手写springmvc框架版本2
文章目录
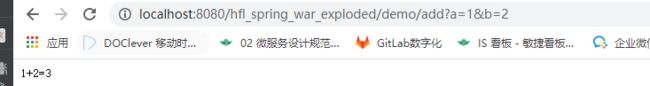
- 测试下:
上一篇文章,简单写了一个版本,但是有诸多问题,如map既有bean,又有url和方法的映射,还有各种包下的所有java类,很凌乱;
而且参数映射是写死的。这个版本改写DispatcherServle.
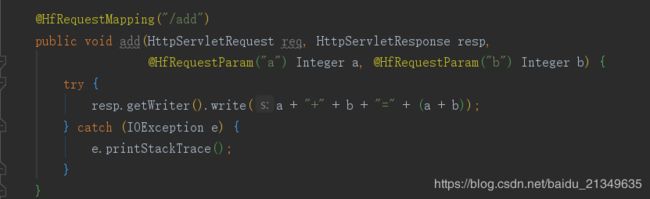
具体代码如下:方便以后自己多多琢磨:
package com.hfl.mvcframework.servlet.v2;
import com.hfl.mvcframework.annotation.*;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.*;
/**
* Created by Tom on 2019/3/24.
*/
public class HfDispatcherServlet extends HttpServlet{
//保存application.properties配置文件中的内容
private Properties contextConfig = new Properties();
//保存扫描的所有的类名
private List<String> classNames = new ArrayList<String>();
//传说中的IOC容器,我们来揭开它的神秘面纱
//为了简化程序,暂时不考虑ConcurrentHashMap
// 主要还是关注设计思想和原理
private Map<String,Object> ioc = new HashMap<String,Object>();
//保存url和Method的对应关系
// private Map handlerMapping = new HashMap();
//思考:为什么不用Map
//你用Map的话,key,只能是url
//Handler 本身的功能就是把url和method对应关系,已经具备了Map的功能
//根据设计原则:冗余的感觉了,单一职责,最少知道原则,帮助我们更好的理解
private List<Handler> handlerMapping = new ArrayList<Handler>();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req,resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//6、调用,运行阶段
try {
doDispatch(req,resp);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
resp.getWriter().write("500 Exection,Detail : " + Arrays.toString(e.getStackTrace()));
}
}
private void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws Exception {
Handler handler = getHandler(req);
if(handler == null){
// if(!this.handlerMapping.containsKey(url)){
resp.getWriter().write("404 Not Found!!!");
return;
}
//获得方法的形参列表
Class<?> [] paramTypes = handler.getParamTypes();
Object [] paramValues = new Object[paramTypes.length];
Map<String,String[]> params = req.getParameterMap();
for (Map.Entry<String, String[]> parm : params.entrySet()) {
String value = Arrays.toString(parm.getValue()).replaceAll("\\[|\\]","")
.replaceAll("\\s",",");
if(!handler.paramIndexMapping.containsKey(parm.getKey())){continue;}
int index = handler.paramIndexMapping.get(parm.getKey());
paramValues[index] = convert(paramTypes[index],value);
}
if(handler.paramIndexMapping.containsKey(HttpServletRequest.class.getName())) {
int reqIndex = handler.paramIndexMapping.get(HttpServletRequest.class.getName());
paramValues[reqIndex] = req;
}
if(handler.paramIndexMapping.containsKey(HttpServletResponse.class.getName())) {
int respIndex = handler.paramIndexMapping.get(HttpServletResponse.class.getName());
paramValues[respIndex] = resp;
}
Object returnValue = handler.method.invoke(handler.controller,paramValues);
if(returnValue == null || returnValue instanceof Void){ return; }
resp.getWriter().write(returnValue.toString());
}
private Handler getHandler(HttpServletRequest req) {
if(handlerMapping.isEmpty()){return null;}
//绝对路径
String url = req.getRequestURI();
//处理成相对路径
String contextPath = req.getContextPath();
url = url.replaceAll(contextPath,"").replaceAll("/+","/");
for (Handler handler : this.handlerMapping) {
Matcher matcher = handler.getPattern().matcher(url);
if(!matcher.matches()){ continue;}
return handler;
}
return null;
}
//url传过来的参数都是String类型的,HTTP是基于字符串协议
//只需要把String转换为任意类型就好
private Object convert(Class<?> type,String value){
//如果是int
if(Integer.class == type){
return Integer.valueOf(value);
}
else if(Double.class == type){
return Double.valueOf(value);
}
//如果还有double或者其他类型,继续加if
//这时候,我们应该想到策略模式了
//在这里暂时不实现,希望小伙伴自己来实现
return value;
}
//初始化阶段
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
//1、加载配置文件
doLoadConfig(config.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation"));
//2、扫描相关的类
doScanner(contextConfig.getProperty("scanPackage"));
//3、初始化扫描到的类,并且将它们放入到ICO容器之中
doInstance();
//4、完成依赖注入
doAutowired();
//5、初始化HandlerMapping
initHandlerMapping();
System.out.println("Hf Spring framework is init.");
}
//初始化url和Method的一对一对应关系
private void initHandlerMapping() {
if(ioc.isEmpty()){ return; }
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : ioc.entrySet()) {
Class<?> clazz = entry.getValue().getClass();
if(!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(HfController.class)){continue;}
//保存写在类上面的@HfRequestMapping("/demo")
String baseUrl = "";
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(HfRequestMapping.class)){
HfRequestMapping requestMapping = clazz.getAnnotation(HfRequestMapping.class);
baseUrl = requestMapping.value();
}
//默认获取所有的public方法
for (Method method : clazz.getMethods()) {
if(!method.isAnnotationPresent(HfRequestMapping.class)){continue;}
HfRequestMapping requestMapping = method.getAnnotation(HfRequestMapping.class);
//优化
// //demo///query
String regex = ("/" + baseUrl + "/" + requestMapping.value())
.replaceAll("/+","/");
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex);
this.handlerMapping.add(new Handler(pattern,entry.getValue(),method));
// handlerMapping.put(url,method);
System.out.println("Mapped :" + pattern + "," + method);
}
}
}
//自动依赖注入
private void doAutowired() {
if(ioc.isEmpty()){return;}
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : ioc.entrySet()) {
//Declared 所有的,特定的 字段,包括private/protected/default
//正常来说,普通的OOP编程只能拿到public的属性
Field[] fields = entry.getValue().getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if(!field.isAnnotationPresent(HfAutowired.class)){continue;}
HfAutowired autowired = field.getAnnotation(HfAutowired.class);
//如果用户没有自定义beanName,默认就根据类型注入
//这个地方省去了对类名首字母小写的情况的判断,这个作为课后作业
//小伙伴们自己去完善
String beanName = autowired.value().trim();
if("".equals(beanName)){
//获得接口的类型,作为key待会拿这个key到ioc容器中去取值
beanName = field.getType().getName();
}
//如果是public以外的修饰符,只要加了@Autowired注解,都要强制赋值
//反射中叫做暴力访问, 强吻
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
//用反射机制,动态给字段赋值
field.set(entry.getValue(),ioc.get(beanName));
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
private void doInstance() {
//初始化,为DI做准备
if(classNames.isEmpty()){return;}
try {
for (String className : classNames) {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
//什么样的类才需要初始化呢?
//加了注解的类,才初始化,怎么判断?
//为了简化代码逻辑,主要体会设计思想,只举例 @Controller和@Service,
// @Componment...就一一举例了
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(HfController.class)){
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
//Spring默认类名首字母小写
String beanName = toLowerFirstCase(clazz.getSimpleName());
ioc.put(beanName,instance);
}else if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(HfService.class)){
//1、自定义的beanName
HfService service = clazz.getAnnotation(HfService.class);
String beanName = service.value();
//2、默认类名首字母小写
if("".equals(beanName.trim())){
beanName = toLowerFirstCase(clazz.getSimpleName());
}
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
ioc.put(beanName,instance);
//3、根据类型自动赋值,投机取巧的方式
for (Class<?> i : clazz.getInterfaces()) {
if(ioc.containsKey(i.getName())){
throw new Exception("The “" + i.getName() + "” is exists!!");
}
//把接口的类型直接当成key了
ioc.put(i.getName(),instance);
}
}else {
continue;
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//如果类名本身是小写字母,确实会出问题
//但是我要说明的是:这个方法是我自己用,private的
//传值也是自己传,类也都遵循了驼峰命名法
//默认传入的值,存在首字母小写的情况,也不可能出现非字母的情况
//为了简化程序逻辑,就不做其他判断了,大家了解就OK
//其实用写注释的时间都能够把逻辑写完了
private String toLowerFirstCase(String simpleName) {
char [] chars = simpleName.toCharArray();
//之所以加,是因为大小写字母的ASCII码相差32,
// 而且大写字母的ASCII码要小于小写字母的ASCII码
//在Java中,对char做算学运算,实际上就是对ASCII码做算学运算
chars[0] += 32;
return String.valueOf(chars);
}
//扫描出相关的类
private void doScanner(String scanPackage) {
//scanPackage = com.gupaoedu.demo ,存储的是包路径
//转换为文件路径,实际上就是把.替换为/就OK了
//classpath
URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("/" + scanPackage.replaceAll("\\.","/"));
File classPath = new File(url.getFile());
for (File file : classPath.listFiles()) {
if(file.isDirectory()){
doScanner(scanPackage + "." + file.getName());
}else{
if(!file.getName().endsWith(".class")){ continue;}
String className = (scanPackage + "." + file.getName().replace(".class",""));
classNames.add(className);
}
}
}
//加载配置文件
private void doLoadConfig(String contextConfigLocation) {
//直接从类路径下找到Spring主配置文件所在的路径
//并且将其读取出来放到Properties对象中
//相对于scanPackage=com.gupaoedu.demo 从文件中保存到了内存中
InputStream fis = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(contextConfigLocation);
try {
contextConfig.load(fis);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(null != fis){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//保存一个url和一个Method的关系
public class Handler {
//必须把url放到HandlerMapping才好理解吧
private Pattern pattern; //正则
private Method method;
private Object controller;
private Class<?> [] paramTypes;
public Pattern getPattern() {
return pattern;
}
public Method getMethod() {
return method;
}
public Object getController() {
return controller;
}
public Class<?>[] getParamTypes() {
return paramTypes;
}
//形参列表
//参数的名字作为key,参数的顺序,位置作为值
private Map<String,Integer> paramIndexMapping;
public Handler(Pattern pattern, Object controller, Method method) {
this.pattern = pattern;
this.method = method;
this.controller = controller;
paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
paramIndexMapping = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
putParamIndexMapping(method);
}
private void putParamIndexMapping(Method method){
//提取方法中加了注解的参数
//把方法上的注解拿到,得到的是一个二维数组
//因为一个参数可以有多个注解,而一个方法又有多个参数
Annotation [] [] pa = method.getParameterAnnotations();
for (int i = 0; i < pa.length ; i ++) {
for(Annotation a : pa[i]){
if(a instanceof HfRequestParam){
String paramName = ((HfRequestParam) a).value();
if(!"".equals(paramName.trim())){
paramIndexMapping.put(paramName, i);
}
}
}
}
//提取方法中的request和response参数
Class<?> [] paramsTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < paramsTypes.length ; i ++) {
Class<?> type = paramsTypes[i];
if(type == HttpServletRequest.class ||
type == HttpServletResponse.class){
paramIndexMapping.put(type.getName(),i);
}
}
}
}
}
其他步骤和上篇文章一样。
测试下:
这个代码主要学习了委派模式转发请求,策略模式封装url和方法的映射。初始化参数中形参列表的设计和请求时的赋值技巧。
完