Python程序设计 课程代码(一)
Python程序设计(一)
- 前言
- 0.关键字
- 01.turtle绘图
- 1.波浪图+爱心绘制
- 2.五角星绘制
- 3.六角形绘制
- 4.叠加三角形绘制
- 02.数字运算
- 1.天天向上的力量
- 2.M与N的数学运算
- 3.三角函数计算
- 4.数学公式计算
- 5.水仙花数计算
- 6.整数阶乘组合计算
- 03.字符串
- 1.月份缩写
- 2.凯撒密码
- 3.字符替代
- 4.字符串垂直打印
- 5.字符串反码 A
- 6.星号三角形打印
前言
halo!这里是 不会打代码的大学程序员~~Zivid
这篇是整理的python课程作业中基础编程代码,如有歧义,望众君指出~
0.关键字
– python3的33个保留字列表 –
| True | break | elif | if | not | try |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| False | class | except | import | yield | while |
| None | continue | finally | in | or | with |
| and | def | for | is | pass | |
| assert | del | from | lambda | raise | |
| as | else | global | nonlocal | return |
01.turtle绘图
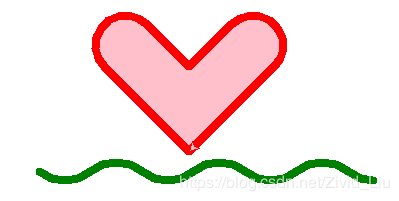
1.波浪图+爱心绘制
from turtle import *
# 或import turtle,此时所有的turtle语句变改,例如turtle.pu()
def sna(a,b,c):
pencolor("green")
seth(-a)
for i in range(3):
circle(a, b)
circle(-a, b)
circle(a, b / 2)
# 画爱心
pu()
setpos(0,20)
pd()
color("red","pink")
begin_fill()
left(135)
fd(120)
right(180)
circle(30,-180)
bk(60)
right(90)
fd(60)
circle(-30,180)
fd(120)
end_fill()
setup(650, 350, None,None)
penup()
fd(-150)
pendown()
pensize(8)
sna(40,80,4)
done
2.五角星绘制
from turtle import *
# 方法一
begin_fill()
fillcolor('red')
while True:
fd(200)
right(144)
if abs(pos())<1:#abs()是绝对值函数;pos()是turtle库返回当前位置的函数,返回值是x, y;
break #abs(pos())计算坐标(x,y)到原点(0,0)的距离.从原点出发,回到原点结束。
end_fill()
# 方法二
from turtle import *
begin_fill()
pensize(1)
color("black","red")
pu()
goto(-150,75)
pd()
for i in range (5):
fd(300)
right(144)
end_fill()
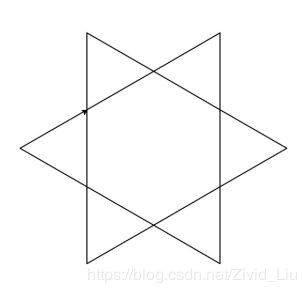
3.六角形绘制
from turtle import *
pensize(1)
for i in range (3):
fd(150)
right(120)
pu()
goto(0,-85)
pd()
for i in range (3):
fd(150)
right(-120)
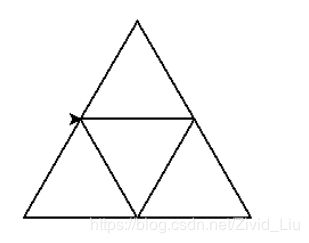
4.叠加三角形绘制
import turtle
turtle.seth(60)
turtle.fd(100)
turtle.seth(-60)
turtle.fd(100)
turtle.seth(180)
turtle.fd(50)
turtle.seth(120)
turtle.fd(50)
turtle.seth(0)
turtle.fd(50)
turtle.seth(-120)
turtle.fd(50)
turtle.seth(180)
turtle.fd(50)
02.数字运算
1.天天向上的力量
一年365天,以第1天的能力值为基数,记为1.0。
当好好学习时,能力值相比前一天提高N‰;当没有学习时,由于遗忘等原因能力值相比前一天下降N‰。
每天努力或每天放任,一年下来的能力值相差多少呢?其中,N的取值范围是1到10,N可以是小数。
要求:
- 获得用户输入N
- 计算每天努力和每天放任365天后的能力值及能力间比值,其中,
(1)能力值保留小数点后2位,
(2)能力间比值输出整数,
(3)输出结果间采用“逗号+空格”格式。
import math
m = eval(input(""))
n = m / 1000
du = math.pow((n + 1),364)
dd = math.pow((1 - n),364)
print("{:.2f}, {:.2f}, {}".format(du,dd,int(du/dd)))
| 示例 | 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1.44, 0.69, 2 |
2.M与N的数学运算
输出5种数学运算:
M与N的和、M与N的乘积、M的N次幂、M除N的余数、M和N中较大的值
m = eval(input())
n = eval(input())
i = max(m, n)
print(m + n, m * n, m ** n, m % n, i)
3.三角函数计算
根据下述公式计算并输出x的值,a、b和angle由用户输入,弧度值angle的取值范围为[0,360)。
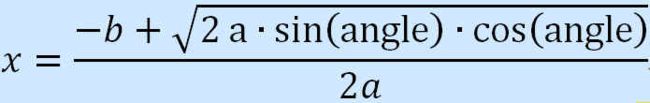
import math
a = eval(input())
b = eval(input())
ag = eval(input())
doub = 2*a*math.sin(ag)*math.cos(ag)
x = (-b + math.sqrt(doub))/(2 * a)
print(x)
示例:
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 2 | |
| 5 | |
| 60 | -0.9805999294236557 |
4.数学公式计算
from math import *
n = eval(input())
x = eval(input())
a = exp(x) / factorial(n)
q = pow(x,2*n )
w = sqrt(n * (n - 1))
e = q*w / fabs(x)
c = ceil(1 + a + e)
print("运算结果为:{}。".format(c))
5.水仙花数计算
“3位水仙花数”是指一个三位整数,其各位数字的3次方和等于该数本身。例如:ABC是一个“3位水仙花数”,则:A的3次方+B的3次方+C的3次方 = ABC
#方法一 列表
list = []
for N in range(100, 1000): # 三位数范围
n = str(N)
a = int(n[0])
b = int(n[1])
c = int(n[2])
if a ** 3 + b ** 3 + c ** 3 == N:
list.append(N)
n = str(list)
print(n[1:-1]) #n[1]和n[-1]分别是'[',']'这个框框
#方法二 运算
for i in range(100, 1000):
# 分别取到个、十、百位上的数字
bai_wei = i // 100
shi_wei = (i-bai_wei*100) // 10
ge_wei = (i - bai_wei*100 - shi_wei * 10) // 1
# 水仙花数成立条件
if bai_wei**3 + shi_wei**3 + ge_wei**3 == i:
print(i,end=",")
6.整数阶乘组合计算
from math import *
n,a = eval(input())
for k in range(0,500):
if (factorial(n) % (a ** k) == 0):
if(factorial(n) % a**(k+1)) != 0:
print(k)
| 输入 | 100,9 |
|---|---|
| 输出 | 24 |
03.字符串
1.月份缩写
months=“Jan.Feb.Mar.Apr.May.Jun.Jul.Aug.Sep.Oct.Nov.Dec.”,
编写一个程序,用户输入一个数字代表月份,输出结果为months中对应的月份缩写。
months="Jan.Feb.Mar.Apr.May.Jun.Jul.Aug.Sep.Oct.Nov.Dec."
a = eval(input(""))
b = (a - 1)*4
print(months[b:b+4])
| 输入 | 4 |
|---|---|
| 输出 | Apr. |
2.凯撒密码
替换方法对信息中的每一个英文字符循环替换为字母表序列中该字符后面的第三个字符
原文:A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
密文:D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z A B C
x = input()
y = ""#将b转换为字符串str
for i in x:#在a内循环
if 'a' <= i <= 'z': #str直接比较的
y = chr( ord('a') + ((ord(i)-ord('a')) + 3 )%26 )
elif 'A'<=i<='Z':
y = chr( ord('A') + ((ord(i)-ord('A')) + 3 )%26 )
else:
y = i
print(y,end='')
3.字符替代
一段文字中有单独字母“P”被误写为“p”,请编写程序进行纠正。
a = input()
b = len(a)
for i in range(b):
if a[i] == 'p':
print('P',end='')#字符平行打印
else:
print(a[i],end='')
| 输入 | pig is so cute. |
|---|---|
| 输出 | Pig is so cute. |
4.字符串垂直打印
a = input()
for i in range(len(a)):
print(a[i])
5.字符串反码 A
字符串反码的定义为:字符串所包含字符的反码组成的字符串。
字符反码的定义为:
(1) 对于小写英文字符,它的反码也是一个小写英文字符,且该字符与’a’的距离等于其反码与’z’的距离;
(2) 对于大写英文字符,它的反码也是一个大写英文字符,且该字符与’A’的距离等于其反码与’Z’的距离;
两个字符距离指其对应unicode编码之差。
x = input()
y = ""#将b转换为字符串str
for i in x:#在a内循环
if 'a' <= i <= 'z': #str直接比较的
y = chr( ord('z') - (ord(i)-ord('a')) )
elif 'A'<=i<='Z':
y = chr( ord('Z') - (ord(i)-ord('A')) )
else:
y = i
print(y,end='')
| 输入 | Well-Done |
|---|---|
| 输出 | Dvoo-Wlmv |
6.星号三角形打印
a = eval(input())
b = a // 2 + 1
c = 1
for i in range (b):
print((" " * ((a-c)//2)) + ("*" * c) +(" " * ((a-c)//2)))
c+= 2
| 输入 | 5 |
|---|---|
| 输出 |  |
Python程序设计 课程代码(二)
Python程序设计 课程代码(三)