Python内置函数功能汇总
前言
今天整理的内容是Python的一些内置函数。下面这张图是老师在课堂上的一张PPT:
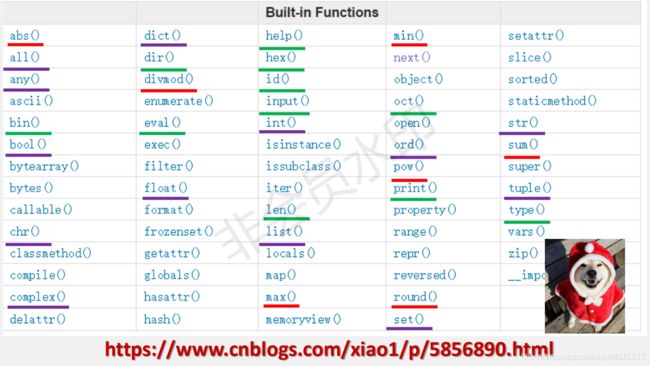
从图中我们可以看到,Python有68个内置函数,其中标有下划线的是老师要求必须记牢的,其实这些也是我们在使用Python时会用到最多的一些内置函数。图片下面的链接是老师推荐给我们去学习了解的关于Python内置函数的一篇博客。看到有博主将这68个内置函数归为10类,感觉很细致很清晰,在此就仿照这种格式来进行汇总了。
一、数字运算(7个)
1.abs():获取绝对值
>>>abs(-1)
1
>>>abs(1)
1
>>>abs(0)
0
2.divmod(a,b):分别返回商和余的值
>>>divmod(15,2)
(7, 1)
>>>divmod(2.7,2) #若为浮点数,则返回的商和余的值也均为浮点数
(1.0, 0.7)
3.sum(): 求和
>>>sum(1,2,3,4)
10
4.pow():返回两个数值的幂运算值或与指定整数的模
>>>pow(2, 10) #等价于 2 ** 10
1024
>>>pow(2, 3, 5) #等价于 (2 ** 3) % 5
3
5.round():对浮点数进行四舍五入
>>>round(3.14159) #若没有参数,则默认保留0位小数
3
>>>round(3.14159,2) # 表示保留2位小数
3.14
>>>round(2586,-2)
2600 #表示从小数点左边第2位四舍五入
6.min():返回最小值
>>>min(1,2,3,4,5)
1
>>>min('12345')
'1'
>>>min(-1, -2, key = abs) #比较两数的绝对值大小,返回绝对值小的数
-1
7.max():返回最大值,用法同上
二、类型转换(24个)
1.int():返回整数
>>> int() #不传入参数时,得到结果0
0
>>> int(3)
3
>>> int(3.7)
3
2.float():返回浮点数
>>> float() #不传入参数的时候,得到结果0.0
0.0
>>> float(3)
3.0
>>> float('3')
3.0
3.complex():返回复数
>>> complex()
0j
>>> complex(1, 2)
(1+2j)
>>> complex('1+2j')
(1+2j)
4.str():返回字符串
>>> str()
''
>>> str(None)
'None'
>>> str(abc)
'abc'
>>> str(123)
'123'
5.ord():返回Unicode字符对应的整数
>>> ord('a')
97
6.chr():返回整数所对应的Unicode字符
>>> chr(97) #参数类型为整数
'a'
7.bool():根据传入的参数的逻辑值创建一个新的布尔值
>>>bool()
False
>>>bool(0)
False
>>>bool(1)
True
>>>bool(7)
True
#参数在空、0、False等值时才会返回False
8.bin():将整数转换成二进制字符串
>>> bin(2)
'0b10'
9.oct():将整数转换成八进制字符串
>>> oct(11)
'0o13'
10.hex():将整数转换成16进制字符串
>>> hex(15)
'0xf'
11.tuple():根据传入的参数创建一个新的元组
>>> tuple() #不传入参数时创建空元组
()
>>> tuple('123') #传入可迭代对象。使用其元素创建新的元组
('1','2','3')
12.list():根据传入的参数创建一个新的列表
>>>list() #不传入参数时创建空列表
[]
>>> list('abc') #传入可迭代对象,使用其元素创建新的列表
['a','b','c']
13.dict():根据传入的参数创建一个新的字典
>>> dict() #不传入任何参数时返回空字典。
{}
>>> dict(a = 1,b = 2) #可以传入键值对创建字典。
{'b': 2,'a': 1}
>>> dict(zip(['a','b'],[1,2])) #可以传入映射函数创建字典。
{'b': 2,'a': 1}
>>> dict((('a',1),('b',2))) #可以传入可迭代对象创建字典。
{'b': 2,'a': 1}
14.set():根据传入的参数创建一个新的集合
>>>set() #不传入参数时创建空集合
set()
>>> a = set(range(5)) #传入可迭代对象,创建集合
>>> a
{0,1,2,3,4}
15.range():根据传入的参数创建一个新的range对象
>>> a = range(5); a
range(0, 5)
>>> list(a)
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
16.bytearray():根据传入的参数创建一个新的字节数组
17.bytes():根据传入的参数创建一个新的不可变字节数组
18.memoryview():根据传入的参数创建一个新的内存查看对象
19.frozenset():根据传入的参数创建一个新的不可变集合
20.enumerate():根据可迭代对象创建枚举对象
21.iter():根据传入的参数创建一个新的可迭代对象
22.slice():根据传入的参数创建一个新的切片对象
23.super():根据传入的参数创建一个新的子类和父类关系的代理对象
24.object():创建一个新的object对象
三、序列操作(8个)
1.all():判断每个元素是否都为True值
>>> all([1,2]) #列表中每个元素逻辑值均为True,返回True
True
>>> all([0,1,2]) #列表中0的逻辑值为False,返回False
False
2.any():判断是否有为True值的元素
>>> any([0,1,2]) #列表元素有一个为True,则返回True
True
>>> any([0,0]) #列表元素全部为False,则返回False
False
3.filter():使用指定方法过滤元素
>>> a = list(range(1,10)) #定义序列
>>> a
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> def if_even(x): #定义偶数判断函数
return x%2==0
>>> list(filter(if_even,a)) #筛选序列中的偶数
[2,4,6,8]
4. map():使用指定方法去作用传入的每个可迭代对象的元素,生成新的可迭代对象
5.next():返回可迭代对象中的下一个元素值
6.reversed():反转序列生成新的可迭代对象
7.sorted():对可迭代对象进行排序,返回一个新的列表
8.zip():聚合传入的每个迭代器中相同位置的元素,返回一个新的元组类型迭代器
四、对象操作(9个)
1.help():返回对象的帮助信息
>>> help(input)
Help on built-in function input in module builtins:
input(prompt=None, /)
Read a string from standard input. The trailing newline is stripped.
The prompt string, if given, is printed to standard output without a
trailing newline before reading input.
If the user hits EOF (*nix: Ctrl-D, Windows: Ctrl-Z+Return), raise EOFError.
On *nix systems, readline is used if available.
2.dir():返回对象或者当前作用域内的属性列表
>>> dir(int)
['__abs__', '__add__', '__and__', '__bool__', '__ceil__', '__class__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__divmod__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__float__', '__floor__', '__floordiv__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getnewargs__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__index__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__int__', '__invert__', '__le__', '__lshift__', '__lt__', '__mod__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__neg__', '__new__', '__or__', '__pos__', '__pow__', '__radd__', '__rand__', '__rdivmod__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rfloordiv__', '__rlshift__', '__rmod__', '__rmul__', '__ror__', '__round__', '__rpow__', '__rrshift__', '__rshift__', '__rsub__', '__rtruediv__', '__rxor__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__sub__', '__subclasshook__', '__truediv__', '__trunc__', '__xor__', 'bit_length', 'conjugate', 'denominator', 'from_bytes', 'imag', 'numerator', 'real', 'to_bytes']
3. id():返回对象的唯一标识符
>>> a = 'today'
>>> id(a)
51891680
4.hash():获取对象的哈希值
>>> hash('Python')
-161550816
5.len():返回对象的长度
>>> len('abc123$,.')
9
>>> len({'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3})
3
>>> len(range(5))
5
6.format():格式化显示值
>>> format(5,'b') #转换成二进制
'110'
>>> format(97,'c') #转换unicode成字符
'a'
>>> format(77,'d') #转换成10进制
'77'
>>> format(17,'o') #转换成8进制
'21'
7.type():返回对象的类型,或者根据传入的参数创建一个新的类型
>>> type(1.7) # 返回对象的类型
8.ascii():返回对象的可打印表字符串表现方式
9.vars():返回当前作用域内的局部变量和其值组成的字典,或者返回对象的属性列表
五、反射操作(8个)
1.__import__():动态导入模块
index = __import__('index')
index.sayHello()
2.isinstance:判断对象是否是类或者类型元组中任意类元素的实例
3.issubclass:判断类是否是另外一个类或者类型元组中任意类元素的子类
4.hasattr:检查对象是否含有属性
5.getattr:获取对象的属性值
6.setattr:设置对象的属性值
7.delattr:删除对象的属性
8.callable:检测对象是否可被调用
六、变量操作(2个)
1.globals():返回当前作用域内的全局变量和其值组成的字典
>>> globals()
{'__name__': '__main__', '__doc__': None, '__package__': None, '__loader__': , '__spec__': None, '__annotations__': {}, '__builtins__': , 'a': 'today'}
2. locals:返回当前作用域内的局部变量和其值组成的字典
七、交互操作(2个)
1.input():读取用户输入值
2.print():向标准输出对象打印输出
八、 文件操作(1个)
1.open():使用指定的模式和编码打开文件,返回文件读写对象
九、编译执行(4个)
1.eval():执行动态表达式求值
>>> eval('1+2+3')
6
2.exec():执行动态语句块
>>> exec('a=1+2+3') #执行语句
>>> a
6
3.compile:将字符串编译为代码或者AST对象,使之能够通过exec语句来执行或者eval进行求值
4.repr():返回一个对象的字符串表现形式(给解释器)
十、装饰器(3个)
1.property:标示属性的装饰器
2.classmethod:标示方法为类方法的装饰器
3.staticmethod:标示方法为静态方法的装饰器
内容来源于:1.Python内置函数功能汇总
2.Python内置函数详解——总结篇
3.图片中博客