图像处理(三)直方图匹配
直方图匹配,又称直方图规定化,即变换原图的直方图为规定的某种形式的直方图,从而使两幅图像具有类似的色调和反差。直方图匹配属于非线性点运算。
直方图规定化的原理:对两个直方图都做均衡化,变成相同的归一化的均匀直方图,以此均匀直方图为媒介,再对参考图像做均衡化的逆运算
以下是算法实现(C#)
///
/// 直方图匹配
///
/// 原始图像
/// 匹配图像
/// 处理后图像
/// 处理成功 true 失败 false
public static bool HistogramMatching(Bitmap srcBmp, Bitmap matchingBmp, out Bitmap dstBmp) {
if (srcBmp == null || matchingBmp == null) {
dstBmp = null;
return false;
}
dstBmp = new Bitmap(srcBmp);
Bitmap tempSrcBmp = new Bitmap(srcBmp);
Bitmap tempMatchingBmp = new Bitmap(matchingBmp);
double[] srcCpR = null;
double[] srcCpG = null;
double[] srcCpB = null;
double[] matchCpB = null;
double[] matchCpG = null;
double[] matchCpR = null;
//分别计算两幅图像的累计概率分布
getCumulativeProbabilityRGB(tempSrcBmp, out srcCpR, out srcCpG, out srcCpB);
getCumulativeProbabilityRGB(tempMatchingBmp, out matchCpR, out matchCpG, out matchCpB);
double diffAR = 0, diffBR = 0, diffAG = 0, diffBG = 0, diffAB = 0, diffBB = 0;
byte kR = 0, kG = 0, kB = 0;
//逆映射函数
byte[] mapPixelR = new byte[256];
byte[] mapPixelG = new byte[256];
byte[] mapPixelB = new byte[256];
//分别计算RGB三个分量的逆映射函数
//R
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
diffBR = 1;
for (int j = kR; j < 256; j++) {
//找到两个累计分布函数中最相似的位置
diffAR = Math.Abs(srcCpR[i] - matchCpR[j]);
if (diffAR - diffBR < 1.0E-08) {//当两概率之差小于0.000000001时可近似认为相等
diffBR = diffAR;
//记录下此时的灰度级
kR = (byte)j;
}
else {
kR = (byte)Math.Abs(j - 1);
break;
}
}
if (kR == 255) {
for (int l = i; l < 256; l++) {
mapPixelR[l] = kR;
}
break;
}
mapPixelR[i] = kR;
}
//G
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
diffBG = 1;
for (int j = kG; j < 256; j++) {
diffAG = Math.Abs(srcCpG[i] - matchCpG[j]);
if (diffAG - diffBG < 1.0E-08) {
diffBG = diffAG;
kG = (byte)j;
}
else {
kG = (byte)Math.Abs(j - 1);
break;
}
}
if (kG == 255) {
for (int l = i; l < 256; l++) {
mapPixelG[l] = kG;
}
break;
}
mapPixelG[i] = kG;
}
//B
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
diffBB = 1;
for (int j = kB; j < 256; j++) {
diffAB = Math.Abs(srcCpB[i] - matchCpB[j]);
if (diffAB - diffBB < 1.0E-08) {
diffBB = diffAB;
kB = (byte)j;
}
else {
kB = (byte)Math.Abs(j - 1);
break;
}
}
if (kB == 255) {
for (int l = i; l < 256; l++) {
mapPixelB[l] = kB;
}
break;
}
mapPixelB[i] = kB;
}
//映射变换
BitmapData bmpData = dstBmp.LockBits(new Rectangle(0, 0, dstBmp.Width, dstBmp.Height), ImageLockMode.ReadWrite, PixelFormat.Format24bppRgb);
unsafe {
byte* ptr = null;
for (int i = 0; i < dstBmp.Height; i++) {
ptr = (byte*)bmpData.Scan0 + i * bmpData.Stride;
for (int j = 0; j < dstBmp.Width; j++) {
ptr[j * 3 + 2] = mapPixelR[ptr[j * 3 + 2]];
ptr[j * 3 + 1] = mapPixelG[ptr[j * 3 + 1]];
ptr[j * 3] = mapPixelB[ptr[j * 3]];
}
}
}
dstBmp.UnlockBits(bmpData);
return true;
}
///
/// 计算各个图像分量的累计概率分布
///
/// 原始图像
/// R分量累计概率分布
/// G分量累计概率分布
/// B分量累计概率分布
private static void getCumulativeProbabilityRGB(Bitmap srcBmp, out double[] cpR, out double[] cpG, out double[] cpB) {
if (srcBmp == null) {
cpB = cpG = cpR = null;
return;
}
cpR = new double[256];
cpG = new double[256];
cpB = new double[256];
int[] hR = null;
int[] hG = null;
int[] hB = null;
double[] tempR = new double[256];
double[] tempG = new double[256];
double[] tempB = new double[256];
getHistogramRGB(srcBmp, out hR, out hG, out hB);
int totalPxl = srcBmp.Width * srcBmp.Height;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
if (i != 0) {
tempR[i] = tempR[i - 1] + hR[i];
tempG[i] = tempG[i - 1] + hG[i];
tempB[i] = tempB[i - 1] + hB[i];
}
else {
tempR[0] = hR[0];
tempG[0] = hG[0];
tempB[0] = hB[0];
}
cpR[i] = (tempR[i] / totalPxl);
cpG[i] = (tempG[i] / totalPxl);
cpB[i] = (tempB[i] / totalPxl);
}
} ///
/// 获取图像三个分量的直方图数据
///
/// 图像
/// R分量直方图数据
/// G分量直方图数据
/// B分量直方图数据
public static void getHistogramRGB(Bitmap srcBmp, out int[] hR, out int[] hG, out int[] hB) {
if (srcBmp == null) {
hR = hB = hG = null;
return;
}
hR = new int[256];
hB = new int[256];
hG = new int[256];
BitmapData bmpData = srcBmp.LockBits(new Rectangle(0, 0, srcBmp.Width, srcBmp.Height), ImageLockMode.ReadOnly, PixelFormat.Format24bppRgb);
unsafe {
byte* ptr = null;
for (int i = 0; i < srcBmp.Height; i++) {
ptr = (byte*)bmpData.Scan0 + i * bmpData.Stride;
for (int j = 0; j < srcBmp.Width; j++) {
hB[ptr[j * 3]]++;
hG[ptr[j * 3 + 1]]++;
hR[ptr[j * 3 + 2]]++;
}
}
}
srcBmp.UnlockBits(bmpData);
return;
}效果图:
补充:
假设pr(r)是原始图像灰度分布的概率密度函数,pz(z)是希望得到的概率密度函数,如何建立这两个概率密度函数之间的联系就是直方图规定化处理的关键。这两个概率密度函数直接进行转换是比较困难的,这里我们需要一个“桥梁”来做一个转换。这个“桥梁”就是直方图均衡化中所使用的累计概率密度函数。
所以第一步就是将两个图像都做均衡化处理。
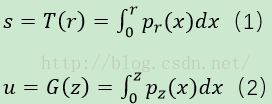
由于两幅图像都做了均衡化处理,所以,pr(r)和pz(z)具有同样的均匀密度。(2)的逆过程为![]()
这样,如果用原始图像中得到的均匀灰度级s来代替逆过程中的u,其结果灰度级就是所要求的概率密度函数pz(z)的灰度级。