SpringBoot集成springfox-swagger2构建restful API
上面文章SpringMVC集成springfox-swagger2构建restful API简单写了如何在springmvc中集成swagger2。这边记录下在springboot中如何集成swagger2。其实使用基本相同。
- 引用相关jar包。
本次使用的maven,在pom.xml中引用相关依赖。
io.springfox
springfox-swagger2
2.4.0
io.springfox
springfox-swagger-ui
2.4.0
- 创建swagger的配置类
这个配置类和springmvc的写法完全一致。为了区分我又重命名一个。
package com.xingguo.springboot;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.service.Contact;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class Swagger2Configuration {
@Bean
public Docket buildDocket(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(buildApiInf())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.xingguo.springboot.controller"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
private ApiInfo buildApiInf(){
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("xingguo大标题")
.description("springboot swagger2")
.termsOfServiceUrl("http://blog.csdn.net/u014231523网址链接")
.contact(new Contact("diaoxingguo", "http://blog.csdn.net/u014231523", "[email protected]"))
.build();
}
}
- 在controller添加相关的注解
原来使用在类上使用@controller,现在可以使用@RestController,然后方法的@ResponseBody就可以不用写了,因为@RestController的注解接口上已经添加了,要求版本在4.0.1之后。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public @interface RestController {
/**
* The value may indicate a suggestion for a logical component name,
* to be turned into a Spring bean in case of an autodetected component.
* @return the suggested component name, if any
* @since 4.0.1
*/
String value() default "";
}
常用的注解如下:
- @Api()用于类名
- @ApiOperation()用于方法名
- @ApiParam()用于参数说明
- @ApiModel()用于实体类
- @ApiModelProperty用于实体类属性
更加详细的含义可以参考官方说明wiki
下面会用代码和示例图说明。
- 浏览器上查看swagger
启动项目在浏览器上输入url: http://{ip}:{port}/swagger-ui.html
application.properties中可以设置的自己的端口号为9090(如果不设置,默认为8080) ,显示效果如下:
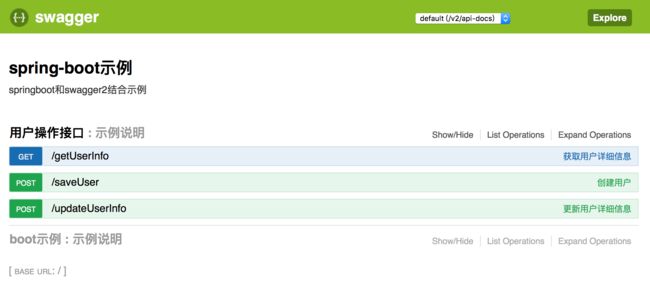
这里会把相应包下的所有controller按类进行显示。
我们看下其中一个类UserController.java,(请忽略业务逻辑,只看注解)
package com.xingguo.springboot.controller;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiParam;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.xingguo.springboot.model.User;
import com.xingguo.springboot.service.UserService;
/**
* Created by diaoxingguo on 2016/10/24.
*/
@Api(value="用户controller",description="用户操作",tags={"用户操作接口"})
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Resource
private UserService userService;
@ApiOperation("获取用户信息")
@GetMapping("/getUserInfo")
public User getUserInfo(@ApiParam(name="id",value="用户id",required=true) Long id,@ApiParam(name="username",value="用户名") String username) {
User user = userService.getUserInfo();
return user;
}
@ApiOperation("更改用户信息")
@PostMapping("/updateUserInfo")
public int updateUserInfo(@RequestBody @ApiParam(name="用户对象",value="传入json格式",required=true) User user){
int num = userService.updateUserInfo(user);
return num;
}
@ApiOperation("添加用户信息")
@PostMapping("/saveUser")
public String saveUser(@RequestBody @ApiParam(name="user",value="json fromat",required=true) User user) {
userService.saveUser(user);
return "success";
}
}
这里说明下,在使用对象作为参数时,可以在对象上添加相应的注解,用户页面显示。
如:
package com.xingguo.springboot.model;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by diaoxingguo on 2016/10/24.
*/
@ApiModel(description="用户对象user")
public class User {
@ApiModelProperty(value="用户名",name="username")
private String username;
@ApiModelProperty(value="状态",name="state",required=true)
private Integer state;
private String password;
private String nickName;
private Integer isDeleted;
private String[] ids;
private List idList;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public Integer getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(Integer state) {
this.state = state;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String[] getIds() {
return ids;
}
public void setIds(String[] ids) {
this.ids = ids;
}
public List getIdList() {
return idList;
}
public void setIdList(List idList) {
this.idList = idList;
}
public String getNickName() {
return nickName;
}
public void setNickName(String nickName) {
this.nickName = nickName;
}
public Integer getIsDeleted() {
return isDeleted;
}
public void setIsDeleted(Integer isDeleted) {
this.isDeleted = isDeleted;
}
}
显示的效果如图:


看上图红框的部分,其中一个是json格式的点击就可以获取参数格式。
第二张中可以看到字段相应的注释和是否必填。
如果在字段上添加注释@ApiModelProperty(required=true)就是必填(默认是false),相应的页面optional标识也会消失,标识这个字段必填。
点击下面的try it out按钮就可以进行调试。
在使用单个参数时,如上面代码中的getUserInfo()方法,对应的效果图如下:

这里如果是添加required=true,@ApiParam(required=true)则会在页面上显示required的标识。同样默认为false。
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/u014231523/article/details/54562695