MYsql-sql语句进阶
数据类型
MySQL中定义数据字段的类型对你数据库的优化是非常重要的。
MySQL支持多种类型,大致可以分为三类:数值、日期/时间和字符串(字符)类型。
tinyint,占1字节,有符号:-128~127,无符号位:0~255
smallint,占2字节,有符号:-32768~32767,无符号位:0~65535
mediumint,占3字节,有符号:-8388608~8388607,无符号位:0~16777215
int,占4字节,有符号:-2147483648~2147483647,无符号位:0~4284967295
bigint,占8字节
bool 等价于tinyint(1) 布尔型
浮点型
float([m[,d]]) 占4字节,1.17E-38~3.4E+38
double([m[,d]]) 占8字节
decimal([m[,d]]) 以字符串形式表示的浮点数
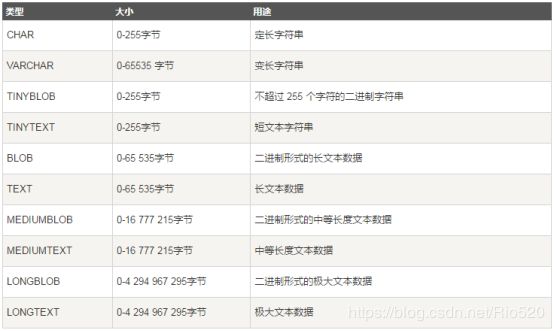
字符型
char([m]):固定长度的字符,占用m字节
varchar[(m)]:可变长度的字符,占用m+1字节,大于255个字符:占用m+2
tinytext,255个字符(2的8次方)
text,65535个字符(2的16次方)
mediumtext,16777215字符(2的24次方)
longtext,(2的32次方)
enum(value,value,...)占1/2个字节 最多可以有65535个成员
set(value,value,...)占1/2/3/4/8个字节,最多可以有64个成员
常用select命令
使用select命令查看mysql数据库系统信息:
– 打印当前的日期和时间
mysql> select now();
+---------------------+
| now() |
+---------------------+
| 2019-10-21 16:22:35 |
+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
– 打印当前的日期
mysql> select curdate();
+------------+
| curdate() |
+------------+
| 2019-10-21 |
+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
– 打印当前的时间
mysql> select curtime();
+-----------+
| curtime() |
+-----------+
| 16:42:00 |
+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
– 打印当前数据库
mysql> select database();
+------------+
| database() |
+------------+
| TEST |
+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
– 打印MySQL版本
mysql> select version();
+-----------+
| version() |
+-----------+
| 5.7.28 |
+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
– 打印当前用户
mysql> select user();
+----------------+
| user() |
+----------------+
| root@localhost |
+----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
–查看系统信息
show variables;
show global variables;
show global variables like '%version%';
show variables like '%storage_engine%'; 默认的存储引擎
like模糊搜索还可用户where字句,例如
select * from students where stname like '%l%1%2%3%';
除了like 还有not like
show engines;查看支持哪些存储引擎
–查看系统运行状态信息
show status;
show global status like 'Thread%';
命令不知如何使用可以用help
导出,导入数据库
方法一
导入数据库
导入数据库前必须创建一个空数据库
mysql> create database app;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
可以这样建库
[root@localhost ~]# mysql -e 'create database app' -uroot -p123456
导入数据
[root@localhost ~]# mysql -uroot -p123456 app < V6.sql
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure. #这个警告说,在命令行写密码不安全
登录查看导入的数据
mysql> use app;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
mysql> show tables;
+----------------+
| Tables_in_app |
+----------------+
| prefix_admin |
| prefix_app |
| prefix_buylog |
| prefix_key |
| prefix_mail |
| prefix_paylog |
| prefix_signlog |
| prefix_user |
+----------------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
数据导入成功
方法二
建库
mysql> create database app2;
进到新建的数据库
mysql> use app2;
Database changed
mysql> source /root/V6.sql #sql语句所在的位置,写绝对路径
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
查看数据
mysql> show tables;
+----------------+
| Tables_in_app2 |
+----------------+
| prefix_admin |
| prefix_app |
| prefix_buylog |
| prefix_key |
| prefix_mail |
| prefix_paylog |
| prefix_signlog |
| prefix_user |
+----------------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
导出数据库
导出数据库:mysqldump -u 用户名 -p 数据库名 > 导出的文件名
[root@localhost ~]# mysqldump -uroot -p123456 app > qq.sql
mysqldump: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
[root@localhost ~]#mysqldump –uroot –p123456 –B 库名>文件.sql
-B : 导出整个库包含建库语句
-A:导出全部数据库
如何把一个select的结果导出到文本
select * into outfile ‘/tmp/123.txt’ from books; 此处有个文件访问权限问题,mysql用户是可以访问/tmp路径的,所以这里放到tmp下
select * from books into outfile ‘/tmp/456.txt’;
其实就是备份数据库
mysql> select * from prefix_app into outfile '/tmp/123txt';
ERROR 1290 (HY000): The MySQL server is running with the --secure-file-priv option so it cannot execute this statement
5.7版本导出报错,可以设置my.cnf 加上secure-file-priv="/ " #这个地方可以写路径
配置完之后,重启数据库
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart mysqld
登录数据库,进到需要备份的数据库
mysql> use app;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> select * from prefix_app into outfile '/tmp/123.txt'; #将查询的结果导到txt文档
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Sql查询语句进阶
查看表
mysql> use app;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> show tables;
+----------------+
| Tables_in_app |
+----------------+
| prefix_admin |
| prefix_app |
| prefix_buylog |
| prefix_key |
| prefix_mail |
| prefix_paylog |
| prefix_signlog |
| prefix_user |
+----------------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
查看表的内容
mysql> select * from prefix_app;
查看字段类型
desc 表名
mysql> desc prefix_app;
逻辑运算符:
and or not
and 且
or 或
not 非
选择出 in_id=6的记录
mysql> select in_id,in_uid,in_form from prefix_app where in_id=6;
+-------+--------+---------+
| in_id | in_uid | in_form |
+-------+--------+---------+
| 6 | 2 | Android |
+-------+--------+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
算术运算符
= 等于
<> 不等于 !=
> 大于
< 小于
>= 大于等于
<= 小于等于
in 运算符
IN 运算符用于 WHERE 表达式中,以列表项的形式支持多个选择,语法如下:
WHERE column IN (value1,value2,...)
WHERE column NOT IN (value1,value2,...)
Not in 与in相反
当 IN 前面加上 NOT 运算符时,表示与 IN 相反的意思,即不在这些列表项内选择。
找出价格大于60的记录
mysql> select bName,price from books where price>60;
找出价格为60的
mysql> select bName,price from books where price=60;
找出价格不等于60的
mysql> select bName,price from books where price<>60;
找出价格是60,50,70的记录
mysql> select bName,price from books where price in (50,60,70);
找出价格不是60,50,70的记录
mysql> select bName,price from books where price not in (50,60,70);
排序
升序:order by “排序的字段” asc 默认
降序:oredr by “排序的字段” desc
mysql> select bName,price from books where price in (50,60,70) order by price asc;
多个字段排序
mysql> select bName,price from books where price in (50,60,70) order by price desc,bName desc;
范围运算
[not]between ....and....
Between and 可以使用大于小于的方式来代替,并且使用大于小于意义表述更明确
查找价格不在30到60之间的书名和价格
mysql> select bName,price from books where price not between 30 and 60 order by price desc;
注:
这里的查询条件有三种:between。。。and,or 和 in
(30,60) >30 and <60
[30,60] >=30 and <=60
模糊匹配查询
字段名 [not]like '通配符' ----》% 任意多个字符
查找书名中包括"程序"字样记录
mysql> select bName from books where bName like '%程序%';
不含有
mysql> select bName from books where bName not like '%程序%';
MySQL子查询
概念:在select 的where条件中又出现了select
查询中嵌套着查询
选择 类型名为“网络技术”的图书:
mysql> select bName,bTypeId from books where bTypeId=(select bTypeId from category where bTypeName='网络技术');
选择类型名称为“黑客”的图书;
mysql> select bName,bTypeId from books where bTypeId=(select bTypeId from category where bTypeName='黑客');
Limit限定显示的条目
SELECT * FROM table LIMIT [offset,] rows
偏移量 行数
LIMIT 子句可以被用于强制 SELECT 语句返回指定的记录数。LIMIT 接受一个或两个数字参数。参数必须是一个整数常量。如果给定两个参数,第一个参数指定第一个返回记录行的偏移量,第二个参数指定返回记录行的最大数目。初始记录行的偏移量是 0(而不是 1):
比如select * from table limit m,n语句
表示其中m是指记录开始的index,从0开始,表示第一条记录
n是指从第m+1条开始,取n条。
查出category表中第2条到第6行的记录。
首先2到6行有2,3,4,5,6总共有5个数字,从2开始,偏移量为1
mysql> select * from category limit 1,5;
查看所有书籍中价格中最低的三条记录
我们对所有记录排序以升序排列,取出前面3个来
mysql> select bName,price from books order by price asc limit 0,3;
将子查询和限制条目,算术运算结合起来查询
显示字段bName ,price ;条件:找出价格比电子工业出版社出版的书中最便宜还要便宜的书。
针对这种查询,我们一步步的来,先找出电子工业出版社出版中最便宜的书
mysql> select bName,price from books where publishing="电子工业出版社" order by price asc limit 0,1;
mysql> select bName,price from books where price<(select price from books where publishing="电子工业出版社" order by price asc limit 0,1);
或者
多行子查询: all表示小于子查询中返回全部值中的最小值
mysql> select bName,price from books where price<all(select price from books where publishing="电子工业出版社");
连接查询:
以一个共同的字段,求两张表当中符合条件的并集。 通过共同字段把这两张表连接起来。
常用的连接:
内连接:根据表中的共同字段进行匹配
外连接分两种:左外连接、右外链接。
内连接
语法:
select 字段 from 表1 inner join 表2 on 表1.字段=表2.字段
内连接:根据表中的共同字段进行匹配
测试
mysql>Select a.bname,a.price,b.btypename from books a inner join category b on a.btypeid=b.btypeid;
实际使用中inner可省略掉
跟WHERE 子句结果一样
mysql>select a.bname,a.price,b.btypename from books a, category b where a.btypeid=b.btypeid;
外连接 (分为左外连接;右外连接)
1.左连接: select 字段 from a表 left join b表 on 连接条件
a表是主表,都显示。
b表从表
主表内容全都有,从表内没有的显示null。
mysql>Select a.bname,a.price,b.btypename from books a left join category b on a.btypeid=b.btypeid;
2.右连接:select 字段 from a表 right join b表 on 条件
a表是从表,
b表主表,都显示。
mysql> select a.bname,b.* from books a right join category b on a.btypeid=b.btypeid;
右连接,可以多表连接
聚合函数
函数:执行特定功能的代码块。
算数运算函数:
Sum()求和
显示所有图书单价的总合
mysql> select sum(price) from books; 或select sum(price) as 图书总价 from books;
avg()平均值:
求书籍Id小于3的所有书籍的平均价格
mysql> select avg(price) from books where bId<=3;
max() 最大值:
求所有图书中价格最贵的书籍
mysql> select bName,max(price) from books; 这种方法是错误的
查一下最贵的图书是哪本?
mysql>select bname,price from books order by desc price limit 0,3;
可见最贵书是Javascript与Jscript从入门到精通,而不是网站制作直通车
mysql>select bName,price from books where price=(select max(price) from books);
min()最小值
求所有图书中价格便宜的书籍
mysql> select bName,price from books where price=(select min(price) from books);
count()统计记录数
统计价格大于40的书籍数量
mysql> select count(*) from books where price>40;
Count()中还可以增加你需要的内容,比如增加distinct来配合使用
select count(distinct price) from books where price>40;
算数运算:
+ - * /
给所有价格小于40元的书籍,涨价5元
mysql> update books set price=price+5 where price<40;
给所有价格高于70元的书籍打8折
mysql> update books set price=price*0.8 where price>70;
字符串函数:
substr(string ,start,len) 截取:从start开始,截取len长.start 从1开始算起。
mysql> select substr(bTypeName,1,7) from category where bTypeId=10;
mysql>select substr(bTypeName,8,2)from category where bTypeId=10;
concat(str1,str2,str3…) 拼接。 把多个字段拼成一个字段输出
mysql> select concat(bName,publishing) from books;
mysql> select concat(bName,"-----",publishing) from books;
大小写转换
upper()大写 : 转为大写输出
mysql> select upper(bname) from books where bId=9;
这样转换中文会出现乱码
lower()小写 :转为小写输出
mysql> select lower(bName) from books where bId=10;