大数据项目之ip条数统计 nginx flume kafka hive
一.项目目的
对日志中ip条数进行统计统计
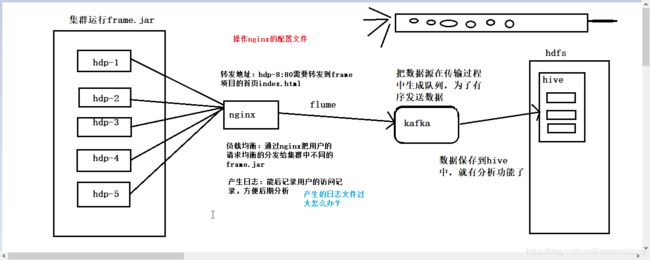
二.项目流程
图片出自:https://blog.csdn.net/lucasmaluping/article/details/102685434
三.项目操作
1.frame打成jar包上传到linux集群
通过java -jar,测试是否 运行成功:hdp-1:8889
2.修改配置文件,自定义ngnix输出日志的格式
修改配置文件 cd /usr/local/nginx/conf vi nginx.conf
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
##ngnix输出日志的格式
log_format main '{ time:"$time_iso8601", '
'ip:$remote_addr", '
'referer":"$http_referer", '
'request:"$request", '
'status": $status, '
'bytes":$body_bytes_sent, '
'agent": "$http_user_agent", '
'x_forwarded:"$http_x_forwarded_for", }';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
##指明nginx转发地址
upstream frame-tomcat {
server hdp-1:8889;
}
##nginx的服务地址
server {
listen 80;
server_name hdp-1;
#charset koi8-r;
##输出生成的日志文件的路径和格式
access_log logs/frame.access.log main;
##代理传递(转发)
location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
proxy_pass http://frame-tomcat;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl on;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_protocols SSLv2 SSLv3 TLSv1;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}3.编写flume采集nginx日志数据下沉到kafka的topic配置文件
cd apps/flume-1.6.0/conf vi nginxtokafka.conf
a1.sources = source1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
##指明数据源来自于一个可执行指令
a1.sources.source1.type = exec
##可执行指令,跟踪一个文件中的内容
a1.sources.source1.command = tail -F /usr/local/nginx/logs/frame.access.log
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = org.apache.flume.sink.kafka.KafkaSink
a1.sinks.k1.topic = animal
a1.sinks.k1.brokerList = hdp-1:9092,hdp-2:9092,hdp-3:9092
a1.sinks.k1.requiredAcks = 1
a1.sinks.k1.batchSize = 20
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.source1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c14.编写flume采集kafka下沉到hive配置文件
cd apps/flume-1.6.0/conf vi kafkatohive.conf
#Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.type=org.apache.flume.source.kafka.KafkaSource
a1.sources.r1.zookeeperConnect=hdp-1:2181,hdp-2:2181,hdp-3:2181
a1.sources.r1.kafka.bootstrap.servers=hdp-1:9092,hdp-2:9092,hdp-3:9092
a1.sources.r1.batchSize=10
##自己的topic
a1.sources.r1.topic=animal
a1.sources.r1.channels=c1
a1.sources.r1.consumer.timeout.ms=1000
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
# 收集到hdfs的地址
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://hdp-1:9000/kafka/log/
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.writeFormat = Text
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 10
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 0
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = %Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
# Use a channel which buffers events in file
a1.channels.c1.type = file
a1.channels.c1.checkpointDir = /home/hadoop/flume/checkpoint
a1.channels.c1.dataDirs = /home/hadoop/flume/data
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c15.Hive中创建数据库和表
首先启动zookeeper 然后启动hive,在hive中建外部表
字段名与类型与nginx日志输出的格式一样
create external table t_access(time String,ip String,referer String,request String,status Int,bytes String,agent String,x_forwarded String)row format delimited
fields terminated by ','
location '/kafka/log';6.启动hdfs
在hdp-1上执行脚本:start-all.sh
7.启动kafka
在hdp-1上执行脚本:./start-kafka-cluster.sh
8.启动nginx
在hdp-1上执行:cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin ./nginx
9.启动flume采集nginx日志数据下沉到kafka的topic
在hdp-1上执行:cd apps/flume-1.6.0/bin/
./flume-ng agent -c conf -n a1 -f ../conf/nginxtokafka.conf -Dflume.root.logger=DEBUG,console
注意:这里可以开启一个consumer来消费消息,验证这一步是否下沉成功
cd apps/kafka_2.12-2.2.0/bin/
启动消费者
./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server hdp-1:9092,hdp-2:9092,hdp-3:9092 --topic animal --from-beginning
10.启动flume采集kafka下沉到hive
在hdp-1上执行:cd apps/flume-1.6.0/bin/
./flume-ng agent -c conf -n a1 -f ../conf/kafkatohive.conf -Dflume.root.logger=DEBUG,console
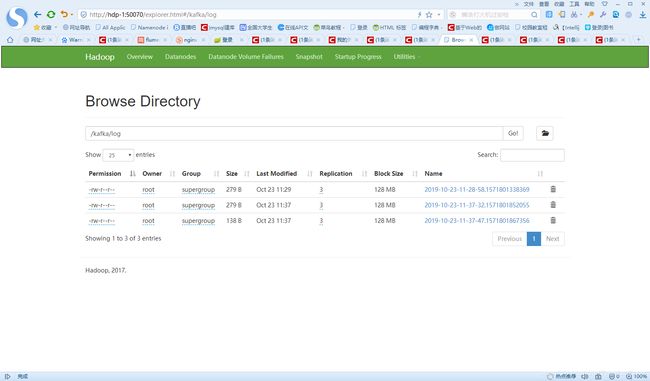
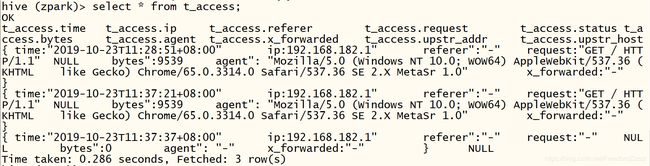
11.查看数据是否下沉到hive中
数据下沉成功,查询到数据。
12.使用聚合函数查看ip的总条数
完成!查询到ip条数为3