
name2label[name] = len(name2label.keys())
# 读取Lable信息
# [file1,file2],[3, 1]
images, labels = load_csv(root, 'image.csv', name2label)
if mode == 'train': # 60%
images = images[:int(0.6 * len(images))]
labels = labels[:int(0.6 * len(labels))]
elif mode == 'val': # 20% = 60%->80%
images = images[int(0.6 * len(images)):int(0.8 * len(images))]
labels = labels[int(0.6 * len(labels)):int(0.8 * len(labels))]
else: # 20% = 80%->100%
images = images[int(0.8 * len(images)):]
labels = labels[int(0.8 * len(labels)):]
return images, labels, name2label
# 这里的mean和std根据真实的数据计算获得,比如ImageNet
img_mean = tf.constant([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
img_std = tf.constant([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
def normalize(x, mean=img_mean, std=img_std):
# 标准化
x = (x-mean)/std
return x
def denormalize(x, mean=img_mean, std=img_std):
# 标准化的逆过程
x = x*std + mean
return x
def preprocess(x, y):
# x: 图片的路径List,y:图片的数字编码List
x = tf.io.read_file(x) # 根据路径读取图片
x = tf.image.decode_jpeg(x, channels=3) # 图片解码
x = tf.image.resize(x, [244, 244]) # 图片缩放
# data augmentation(数据增强)
# x = tf.image.random_flip_up_down(x) # 上下翻转
x = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(x) # 左右翻转
x = tf.image.random_crop(x, [224, 224, 3])
x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32)/255.
# 0~1 => D(0,1) normalize
x = normalize(x) # 标准化
y = tf.convert_to_tensor(y)
return x, y
def main():
import time
# 加载pokemon数据集,指定加载训练集
images, labels, table = load_train('train1', 'train')
print('images:', len(images), images)
print('labels:', len(labels), labels)
print('table:', table)
# images: string path
# labels: number
db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((images, labels))
db = db.shuffle(1000).map(preprocess).batch(32)
# 创建TensorBoard(可视化)对象
writter = tf.summary.create_file_writer('logs')
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(db):
# x:[32, 224, 224, 3]
# y:[32]
with writter.as_default():
x = denormalize(x) # 反向normalize,方便可视化
# 写入图片数据
tf.summary.image('img', x, step=step, max_outputs=9)
time.sleep(3)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()1.将png转化为vsc文件格式
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers,Sequential
tf.random.set_seed(22)
np.random.seed(22)
assert tf.__version__.startswith('2.')
class ResnetBlock(keras.Model):
def __init__(self, channels, strides=1):
super(ResnetBlock, self).__init__()
self.channels = channels
self.strides = strides
self.conv1 = layers.Conv2D(channels, (3, 3), strides=strides,
padding='same')
self.bn1 = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()
self.conv2 = layers.Conv2D(channels, (3, 3), strides=1,
padding='same')
self.bn2 = keras.layers.BatchNormalization()
if strides != 1:
self.down_conv = layers.Conv2D(channels, (1, 1), strides=strides)
self.down_bn = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()
def call(self, inputs, training=None):
residual = inputs
x = self.conv1(inputs)
x = tf.nn.relu(x)
x = self.bn1(x, training=training)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = tf.nn.relu(x)
x = self.bn2(x, training=training)
# 残差连接
if self.strides != 1:
residual = self.down_conv(inputs)
residual = tf.nn.relu(residual)
residual = self.down_bn(residual, training=training)
x = x + residual
x = tf.nn.relu(x)
return x
class ResNet(keras.Model):
def __init__(self, num_classes, initial_filters=16):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
# self.stem = layers.Conv2D(initial_filters, (3, 3), strides=3, padding='valid')
self.stem = Sequential([layers.Conv2D(initial_filters, (3, 3), strides=3, padding='valid'),
layers.BatchNormalization(),
layers.Activation('relu'),
layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=[2, 2], strides=(1, 1), padding='same')])
self.blocks = keras.models.Sequential([
ResnetBlock(initial_filters * 2, strides=3),
ResnetBlock(initial_filters * 2, strides=1),
layers.Dropout(rate=0.5),
ResnetBlock(initial_filters * 4, strides=3),
ResnetBlock(initial_filters * 4, strides=1),
layers.Dropout(rate=0.5),
ResnetBlock(initial_filters * 8, strides=2),
ResnetBlock(initial_filters * 8, strides=1),
layers.Dropout(rate=0.5),
ResnetBlock(initial_filters * 16, strides=2),
ResnetBlock(initial_filters * 16, strides=1),
])
self.final_bn = layers.BatchNormalization()
self.avg_pool = layers.GlobalMaxPool2D()
self.fc = layers.Dense(num_classes)
def call(self, inputs, training=None):
# print('x:',inputs.shape)
out = self.stem(inputs)
out = tf.nn.relu(out)
# print('stem:',out.shape)
out = self.blocks(out, training=training)
# print('res:',out.shape)
out = self.final_bn(out, training=training)
# out = tf.nn.relu(out)
out = self.avg_pool(out)
# print('avg_pool:',out.shape)
out = self.fc(out)
# print('out:',out.shape)
return out
def main():
num_classes = 5
resnet18 = ResNet(num_classes=5)
resnet18.build(input_shape=(4, 224, 224, 3))
resnet18.summary()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
2.基于VGG神经网络,进行二分类,由于只训练了400-500张的数据集,正确率只有91%。
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
import cv2.cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers, optimizers, Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping
from image预处理 import load_train, normalize
from resnet18 import ResNet
tf.random.set_seed(1234)
np.random.seed(1234)
# transfer
gpus = tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices(device_type='GPU')
for gpu in gpus:
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(device=gpu, enable=True)
def preprocess(x, y):
# x: 图片的路径List,y:图片的数字编码List
x = tf.io.read_file(x) # 根据路径读取图片
x = tf.image.decode_jpeg(x, channels=3) # 图片解码
x = tf.image.resize(x, [244, 244]) # 图片缩放
# data augmentation(数据增强)
# x = tf.image.random_flip_up_down(x) # 上下翻转
x = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(x) # 左右翻转
x = tf.image.random_crop(x, [224, 224, 3])
x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
# 0~1 => D(0,1) normalize
x = normalize(x) # 标准化
y = tf.convert_to_tensor(y)
y = tf.one_hot(y, depth=5)
return x, y
batchsz = 16
images, labels, _ = load_train('train1', mode='train')
db_train = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((images, labels))
db_train = db_train.map(preprocess).shuffle(500).batch(batchsz)
images2, labels2, _ = load_train('train1', mode='val')
db_val = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((images2, labels2))
db_val = db_val.map(preprocess).batch(batchsz)
images3, labels3, _ = load_train('train1', mode='test')
db_test = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((images3, labels3))
db_test = db_test.map(preprocess).batch(batchsz)
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(r'D:\甘露\train', 'train.h5')):
# 导入已经训练好的经典网络
net = keras.applications.VGG19(weights='imagenet', include_top=False, pooling='max')
net.trainable = False
newnet = Sequential([
net,
layers.Dense(5)
])
# resnet = ResNet(5)
newnet.build(input_shape=(None, 224, 224, 3))
newnet.summary()
# 监听指定指标
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(
monitor='val_accuracy',
min_delta=0.001,
patience=5 # 连续5次没有增加0.001
)
newnet.compile(optimizer=optimizers.Adam(1e-3),
loss=tf.losses.CategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=['accuracy'])
newnet.fit(db_train, epochs=5, validation_data=db_val, validation_freq=1, callbacks=[early_stopping])
newnet.evaluate(db_test)
newnet.save('facialmask.h5')
print('saved total model.')
else:
newnet = tf.keras.models.load_model('facialmask.h5')
print('load model from file!')
table = ['狗', '猫']
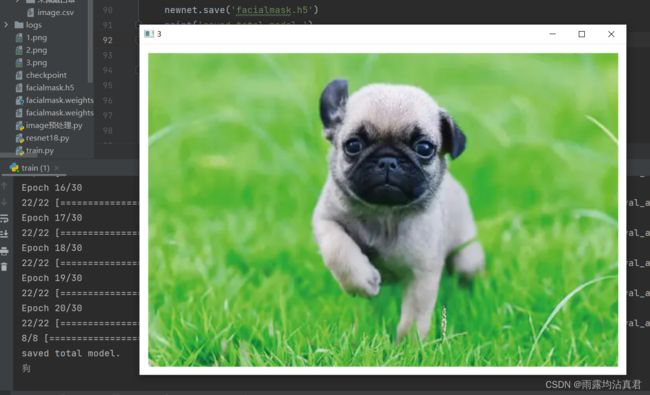
x = tf.io.read_file('2.png') # 根据路径读取图片
img = cv.imread('2.png')
cv.imshow('3', img)
x = tf.image.decode_jpeg(x, channels=3) # 图片解码
x = tf.image.resize(x, [224, 224]) # 图片缩放
x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
# 0~1 => D(0,1) normalize
x = normalize(x) # 标准化
x = tf.reshape(x, [1, 224, 224, 3])
logits = newnet(x)
prob = tf.nn.softmax(logits, axis=1)
pred = tf.argmax(prob, axis=1)
pred = tf.cast(pred, dtype=tf.int32)
num = int(pred)
print(table[num])
cv.waitKey(0)由于电脑配置的问题,epoch只能30次