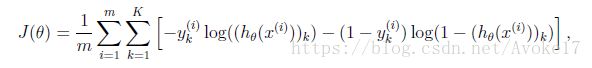Coursera-Machine-Learning-ex4
上一个练习中我们使用给定的权重矩阵对手写数字进行预测,本次练习中,我们尝试去学习参数θ。
Neural Networks
首先使用displayData方法对训练集数据进行可视化。
和之前的训练集一样,共5000个训练样本,每个样本为20*20像素的图片,展开以400维向量形式给出。训练样本处理如下:
首先确定结构,我们本次使用三层结构,一个输入层,一个隐藏层,一个输出层。由于我们每个样本输入有400个元素,所以我们设定400个输入单元(不计算偏置单元),那么我们需要θ1和θ2两个权重矩阵需要学习,其中隐藏层有25个单元,输出层有10个单元。
然后我们首先完成代价函数和梯度下降计算部分。首先利用公式写出h(x)的计算结果,写出不含正则项的代价函数。
经过程序验证后可以加入正则项,公式如下:
然后我们需要使用反向传播算法写出偏导项的计算公式,反向传播算法和nnCostFunction.m代码如下:
function [J grad] = nnCostFunction(nn_params, ...
input_layer_size, ...
hidden_layer_size, ...
num_labels, ...
X, y, lambda)
%NNCOSTFUNCTION Implements the neural network cost function for a two layer
%neural network which performs classification
% [J grad] = NNCOSTFUNCTON(nn_params, hidden_layer_size, num_labels, ...
% X, y, lambda) computes the cost and gradient of the neural network. The
% parameters for the neural network are "unrolled" into the vector
% nn_params and need to be converted back into the weight matrices.
%
% The returned parameter grad should be a "unrolled" vector of the
% partial derivatives of the neural network.
%
% Reshape nn_params back into the parameters Theta1 and Theta2, the weight matrices
% for our 2 layer neural network
Theta1 = reshape(nn_params(1:hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + 1)), ...
hidden_layer_size, (input_layer_size + 1));
Theta2 = reshape(nn_params((1 + (hidden_layer_size * (input_layer_size + 1))):end), ...
num_labels, (hidden_layer_size + 1));
% Setup some useful variables
m = size(X, 1);
% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
Theta1_grad = zeros(size(Theta1));
Theta2_grad = zeros(size(Theta2));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: You should complete the code by working through the
% following parts.
%
% Part 1: Feedforward the neural network and return the cost in the
% variable J. After implementing Part 1, you can verify that your
% cost function computation is correct by verifying the cost
% computed in ex4.m
%
% Part 2: Implement the backpropagation algorithm to compute the gradients
% Theta1_grad and Theta2_grad. You should return the partial derivatives of
% the cost function with respect to Theta1 and Theta2 in Theta1_grad and
% Theta2_grad, respectively. After implementing Part 2, you can check
% that your implementation is correct by running checkNNGradients
%
% Note: The vector y passed into the function is a vector of labels
% containing values from 1..K. You need to map this vector into a
% binary vector of 1's and 0's to be used with the neural network
% cost function.
%
% Hint: We recommend implementing backpropagation using a for-loop
% over the training examples if you are implementing it for the
% first time.
%
% Part 3: Implement regularization with the cost function and gradients.
%
% Hint: You can implement this around the code for
% backpropagation. That is, you can compute the gradients for
% the regularization separately and then add them to Theta1_grad
% and Theta2_grad from Part 2.
%
a1 = [ones(m, 1) X];
z2 = a1 * Theta1';
a2 = sigmoid(z2);
a2 = [ones(m, 1) a2];
z3 = a2 * Theta2';
h = sigmoid(z3);
yk = zeros(m, num_labels);
for i = 1:m
yk(i, y(i)) = 1;
end
J = (1/m)* sum(sum(((-yk) .* log(h) - (1 - yk) .* log(1 - h))));
r = (lambda / (2 * m)) * (sum(sum(Theta1(:, 2:end) .^ 2))
+ sum(sum(Theta2(:, 2:end) .^ 2)));
J = J + r;
for row = 1:m
a1 = [1 X(row,:)]';
z2 = Theta1 * a1;
a2 = sigmoid(z2);
a2 = [1; a2];
z3 = Theta2 * a2;
a3 = sigmoid(z3);
z2 = [1; z2];
delta3 = a3 - yk'(:, row);
delta2 = (Theta2' * delta3) .* sigmoidGradient(z2);
delta2 = delta2(2:end);
Theta1_grad = Theta1_grad + delta2 * a1';
Theta2_grad = Theta2_grad + delta3 * a2';
end
Theta1_grad = Theta1_grad ./ m;
Theta1_grad(:, 2:end) = Theta1_grad(:, 2:end) ...
+ (lambda/m) * Theta1(:, 2:end);
Theta2_grad = Theta2_grad ./ m;
Theta2_grad(:, 2:end) = Theta2_grad(:, 2:end) + ...
+ (lambda/m) * Theta2(:, 2:end);
% -------------------------------------------------------------
% =========================================================================
% Unroll gradients
grad = [Theta1_grad(:) ; Theta2_grad(:)];
end进行神经网络训练时,权重矩阵的随机初始化很重要。这里我们设置初始化的随机值在-0.12至0.12之间,设定一个较小的值以确保证学习过程更有效率。randInitializeWeights.m的代码如下:
function W = randInitializeWeights(L_in, L_out)
%RANDINITIALIZEWEIGHTS Randomly initialize the weights of a layer with L_in
%incoming connections and L_out outgoing connections
% W = RANDINITIALIZEWEIGHTS(L_in, L_out) randomly initializes the weights
% of a layer with L_in incoming connections and L_out outgoing
% connections.
%
% Note that W should be set to a matrix of size(L_out, 1 + L_in) as
% the first column of W handles the "bias" terms
%
% You need to return the following variables correctly
W = zeros(L_out, 1 + L_in);
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Initialize W randomly so that we break the symmetry while
% training the neural network.
%
% Note: The first column of W corresponds to the parameters for the bias unit
%
epsilon_init=0.12;
W=rand(L_out,1+L_in)*2*epsilon_init-epsilon_init;
% =========================================================================
end然后我们加入梯度验证,使用近似项计算偏导项值,checkNNGradients.m代码如下:
function numgrad = computeNumericalGradient(J, theta)
%COMPUTENUMERICALGRADIENT Computes the gradient using "finite differences"
%and gives us a numerical estimate of the gradient.
% numgrad = COMPUTENUMERICALGRADIENT(J, theta) computes the numerical
% gradient of the function J around theta. Calling y = J(theta) should
% return the function value at theta.
% Notes: The following code implements numerical gradient checking, and
% returns the numerical gradient.It sets numgrad(i) to (a numerical
% approximation of) the partial derivative of J with respect to the
% i-th input argument, evaluated at theta. (i.e., numgrad(i) should
% be the (approximately) the partial derivative of J with respect
% to theta(i).)
%
numgrad = zeros(size(theta));
perturb = zeros(size(theta));
e = 1e-4;
for p = 1:numel(theta)
% Set perturbation vector
perturb(p) = e;
loss1 = J(theta - perturb);
loss2 = J(theta + perturb);
% Compute Numerical Gradient
numgrad(p) = (loss2 - loss1) / (2*e);
perturb(p) = 0;
end
end
一旦计算出的值和近似值之差很小,我们就可以确认梯度计算是正确的。关闭梯度检验,然后我们使用fmincg来学习参数θ,便可以得到使代价函数最小的参数。