torch.gather()函数
b = torch.Tensor([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
print(b)
index_1 = torch.LongTensor([[0,1],[2,0]])
index_2 = torch.LongTensor([[0,1,1],[0,0,0]])
print (torch.gather(b, dim=1, index=index_1))
print (torch.gather(b, dim=0, index=index_2))
输出:
tensor([[1., 2., 3.],
[4., 5., 6.]])
tensor([[1., 2.],
[6., 4.]])
tensor([[1., 5., 6.],
[1., 2., 3.]])
根据维度dim按照索引列表index从input中选取指定元素
如上述例子,个人理解如下:
 又如:
又如:
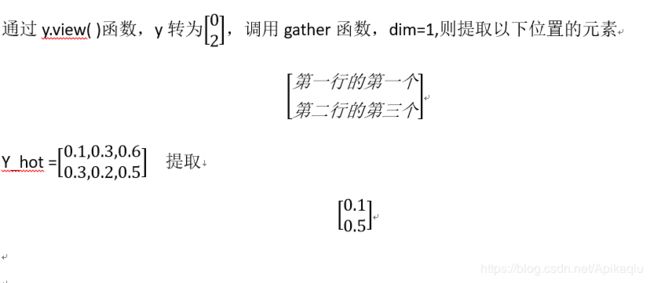
y_hat = torch.tensor([[0.1, 0.3, 0.6], [0.3, 0.2, 0.5]])
y = torch.LongTensor([0, 2])
y_hat.gather(1, y.view(-1, 1))
输出:
tensor([[0.1000],
[0.5000]])
官方文档的解释
torch.gather(input, dim, index, out=None) → Tensor
Gathers values along an axis specified by dim.
For a 3-D tensor the output is specified by:
out[i][j][k] = input[index[i][j][k]][j][k] # dim=0
out[i][j][k] = input[i][index[i][j][k]][k] # dim=1
out[i][j][k] = input[i][j][index[i][j][k]] # dim=2
Parameters:
input (Tensor) – The source tensor
dim (int) – The axis along which to index
index (LongTensor) – The indices of elements to gather
out (Tensor, optional) – Destination tensor
Example:
>>> t = torch.Tensor([[1,2],[3,4]])
>>> torch.gather(t, 1, torch.LongTensor([[0,0],[1,0]]))
1 1
4 3
[torch.FloatTensor of size 2x2]