ZooKeeper leader选举 源码分析
文章目录
- Leader选举算法
- 一句话概况选举算法精髓
- 选举算法流程解析--lookForLeader
- 如何跟其他节点交换投票:网络I/O
Leader选举算法
一句话概况选举算法精髓
所有节点都有两个属性,SID:节点ID,zoo.cfg中配置的myid,ZXID:节点当前的最大事务ID
选举的目的就是选目前所有节点中拥有最大ZXID的节点作为Leader,如果拥有的ZXID相同,就选取SID最大的节点作为Leader
选举算法流程解析–lookForLeader
在实现选举的过程中,其实还有很多细节需要注意,那么接下来看下选举的具体细节:
在ZooKeeper中,提供了3种Leader的选举算法,分别是LeaderElection、 UDP版本的FastLeaderElection、TCP版本的FastLeaderElection,可以通过再配置文件zoo.cfg中使用electionAlg属性来指定。从3.4.0版本开始,ZooKeeper废弃了前2种算法,只保留了TCP版本的FastLeaderElection算法。所有算法都实现了Election接口:
public interface Election {
//选举的核心算法
public Vote lookForLeader() throws InterruptedException;
//关闭选举过程中创建了链接及启动的线程
public void shutdown();
}
先看下选举算法核心部分(FastLeaderElection.lookForLeader)的流程示意图:
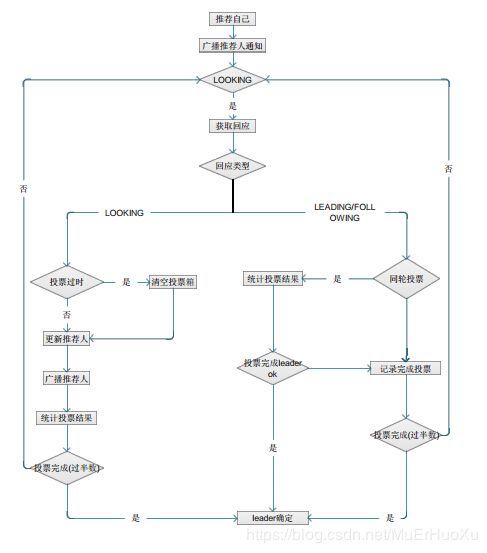
lookForLeader详细源码
- 每次选举开始,各个节点都会先为自己投票(原子操作),其中logicalclock代表选举逻辑时钟(类比现实中的第十八次全国人大、第十九次全国人大……),这个值从0开始递增,在同一次选举中,各节点的值基本相同,也有例外情况,比如在第18次选举中,某个节点A挂了,其他节点完成了Leader选举,但没过多久,该Leader又挂了,于是进入了第19次Leader选举,同时节点A此时恢复,加入到Leader选举中,那么节点A的logicallock为18,而其他节点的logicallock为19,针对这种情况,节点A的logicallock会被直接更新为19并参与到第19次Leader选举中。
其中getInitId()是当前节点的serverId, getInitLastLoggedZxid()是当前节点的最大事务ID,getPeerEpoch当前节点选举轮次,即当前节点Zxid的高位代表的epoch其中getInitId()是当前节点的serverId, getInitLastLoggedZxid()是当前节点的最大事务ID,getPeerEpoch当前节点选举轮次,即当前节点Zxid的高位代表的epoch
public Vote lookForLeader() throws InterruptedException {
{...}
try {
HashMap recvset = new HashMap();
HashMap outofelection = new HashMap();
int notTimeout = finalizeWait;
//1.初始化选票,首先为自己投票
synchronized(this){
logicalclock++;
updateProposal(getInitId(), getInitLastLoggedZxid(), getPeerEpoch());
}
//2.向所有节点发送投票信息
sendNotifications();
/*
* Loop in which we exchange notifications until we find a leader
* 3.循环交换投票直至选出Leader
*/
while ((self.getPeerState() == ServerState.LOOKING) &&
(!stop)){...}
}
}
- 向所有节点发送投票信息
private void sendNotifications() {
for (QuorumServer server : self.getVotingView().values()) {
long sid = server.id;
ToSend notmsg = new ToSend(ToSend.mType.notification,
proposedLeader, //推荐的leader的id,就是配置文件中写好的每个服务器的id
proposedZxid, //推荐的leader的zxid,zookeeper中的每份数据,都有一个对应的zxid值,越新的数据,zxid值就越大
logicalclock, //选举的逻辑时钟
QuorumPeer.ServerState.LOOKING,
sid,
proposedEpoch);
sendqueue.offer(notmsg);
}
}
- 循环交换投票直至选出Leader
while ((self.getPeerState() == ServerState.LOOKING) &&
(!stop)){
//从接收投票的队列中取出一条投票信息
Notification n = recvqueue.poll(notTimeout,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if(n == null){...}
else if(self.getVotingView().containsKey(n.sid)) {
switch (n.state) {
case LOOKING://拿别人的票跟自己对比,谁的更合理,就发出去更合理的选票(类似于冒泡排序算法,每次对比,都选比自己大/小的数)
case OBSERVING://观察者是不参与Leader选举的
case FOLLOWING:
case LEADING://当已经收到LEADING和FOLLOWING表示已经票选出Leader,然后投最后一票给Leader,结束投票
default:
}
}
}
LOOKING相关部分是leader选举的精髓所在,注释中提到的更合理的选票,其实就是在两两PK中,更适合做Leader的选票。谁的选票更合理,大家就选谁为Leader,如果过半数的节点都选择了某个服务器为Leader,那该服务器就成了真正的Leader。看下它具体是如何实现的
/ * 表示投票轮次大于本节点记录的轮次,表示自己已经落后投票了,将自己的
* 投票轮次设置为最新的,清空自己的票箱,这个票箱记录了集群中其他节点
* 的投票结果
*/
if (n.electionEpoch > logicalclock) {
logicalclock = n.electionEpoch;
recvset.clear();
/*
* 将n节点的投票结果与自己的投票结果比较,如果投票比自己的投票合理,
* 覆盖自己的投票,否则还是投自己
*/
if(totalOrderPredicate(n.leader, n.zxid, n.peerEpoch,getInitId(), getInitLastLoggedZxid(), getPeerEpoch())) {
updateProposal(n.leader, n.zxid, n.peerEpoch);
} else {
updateProposal(getInitId(),getInitLastLoggedZxid(),getPeerEpoch());
}
//发送在此次PK过程中,发送更加合理的选票给其他节点
sendNotifications();
} else if (n.electionEpoch < logicalclock) {
// 投票轮次比自己记录的轮次小,说明这个投票已经过时,不处理
break;
} else if (totalOrderPredicate(n.leader, n.zxid, n.peerEpoch,proposedLeader, proposedZxid, proposedEpoch)) {
// 如果是一个轮次,将n节点的投票与自己PK,如果n节点的投票更合理,覆盖自己投票,并将更合理的选票给其他节点
updateProposal(n.leader, n.zxid, n.peerEpoch);
sendNotifications();
}
// 将n节点的投票记录下来
recvset.put(n.sid, new Vote(n.leader, n.zxid, n.electionEpoch, n.peerEpoch));
/*
* 尝试通过现在已经收到的信息,判断是否已经足够确认最终的leader了,通过方法termPredicate() ,判断标准很简单:是否已经有超过半数的机
* 器所推举的leader为当前自己所推举的leader.如果是,保险起见,最多再等待finalizeWait(默认200ms)的时间进行最后的确认,如果发现有
* 了更新的leader信息,则把这个Notification重新放回recvqueue,显然,选举将继续进行。否则,选举结束,根据选举的leader是否是自己,设
* 置自己的状态为LEADING或者OBSERVING或者FOLLOWING。
*/
if (termPredicate(recvset,new Vote(proposedLeader, proposedZxid, logicalclock, proposedEpoch))) {
while((n = recvqueue.poll(finalizeWait,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) != null){
if(totalOrderPredicate(n.leader, n.zxid, n.peerEpoch, proposedLeader, proposedZxid, proposedEpoch)){
recvqueue.put(n);
break;
}
}
//队列中所有的投票都已处理完,则选举出Leader,并判断是否属于自己
if (n == null) {
self.setPeerState((proposedLeader == self.getId()) ? ServerState.LEADING: learningState());
Vote endVote = new Vote(proposedLeader, proposedZxid, proposedEpoch);
leaveInstance(endVote);
return endVote;
}
}
break;
totalOrderPredicate为判断更合理的逻辑,比较的顺序是Epoch、zxid、Id,优先选投票轮次高的,投票轮次相同选Zxid高的,Zxid相同选id高的,因此在Zookeeper启动的时候,往往id高的获得Leader,但不绝对,比如在5个节点的集群中,启动顺序分别是1->2->3->4->5,当票选到节点3时已经票选超过半数,那么后面启动的4和5就直接成为follower
protected boolean totalOrderPredicate(long newId, long newZxid, long newEpoch, long curId, long curZxid, long curEpoch) {
if(self.getQuorumVerifier().getWeight(newId) == 0){
return false;
}
/*
返回true说明接收到的外部投票更合理,要覆盖内部投票
* We return true if one of the following three cases hold:
* 1- New epoch is higher
* 2- New epoch is the same as current epoch, but new zxid is higher
* 3- New epoch is the same as current epoch, new zxid is the same
* as current zxid, but server id is higher.
*/
return ((newEpoch > curEpoch) ||
((newEpoch == curEpoch) &&
((newZxid > curZxid) || ((newZxid == curZxid) && (newId > curId)))));
}
termPredicate为判断过半的逻辑,在默认实现类QuorumMaj中进行过半的判断:
private boolean termPredicate(
HashMap votes,
Vote vote) {
HashSet set = new HashSet();
/*
* First make the views consistent. Sometimes peers will have
* different zxids for a server depending on timing.
*/
for (Map.Entry entry : votes.entrySet()) {
if (vote.equals(entry.getValue())){
set.add(entry.getKey());
}
}
//默认实现类为QuorumMaj
return self.getQuorumVerifier().containsQuorum(set);
}
步骤3的循环,最终会得到超过半数节点认同的Leader的投票,至此完成Leader选举。
如何跟其他节点交换投票:网络I/O
在看了以上的代码实现,似乎遗漏了一个重要环节,就是向其他节点发送选票、接收其他节点的投票,具体是如何实现的呢?这离不开QuorumCnxManager这个大功臣,让我们一点点往下来看:
系统初始化时,每一个QuorumPeer对象(一个QuorumPeer可以理解为一个准备参加选举的ZK的server,即配置文件zoo.cfg中配置的服务器)维护了一个FastLeaderElection对象来为自己的选举工作进行代言。在选举过程中需要进行消息的沟通,因此在FastLeaderElection中维护了两个变量:
LinkedBlockingQueue sendqueue;
LinkedBlockingQueue recvqueue;
recvqueue中存放了选举过程中接收到的消息,这些消息被交给了FastLeaderElection的最核心方法lookForLeader()进行处理以选举出leader。而sendqueue中存放了待发送出去的消息。
同时,每一个FastLeaderElection变量维护了一个内置类Messager,Messager类包含了两个实现了Runnable接口的类WorkerReceiver和WorkerSender,从名字可以看出,这两个类分别负责消息的发送和接收。即WorkerReceiver负责接收消息并将接收到的消息放入recvqueue中等待处理,WorkerSender负责从sendqueue中取出待发送消息,交给下层的连接管理类QuorumCnxManager进行发送。
每一个QuorumPeer都有一个QuorumCnxManager对象负责选举期间QuorumPeer之间连接的建立和发送、接收消息队列的维护,而这些消息是通过以下3个集合被处理的:
//发送器集合。每个SenderWorker消息发送器,都对应一台远程ZooKeeper服务器,负责消息的发送,在这个集合中,key为SID
final ConcurrentHashMap senderWorkerMap;
//每个SID需要发送的消息队列
final ConcurrentHashMap> queueSendMap;
//最近发送过的消息。在这个集合中,为每个SID保留最近发送过的一个消息
final ConcurrentHashMap lastMessageSent;
QuorumCnxManager还有分别负责消息的发送和接收的SenderWorker和RecvWorker两个继承了Runnable接口的线程类,这两个线程类的构造方法如下:
SendWorker(Socket sock, Long sid) {
super("SendWorker:" + sid);
this.sid = sid;
this.sock = sock;
recvWorker = null;
try {
dout = new DataOutputStream(sock.getOutputStream());
} catch (IOException e) {
LOG.error("Unable to access socket output stream", e);
closeSocket(sock);
running = false;
}
LOG.debug("Address of remote peer: " + this.sid);
}
RecvWorker(Socket sock, Long sid, SendWorker sw) {
super("RecvWorker:" + sid);
this.sid = sid;
this.sock = sock;
this.sw = sw;
try {
din = new DataInputStream(sock.getInputStream());
// OK to wait until socket disconnects while reading.
sock.setSoTimeout(0);
} catch (IOException e) {
LOG.error("Error while accessing socket for " + sid, e);
closeSocket(sock);
running = false;
}
}
每个SenderWorker或者RecvWorker都有一个sid变量,显然,每一个sid对应的QuorumPeer都会有与之对应的SenderWorker和RecvWorker来专门负责处理接收到的它的消息或者向它发送消息。
接下来再看下对应的run()方法做了什么操作
SendWorker.run()
pubic void run() {
threadCnt.incrementAndGet();
try {
/**
* If there is nothing in the queue to send, then we
* send the lastMessage to ensure that the last message
* was received by the peer. The message could be dropped
* in case self or the peer shutdown their connection
* (and exit the thread) prior to reading/processing
* the last message. Duplicate messages are handled correctly
* by the peer.
*
* If the send queue is non-empty, then we have a recent
* message than that stored in lastMessage. To avoid sending
* stale message, we should send the message in the send queue.
*/
ArrayBlockingQueue bq = queueSendMap.get(sid);
if (bq == null || isSendQueueEmpty(bq)) {
ByteBuffer b = lastMessageSent.get(sid);
if (b != null) {
LOG.debug("Attempting to send lastMessage to sid=" + sid);
send(b);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
LOG.error("Failed to send last message. Shutting down thread.", e);
this.finish();
}
try {
while (running && !shutdown && sock != null) {
ByteBuffer b = null;
try {
ArrayBlockingQueue bq = queueSendMap
.get(sid);
if (bq != null) {
b = pollSendQueue(bq, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
LOG.error("No queue of incoming messages for " +
"server " + sid);
break;
}
if(b != null){
lastMessageSent.put(sid, b);
send(b);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
LOG.warn("Interrupted while waiting for message on queue",
e);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.warn("Exception when using channel: for id " + sid + " my id = " +
self.getId() + " error = " + e);
}
this.finish();
LOG.warn("Send worker leaving thread");
}
}
RecvWorker.run()
public void run() {
threadCnt.incrementAndGet();
try {
while (running && !shutdown && sock != null) {
/**
* Reads the first int to determine the length of the
* message
*/
int length = din.readInt();
if (length <= 0 || length > PACKETMAXSIZE) {
throw new IOException(
"Received packet with invalid packet: "
+ length);
}
/**
* Allocates a new ByteBuffer to receive the message
*/
byte[] msgArray = new byte[length];
din.readFully(msgArray, 0, length);
ByteBuffer message = ByteBuffer.wrap(msgArray);
addToRecvQueue(new Message(message.duplicate(), sid));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.warn("Connection broken for id " + sid + ", my id = " +
self.getId() + ", error = " , e);
} finally {
LOG.warn("Interrupting SendWorker");
sw.finish();
if (sock != null) {
closeSocket(sock);
}
}
}
从代码可以看到,SenderWorker负责不断从全局的queueSendMap中读取自己所负责的sid对应的消息的列表,然后将消息发送给对应的sid。
而RecvWorker负责从与自己负责的sid建立的TCP连接中读取数据放入到recvQueue的末尾。
从QuorumCnxManager.SenderWorker和QuorumCnxManager.RecvWorker的run方法中可以看出,这两个worker都是基于QuorumCnxManager建立的连接,与对应的server进行消息的发送和接收,而要发送的消息则来自FastLeaderElection,接收到的消息,也是被FastLeaderElection处理,因此,QuorumCnxManager的两个worker并不负责具体的算法实现,只是消息发送、接收的代理类,FastLeaderElection不需要理睬怎么与其它的server通信、怎么获得其它server的投票信息这些细节,只需要从QuorumCnxManager提供的队列里面取消息或者放入消息。
下面,我们来看看FastLeaderElection.Messager.WorkekSender和 FastLeaderElection.Messager.WorkerReceiver各自的run方法:
WorkerReceiver.run()
public void run() {
Message response;
while (!stop) {
try{
//从QuorumCnxManager的recvqueue队列中取出一个Message
response = manager.pollRecvQueue(3000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if(response == null) continue;
/*
* 如果该消息来自一个未知的发送者(自己没有维护这个发送者的sid,即配置文件中没有配置这个sid),就把自己当前的投票结果
* 发送给对方。
*/
if(!self.getVotingView().containsKey(response.sid)){
Vote current = self.getCurrentVote();
ToSend notmsg = new ToSend(ToSend.mType.notification,
current.getId(),
current.getZxid(),
logicalclock,
self.getPeerState(),
response.sid,
current.getPeerEpoch());
sendqueue.offer(notmsg);
} else {
{...}
// Instantiate Notification and set its attributes
Notification n = new Notification();
n.leader = response.buffer.getLong();
n.zxid = response.buffer.getLong();
n.electionEpoch = response.buffer.getLong();
n.state = ackstate;
n.sid = response.sid;
if(!backCompatibility){
n.peerEpoch = response.buffer.getLong();
} else {
if(LOG.isInfoEnabled()){
LOG.info("Backward compatibility mode, server id=" + n.sid);
}
n.peerEpoch = ZxidUtils.getEpochFromZxid(n.zxid);
}
/*
* If this server is looking, then send proposed leader
*/
if(self.getPeerState() == QuorumPeer.ServerState.LOOKING){
//放入到recvqueue队列中,待处理
recvqueue.offer(n);
{...}
}
}
WorkerSender.run()
public void run() {
while (!stop) {
try {
ToSend m = sendqueue.poll(3000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if(m == null) continue;
//交给了QuorumCnxManager来处理消息的发送
process(m);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
}
}
LOG.info("WorkerSender is down");
}
以上就是Leader选举的源码实现,欢迎交流~~~
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/zhanyuanlin/article/details/50662921
https://blog.csdn.net/oDaiLiDong/article/details/41855613
http://fenlan.github.io/2018/04/19/ZookeeperLeaderElection/