爬虫动态渲染页面爬取Selenium高级篇
一 执行JavaScript
1 点睛
对于某些操作,Selenium API并没有提供。比如,下拉进度条,它可以直接模拟运行JavaScript,此时使用execute_script()方法即可实现。
2 代码
from selenium import webdriver
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
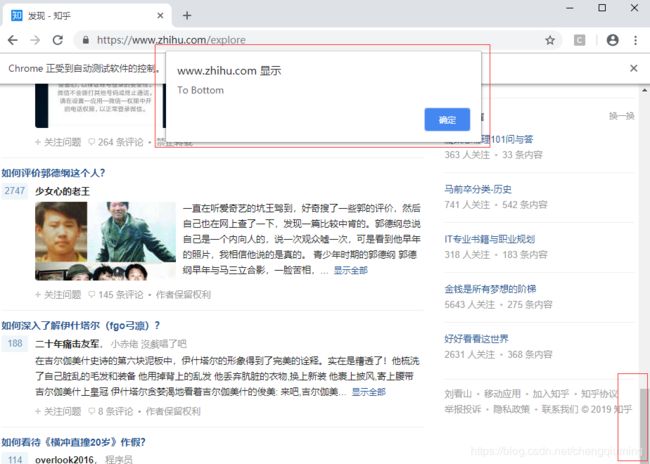
browser.get('https://www.zhihu.com/explore')
browser.execute_script('window.scrollTo(0, document.body.scrollHeight)')
browser.execute_script('alert("To Bottom")')3 结果
这里就利用execute_script()方法将进度条下拉到最底部,然后弹出alert提示框。
所以说有了这个方法,基本上API没有提供的所有功能都可以用执行JavaScript的方式来实现了。
二 获取节点信息
1 点睛
通过page_source属性可以获取网页的源代码,接着就可以使用解析库(如正则表达式、Beautiful Soup、pyquery等)来提取信息了。
不过,既然Selenium已经提供了选择节点的方法,返回的是WebElement类型,那么它也有相关的方法和属性来直接提取节点信息,如属性、文本等。这样的话,我们就可以不用通过解析源代码来提取信息了,非常方便。
2 获取属性
2.1 点睛
我们可以使用get_attribute()方法来获取节点的属性,但是其前提是先选中这个节点。
2.2 代码
from selenium import webdriver
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
url = 'https://www.zhihu.com/explore'
browser.get(url)
logo = browser.find_element_by_id('zh-top-link-logo')
print(logo)
print(logo.get_attribute('class'))2.3 结果
E:\WebSpider\venv\Scripts\python.exe E:/WebSpider/7_1.py
zu-top-link-logo 2.4 说明
通过get_attribute()方法,然后传入想要获取的属性名,就可以得到它的值了。
3 获取文本值
3.1 点睛
每个WebElement节点都有text属性,直接调用这个属性就可以得到节点内部的文本信息,这相当于Beautiful Soup的get_text()方法、pyquery的text()方法。
3.2 代码
from selenium import webdriver
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
url = 'https://www.zhihu.com/explore'
# 依然先打开知乎页面,然后获取“提问”按钮这个节点,再将其文本值打印出来。
browser.get(url)
input = browser.find_element_by_class_name('zu-top-add-question')
print(input.text)3.3 结果
E:\WebSpider\venv\Scripts\python.exe E:/WebSpider/7_1.py
提问4 获取id、位置、标签名和大小
4.1 点睛
WebElement节点还有一些其他属性,比如id属性可以获取节点id,location属性可以获取该节点在页面中的相对位置,tag_name属性可以获取标签名称,size属性可以获取节点的大小,也就是宽高,这些属性有时候还是很有用的。
4.2 代码
from selenium import webdriver
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
url = 'https://www.zhihu.com/explore'
browser.get(url)
# 首先获得“提问”按钮这个节点,然后调用其id、location、tag_name、size属性来获取对应的属性值。
input = browser.find_element_by_class_name('zu-top-add-question')
print(input.id)
print(input.location)
print(input.tag_name)
print(input.size)4.3 结果
E:\WebSpider\venv\Scripts\python.exe E:/WebSpider/7_1.py
0.27877331896029833-1
{'x': 675, 'y': 7}
button
{'height': 32, 'width': 66}二 切换Frame
1 点睛
我们知道网页中有一种节点叫作iframe,也就是子Frame,相当于页面的子页面,它的结构和外部网页的结构完全一致。Selenium打开页面后,它默认是在父级Frame里面操作,而此时如果页面中还有子Frame,它是不能获取到子Frame里面的节点的。这时就需要使用switch_to.frame()方法来切换Frame。
2 代码
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.common.exceptions import NoSuchElementException
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
url = 'http://www.runoob.com/try/try.php?filename=jqueryui-api-droppable'
browser.get(url)
browser.switch_to.frame('iframeResult')
try:
logo = browser.find_element_by_class_name('logo')
except NoSuchElementException:
print('NO LOGO')
browser.switch_to.parent_frame()
logo = browser.find_element_by_class_name('logo')
print(logo)
print(logo.text)3 结果
E:\WebSpider\venv\Scripts\python.exe E:/WebSpider/7_1.py
NO LOGO
RUNOOB.COM 4 说明
首先通过switch_to.frame()方法切换到子Frame里面,然后尝试获取父级Frame里的logo节点(这是不能找到的),如果找不到的话,就会抛出NoSuchElementException异常,异常被捕捉之后,就会输出NO LOGO。接下来,重新切换回父级Frame,然后再次重新获取节点,发现此时可以成功获取了。
所以,当页面中包含子Frame时,如果想获取子Frame中的节点,需要先调用switch_to.frame()方法切换到对应的Frame,然后再进行操作。
三 延时等待
1 点睛
在Selenium中,get()方法会在网页框架加载结束后结束执行,此时如果获取page_source,可能并不是浏览器完全加载完成的页面,如果某些页面有额外的Ajax请求,我们在网页源代码中也不一定能成功获取到。所以,这里需要延时等待一定时间,确保节点已经加载出来。
这里等待的方式有两种:一种是隐式等待,一种是显式等待。
2 隐式等待
2.1 点睛
当使用隐式等待执行测试的时候,如果Selenium没有在DOM中找到节点,将继续等待,超出设定时间后,则抛出找不到节点的异常。换句话说,当查找节点而节点并没有立即出现的时候,隐式等待将等待一段时间再查找DOM,默认的时间是0。
2.2 代码
from selenium import webdriver
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
# 这里用implicitly_wait()实现了隐式等待
browser.implicitly_wait(10)
browser.get('https://www.zhihu.com/explore')
input = browser.find_element_by_class_name('zu-top-add-question')
print(input)2.3 结果
E:\WebSpider\venv\Scripts\python.exe E:/WebSpider/7_1.py
3 显示等待
3.1 点睛
隐式等待的效果其实并没有那么好,因为我们只规定了一个固定时间,而页面的加载时间会受到网络条件的影响。
这里还有一种更合适的显式等待方法,它指定要查找的节点,然后指定一个最长等待时间。如果在规定时间内加载出来了这个节点,就返回查找的节点;如果到了规定时间依然没有加载出该节点,则抛出超时异常。
3.2 代码
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.support.ui import WebDriverWait
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get('https://www.taobao.com/')
wait = WebDriverWait(browser, 10)
input = wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.ID, 'q')))
button = wait.until(EC.element_to_be_clickable((By.CSS_SELECTOR, '.btn-search')))
print(input, button)3.3 结果
E:\WebSpider\venv\Scripts\python.exe E:/WebSpider/7_1.py
3.4 说明
这里首先引入WebDriverWait这个对象,指定最长等待时间,然后调用它的until()方法,传入要等待条件expected_conditions。比如,这里传入了presence_of_element_located这个条件,代表节点出现的意思,其参数是节点的定位元组,也就是ID为q的节点搜索框。
这样可以做到的效果就是,在10秒内如果ID为q的节点(即搜索框)成功加载出来,就返回该节点;如果超过10秒还没有加载出来,就抛出异常。
对于按钮,可以更改一下等待条件,比如改为element_to_be_clickable,也就是可点击,所以查找按钮时查找CSS选择器为.btn-search的按钮,如果10秒内它是可点击的,也就是成功加载出来了,就返回这个按钮节点;如果超过10秒还不可点击,也就是没有加载出来,就抛出异常。
运行代码,在网速较佳的情况下是可以成功加载出来的。
3.5 等待条件及含义
| 等待条件 |
含义 |
| title_is |
标题是某内容 |
| title_contains |
标题包含某内容 |
| presence_of_element_located |
节点加载出来,传入定位元组,如(By.ID, 'p') |
| visibility_of_element_located |
节点可见,传入定位元组 |
| visibility_of |
可见,传入节点对象 |
| presence_of_all_elements_located |
所有节点加载出来 |
| text_to_be_present_in_element |
某个节点文本包含某文字 |
| text_to_be_present_in_element_value |
某个节点值包含某文字 |
| frame_to_be_available_and_switch_to_it |
加载并切换 |
| invisibility_of_element_located |
节点不可见 |
| element_to_be_clickable |
节点可点击 |
| staleness_of |
判断一个节点是否仍在DOM,可判断页面是否已经刷新 |
| element_to_be_selected |
节点可选择,传节点对象 |
| element_located_to_be_selected |
节点可选择,传入定位元组 |
| element_selection_state_to_be |
传入节点对象以及状态,相等返回True,否则返回False |
| element_located_selection_state_to_be |
传入定位元组以及状态,相等返回True,否则返回False |
| alert_is_present |
是否出现警告 |