cocos2dx 3.5 ”hello world“解析
cocos2dx 3.5工程下自带的helloworld程序目录如下:
先看看main.h和main.cpp:
#ifndef __MAIN_H__
#define __MAIN_H__
#define WIN32_LEAN_AND_MEAN // Exclude rarely-used stuff from Windows headers
// Windows Header Files:
#include
#include
// C RunTime Header Files
#include "CCStdC.h"
#endif // __MAIN_H__
#include "main.h"
#include "../Classes/AppDelegate.h"
USING_NS_CC;
int APIENTRY _tWinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance,
HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,
LPTSTR lpCmdLine,
int nCmdShow)
{
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(hPrevInstance);
UNREFERENCED_PARAMETER(lpCmdLine);
// create the application instance
AppDelegate app;
return Application::getInstance()->run();
}以下看看我们的应用代理类(AppDelegate.h和AppDelegate.cpp):
#ifndef _APP_DELEGATE_H_
#define _APP_DELEGATE_H_
#include "cocos2d.h"
/**
@brief The cocos2d Application.
The reason for implement as private inheritance is to hide some interface call by Director.
*/
class AppDelegate : private cocos2d::Application
{
public:
AppDelegate();
virtual ~AppDelegate();
virtual void initGLContextAttrs();
/**
@brief Implement Director and Scene init code here.
@return true Initialize success, app continue.
@return false Initialize failed, app terminate.
*/
virtual bool applicationDidFinishLaunching();
/**
@brief The function be called when the application enter background
@param the pointer of the application
*/
virtual void applicationDidEnterBackground();
/**
@brief The function be called when the application enter foreground
@param the pointer of the application
*/
virtual void applicationWillEnterForeground();
};
#endif // _APP_DELEGATE_H_#include "AppDelegate.h"
#include
#include
#include "HelloWorldScene.h"
#include "AppMacros.h"
USING_NS_CC;
using namespace std;
AppDelegate::AppDelegate() {
}
AppDelegate::~AppDelegate()
{
}
void AppDelegate::initGLContextAttrs()
{
GLContextAttrs glContextAttrs = {8, 8, 8, 8, 24, 8};
GLView::setGLContextAttrs(glContextAttrs);
}
bool AppDelegate::applicationDidFinishLaunching() {
// initialize director
auto director = Director::getInstance();
auto glview = director->getOpenGLView();
if(!glview) {
glview = GLViewImpl::create("Cpp Empty Test");
director->setOpenGLView(glview);
}
director->setOpenGLView(glview);
// Set the design resolution
#if (CC_TARGET_PLATFORM == CC_PLATFORM_WP8)
// a bug in DirectX 11 level9-x on the device prevents ResolutionPolicy::NO_BORDER from working correctly
glview->setDesignResolutionSize(designResolutionSize.width, designResolutionSize.height, ResolutionPolicy::SHOW_ALL);
#else
glview->setDesignResolutionSize(designResolutionSize.width, designResolutionSize.height, ResolutionPolicy::SHOW_ALL);
#endif
Size frameSize = glview->getFrameSize();
vector searchPath;
// In this demo, we select resource according to the frame's height.
// If the resource size is different from design resolution size, you need to set contentScaleFactor.
// We use the ratio of resource's height to the height of design resolution,
// this can make sure that the resource's height could fit for the height of design resolution.
// if the frame's height is larger than the height of medium resource size, select large resource.
if (frameSize.height > mediumResource.size.height)
{
searchPath.push_back(largeResource.directory);
director->setContentScaleFactor(MIN(largeResource.size.height/designResolutionSize.height, largeResource.size.width/designResolutionSize.width));
}
// if the frame's height is larger than the height of small resource size, select medium resource.
else if (frameSize.height > smallResource.size.height)
{
searchPath.push_back(mediumResource.directory);
director->setContentScaleFactor(MIN(mediumResource.size.height/designResolutionSize.height, mediumResource.size.width/designResolutionSize.width));
}
// if the frame's height is smaller than the height of medium resource size, select small resource.
else
{
searchPath.push_back(smallResource.directory);
director->setContentScaleFactor(MIN(smallResource.size.height/designResolutionSize.height, smallResource.size.width/designResolutionSize.width));
}
// set searching path
FileUtils::getInstance()->setSearchPaths(searchPath);
// turn on display FPS
director->setDisplayStats(true);
// set FPS. the default value is 1.0/60 if you don't call this
director->setAnimationInterval(1.0 / 60);
// create a scene. it's an autorelease object
auto scene = HelloWorld::scene();
// run
director->runWithScene(scene);
return true;
}
// This function will be called when the app is inactive. When comes a phone call,it's be invoked too
void AppDelegate::applicationDidEnterBackground() {
Director::getInstance()->stopAnimation();
// if you use SimpleAudioEngine, it must be pause
// SimpleAudioEngine::sharedEngine()->pauseBackgroundMusic();
}
// this function will be called when the app is active again
void AppDelegate::applicationWillEnterForeground() {
Director::getInstance()->startAnimation();
// if you use SimpleAudioEngine, it must resume here
// SimpleAudioEngine::sharedEngine()->resumeBackgroundMusic();
}
1)程序启动后,创建应用程序代理对象,此时会调用其基类构造函数:
Application::Application()
: _instance(nullptr)
, _accelTable(nullptr)
{
_instance = GetModuleHandle(nullptr);
_animationInterval.QuadPart = 0;
CC_ASSERT(! sm_pSharedApplication);
sm_pSharedApplication = this;
}可以看出这里主要是获取了当前进程模块的句柄以及保存了当前的应用程序对象指针。之后便run起来了:
Application::getInstance()->run();
int Application::run()
{
PVRFrameEnableControlWindow(false);
// Main message loop:
LARGE_INTEGER nLast;
LARGE_INTEGER nNow;
QueryPerformanceCounter(&nLast);
initGLContextAttrs();
// Initialize instance and cocos2d.
if (!applicationDidFinishLaunching())
{
return 0;
}
auto director = Director::getInstance();
auto glview = director->getOpenGLView();
// Retain glview to avoid glview being released in the while loop
glview->retain();
while(!glview->windowShouldClose())
{
QueryPerformanceCounter(&nNow);
if (nNow.QuadPart - nLast.QuadPart > _animationInterval.QuadPart)
{
nLast.QuadPart = nNow.QuadPart - (nNow.QuadPart % _animationInterval.QuadPart);
director->mainLoop();
glview->pollEvents();
}
else
{
Sleep(1);
}
}
// Director should still do a cleanup if the window was closed manually.
if (glview->isOpenGLReady())
{
director->end();
director->mainLoop();
director = nullptr;
}
glview->release();
return true;
}从这里可以看出,我们自己所写的AppDelegate类中的applicationDidFinishLaunching,initGLContextAttrs等函数的调用时机。可以看出以上代码关键部分为消息循环:
while(!glview->windowShouldClose())
{
QueryPerformanceCounter(&nNow);
if (nNow.QuadPart - nLast.QuadPart > _animationInterval.QuadPart)
{
nLast.QuadPart = nNow.QuadPart - (nNow.QuadPart % _animationInterval.QuadPart);
director->mainLoop();
glview->pollEvents();
}
else
{
Sleep(1);
}}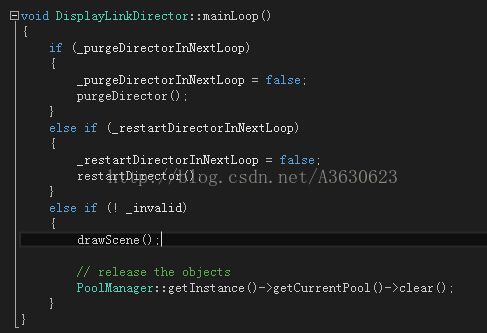
可看出这里主要是做渲染场景的工作,glview->pollEvents()代码主要为:
void GLViewImpl::pollEvents()
{
glfwPollEvents();
}// Draw the Scene
void Director::drawScene()
{
// calculate "global" dt
calculateDeltaTime();
if (_openGLView)
{
_openGLView->pollEvents();
}
//tick before glClear: issue #533
if (! _paused)
{
_scheduler->update(_deltaTime);
_eventDispatcher->dispatchEvent(_eventAfterUpdate);
}
_renderer->clear();
/* to avoid flickr, nextScene MUST be here: after tick and before draw.
* FIXME: Which bug is this one. It seems that it can't be reproduced with v0.9
*/
if (_nextScene)
{
setNextScene();
}
pushMatrix(MATRIX_STACK_TYPE::MATRIX_STACK_MODELVIEW);
if (_runningScene)
{
#if CC_USE_PHYSICS
auto physicsWorld = _runningScene->getPhysicsWorld();
if (physicsWorld && physicsWorld->isAutoStep())
{
physicsWorld->update(_deltaTime, false);
}
#endif
//clear draw stats
_renderer->clearDrawStats();
//render the scene
_runningScene->render(_renderer);
_eventDispatcher->dispatchEvent(_eventAfterVisit);
}
// draw the notifications node
if (_notificationNode)
{
_notificationNode->visit(_renderer, Mat4::IDENTITY, 0);
}
if (_displayStats)
{
showStats();
}
_renderer->render();
_eventDispatcher->dispatchEvent(_eventAfterDraw);
popMatrix(MATRIX_STACK_TYPE::MATRIX_STACK_MODELVIEW);
_totalFrames++;
// swap buffers
if (_openGLView)
{
_openGLView->swapBuffers();
}
if (_displayStats)
{
calculateMPF();
}
}可以看出关键的逻辑更新代码_scheduler->update(_deltaTime);为
// main loop
void Scheduler::update(float dt)
{
_updateHashLocked = true;
if (_timeScale != 1.0f)
{
dt *= _timeScale;
}
//
// Selector callbacks
//
// Iterate over all the Updates' selectors
tListEntry *entry, *tmp;
// updates with priority < 0
DL_FOREACH_SAFE(_updatesNegList, entry, tmp)
{
if ((! entry->paused) && (! entry->markedForDeletion))
{
entry->callback(dt);
}
}
// updates with priority == 0
DL_FOREACH_SAFE(_updates0List, entry, tmp)
{
if ((! entry->paused) && (! entry->markedForDeletion))
{
entry->callback(dt);
}
}
// updates with priority > 0
DL_FOREACH_SAFE(_updatesPosList, entry, tmp)
{
if ((! entry->paused) && (! entry->markedForDeletion))
{
entry->callback(dt);
}
}
// Iterate over all the custom selectors
for (tHashTimerEntry *elt = _hashForTimers; elt != nullptr; )
{
_currentTarget = elt;
_currentTargetSalvaged = false;
if (! _currentTarget->paused)
{
// The 'timers' array may change while inside this loop
for (elt->timerIndex = 0; elt->timerIndex < elt->timers->num; ++(elt->timerIndex))
{
elt->currentTimer = (Timer*)(elt->timers->arr[elt->timerIndex]);
elt->currentTimerSalvaged = false;
elt->currentTimer->update(dt);
if (elt->currentTimerSalvaged)
{
// The currentTimer told the remove itself. To prevent the timer from
// accidentally deallocating itself before finishing its step, we retained
// it. Now that step is done, it's safe to release it.
elt->currentTimer->release();
}
elt->currentTimer = nullptr;
}
}
// elt, at this moment, is still valid
// so it is safe to ask this here (issue #490)
elt = (tHashTimerEntry *)elt->hh.next;
// only delete currentTarget if no actions were scheduled during the cycle (issue #481)
if (_currentTargetSalvaged && _currentTarget->timers->num == 0)
{
removeHashElement(_currentTarget);
}
}
// delete all updates that are marked for deletion
// updates with priority < 0
DL_FOREACH_SAFE(_updatesNegList, entry, tmp)
{
if (entry->markedForDeletion)
{
this->removeUpdateFromHash(entry);
}
}
// updates with priority == 0
DL_FOREACH_SAFE(_updates0List, entry, tmp)
{
if (entry->markedForDeletion)
{
this->removeUpdateFromHash(entry);
}
}
// updates with priority > 0
DL_FOREACH_SAFE(_updatesPosList, entry, tmp)
{
if (entry->markedForDeletion)
{
this->removeUpdateFromHash(entry);
}
}
_updateHashLocked = false;
_currentTarget = nullptr;
#if CC_ENABLE_SCRIPT_BINDING
//
// Script callbacks
//
// Iterate over all the script callbacks
if (!_scriptHandlerEntries.empty())
{
for (auto i = _scriptHandlerEntries.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
SchedulerScriptHandlerEntry* eachEntry = _scriptHandlerEntries.at(i);
if (eachEntry->isMarkedForDeletion())
{
_scriptHandlerEntries.erase(i);
}
else if (!eachEntry->isPaused())
{
eachEntry->getTimer()->update(dt);
}
}
}
#endif
//
// Functions allocated from another thread
//
// Testing size is faster than locking / unlocking.
// And almost never there will be functions scheduled to be called.
if( !_functionsToPerform.empty() ) {
_performMutex.lock();
// fixed #4123: Save the callback functions, they must be invoked after '_performMutex.unlock()', otherwise if new functions are added in callback, it will cause thread deadlock.
auto temp = _functionsToPerform;
_functionsToPerform.clear();
_performMutex.unlock();
for( const auto &function : temp ) {
function();
}
}
}Scene* HelloWorld::scene()
{
// 'scene' is an autorelease object
auto scene = Scene::create();
// 'layer' is an autorelease object
HelloWorld *layer = HelloWorld::create();
// add layer as a child to scene
scene->addChild(layer);
// return the scene
return scene;
}#define CREATE_FUNC(__TYPE__) \
static __TYPE__* create() \
{ \
__TYPE__ *pRet = new(std::nothrow) __TYPE__(); \
if (pRet && pRet->init()) \
{ \
pRet->autorelease(); \
return pRet; \
} \
else \
{ \
delete pRet; \
pRet = NULL; \
return NULL; \
} \
}最后,我们欣赏下glfw框架下的helloworld程序:
#include
int main(void)
{
GLFWwindow* window;
/* Initialize the library */
if (!glfwInit())
return -1;
/* Create a windowed mode window and its OpenGL context */
window = glfwCreateWindow(480, 320, "Hello World", NULL, NULL);
if (!window)
{
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
/* Make the window's context current */
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
/* Loop until the user closes the window */
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
/* Draw a triangle */
glBegin(GL_TRIANGLES);
glColor3f(1.0, 0.0, 0.0); // Red
glVertex3f(0.0, 1.0, 0.0);
glColor3f(0.0, 1.0, 0.0); // Green
glVertex3f(-1.0, -1.0, 0.0);
glColor3f(0.0, 0.0, 1.0); // Blue
glVertex3f(1.0, -1.0, 0.0);
glEnd();
/* Swap front and back buffers */
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
/* Poll for and process events */
glfwPollEvents();
}
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}