Service 启动和绑定流程
流程图
这几天抽出空又把主席的《Android开发艺术探索》的Service启动看了遍,用精简的语言总结下。
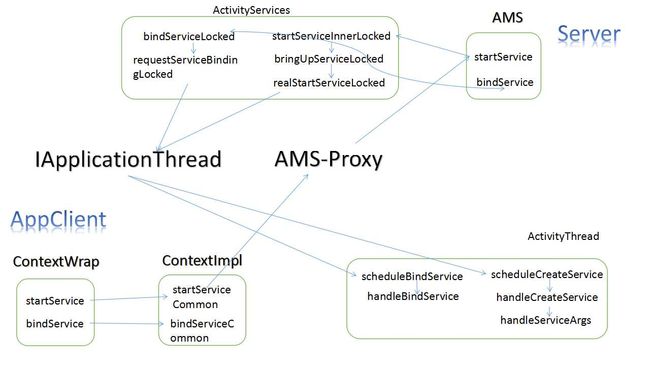
分析
- 当我们调用startService()方法的时候,其实就是调用了AMS的代理对象执行了次IPC操作,当AMS执行到realStartServiceLocked的时候,执行了
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);那么这个app.thread其实也是ApplicationThread的Proxy,至于AMS和他依附的时期是在ActivityThread的attach()方法里面
private void attach(boolean system) {
......
RuntimeInit.setApplicationObject(mAppThread.asBinder());
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
try {
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// Ignore
}
......
}那么,最终还是执行到ActivityThread中的ApplicationThread中scheduleCreateService()方法,
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token,
ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.info = info;
s.compatInfo = compatInfo;
sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s);
}所以,我们要到H中去找标示识CREATE_SERVICE的分支,最终到handleCreateService方法内
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
// If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
// we are back active so skip it.
unscheduleGcIdler();
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);
Service service = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating service " + data.info.name);
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);
context.setOuterContext(service);
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault());
service.onCreate();
mServices.put(data.token, service);
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// nothing to do.
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to create service " + data.info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}最终,我们看到用到ClassLoader去newInstance,生成我们的Service。
- 当我们bindService和startService有什么区别呢,首先是bindServiceCommon()的方法
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags,
UserHandle user) {
IServiceConnection sd;
if (conn == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("connection is null");
}
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(),
mMainThread.getHandler(), flags);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Not supported in system context");
}
validateServiceIntent(service);
try {
IBinder token = getActivityToken();
if (token == null && (flags&BIND_AUTO_CREATE) == 0 && mPackageInfo != null
&& mPackageInfo.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion
< android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH) {
flags |= BIND_WAIVE_PRIORITY;
}
service.prepareToLeaveProcess();
int res = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().bindService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
if (res < 0) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Not allowed to bind to service " + service);
}
return res != 0;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failure from system", e);
}
}可以看到在调用AMS Proxy执行bindService之前,生成一个sd,这个是干啥的。
static final class ServiceDispatcher {
private final ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection mIServiceConnection;
private final ServiceConnection mConnection;
private final Context mContext;
private final Handler mActivityThread;
private final ServiceConnectionLeaked mLocation;
private final int mFlags;
private RuntimeException mUnbindLocation;
private boolean mDied;
private boolean mForgotten;
private static class ConnectionInfo {
IBinder binder;
IBinder.DeathRecipient deathMonitor;
}
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
final WeakReference mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service);
}
}
}
......
} 可以看到,ServiceDispatcher 类中维护了mIServiceConnection对象,而此对象是个Binder。因为可能binderService可能是跨进程形式的,所以要通过Binder去传输数据。最终执行到ActivityThread中的handleBinderService()方法中
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, "handleBindService s=" + s + " rebind=" + data.rebind);
if (s != null) {
try {
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
data.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
try {
if (!data.rebind) {
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
s.onRebind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
ensureJitEnabled();
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(s, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to bind to service " + s
+ " with " + data.intent + ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
}
在调用s.onBind()方法之后,就已经确认是绑定状态了,但是我们还需要回调onServiceConnected方法,确认已经连接上了。
void publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "PUBLISHING " + r
+ " " + intent + ": " + service);
if (r != null) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter
= new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord b = r.bindings.get(filter);
if (b != null && !b.received) {
b.binder = service;
b.requested = true;
b.received = true;
for (int conni=r.connections.size()-1; conni>=0; conni--) {
ArrayList clist = r.connections.valueAt(conni);
for (int i=0; i
ConnectionRecord c = clist.get(i);
if (!filter.equals(c.binding.intent.intent)) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(
TAG_SERVICE, "Not publishing to: " + c);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(
TAG_SERVICE, "Bound intent: " + c.binding.intent.intent);
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(
TAG_SERVICE, "Published intent: " + intent);
continue;
}
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Publishing to: " + c);
try {
c.conn.connected(r.name, service);
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failure sending service " + r.name +
" to connection " + c.conn.asBinder() +
" (in " + c.binding.client.processName + ")", e);
}
}
}
}
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, mDestroyingServices.contains(r), false);
}
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
c.conn.connected()调用的方法如下:
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
if (mActivityThread != null) {
mActivityThread.post(new RunConnection(name, service, 0));
} else {
doConnected(name, service);
}
}最后两个都调用了
public void doConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo old;
ServiceDispatcher.ConnectionInfo info;
synchronized (this) {
if (mForgotten) {
// We unbound before receiving the connection; ignore
// any connection received.
return;
}
old = mActiveConnections.get(name);
if (old != null && old.binder == service) {
// Huh, already have this one. Oh well!
return;
}
if (service != null) {
// A new service is being connected... set it all up.
mDied = false;
info = new ConnectionInfo();
info.binder = service;
info.deathMonitor = new DeathMonitor(name, service);
try {
service.linkToDeath(info.deathMonitor, 0);
mActiveConnections.put(name, info);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// This service was dead before we got it... just
// don't do anything with it.
mActiveConnections.remove(name);
return;
}
} else {
// The named service is being disconnected... clean up.
mActiveConnections.remove(name);
}
if (old != null) {
old.binder.unlinkToDeath(old.deathMonitor, 0);
}
}
// If there was an old service, it is not disconnected.
if (old != null) {
mConnection.onServiceDisconnected(name);
}
// If there is a new service, it is now connected.
if (service != null) {
mConnection.onServiceConnected(name, service);
}
}这样,就调用了客户端的onServiceConnected()方法了。