前一段时间,和大家分享了 ASP.NET Core技术研究-探秘Host主机启动过程
但是没有深入说明主机的设计。今天整理了一下主机的一些知识,结合先前的博文,完整地介绍一下.NET Core的主机的设计和构建启动过程。
一、什么是主机
主机是一个封装了应用资源的对象,即:主机封装了一堆应用资源,封装了哪些应用资源呢?
- 依赖注入框架 DI
- Logging日志
- Configuration 配置
- 托管服务:IHostedService服务接口的实现
二、Web主机和通用主机
先说Web主机:即ASP.NET Core Web主机,概括的讲就是托管Web程序的Host。在低于 3.0 的 ASP.NET Core 版本中,Web 主机用于 HTTP 工作负载。
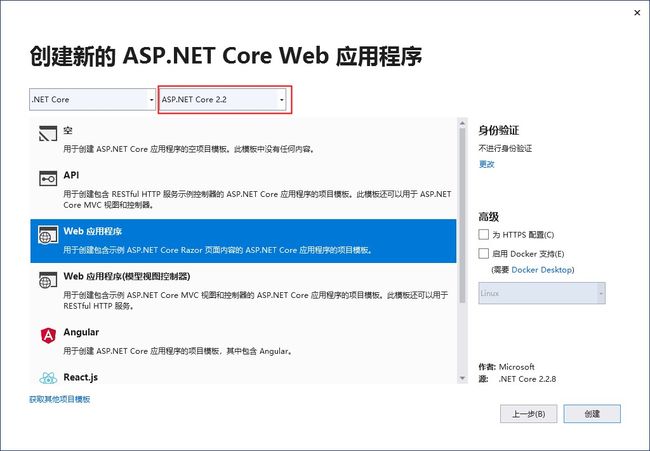
我们新建一个ASP.NET Core2.2的Web应用程序,在Program类的Main函数中我们可以看到整个WebHost的构造、启动过程:
.NET Core提供Web主机的同时,还提供了一个通用主机的概念。
通用主机Host和Web主机提供了类似的架构和功能,包含依赖注入框架DI、日志、配置、各类应用(托管服务)。通用主机的出现,给了我们更多开发的选择,比如说后台处理任务场景。
在.NET Core3.1版本后,微软不再建议将 Web 主机用于 Web 应用,直接使用Host通用主机来替换WebHost,
一句话:通用主机可以托管任何类型的应用,包括 Web 应用。 通用主机将替换 Web 主机。为了向下兼容,WebHost依然可以使用。
我们新建一个ASP.NET Core3.1的Web应用程序,在Program类的Main函数中我们可以看到整个WebHost的构造、启动过程:
接下来,我们将以ASP.NET Core 3.1这个版本,介绍一下主机的构建过程和启动过程
三、主机是如何构建的
从上述代码可以看到,Main函数中首先调用CreateHostBuilder方法,返回一个IHostBuilder。然后调用IHostBuilder.Build()方法完成
1. 通过Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args): 构造IHostBuilder的默认实现HostBuilder
在CreateHostBuilder方法内部,首先调用了Host.CreateDefaultBuilder构造了一个HostBuilder,这个我们先看下源码,看看到底Host类内部做了什么操作:
public static IHostBuilder CreateDefaultBuilder(string[] args)
{
var builder = new HostBuilder();
builder.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory());
builder.ConfigureHostConfiguration(config =>
{
config.AddEnvironmentVariables(prefix: "DOTNET_");
if (args != null)
{
config.AddCommandLine(args);
}
});
builder.ConfigureAppConfiguration((hostingContext, config) =>
{
var env = hostingContext.HostingEnvironment;
config.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true)
.AddJsonFile($"appsettings.{env.EnvironmentName}.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true);
if (env.IsDevelopment() && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(env.ApplicationName))
{
var appAssembly = Assembly.Load(new AssemblyName(env.ApplicationName));
if (appAssembly != null)
{
config.AddUserSecrets(appAssembly, optional: true);
}
}
config.AddEnvironmentVariables();
if (args != null)
{
config.AddCommandLine(args);
}
})
.ConfigureLogging((hostingContext, logging) =>
{
var isWindows = RuntimeInformation.IsOSPlatform(OSPlatform.Windows);
// IMPORTANT: This needs to be added *before* configuration is loaded, this lets
// the defaults be overridden by the configuration.
if (isWindows)
{
// Default the EventLogLoggerProvider to warning or above
logging.AddFilter(level => level >= LogLevel.Warning);
}
logging.AddConfiguration(hostingContext.Configuration.GetSection("Logging"));
logging.AddConsole();
logging.AddDebug();
logging.AddEventSourceLogger();
if (isWindows)
{
// Add the EventLogLoggerProvider on windows machines
logging.AddEventLog();
}
})
.UseDefaultServiceProvider((context, options) =>
{
var isDevelopment = context.HostingEnvironment.IsDevelopment();
options.ValidateScopes = isDevelopment;
options.ValidateOnBuild = isDevelopment;
});
return builder;
}
从上述.NET Core源代码中,可以看到CreateDefaultBuilder内部构造了一个HostBuilder,同时设置了:
- 将内容根目录(contentRootPath)设置为由 GetCurrentDirectory 返回的路径。
- 通过以下源加载主机配置
- 环境变量(DOTNET_前缀)配置
- 命令行参数配置
- 通过以下对象加载应用配置
- appsettings.json
- appsettings.{Environment}.json
- 密钥管理器 当应用在 Development 环境中运行时
- 环境变量
- 命令行参数
- 添加日志记录提供程序
- 控制台
- 调试
- EventSource
- EventLog( Windows环境下)
- 当环境为“开发”时,启用范围验证和依赖关系验证。
以上构造完成了HostBuilder,针对ASP.NET Core应用,代码继续调用了HostBuilder.ConfigureWebHostDefaults方法。
2. IHostBuilder.ConfigureWebHostDefaults:通过GenericWebHostBuilder对HostBuilder增加ASP.NET Core的运行时设置
构造完成HostBuilder之后,针对ASP.NET Core应用,继续调用了HostBuilder.ConfigureWebHostDefaults方法。这是一个ASP.NET Core的一个扩展方法:
![]()
我们继续看ConfigureWebHostDefaults扩展方法内部做了哪些事情:
ASP.NET Core源码连接:https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/master/src/DefaultBuilder/src/GenericHostBuilderExtensions.cs
using System;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore;
namespace Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting
{
///
/// Extension methods for configuring the IWebHostBuilder.
///
public static class GenericHostBuilderExtensions
{
///
/// Initializes a new instance of the
///
/// The following defaults are applied to the
/// The The
public static IHostBuilder ConfigureWebHostDefaults(this IHostBuilder builder, Action configure)
{
return builder.ConfigureWebHost(webHostBuilder =>
{
WebHost.ConfigureWebDefaults(webHostBuilder);
configure(webHostBuilder);
});
}
}
}
© 2020 GitHub, Inc.
首先,通过类GenericHostWebHostBuilderExtensions,对IHostBuilder扩展一个方法:ConfigureWebHost:builder.ConfigureWebHost
在这个扩展方法中实现了对IWebHostBuilder的依赖注入:即将GenericWebHostBuilder实例传入方法ConfigureWebHostDefaults内部
代码连接:https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/release/3.1/src/Hosting/Hosting/src/GenericHostWebHostBuilderExtensions.cs
using System;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
namespace Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting
{
public static class GenericHostWebHostBuilderExtensions
{
public static IHostBuilder ConfigureWebHost(this IHostBuilder builder, Action configure)
{
var webhostBuilder = new GenericWebHostBuilder(builder);
configure(webhostBuilder);
builder.ConfigureServices((context, services) => services.AddHostedService());
return builder;
}
}
}
通过GenericWebHostBuilder的构造函数GenericWebHostBuilder(buillder),将已有的HostBuilder增加了ASP.NET Core运行时设置。
可以参考ASP.NET Core源代码:https://github.com/dotnet/aspnetcore/blob/release/3.1/src/Hosting/Hosting/src/GenericHost/GenericWebHostBuilder.cs
先看到这,让我们回到ConfigureWebHostDefaults:
将上面两段代码合并一下进行理解:ConfigureWebHostDefaults做了两件事情:
①. 扩展IHostBuilder增加ConfigureWebHost,引入IWebHostBuilder的实现GenericWebHostBuilder,将已有的HostBuilder增加ASP.NET Core运行时的设置。
② ConfigureWebHost代码中的configure(webhostBuilder):对注入的IWebHostBuilder,调用 WebHost.ConfigureWebDefaults(webHostBuilder),启用各类设置,如下代码解读:
internal static void ConfigureWebDefaults(IWebHostBuilder builder)
{
builder.ConfigureAppConfiguration((ctx, cb) =>
{
if (ctx.HostingEnvironment.IsDevelopment())
{
StaticWebAssetsLoader.UseStaticWebAssets(ctx.HostingEnvironment, ctx.Configuration);
}
});
builder.UseKestrel((builderContext, options) =>
{
options.Configure(builderContext.Configuration.GetSection("Kestrel"));
})
.ConfigureServices((hostingContext, services) =>
{
// Fallback
services.PostConfigure(options =>
{
if (options.AllowedHosts == null || options.AllowedHosts.Count == 0)
{
// "AllowedHosts": "localhost;127.0.0.1;[::1]"
var hosts = hostingContext.Configuration["AllowedHosts"]?.Split(new[] { ';' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
// Fall back to "*" to disable.
options.AllowedHosts = (hosts?.Length > 0 ? hosts : new[] { "*" });
}
});
// Change notification
services.AddSingleton>(
new ConfigurationChangeTokenSource(hostingContext.Configuration));
services.AddTransient();
if (string.Equals("true", hostingContext.Configuration["ForwardedHeaders_Enabled"], StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
services.Configure(options =>
{
options.ForwardedHeaders = ForwardedHeaders.XForwardedFor | ForwardedHeaders.XForwardedProto;
// Only loopback proxies are allowed by default. Clear that restriction because forwarders are
// being enabled by explicit configuration.
options.KnownNetworks.Clear();
options.KnownProxies.Clear();
});
services.AddTransient();
}
services.AddRouting();
})
.UseIIS()
.UseIISIntegration();
}
其内部实现了:
- 前缀为 ASPNETCORE_ 的环境变量加载主机配置。
- 将 Kestrel作为默认的Web服务器
- 添加HostFiltering中间件(主机筛选中间件)
- 如果ASPNETCORE_FORWARDEDHEADERS_ENABLED=true,添加转接头中间件ForwardedHeaders
- 启用IIS集成
3. 返回ConfigureWebHostDefaults代码中的configure(webHostBuilder):执行Program类中的webBuilder.UseStartup
以上过程完成了IHostBuilder.ConfigureWebHostDefaults,通过GenericWebHostBuilder对HostBuilder增加ASP.NET Core的运行时设置。
接下来就是主机的Build过程了:
4. CreateHostBuilder(args).Build()
CreateHostBuilder返回的IHostBuilder,我们通过代码Debug,看一下具体的类型:Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting.HostBuilder。
![]()
具体的Build过程是怎么样的?先看下Build的源码:https://github.com/dotnet/extensions/blob/release/3.1/src/Hosting/Hosting/src/HostBuilder.cs
![]()
主机Build的过程主要完成了:
- BuildHostConfiguration: 构造配置系统,初始化 IConfiguration _hostConfiguration;
- CreateHostingEnvironment:构建主机HostingEnvironment环境信息,包含ApplicationName、EnvironmentName、ContentRootPath等
- CreateHostBuilderContext:创建主机Build上下文HostBuilderContext,上下文中包含:HostingEnvironment和Configuration
- BuildAppConfiguration:构建应用程序配置
- CreateServiceProvider:创建依赖注入服务提供程序, 即依赖注入容器
四、主机是如何启动运行的
我们先通过Debug,看一下Host的信息:Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting.Internal.Host
![]()
这个Run方法也是一个扩展方法:HostingAbstractionsHostExtensions.Run
ASP.NET Core源代码链接:https://github.com/dotnet/extensions/blob/release/3.1/src/Hosting/Abstractions/src/HostingAbstractionsHostExtensions.cs
![]()
其实内部转调的还是Host.StartAsync方法,在内部启动了DI依赖注入容器中所有注册的服务。
.NET Core代码链接:https://github.com/dotnet/extensions/blob/release/3.1/src/Hosting/Hosting/src/Internal/Host.cs
![]()
五、主机中注册一个托管服务
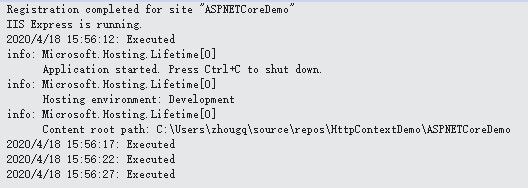
以一个后台自更新(每隔5s 检查一次程序变更、进行输出)场景作为Demo,我们看一下如何在主机中注册一个托管服务。
自更新服务UpdateService,需要继承接口IHostService。
public class UpdateService : IHostedService
{
Task updateTask = null;
CancellationTokenSource cancellationTokenSource = new CancellationTokenSource();
public Task StartAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
updateTask = Task.Run(() =>
{
while (cancellationTokenSource.Token.IsCancellationRequested==false)
{
//Check new data...
Console.WriteLine(DateTime.Now + ": Executed");
Task.Delay(5000).Wait();
}
});
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
public Task StopAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
cancellationTokenSource.Cancel();
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
}
同时,我们需要在ConfigureServices方法中,将UpdateService添加到IoC服务容器中
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddSingleton();
services.AddControllers();
}
程序启动后,可以看到以下输出:
以上是对.NET Core主机的概念、设计初衷、构建过程、启动运行过程、服务注册的整理和分享。
周国庆
2020/4/18