ROS(indigo) 安装和使用更新版本的Gazebo----3,4,5,6,7 附:中国机器人大赛中型组仿真比赛说明
ROS(indigo) 安装和使用更新版本的Gazebo,本文以7为例。
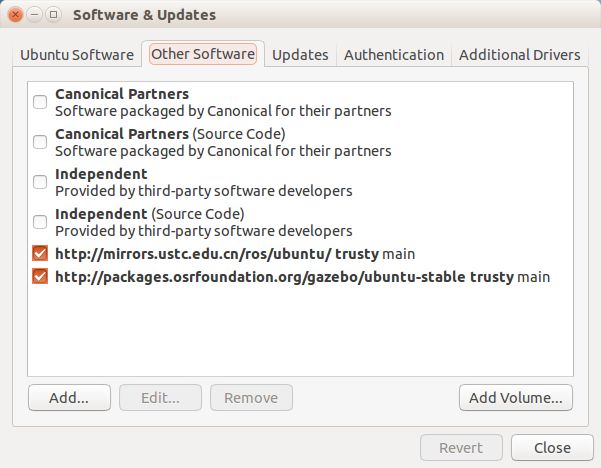
Gazebo7支持更多新的功能,如果使用下面命令安装ROS(indigo):
~$ sudo apt-get install ros-indigo-desktop-full那么配套安装的是Gazebo2,如何在ROS(indigo)中使用更新版本的Gazebo呢?
首先,需要卸载ros-indigo-desktop-full等,如下:
sudo apt-get remove ros-indigo-desktop-full 然后,依次输入下面命令:
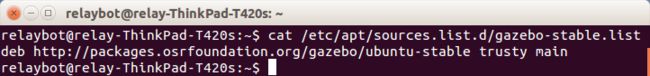
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://packages.osrfoundation.org/gazebo/ubuntu-stable `lsb_release -cs` main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/gazebo-stable.list'可以用:cat /etc/apt/sources.list.d/gazebo-stable.list ,查看,如下:
添加秘钥:
~$ wget http://packages.osrfoundation.org/gazebo.key -O - | sudo apt-key add -
--2016-11-24 12:39:26-- http://packages.osrfoundation.org/gazebo.key
Resolving packages.osrfoundation.org (packages.osrfoundation.org)... 54.193.183.180
Connecting to packages.osrfoundation.org (packages.osrfoundation.org)|54.193.183.180|:80... [sudo] password for relaybot: connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 1772 (1.7K) [application/pgp-keys]
Saving to: ‘STDOUT’
100%[======================================>] 1,772 --.-K/s in 0s
2016-11-24 12:39:26 (7.08 MB/s) - written to stdout [1772/1772]
OK
完成后,更新:
sudo apt-get update这时,在终端输入gazebo和libgazebo,并用tab键查看:
sudo apt-get install gazebo
gazebo2 gazebo5-plugin-base-prerelease
gazebo2-dbg gazebo5-prerelease
gazebo3 gazebo6
gazebo3-common gazebo6-common
gazebo3-dbg gazebo6-common-prerelease
gazebo3-doc gazebo6-dbg
gazebo3-plugin-base gazebo6-dbg-prerelease
gazebo4 gazebo6-doc
gazebo4-common gazebo6-doc-prerelease
gazebo4-common-prerelease gazebo6-plugin-base
gazebo4-dbg gazebo6-plugin-base-prerelease
gazebo4-dbg-prerelease gazebo6-prerelease
gazebo4-doc gazebo6-robocup3ds
gazebo4-doc-prerelease gazebo6-robocup3ds-common
gazebo4-plugin-base gazebo7
gazebo4-plugin-base-prerelease gazebo7-common
gazebo4-prerelease gazebo7-dbg
gazebo5 gazebo7-doc
gazebo5-build-deps gazebo7-haptix
gazebo5-common gazebo7-haptix-common
gazebo5-common-prerelease gazebo7-haptix-dbg
gazebo5-dbg gazebo7-haptix-doc
gazebo5-dbg-prerelease gazebo7-haptix-plugin-base
gazebo5-doc gazebo7-plugin-base
gazebo5-doc-prerelease gazebo7-robocup3ds
gazebo5-plugin-base gazebo7-robocup3ds-common~$ sudo apt-get install libgazebo
libgazebo3 libgazebo6-dev
libgazebo4 libgazebo6-dev-prerelease
libgazebo4-dev libgazebo6-prerelease
libgazebo4-dev-prerelease libgazebo6-robocup3ds
libgazebo4-prerelease libgazebo7
libgazebo5 libgazebo7-dev
libgazebo5-dbg libgazebo7-haptix
libgazebo5-dev libgazebo7-haptix-dev
libgazebo5-dev-prerelease libgazebo7-robocup3ds
libgazebo5-prerelease libgazebo-dev
libgazebo6 如果需要开发gazebo,需安装libgazebo*-dev,如果只是使用,安装gazebo*,如下:
sudo apt-get install gazebo7安装完毕后,在终端输入gazebo,查看:
gazebo
但是到这里只是安装了Gazebo的新版,需要重新安装ROS。
sudo apt-get install ros-indigo-desktop注意不要安装full版,Gazebo2不能与更新版本的Gazebo共存,需要单独安装所需功能包即可。
然后,安装ros-gazebo接口库等,以7为例如下:
:~$ sudo apt-get install ros-indigo-gazebo7-
ros-indigo-gazebo7-msgs ros-indigo-gazebo7-ros-control
ros-indigo-gazebo7-plugins ros-indigo-gazebo7-ros-pkgs
ros-indigo-gazebo7-ros安装完毕后,ROS(indigo)就可以和Gazebo7一起使用了。
这里,以ROS机器人程序设计(原书第2版)的第7章214页的示例,测试键盘控制Gazebo7.4中小车的移动:
第一步,如下:
~$ roslaunch robot1_gazebo gazebo_wg.launch
... logging to /home/relaybot/.ros/log/247f85e8-b203-11e6-85e0-0811968dc4b0/roslaunch-relay-ThinkPad-T420s-4397.log
Checking log directory for disk usage. This may take awhile.
Press Ctrl-C to interrupt
Done checking log file disk usage. Usage is <1GB.
started roslaunch server http://relay-ThinkPad-T420s:59553/
SUMMARY
========
PARAMETERS
* /robot_description: , set to ""
[ INFO] [1479963727.915187439, 0.001000000]: Laser Plugin (ns = /) , set to ""
[ INFO] [1479963727.948279641, 0.001000000]: Loading gazebo_ros_control plugin
[ INFO] [1479963727.948487708, 0.001000000]: Starting gazebo_ros_control plugin in namespace: /robot
[ INFO] [1479963727.950724362, 0.001000000]: gazebo_ros_control plugin is waiting for model URDF in parameter [/robot_description] on the ROS param server.
[urdf_spawner-5] process has finished cleanly
log file: /home/relaybot/.ros/log/247f85e8-b203-11e6-85e0-0811968dc4b0/urdf_spawner-5*.log
[ INFO] [1479963728.200219231, 0.001000000]: Loaded gazebo_ros_control.
[ INFO] [1479963728.205156602, 0.001000000]: Starting GazeboRosSkidSteerDrive Plugin (ns = /)!
[ INFO] [1479963728.242052698, 0.022000000]: waitForService: Service [/gazebo/set_physics_properties] is now available.
[ INFO] [1479963728.346945001, 0.110000000]: Physics dynamic reconfigure ready 第二步,如下:
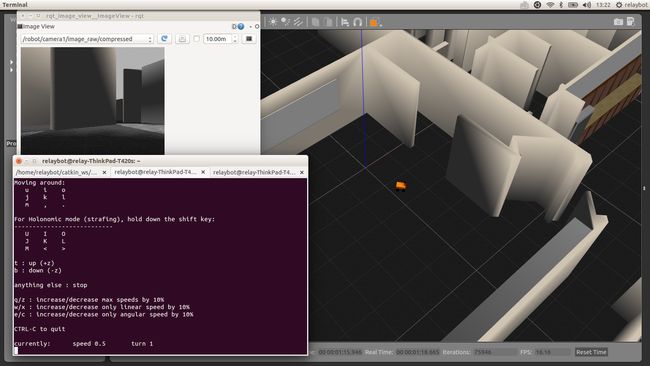
~$ rosrun teleop_twist_keyboard teleop_twist_keyboard.py
Reading from the keyboard and Publishing to Twist!
---------------------------
Moving around:
u i o
j k l
m , .
For Holonomic mode (strafing), hold down the shift key:
---------------------------
U I O
J K L
M < >
t : up (+z)
b : down (-z)
anything else : stop
q/z : increase/decrease max speeds by 10%
w/x : increase/decrease only linear speed by 10%
e/c : increase/decrease only angular speed by 10%
CTRL-C to quit
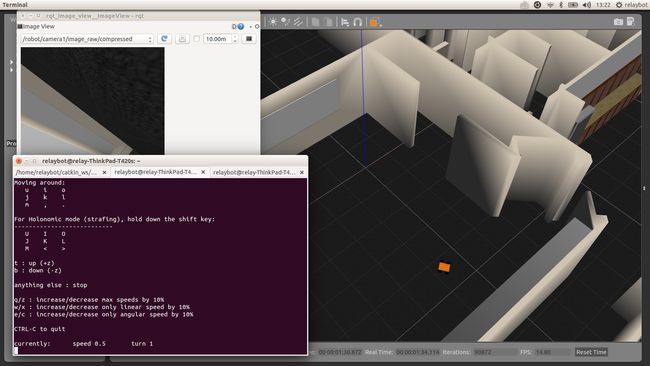
currently: speed 0.5 turn 1 使用键盘控制小车在环境中运动,也可以查看其他数据,如小车摄像头等,利用rviz和rqt_image_view,如下:
翻车后:
补充与巩固:
编译并运行,https://github.com/nubot-nudt/simatch:
中国机器人大赛中型组仿真比赛
China Robot Competition Middle Size Simulation League (With English User Manual)
-End-
附,需要请阅读:
中国机器人大赛中型组仿真比赛
China Robot Competition Middle Size Simulation League (With English User Manual)
演示视频 Demo Video
Two options:
1. 优酷Youku
2. Youtube
说明
该软件包包括了robot_code模块,gazebo_visual模块,coach4sim模块,common模块以及auto_referee模块,其中,参赛选手主要注重robot_code模块,里面包含的是控制机器人运动的相关程序。各个模块的介绍如下:
- robot_code: 机器人的感知、规划、运动控制等方面,由NuBot队伍的机器人代码改造而成,其中主要的策略等(在nubot_control软件包中)部分已经删除,选手应自行编写,其余部分可以直接沿用,也可随意改动。
- gazebo_visual: Gazebo仿真平台,除基本的设置(在sim_config文件中)外,不应做其他改动。最终使用版本以比赛时的版本为准。
- coach4sim: 用于仿真的coach,发送比赛开始、暂停、站位等指令。
- common: 包含cmake、手柄驱动等。选手不必做改动。
- auto_referee: 自动裁判盒,模拟refbox以及裁判的功能,自动进行比赛。
请先学习ROS、C++,作为基本技能和知识,然后对机器人策略等方面有一定了解,再进行robot_code的多机器人协同程序的编写。由于目前仿真中可以直接得到准确的全局信息,所以选手可能会倾向于集中式控制,但是,建议选手用分布式机器人控制。在未来会在仿真中增加更多的现实因素,比如考虑单个机器人所能获取信息的局限性等;
可能增加或改变的规则(最终以比赛时为准)
比赛规则参考2016年RoboCup中型组比赛的规则,但是由于仿真比赛的特殊性,不会完全按照里面的所有规则,比如说:
1. 比赛不分上下半场,一共15分钟左右;
2. 任何利用自动裁判盒(auto_referee)的漏洞获取比赛中的优势将视为作弊行为,比赛成绩无效;
3. 比赛时候可能会对gazebo_visual部分作一定的改动,比如根据真实机器人的一般情况限制机器人的平移速度、旋转速度等,这些改动将通知到每一个队伍。所以请参赛队伍记住自己的代码也要考虑真实世界的情况,不要太理想;
4. 比赛过程中是否对机器人获取的信息加入适当的噪声以及加入多少看比赛情况而定,会及时通知参赛队伍;
5. 比赛前可能会有一次“热身”,主要看看本次比赛参赛队伍的整体水平从而或许对规则作相应的改动,最终目的在于促进机器人技术的发展,鼓励大家积极参与;
6. 机器人不得恶意碰撞其他机器人,需要考虑避障;
目前auto_referee中可以检测的规则
- 单个机器人带球不能超过3m,需要传球才可以;
2. 单个机器人带球不能从己方半场过中线到对方半场,必须传球过中线才可以; - 球出界或者射门得分;
- 除了守门员以外其他机器人不得进入小禁区,除了守门员以外在大禁区的机器人数量最多1个;
- 发球时机器人离球距离的限制,具体如下:
(1) 如果是THROWIN,GOALKICK,CORNERKICK或者FREEKICK的情况时,对方机器人离球要超过3m,己方机器人除了开球机器人以外其他机器人要离球超过2m;
(2) 如果是KICKOFF的情况时,除了发球机器人外其余机器人都必须在自己的半场,且对方机器人离球要超过3m,己方机器人除了开球机器人以外其他机器人要离球超过2m;
(3) 如果是DROPBALL的情况时,所有机器人离球必须超过1m,但是如果在自己的大禁区则不受此距离限制;
(4) 如果是比赛过程中的PENALTY情况时,除了守门员外其余机器人不得在大禁区内且除了准备点球的那个机器人外其余机器人必须离球超过3m;
auto_referee即将添加的规则
- 考虑发球等待时延;
- 检测进球无效情况(机器人射门得分前必须有至少一次传球(传球不成功也算),否则得分无效);
比赛流程
假设服务器(即运行Gazebo的由比赛方提供的主机)的IP地址为IpA,主机名(hostname)为hostA; cyan方参赛队主机的IP地址为IpB,主机名为hostB; magenta方参赛队主机的IP地址为IpC,主机名为hostC,那么相应的配置如下:
参赛队主机的配置(由参赛选手完成)
主机只需要运行自己的机器人代码,即robot_code的部分,禁止运行gazebo_visual,auto_refereeoach4sim。比赛过程如非特何人操作参赛主机,否则视为作弊,除非征得裁判和对方队员同意。
服务器的配置(由辅助裁判完成)
- 将所有参赛队伍的IP地址和主机名加入服务器的/etc/hosts文件中;(赛事负责人将提前将每个队伍的参赛主机名以及参赛队伍名称收集好,其中IP地址将固定分配给每个队伍)。
- 在sim_config文件中更改cyan/prefix以及magenta/prefix的值为参赛双方的队伍名字;
- 打开Gazebo,即
$ roslaunch nubot_gazebo game_ready.launch - 待双方参赛队伍机器人代码运行后,开启自动裁判盒开始比赛,即
$ rosrun auto_referee auto_referee -1代表cyan发球
或者$ rosrun auto_referee auto_referee 1代表magenta发球 - 到下一组比赛的时候,重复步骤2,3,4
共同开发
欢迎大家积极共同完善该仿真平台,我们将感谢每一个人的贡献。
本软件使用git作为版本控制,托管于GitHub网站。如果想共同开发该软件包,请fork一下该软件包(首先你要注册一个GitHub帐号),然后git clone到自己的电脑去,改进完代码后,可以git push上来,然后再在GitHub里面发一个pull request。
需要的基本技能和知识:
- 软件编程:
- robot_code: ROS, C++
- gazebo_visual: ROS, C++, Gazebo插件以及编程实现
- coach4sim: ROS, C++, Qt
- 配置文件: Linux bash或其他
- 其他方面
- 使用说明: txt,Markdown
- 软件文档: Doxygen或其他
为了方便大家交流,请大家把遇到的问题发到这里https://github.com/nubot-nudt/simatch/issues,我会抽时间回答,别人能回答的话也帮忙回答。建议所有人都注册一个github帐号,对这个simatch版本库fork一下。fork的目的在于你对它的修改可以提交给我,然后我审批过后就可以融合进来。目前希望大家能够将自己在使用过程终于遇到的问题以及解决办法写到README.md文件,然后提交给我。如果有参考价值,那么我就把它融合进来,这样所有人都能看到,也是对这个软件的一个贡献。
步骤
- 按下图中的fork就行了(前提是你已经登陆了github帐号),这样在你的帐号里就有了simatch。
![]()
2. 然后点进README.md文件,就可以编辑了。把自己遇到的问题和解决部分写在这里questions & answers如下图:

3. 最后创建一个pull request如下图所示,这样我就能够审批通过你的编辑了
联系
软件维护者(Maitainer): [email protected]
Nubot队伍(RoboCup team): [email protected]
用户手册 User manual
NOTE: If you want to have a basic understanding of how Gazebo and ROS combines to work for robots, it is recommended to check out the repository 'single_nubot_gazebo'.This contains how to configure the environment, how to run the simulation, and how the robot is simulated. You could run the ROS tool 'rqt_graph' tounderstand the basic messages and service flow.
Package Summary
- Maintainer status: maintained
- Maintainer: Weijia Yao [email protected]
- Author: NuBot Team
- License: Apache
- Bug / feature tracker: https://github.com/nubot-nudt/simatch/issues
- Source: git https://github.com/nubot-nudt/simatch (branch: master)
Recommended Operating Environment
- Ubuntu 14.04;
- ROS Indigo or ROS Jade. (It is recommended to install ROS Jade)
- Gazebo 5.0 or above;
- gazebo_ros_pkgs; (please read the NOTE below for more information)
- If you decide to use coach4sim with a GUI, you should make sure you have installed Qt5. The recommended install place is /opt. Other versions of Ubuntu, ROS or Gazebo may also work, but we have not tested yet.
NOTE: Concerning how to install appropriate gazebo_ros_pkgs, please read the following according to your own situation:
- 1. If you decide to use ROS Indigo, please read the following:
If you choose "desktop-full" install of ROS Indigo, there is a Gazebo 2.0 included initially. In order to install Gazebo 5.0/5.1, you should first remove Gazebo 2.0 by running:
(The following command is dangerous; it might delete the whole ROS, so please do it carefully or you may find other ways to delete gazebo2)$ sudo apt-get remove gazebo2*
Then you should be able to install Gazebo 5.0 now. To install gazebo_ros_pkgs compatible with Gazebo5.0/5.1, run this command:$ sudo apt-get install ros-indigo-gazebo5-ros-pkgs ros-indigo-gazebo5-ros-control
HOWEVER, if the above command does now work, these packages may be moved to other places. You can check out gazebo_ros and download and install the correct version. - 2. If you decide to use ROS Jade with gazebo 5.0 or 5.1, read the following
ROS Jade has gazebo_ros_pkgs with it; so you don't have to install gazebo_ros_pkgs again.
However, you should do the following steps to fix some of the bugs in ROS Jade related to Gazebo:
- (a)
$ sudo gedit /opt/ros/jade/lib/gazebo_ros/gazebo
In this file, go to line 24 and delete the last '/'. Sosetup_path=$(pkg-config --variable=prefix gazebo)/share/gazebo/
is changed tosetup_path=$(pkg-config --variable=prefix gazebo)/share/gazebo
You can read this link for more information - (b) Install Gazebo 5.
$ sudo apt-get install gazebo5
If this fails, try to run the 'gazebo5_install.sh'(obtained from Gazebo's official website).
Read for more information - (c) Optional: copy resource files to the new gazebo folder.
$ sudo cp -r /usr/share/gazebo-5.0/* /usr/share/gazebo-5.1
- (a)
- 3. If you decide to use ROS Jade with gazebo 7.1, read the following,
- (1) Install gazebo 7.0 by running gazebo7_install.sh(obtained from Gazebo's official website);
- (2) Then run this in the terminal:
-
$ sudo apt-get install ros-jade-gazebo7-ros-pkgs
- (1) Install gazebo 7.0 by running gazebo7_install.sh(obtained from Gazebo's official website);
Compile
Since auto_referee depends on ncurses, if you would like to use it to debug your code, please run this command:
1. sudo apt-get update
2. sudo apt-get install libncurses5-dev
And then you are good to compile as follows:
1. $ sudo chmod +x configure
2. $ ./configure
3. $ catkin_make
Compile Error Solution:
1) Cannot find cmake file related to Qt and therefore cannot complie coach4sim.
- Explanation: This means it cannot find the cmake file to Qt. Since coach4sim uses Qt to draw its GUI, we need Qt to compile the program successfully(solution 1). However, since the function of coach4sim is only to send game commands, you could do this manually by sending approriate ROS messages without using coach4sim(solution 2).
- Solution 1: You should first install Qt and then add the location to CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH. In this case, go to src/coach4sim/CMakeLists.txt and add the path to line 5. The final result would look like this:
set(CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH ${CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH} "/opt/Qt5.3.2/5.3/gcc_64/lib/cmake/Qt5Widgets/") - Solution 2: In another terminal, input the following to send a game command:
rostopic pub -r 1 /nubot/receive_from_coach nubot_common/CoachInfo "
MatchMode: 10
MatchType: 0"
Indeed, when you input until nubot_common/CoachInfo, you could press 'Tab' twice and then the whole definition of the message would show up. Then you could fill up the message. However, you only need to fill in two fields: 'MatchMode' and 'MatchType', where 'MatchMode' is the current game command, 'MatchType' is the previous game command. The coding of the game commands is in core.hpp. For quick reference:
enum MatchMode {
STOPROBOT = 0,
OUR_KICKOFF = 1,
OPP_KICKOFF = 2,
OUR_THROWIN = 3,
OPP_THROWIN = 4,
OUR_PENALTY = 5,
OPP_PENALTY = 6,
OUR_GOALKICK = 7 ,
OPP_GOALKICK = 8,
OUR_CORNERKICK = 9,
OPP_CORNERKICK = 10,
OUR_FREEKICK = 11,
OPP_FREEKICK = 12,
DROPBALL = 13,
STARTROBOT = 15,
PARKINGROBOT = 25,
TEST = 27
};
2) When catkin_make, if it shows "fatal error: Eigen/Eigen: No such file or directory"
- Solution 1: Change all 'Eigen3' to 'Eigen' in CMakeLists.txt of world_model package in robot_code module
- Solution 2: look at /usr/include/eigen3/Eigen, if this folder exists, it means you have already installed Eigen;
Input this command:$ sudo ln -s /usr/include/eigen3/Eigen /usr/include/Eigen
3) if you come across other problems, you could refer to doc/ folder.
Run
You could run the robot_code, gazebo_visal and coach4sim in one computer. However, the simulation speed would be low. So you could also run them with several computers to decrease the burden of one single computer.
With one computer
Assuming you are in the root directory of 'simatch',
If you want to run those modules in one launch, you could
1 $ source devel/setup.bash
You could write this line into ~/.bashrc file so that you don't have to source it every time you open a terminal.
2 $ roslaunch simatch_cyan.launch or $ roslaunch simatch_magenta.launch
If you want to run those modules seperatly, you could
1 $ source devel/setup.bash
You could write this line into ~/.bashrc file so that you don't have to source it every time you open a terminal.
2 To run gazebo_visual,$ roslaunch nubot_gazebo game_ready.launch
3 To run robot_code for cyan or magenta robots:$ rosrun nubot_common cyan_robot.sh or $ rosrun nubot_common magenta_robot.sh
4 To run coach4sim,rosrun coach4sim cyan_coach.sh or rosrun coach4sim magenta_coach.sh
NOTE:
1. You could change some parameters in sim_config(see "Change game parameters" part below) file and relaunch all modules again.
2. You might not watch the robots doing anything because the movement part in 'nubot_control' package is removed. You might need to write some codes by yourself.
With several computers
Configuration of computer A and computer B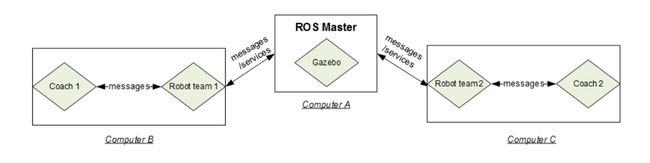
The recommended way to run simulation is with two computers running nubot_ws and gazebo_visual seperately.
For example,computer A runs gazebo_visual to display the movement of robots. Computer B runs nubot_ws to calculate and send movement commands to robots. In addition, computer B should also run coach to send game command such as game start.
The communication between computer A and computer B is via ROS master. The following is the configuration steps:
- In computer A, add computer B's IP address in /etc/hosts; and in computer B, add computer A's IP address in /etc/hostse.g. In computer A,
$ sudo gedit /etc/hosts and add "192.168.8.100 Maggie"In computer B,$ sudo gedit /etc/hosts and add "192.168.8.101 Bart" - In computer A, run gazebo_visual; In computer B, before you run nubot_ws, you should export ROS_MASTER_URI.e.g. In computer B,
$ export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://Bart:11311 - In computer B, run coach and send game command
Change game parameters
You could change some parameters in "sim_config", which is a symbolic link to global_config.yaml. The content of this file is:
# Uses ISO units. For example, use 'm' for length.
general:
dribble_distance_thres: 0.47 # theshold distance between nubot and football below which dribble ball
dribble_angle_thres: 15.0 # kicking mechanism aligning with football; allowed maximum angle error in degrees
noise_scale: 0.00 # the scale of gaussian noise (m)
noise_rate: 0.01 # how frequent the noise is generated
cyan:
prefix: "nubot" # Nubot name prefix.
num: 3
magenta:
prefix: "rival" # Rival name prefix.
num: 3
field:
length: 18 # Use integer! used in spawn_model_script
width: 12 # Use integer! used in spawn_model_script
football:
name: "football" # football model name
chassis_link: "football::chassis" # football body link name
There are 5 parts: "general", "cyan", "magenta", "field" and "football". If you just want to test your code, you are free to change any parameter in these 5 parts. However, in the competition, the parameters of "general", "field", "football" and the number of robots would not be changed by players. However, players are still free to change the prefix of "cyan" or "magenta" robots to reprepsent their own teams but they need to report to the TC staff.
Tutorial
ROS topics, messages and services
The robot movement is realized by a Gazebo model plugin which is called "NubotGazebo" generated by source files "nubot_gazebo.cc" and "nubot_gazebo.hh". Basically the essential part of the plugin is realizing basic motions: omnidirectional locomotion, ball-dribbling and ball-kicking.
The gazebo plugin subscribes to topic "nubotcontrol/velcmd" for omnidirecitonal movement and "omnivision/OmniVisionInfo" which contains messages about the soccer ball and all the robots' information such as position, velocity and etc. like the functions of an omnivision camera. For services, it subscribes to service "BallHandle" and "Shoot" for ball-dribbling and ball-kicking respectively. Since there may be multiple robots, these topics or services names should be prefixed with the robot model names in order to distinguish between each other. For example, if your robot model's name is "nubot1", then the topic names are "/nubot1/nubotcontrol/velcmd" and "/nubot1/omnivision/OmniVisionInfo" and the service names would be changed to "/nubot1/BallHandle" and "/nubot1/Shoot" accordingly. You can customize this code for your robot based on these messages and services as a convenient interface. The types and definitions of the topics and servivces are listed in the following table:
| Topic/Service | Type | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| /nubot1/nubotcontrol/velcmd | nubot_common/VelCmd | float32 Vx float32 Vy float32 w |
| /nubot1/omnivision/OmniVisionInfo | ubot_common/OminiVisionInfo | Header header BallInfo ballinfo ObstaclesInfo obstacleinfo RobotInfo[] robotinfo |
| /nubot1/BallHandle | nubot_common/BallHandle | int64 enable --- int64 BallIsHolding |
| /nubot1/Shoot | nubot_common/Shoot | int64 strength int64 ShootPos --- int64 ShootIsDone |
For the definition of /BallHandle service, when "enable" equals to a non-zero number, a dribble request would be sent. If the robot meets the conditions to dribble the ball, the service response "BallIsHolding" is true.
For the definition of /Shoot service, when "ShootPos" equals to 1, this is a ground pass. In this case, "strength" is the inital speed you would like the soccer ball to have. When "ShootPos" equals to -1, this is a lob shot. In this case, "strength" is useless since the strength is calculated by the Gazebo plugin automatically and the soccer ball would follow a parabola path to enter the goal area. If the robot successfully kicks the ball out even if it failed to goal, the service response "ShootIsDone" is true.
For the definition of the "omnivision/OmniVisionInfo" topic, there are three new message types: "BallInfo", "ObstaclesInfo" and "RoboInfo". The field "robotinfo" is a vector. Before introducing the format of these new messages, three other message types "Point2d", "PPoint" and "Angle" are used in their definitions:
# Point2d.msg, reperesenting a 2-D point.
float32 x # x component
float32 y # y component
# PPoint.msg, representing a 2-D point in polar coordinates.
float32 angle # angle against polar axis
float32 radius # distance from the origin
# Angle.msg, representing the angle
float32 theta # angle of rotation
# BallInfo.msg, representing the information about the ball
Header header # a ROS header message defined by ROS package std_msgs
int32 ballinfostate # the state of the ball information;
Point2d pos # ball position in global reference frame; the origin of the frame is the center of
# the soccer field; x-axis pointed horizentally towards the opponet's center of the
# goal area and y-axis vertiacal to the x-axis using the right-hand rule
PPoint real_pos # ball relative position in robot body frame; the origin of the body frame is the
# center of the robot base; x-axis along the kicking-mechanism and y-axis vertical
# to the x-axis using the right-hand rule
Point2d velocity # ball velocity in global reference frame
bool pos_known # ball position is known(1) or not(0)
bool velocity_known # ball velocity is known(1) or not(0)
# ObstaclesInfo.msg, representing the information about obstacles
Header header # a ROS header message defined by ROS package std_msgs
Point2d[] pos # obstacle position in global reference frame
PPoint[] polar_pos # obstable position in the polar frame of which the origin is the center of the
# robot and the polar axis is along the kicking mechanism
# RobotInfo.msg, representing teammates' information
Header header # a ROS header message defined by ROS package std_msgs
int32 AgentID # ID of the robot
int32 targetNum1 # robot ID to be assigned target position 1
int32 targetNum2 # robot ID to be assigned target position 2
int32 targetNum3 # robot ID to be assigned target position 3
int32 targetNum4 # robot ID to be assigned target position 4
int32 staticpassNum # in static pass, the passer's ID
int32 staticcatchNum # in static pass, the catcher's ID
Point2d pos # robot position in global reference frame
Angle heading # robot heading in global reference frame
float32 vrot # the rotational velcoity in global reference frame
Point2d vtrans # the linear velocity in global reference frame
bool iskick # robot kicks the ball(1) or not(0)
bool isvalid # robot is valid(1) or not(0)
bool isstuck # robot is stuck(1) or not(0)
bool isdribble # robot dribbles the ball(1) or not(0)
char current_role # the current role
float32 role_time # time that the robot keeps the role unchanged
Point2d target # target position
The units of these elements are cm, cm/s, rad and rad/s.
Code samples
Basic motion flow
This is a sample code from nubot_control.cpp. It realizes basic functions such as moving to a target position or a target orientation, dribbling the ball and shooting the goal. It is almost the simpliest version without any use of PID control or other control methods. Anyone should try to improve this code instead of using it directly.
However, the code related to receiving game comamnds and doing corresponding actions should be kept. For example, your code should be able to judge what to do when receiving different game commands such as 'START', 'FREEKICK' or 'PARKING'.
Note: Please take care of the transformation between the global reference frame and the robot body reference frame!
- Global reference frame: origin is the center of the field; x-axis pointing horizontally towards the goal center of the megenta side; z-axis pointing vertically towards the sky; y-axis using right-hand rule to determine.
- Robot body reference frame: origin is the center of the robot base; x-axis points from the origin to the kicking-mechanism; z-axis pointing veritcally towards the sky; y-axis using right-hand rule to determine.
/** 主要的控制框架位于这里*/
void
loopControl(const ros::TimerEvent& event)
{
match_mode_ = world_model_info_.CoachInfo_.MatchMode; //! 当前比赛模式
pre_match_mode_ = world_model_info_.CoachInfo_.MatchType; //! 上一个比赛模式
robot_pos_ = world_model_info_.RobotInfo_[world_model_info_.AgentID_-1].getLocation();
robot_ori_ = world_model_info_.RobotInfo_[world_model_info_.AgentID_-1].getHead();
ball_pos_ = world_model_info_.BallInfo_[world_model_info_.AgentID_-1].getGlobalLocation();
ball_vel_ = world_model_info_.BallInfo_[world_model_info_.AgentID_-1].getVelocity();
nubot_common::VelCmd vel;
nubot_common::Shoot shoot;
nubot_common::BallHandle dribble;
if(match_mode_ == STOPROBOT )
{
vel.Vx = 0;
vel.Vy = 0;
vel.w = 0;
motor_cmd_pub_.publish(vel);
shoot.request.strength = 0;
shoot_client_.call(shoot);
dribble.request.enable = 0;
ballhandle_client_.call(dribble);
}
/** 机器人在开始之前的跑位. 开始静态传接球的目标点计算*/
else if(match_mode_ > STOPROBOT && match_mode_ <= DROPBALL)
positioning();
else if(match_mode_==PARKINGROBOT)
parking();
else// 机器人正式比赛了,进入start之后的机器人状态
{
normalGame();
} // start部分结束
pubStrategyInfo(); // 发送策略消息让其他机器人看到,这一部分一般用于多机器人之间的协同
}
void positioning()
{
DPoint br = ball_pos_ - robot_pos_;
switch(world_model_info_.AgentID_) // 十分简单的实现,固定的站位,建议动态调整站位,写入staticpass.cpp中
{ // 站位还需要考虑是否犯规,但是现在这个程序没有考虑。
case 1:
if(move2target(DPoint(-850.0, 0.0), robot_pos_))
move2ori(br.angle().radian_, robot_ori_.radian_);
break;
case 2:
if(move2target(DPoint(-150.0, 100.0), robot_pos_))
move2ori(br.angle().radian_, robot_ori_.radian_);
break;
case 3:
if(move2target(DPoint(-150.0, -100.0), robot_pos_))
move2ori(br.angle().radian_, robot_ori_.radian_);
break;
case 4:
if(move2target(DPoint(-450.0, 200.0), robot_pos_))
move2ori(br.angle().radian_, robot_ori_.radian_);
break;
case 5:
if(move2target(DPoint(-450.0, -200.0), robot_pos_))
move2ori(br.angle().radian_, robot_ori_.radian_);
break;
}
}
void parking()
{
static double parking_y=-580.0;
cout<<"PARKINGROBOT"<float tar_ori = SINGLEPI_CONSTANT/2.0;
parking_target.x_= -120.0 * world_model_info_.AgentID_;
if(world_model_info_.AgentID_ == 1)
parking_target.x_ = -700;//守门员站在离球门最近的地方
parking_target.y_ = parking_y;
if(move2target(parking_target, robot_pos_)) //停到目标点10cm附近就不用动了,只需调整朝向
move2ori(tar_ori, robot_ori_.radian_);
}
void normalGame()
{
if(world_model_info_.AgentID_ != 1 && isNearestRobot())
{
nubot_common::BallHandle dribble;
DPoint br = ball_pos_ - robot_pos_;
if(move2ori(br.angle().radian_, robot_ori_.radian_)) // 先往足球靠近
{
if(move2target(ball_pos_, robot_pos_, 50.0))
{
dribble.request.enable = 1;
ballhandle_client_.call(dribble);
if(dribble.response.BallIsHolding != true)
{
if(move2target(ball_pos_, robot_pos_, 40.0))
move2ori(br.angle().radian_, robot_ori_.radian_);
}
else // 带上球了
{
DPoint tmp(200.0,300.0);
DPoint dirc = DPoint(900.0 ,0.0) - tmp; // 对准 (900.0 ,0.0)
if(move2target(tmp, robot_pos_) &&
move2ori(dirc.angle().radian_, robot_ori_.radian_, 5.0*DEG2RAD)) // 跑到位以及转到位
{
nubot_common::Shoot shoot;
shoot.request.ShootPos = FLY;
shoot.request.strength = 1.0; // 在FLY模式下,strength不重要,只要非零就行
shoot_client_.call(shoot);
}
}
}
}
}
}
bool isNearestRobot() //找到距离足球最近的机器人
{
float distance_min = 2000.0;
float distance = distance_min;
int robot_id = -1;
for(int i=1;i// 排除守门员
if(world_model_info_.RobotInfo_[i].isValid())
{
distance = ball_pos_.distance(world_model_info_.RobotInfo_[i].getLocation());
if(distance < distance_min)
{
distance_min=distance;
robot_id = i;
}
}
if(robot_id+1 == world_model_info_.AgentID_)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool move2target(DPoint target, DPoint pos, double distance_thres=10.0) // 一个十分简单的实现,可以用PID
{
static nubot_common::VelCmd vel;
DPoint tmp = target - pos;
float tar_theta = tmp.angle().radian_;
if(tmp.norm() > distance_thres)
{
vel.Vx = tmp.norm()*0.7*cos(tar_theta - robot_ori_.radian_); // 注意将全局坐标系下的期望速度转换为在机器人体坐标系下
vel.Vy = tmp.norm()*0.7*sin(tar_theta - robot_ori_.radian_);
vel.w = 0;
motor_cmd_pub_.publish(vel);
return false;
}
else
{
vel.Vx = 0.0;
vel.Vy = 0.0;
vel.w = 0;
motor_cmd_pub_.publish(vel);
return true;
}
}
bool move2ori(double target, double angle, double angle_thres = 8.0*DEG2RAD) // 一个十分简单的实现,可以用PID
{
static nubot_common::VelCmd vel;
double tmp = target - angle;
if(fabs(tmp) > angle_thres) // 容许误差为5度
{
vel.Vx = 0;
vel.Vy = 0;
vel.w = tmp;
motor_cmd_pub_.publish(vel);
return false;
}
else
{
vel.Vx = 0.0;
vel.Vy = 0.0;
vel.w = 0;
motor_cmd_pub_.publish(vel);
return true;
}
}
void pubStrategyInfo()
{
nubot_common::StrategyInfo strategy_info; // 这个消息的定义可以根据个人需要进行修改
strategy_info.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
strategy_info.AgentID = world_model_info_.AgentID_;
strategy_info_pub_.publish(strategy_info);
}
Multi-robot communication and collaboration
Basically, robot communicates via topic "nubotcontrol/strategy". So you could change the message file StrategyInfo.msg and add anything you want to share among robots. Then you could fill thoes fields in the functino pubStrategyInfo() from nubot_control.cpp:
void pubStrategyInfo()
{
nubot_common::StrategyInfo strategy_info; // 这个消息的定义可以根据个人需要进行修改
strategy_info.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
strategy_info.AgentID = world_model_info_.AgentID_;
strategy_info_pub_.publish(strategy_info);
}
The messages flow is as follows:Here, nubot_strategy_pub subscribes to all strategy infomation from all robots such as nubot1~nubot5, and then combines these messages and publishes messages on a new topic named "/nubot/nubotcontrol/strategy". If you robot prefix is not "nubot" but "something" for example, this node would publish messages on a new topic named "/somthing/nubotcontrol/strategy". And then world_model.cpp receives and processes these messages, for example:
/** 仿真程序更新所有的机器人的策略信息,在实际比赛中通过RTDB进行传输,现在采用topic传输*/
void
nubot::World_Model::updateStrategyinfo(const nubot_common::simulation_strategy &_strategyinfo)
{
int nums_robots = _strategyinfo.strategy_msgs.size();
for(int i =0 ; i < nums_robots; i++)
{
nubot_common::StrategyInfo strategyinfo = _strategyinfo.strategy_msgs[i];
int AgentId = strategyinfo.AgentID;
if(AgentId < 1 || AgentId >OUR_TEAM)
continue;
PassCommands & pass_cmd_ = teammatesinfo_[AgentId-1].pass_cmds_;
pass_cmd_.catchrobot_id = strategyinfo.pass_cmd.catch_id;
pass_cmd_.passrobot_id = strategyinfo.pass_cmd.pass_id;
pass_cmd_.is_dynamic_pass = strategyinfo.pass_cmd.is_dynamic_pass;
pass_cmd_.is_static_pass = strategyinfo.pass_cmd.is_static_pass;
pass_cmd_.is_passout = strategyinfo.pass_cmd.is_passout;
pass_cmd_.pass_pt = DPoint(strategyinfo.pass_cmd.pass_pt.x,strategyinfo.pass_cmd.pass_pt.y);
pass_cmd_.catch_pt = DPoint(strategyinfo.pass_cmd.catch_pt.x,strategyinfo.pass_cmd.catch_pt.y);
pass_cmd_.isvalid = strategyinfo.pass_cmd.is_valid;
teammatesinfo_[AgentId-1].robot_info_.setRolePreserveTime(strategyinfo.role_time);
teammatesinfo_[AgentId-1].robot_info_.setCurrentRole(strategyinfo.role);
teammatesinfo_[AgentId-1].robot_info_.setDribbleState(strategyinfo.is_dribble);
teammatesinfo_[AgentId-1].robot_info_.setCurrentAction(strategyinfo.action);
teammatesinfo_[AgentId-1].robot_info_.setTargetNum(1,strategyinfo.targetNum1);
teammatesinfo_[AgentId-1].robot_info_.setTargetNum(2,strategyinfo.targetNum2);
teammatesinfo_[AgentId-1].robot_info_.setTargetNum(3,strategyinfo.targetNum3);
teammatesinfo_[AgentId-1].robot_info_.setTargetNum(4,strategyinfo.targetNum4);
teammatesinfo_[AgentId-1].robot_info_.setcatchNum(strategyinfo.staticcatchNum);
teammatesinfo_[AgentId-1].robot_info_.setpassNum(strategyinfo.staticpassNum);
}
}
So you should also write some code to world_model.cpp.
Questions & Answers
- 问题:使用run教程里提供第一种方法运行所有的模块,没有在终端看到robot_code里的main()函数里的初始化输出信息ROS_INFO("start control process"),这关系到我们如何看到自己添加的调试信息。
解决办法:一次全部运行这些模块是看不到代码中的调试信息,应该使用第二种方法分别运行这些模块,在robot_code模块所在的终端可以看到输出的调试信息,记得每个新的终端下首先应该source一下,否则终端会提示错误。 - 问题: 需要给机器人轮速以驱动其运动吗?
解决办法:不需要。由于本仿真系统主要目的在于测试多机器人协同合作算法或策略,所以忽略了机器人的动力学模型以及运动学模型,所以只需要直接给机器人在其体坐标系下的速度即可; - 问题: 比赛中的一些参数,如机器人数量要怎么改?
解决办法: 在sim_config里面修改即可,其中有些参数与比赛相关,请谨慎修改,具体见README相关部分。 - 问题: 如何让两只球队进行比赛?
解决办法:rosrun nubot_common cyan_robot.sh和rosrun nubot_common magente_robot.sh都要运行,下面两个coach命令也都要运行,rosrun coach4sim cyan_coach.shrosrun coach4sim magenta_coach.sh,分别开始双方比赛。如果不想运行两个coach来发指令的话,也可以运行自动裁判盒,也就是rosrun auto_referee auto_referee -1,最后一个参数如果是-1代表cyan发球,如果是1代表magenta发球。 - 问题:安装ros的时候提示错误“GdkPixbuf-WARNING **: Cannot open pixbuf loader module file '/usr/lib/i386-linux-gnu/gdk-pixbuf-2.0/2.10.0/loaders.cache': 没有那个文件或目录”
解决办法:错误说安装了旧版本的软件包,在实体机上新装ubuntu,一些应用还没更新,所以gazebo会出错。这个错误解决方法是在安装完gazebo后sudo apt-get upgrade。
rosdep install --from-path src/ -y -i
sudo apt-get install ubiquity-frontend-gtk
sudo remastersys clean
sudo remastersys backup