WebRTC源码分析——呼叫建立过程之三(创建PeerConnection)
目录
- 1 引言
- 2 PeerConnection对象的创建
- 2.1 CreatePeerConnection方法参数解析
- 2.1.1 PeerConnectionDependencies依赖
- 2.1.1.1 强制性依赖PeerConnectionObserver
- 2.1.2 RTCConfiguration配置参数
- 2.1.2.1 ICE服务器信息列表 IceServers
- 2.1.2.2 IceTransportsType type
- 2.1.2.3 BundlePolicy bundle_policy
- 2.1.2.4 RtcpMuxPolicy rtcp_mux_policy
- 2.1.2.5 证书RTCCertificate
- 2.1.2.6 候选项池大小ice_candidate_pool_size
- 2.1.2.7 SDP语法 SdpSemantics
- 2.2 CreatePeerConnection方法的实现
- 2.2.1 创建RtcEventLog对象
- 2.2.2 创建Call对象
- 3 PeerConnection简介
- 3.1 PeerConnection构造
- 3.1.1 CNAME
- 3.2 PeerConnection初始化
- 3.2.1 会话ID——Session ID
- 4 总结
1 引言
当WebRTC的端与信令服务器建立连接之后,可以通过与服务器的信令交互获知对等端点的存在,进一步通过信令向对端发起呼叫。在发起呼叫之前,发起方需要在本地做一些初始化工作,创建两个重要的对象:PeerConnectionFactory和PeerConnection,这两个C++对象提供了建立WebRTC会话的API(注意:在JS层,没有PeerConnectionFactory,只有PeerConnection,是基于C++ API层的全局方法以及PeerConnectionFactory和PeerConnection对象的进一步封装)。
在 WebRTC源码分析-呼叫建立过程之二(创建PeerConnectionFactory) 文中已经对PeerConnectionFactory的创建及其功能进行了详尽的分析。 本文将对PeerConnection的创建及其功能进行分析,创建的时机如图中红色字体所示。
![]()
2 PeerConnection对象的创建
在example/peerconnection_client工程中,发起方调用如下代码来创建PeerConnection对象。
webrtc::PeerConnectionInterface::RTCConfiguration config;
config.sdp_semantics = webrtc::SdpSemantics::kUnifiedPlan;
config.enable_dtls_srtp = dtls;
webrtc::PeerConnectionInterface::IceServer server;
server.uri = "stun:stun.l.google.com:19302";
config.servers.push_back(server);
peer_connection_ = peer_connection_factory_->CreatePeerConnection(
config, nullptr, nullptr, this);
2.1 CreatePeerConnection方法参数解析
WebRTC中PeerConnectionFactory提供了两个重载的CreatePeerConnection方法,其声明如下:
rtc::scoped_refptr<PeerConnectionInterface> CreatePeerConnection(
const PeerConnectionInterface::RTCConfiguration& configuration,
std::unique_ptr<cricket::PortAllocator> allocator,
std::unique_ptr<rtc::RTCCertificateGeneratorInterface> cert_generator,
PeerConnectionObserver* observer) override;
rtc::scoped_refptr<PeerConnectionInterface> CreatePeerConnection(
const PeerConnectionInterface::RTCConfiguration& configuration,
PeerConnectionDependencies dependencies) override;
实际上,第一个方法的后三个参数用于填充PeerConnectionDependencies结构体,然后作为了第二个方法的入参。因此,可以将CreatePeerConnection的参数分为两类:
- RTCConfiguration: 表征PeerConnection的全局配置项。全局配置项是提供给WebRTC内部使用的参数信息,可以通过参数来控制WebRTC的内部逻辑、行为方式;
- PeerConnectionDependencies:表征PeerConnection的依赖项。依赖定义了由用户提供的可执行代码,用于执行用户定义的逻辑,其中最重要的就是PeerConnectionObserver,是PeerConnection的事件回调,应用层通过实现这些回调方法来作出自己想要实现的逻辑。
2.1.1 PeerConnectionDependencies依赖
PeerConnectionDependencies声明的源码如下:
struct PeerConnectionDependencies final {
explicit PeerConnectionDependencies(PeerConnectionObserver* observer_in);
// This object is not copyable or assignable.
PeerConnectionDependencies(const PeerConnectionDependencies&) = delete;
PeerConnectionDependencies& operator=(const PeerConnectionDependencies&) =
delete;
// This object is only moveable.
PeerConnectionDependencies(PeerConnectionDependencies&&);
PeerConnectionDependencies& operator=(PeerConnectionDependencies&&) = default;
~PeerConnectionDependencies();
// Mandatory dependencies
PeerConnectionObserver* observer = nullptr;
// Optional dependencies
std::unique_ptr<cricket::PortAllocator> allocator;
std::unique_ptr<webrtc::AsyncResolverFactory> async_resolver_factory;
std::unique_ptr<rtc::RTCCertificateGeneratorInterface> cert_generator;
std::unique_ptr<rtc::SSLCertificateVerifier> tls_cert_verifier;
};
有如下几点需要注意:
- PeerConnectionDependencies被final修饰,不可以被继承,如果有新的依赖,那么只能修改PeerConnectionDependencies结构本身,并将该依赖以unique_ptr来引入,就如可选依赖那样。这样使得依赖能被PeerConnection持有(将使用move语义),从而可以控制这些依赖的生命周期,使得依赖注入比较安全;
- PeerConnectionDependencies对象不可以复制或者赋值,只可以被移动。
- Mandatory dependencies(强制性依赖):只有一个强制性依赖,不可为空,那就是PeerConnectionObserver对象,给应用层提供了介入WebRTC执行逻辑的回调方法,用来监听PeerConnection的所有事件,并执行用户逻辑。
- Optional dependencies(可选性依赖):可选依赖是外部传入参数可以为空,如果为空,内部将创建默认的;这些参数包括PortAllocator端口分配器,AsyncResolverFactory异步地址解析器,RTCCertificateGenerator证书产生器,SSLCertificateVerifier证书验证器。
2.1.1.1 强制性依赖PeerConnectionObserver
PeerConnectionObserver是PeerConnection的回调接口,应用层可以必须提供回调接口的实现,以便响应PeerConnection的事件。这些接口大致分为如下几类:
几个状态相关回调:
- OnSignalingChange:信令状态改变。
- OnConnectionChange:PeerConnection状态改变。
远端流或者轨道的添加或者移出:
- OnAddStream:收到远端Peer的一个新stream。
- OnRemoveStream:收到远端Peer移出一个stream。
- OnAddTrack:当一个receiver和它的track被创建时。Plan B 和 Unified Plan语法下都会被调用,但是Unified Plan语法下更建议使用OnTrack回调,OnAddTrack只是为了兼容之前的Plan B遗留的接口,二者在同样的情况下被回调。
- OnTrack:该方法在收到的信令指示一个transceiver将从远端接收媒体时被调用,实际就是在调用SetRemoteDescription时被触发。该接收track可以通过transceiver->receiver()->track()方法被访问到,其关联的streams可以通过transceiver->receiver()->streams()获取。只有在Unified Plan语法下,该回调方法才会被触发。
- OnRemoveTrack:该方法在收到的信令指示某个track中将不再收到媒体数据时触发。Plan B语法下,对应的receiver将被从PeerConnection中移出,并且对应track将被设置为muted状态;Unified Plan语法下, 对应的receiver将被保留,对应的transceiver将改变direction为仅发送sendonly 或者非活动inactive状态
ICE过程相关:
- OnRenegotiationNeeded:需要重新协商时触发,比如重启ICE时。
- OnIceCandidate:收集到一个新的ICE候选项时触发。
- OnIceCandidateError:收集ICE选项时出错。
- OnIceCandidatesRemoved:当候选项被移除时触发。
- OnStandardizedIceConnectionChange:符合标准的ICE连接状态改变。
- OnIceGatheringChange:ICE收集状态改变。
- OnIceConnectionReceivingChange:ICE连接接收状态改变。
- OnIceSelectedCandidatePairChanged:ICE连接所采用的候选者对改变。
DataChannel相关:
- OnDataChannel:当远端打开data channel通道时触发。
2.1.2 RTCConfiguration配置参数
RTCConfiguration声明的源码如下,由于源码太长,此处删减了RTCConfiguration的构造函数,删减了RTCConfiguration的getter和setter方法。参数罗列如下,分四类:
- 静态参数3个;
- 标准参数6个:与W3C标准提供RTCConfiguration参数一致https://w3c.github.io/webrtc-pc/#rtcconfiguration-dictionary,是最常用的控制参数。
- Deprecated参数8个:提供给约束使用;
- 非标准参数31个:涉及到ICE过程相关的参数,音频jitterbuffer的参数,Sdp语法设置等等,这些给与Native开发提供更多的定制化选项。
struct RTC_EXPORT RTCConfiguration {
// 静态参数
static const int kUndefined = -1;
// Default maximum number of packets in the audio jitter buffer.
static const int kAudioJitterBufferMaxPackets = 50;
// ICE connection receiving timeout for aggressive configuration.
static const int kAggressiveIceConnectionReceivingTimeout = 1000;
// 标准参数
IceServers servers;
IceTransportsType type = kAll;
BundlePolicy bundle_policy = kBundlePolicyBalanced;
RtcpMuxPolicy rtcp_mux_policy = kRtcpMuxPolicyRequire;
std::vector<rtc::scoped_refptr<rtc::RTCCertificate>> certificates;
int ice_candidate_pool_size = 0;
// 提供给约束使用的参数,已被放弃
bool disable_ipv6 = false;
bool disable_ipv6_on_wifi = false;
int max_ipv6_networks = cricket::kDefaultMaxIPv6Networks;
bool disable_link_local_networks = false;
bool enable_rtp_data_channel = false;
absl::optional<int> screencast_min_bitrate;
absl::optional<bool> combined_audio_video_bwe;
absl::optional<bool> enable_dtls_srtp;
// 非标准参数
TcpCandidatePolicy tcp_candidate_policy = kTcpCandidatePolicyEnabled;
CandidateNetworkPolicy candidate_network_policy =
kCandidateNetworkPolicyAll;
int audio_jitter_buffer_max_packets = kAudioJitterBufferMaxPackets;
bool audio_jitter_buffer_fast_accelerate = false;
int audio_jitter_buffer_min_delay_ms = 0;
bool audio_jitter_buffer_enable_rtx_handling = false;
int ice_connection_receiving_timeout = kUndefined;
int ice_backup_candidate_pair_ping_interval = kUndefined;
ContinualGatheringPolicy continual_gathering_policy = GATHER_ONCE;
bool prioritize_most_likely_ice_candidate_pairs = false;
struct cricket::MediaConfig media_config;
bool prune_turn_ports = false;
bool presume_writable_when_fully_relayed = false;
bool enable_ice_renomination = false;
bool redetermine_role_on_ice_restart = true;
absl::optional<int> ice_check_interval_strong_connectivity;
absl::optional<int> ice_check_interval_weak_connectivity;
absl::optional<int> ice_check_min_interval;
absl::optional<int> ice_unwritable_timeout;
absl::optional<int> ice_unwritable_min_checks;
absl::optional<int> ice_inactive_timeout;
absl::optional<int> stun_candidate_keepalive_interval;
absl::optional<rtc::IntervalRange> ice_regather_interval_range;
webrtc::TurnCustomizer* turn_customizer = nullptr;
absl::optional<rtc::AdapterType> network_preference;
SdpSemantics sdp_semantics = SdpSemantics::kPlanB;
bool active_reset_srtp_params = false;
bool use_media_transport = false;
bool use_media_transport_for_data_channels = false;
absl::optional<CryptoOptions> crypto_options;
bool offer_extmap_allow_mixed = false;
更多的关于RTCConfiguration 将于以后学习到各个参数所起作用再详述,本章只介绍与W3C标准一致的选项信息。
2.1.2.1 ICE服务器信息列表 IceServers
IceServers servers是一个IceServer的列表,每一个列表项IceServer用于存储一个STUN or TURN服务器信息,Peer可以向STUN或者TURN服务器查询候选ip地址。
struct IceServer {
std::string uri;
std::vector<std::string> urls;
std::string username;
std::string password;
std::string hostname;
TlsCertPolicy tls_cert_policy = kTlsCertPolicySecure;
std::vector<std::string> tls_alpn_protocols;
std::vector<std::string> tls_elliptic_curves;
};
- uri: server的地址,可以存储多个与服务器相关的地址,其格式定义在RFC7064和RFC7065中,单个地址如文章开头的示例所示:“stun:stun.l.google.com:19302”;
- urls:server的地址列表,用于替代uri;
- username, password:用于服务器进行用户验证;
- hostname:当uri或者是urls为直接ip地址时,该字段用来存储hostname;
- tls_alpn_protocols: TLS的扩展,用于支持应用层协商;
- tls_elliptic_curves: TLS扩展,椭圆曲线加密算法;
- tls_cert_policy :TLS证书策略,如下源码和注释。
// TLS certificate policy.
enum TlsCertPolicy {
// 对于基于TLS的协议,确保不会绕过证书验证
kTlsCertPolicySecure,
// 对于基于TLS协议,跳过证书验证忽略安全性检查
kTlsCertPolicyInsecureNoCheck,
};
2.1.2.2 IceTransportsType type
这是一个枚举,决定了ICE过程中需要收集哪些候选地址,并且只使用这些地址进行联通性检测。候选地址分为如下几类:主机地址、反射地址、replay中继地址。默认收集所有地址,即kAll,这种方式可以显著的减小使用TurnServer的资源,因为会优先使用host和反射地址。可以通过修改该参数来改变默认行为。
enum IceTransportsType {
kNone, // 不收集ICE候选地址
kRelay, // 只收集relay地址
kNoHost, // 不收集主机地址
kAll // 收集所有地址
};
2.1.2.3 BundlePolicy bundle_policy
这是一个枚举,决定了音频轨,视频轨等是否绑定传输,以及如何绑定传输的。参数的详细分析以及如何影响SDP参数的,见 https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-rtcweb-jsep-24#section-4.1.1。 默认多路音频和多路视频按照媒体类型分别绑定到各自的传输通道,即kBundlePolicyBalanced。
enum BundlePolicy {
kBundlePolicyBalanced, // 多路音频,多路视频按照媒体类型分别绑定传输
kBundlePolicyMaxBundle, // 多路音频,多路视频都绑定到一个传输通道
kBundlePolicyMaxCompat // 每路音频,每路视频都分开传输。
};
- kBundlePolicyBalanced:SDP中每种媒体类型(音频、视频、应用数据)第一个m=段(mLine)将包含传输参数。同一种媒体类型的第二个mLine(对于kUnifiedPlan的SDP语法而言)或者是同一媒体类型子序列的mLine(对于kPlanB的SDP语法而言)将被标记为bundle-only。这将导致如果有N个不同的媒体类型,那么候选项将被收集用来产生N个媒体传输流。这个策略平衡了多路复用需求和仍旧可以使用历史遗留接口来协商基本音频和视频的需求。当被呼叫端收到的offer sdp中没有bundle group的信息,那么实现将拒绝所有其他的mLine,只接受每种媒体类型的第一个mLine。
- kBundlePolicyMaxBundle:仅第一个mLine包含传输参数;所有的其他的的流(除去第一个mLine描述的)将被标记为bundle-only。这个策略目标在于:最小化候选项的收集和最大化的传输通道复用,但是与遗留端点不兼容。当接受端收到这个offer sdp时,实现将只接受第一个mLine和与第一个mLine同属一个bundle group的mLine,其他mLine将被拒绝。
- kBundlePolicyMaxCompat:所有mLine将包含传输参数,所有mLine将不会标记为bundle-only。这个传输策略允许所有流被“非绑定感知”的端所接收,但对于每个流都需要收集单独的候选项,也即每个流都采用单独的传输通道。
2.1.2.4 RtcpMuxPolicy rtcp_mux_policy
这是一个枚举,决定了RTP和RTCP是否复用同一个传输通道。当不复用时,比如RTP采用传输端口8000,那么对应的RTCP端口一般采用8001。参数的详细分析以及如何影响SDP参数的,见 https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-rtcweb-jsep-24#section-4.1.1
enum RtcpMuxPolicy {
kRtcpMuxPolicyNegotiate, // 双方协商决定
kRtcpMuxPolicyRequire, // 必须复用同一个通道
};
- kRtcpMuxPolicyNegotiate:实现将收集RTP和RTCP的候选项,并且同时会在offer中提供"a=rtcp-mux"这样的属性,这样可以允许接收端点可以选择是采取RTP/RTCP复用还是不复用同一个传输通道。
- kRtcpMuxPolicyRequire:实现将只收集RTP的候选项,并且同时会在offer中为每个mLine提供"a=rtcp-mux-only"这样的属性,这样将减半需要收集的候选项。应用一个sdp,该sdp中存在mLine没有"a=rtcp-mux"属性,将导致错误并返回。
2.1.2.5 证书RTCCertificate
这是一个证书列表std::vector
2.1.2.6 候选项池大小ice_candidate_pool_size
一个典型的WebRTC应用一般在调用setLocalDescription方法后才开始进行ICE过程,开启候选者收集,因为setLocalDescription得到得本地SDP信息中指示了需要的ICE组件个数(跟需要建立的传输通道数相同,而传输通道数与媒体轨道个数、媒体轨道的绑定策略BundlePolicy、RTP/RTCP的通道复用策略RtcpMuxPolicy都有关系)以及哪些候选项(与IceTransportsType参数有关)需要被收集。然而,为了加速媒体通道建立,一些应用如果提前知道需要的ICE组件个数,那么它可以提前(在调用setLocalDescription之前就开始)收集一个池子的ICE候选项来帮助快速的建立媒体通道。
当setLocalDescription被调用时,开始收集需要的ICE候选者,首先要检查候选项池中是否已经有可用的候选项了。如果候选池中已经有可用的,应该立马通过ICE候选项事件来回调告知应用层已经收集到可用的候选项。如果候选池将耗尽,或者是需要使用的ICE组件个数比预期的要大,或者是候选池没有足够的时间去收集完候选项,那么剩余的候选项将在调用setLocalDescription时照常收集。这个只会出现在首次的offer/answer交换过程中,这个过程结束后候选池将被清空不再被使用。
举个列子:比如一个应用在不久将来的某个时间点有来电呼叫,并希望尽可能减少建立连接所需要的时间。通过预收集候选项到候选池,使得可以在接收到来电呼叫时,可以立马交换候选项并进行联通性检测。注意持有这些预收集的候选项,并保持这些候选项的有效性,应用将占用STUN/TURN资源。
该配置选项影响到上述候选池的大小。默认候选池大小为0,也即不进行预收集候选项。
2.1.2.7 SDP语法 SdpSemantics
该配置不属于标准配置,但是非常重要,SdpSemantics sdp_semantics,该参数影响到了整个SDP数据的格式。有两种类型的语法:kPlanB 和 kUnifiedPlan
// For users who wish to send multiple audio/video streams and need to stay
// interoperable with legacy WebRTC implementations or use legacy APIs,
// specify kPlanB.
//
// For all other users, specify kUnifiedPlan.
enum class SdpSemantics { kPlanB, kUnifiedPlan };
- WebRTC 1.0 规范必须使用kUnifiedPlan;
- RtpTransceiver相关的API也只能使用kUnifiedPlan;
- kPlanB会引发PeerConnection在创建Off或者创建answer的时候,最多一个音频mLine和一个视频mLine。然后,每个mLine中的a=ssrc个数决定了将创建多少个RtpSenders或者RtpReceivers。并且kPlanB会引发PeerConnection忽略SDP中每种媒体类型中的除第一个mLine之外的其他mLine。
- kUnifiedPlan会引发PeerConnection在创建Off或者创建answer的时候,每一个媒体Track一个mLine。多个mLine映射到一个RtpSender和RtpReceiver(也即一个RtpTransceiver),要么每个都是音频,要么都是视频。 并且kUnifiedPlan会引发PeerConnection忽略每个mLine中除了第一个a=ssrc之外的其他a=ssrc。
- 只有在希望发送多个音频/视频流并且需要与旧版WebRTC实现保持互操作性或使用旧版API的用户时,才需要指定为kPlanB,其他情况,必须指定为kUnifiedPlan
2.2 CreatePeerConnection方法的实现
PeerConnectionFactory.CreatePeerConnection位于pc/peer_connection_factory.cc中。源码如下所示:
rtc::scoped_refptr<PeerConnectionInterface>
PeerConnectionFactory::CreatePeerConnection(
const PeerConnectionInterface::RTCConfiguration& configuration,
PeerConnectionDependencies dependencies) {
// 1 断言:改方法必须在信令线程上执行;
// 外部传入的PortAllocator与PacketSocketFactory只能有其一
RTC_DCHECK(signaling_thread_->IsCurrent());
RTC_DCHECK(!(dependencies.allocator && dependencies.packet_socket_factory))
<< "You can't set both allocator and packet_socket_factory; "
"the former is going away (see bugs.webrtc.org/7447";
// 2 可选依赖为空,此处来创建
// 2.1 创建证书生成器RTCCertificateGenerator
if (!dependencies.cert_generator) {
dependencies.cert_generator =
std::make_unique<rtc::RTCCertificateGenerator>(signaling_thread_,
network_thread_);
}
// 2.2 创建端口分配器PortAllocator,PortAllocator需要在网络线程中创建,
// PacketSocketFactory是构造PortAllocator的参数
if (!dependencies.allocator) {
rtc::PacketSocketFactory* packet_socket_factory;
if (dependencies.packet_socket_factory)
packet_socket_factory = dependencies.packet_socket_factory.get();
else
packet_socket_factory = default_socket_factory_.get();
network_thread_->Invoke<void>(RTC_FROM_HERE, [this, &configuration,
&dependencies,
&packet_socket_factory]() {
dependencies.allocator = std::make_unique<cricket::BasicPortAllocator>(
default_network_manager_.get(), packet_socket_factory,
configuration.turn_customizer);
});
}
// 2.3 创建ICE传输工厂
if (!dependencies.ice_transport_factory) {
dependencies.ice_transport_factory =
std::make_unique<DefaultIceTransportFactory>();
}
// 3. 做一些初始化工作
// 3.1 在网络线程上执行PortAllocator.SetNetworkIgnoreMask方法,使得端口分配器在进行操作时忽略特定类型的网络。
// 默认情况network_ignore_mask为ADAPTER_TYPE_LOOPBACK,也即默认情况下忽略回环地址
// 网络类型有如下几类:
// ADAPTER_TYPE_ETHERNET:以太网
// ADAPTER_TYPE_WIFI:无线WIFI网络
// ADAPTER_TYPE_CELLULAR:蜂窝网络(2g,3g,4g,5g)
// ADAPTER_TYPE_VPN:VPN
// ADAPTER_TYPE_LOOPBACK:回环地址
network_thread_->Invoke<void>(
RTC_FROM_HERE,
rtc::Bind(&cricket::PortAllocator::SetNetworkIgnoreMask,
dependencies.allocator.get(), options_.network_ignore_mask));
// 3.2 在工作线程上调用PeerConnectionFactory.CreateRtcEventLog_w来创建RtcEventLog对象。
// 该对象能提供什么功能暂且不提,但注意跟RTC中的一般日志是区别的,RTC_LOG宏与RtcEventLog
// 是两个不相干的系统。
std::unique_ptr<RtcEventLog> event_log =
worker_thread_->Invoke<std::unique_ptr<RtcEventLog>>(
RTC_FROM_HERE,
rtc::Bind(&PeerConnectionFactory::CreateRtcEventLog_w, this));
// 3.3 在工作线程上调用PeerConnectionFactory.CreateCall_w创建Call对象。
// Call对象提供了创建AudioReceiveStream/AudioSendStream
// /VideoSendStream/VideoReceiveStream的功能
std::unique_ptr<Call> call = worker_thread_->Invoke<std::unique_ptr<Call>>(
RTC_FROM_HERE,
rtc::Bind(&PeerConnectionFactory::CreateCall_w, this, event_log.get()));
// 4. 创建并初始化PeerConnection对象
// 4.1 构造PeerConnection对象:传入之前创建的RtcEventLog和Call对象
rtc::scoped_refptr<PeerConnection> pc(
new rtc::RefCountedObject<PeerConnection>(this, std::move(event_log),
std::move(call)));
// 4.2 测试用:在构造PeerConnection对象与初始化PeerConnection对象之间塞入测试代码
// 该方法为虚方法,{}中无具体代码,因此,什么也不干。测试时,可以继承并实现该方法
// 以达测试的目的。
ActionsBeforeInitializeForTesting(pc);
// 4.3 初始化PeerConnection对象:外部传入的全局配置参数和依赖参数用来初始化PeerConnection
if (!pc->Initialize(configuration, std::move(dependencies))) {
return nullptr;
}
// 5. 创建并返回PeerConnectionProxy对象。
return PeerConnectionProxy::Create(signaling_thread(), pc);
}
CreatePeerConnection创建PeerConnection过程大致分为5步,如源码以及注释所示,此处不再赘述。仍有如下几点需要注意。
- 在步骤3中 PortAllocator设置需要忽略网络类型,以及创建RtcEventLog、Call对象时,都需要在特定的线程上去执行。此时,是通过Thread.Invoke方法提供的这样的能力,该方法的原理分析见文章 WebRTC源码分析-线程基础之消息循环,消息投递
- 最后 CreatePeerConnection方法最终返回给应用层的是PeerConnectionProxy对象,而非PeerConnection对象。正如上一篇介绍PeerConnectionFactory文章作用一样,PeerConnectionProxy可以使得应用层调用的公有方法,都被代理到PeerConnection对象上执行对应的方法,并且是在恰当的线程中执行。这个是WebRTC中防止线程乱入的通用操作,详细分析见WebRTC源码分析-线程安全之Proxy,防止线程乱入
2.2.1 创建RtcEventLog对象
RtcEventLog对象的创建直接依赖于工厂对象RtcEventLogFactory。创建过程如下图所示
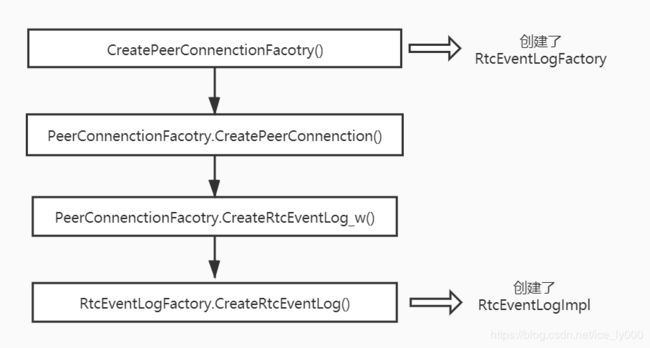
需要留意的有如下几点:
- RtcEventLogFactory在创建PeerConnectionFactory时被创建出来,并被PeerConnectionFactory持有。
- RtcEventLog对象在创建PeerConnection时被创建出来,并被PeerConnection持有。
- RtcEventLog类只是Interface,实体类是RtcEventLogImpl,因此,想要详细了解RtcEventLog工作原理,需要进一步对RtcEventLogImpl类进行剖析。
- PeerConnection持有RtcEventLog类,通过RtcEventLog实现并对外暴露运行事件日志系统、记录事件日志、停止事件日志系统的几个接口。
RtcEventLog作为WebRTC中的重要模块,将单独列一篇文章来分析 WebRTC源码分析——RtcEventLog事件日志 。
2.2.2 创建Call对象
Call对象的创建直接依赖于工厂对象CallFactory。创建过程如下图所示:

需要留意的有如下几点:
- CallFactory在创建PeerConnectionFactory时被创建出来,并被PeerConnectionFactory持有。
- Call对象在创建PeerConnection时被创建出来,并被PeerConnection持有。
- PeerConnection持有Call,并利用Call对应用层提供了发送码率设置(包含最大码率、最小码率、初始码率,初始码率作为编码器的初始参数以及带宽估计的先验值);提供获取传输统计数据途径(包含估算的可用发送带宽、估算的可用接收带宽、平滑发送引入的延迟、RTT估计值、累计的最大填充bit);提供获取所有发送的数据包回调;另外其还持有PacketReceiver对象,因此,所有接收到RTP/RTCP数据包,也将经过Call。
- Call对象可以包含多个发送/接收流,且这些流对应同一个远端端点,并共享码率估计等。其对内部还提供了其他重要的功能,最重要的莫过于创建AudioReceiveStream、AudioSendStream、VideoSendStream、VideoReceiveStream的功能。
Call模块是WebRTC会话中的特别重要的模块,将单列一篇文章来分析 WebRTC源码分析——Call模块
3 PeerConnection简介
PeerConnection对象是WebRTC对应用层暴露的重要的API对象,其持有了大量的低层次内部对象,并提供了相当多的功能。一篇文章是不可能尽述的,因此,本文只做粗浅的分析,并着重分析CreatePeerConnection方法中调用的PeerConnection构造函数以及PeerConnection初始化函数Initialize。
PeerConnection实体类的位于 pc/peer_connection.h 和 pc/peer_connection.cc中,其声明如下:
// PeerConnection is the implementation of the PeerConnection object as defined
// by the PeerConnectionInterface API surface.
// The class currently is solely responsible for the following:
// - Managing the session state machine (signaling state).
// - Creating and initializing lower-level objects, like PortAllocator and
// BaseChannels.
// - Owning and managing the life cycle of the RtpSender/RtpReceiver and track
// objects.
// - Tracking the current and pending local/remote session descriptions.
// The class currently is jointly responsible for the following:
// - Parsing and interpreting SDP.
// - Generating offers and answers based on the current state.
// - The ICE state machine.
// - Generating stats.
class PeerConnection : public PeerConnectionInternal,
public JsepTransportController::Observer,
public RtpSenderBase::SetStreamsObserver,
public rtc::MessageHandler,
public sigslot::has_slots<> {
...
}
PeerConnection继承了PeerConnectionInternal、JsepTransportController::Observer、RtpSenderBase::SetStreamsObserver、rtc::MessageHandler、sigslot::has_slots<>,从继承中获取了不少的功能,同时其本身自带了很多功能。尤其注意sigslot::has_slots<>所带来的信号-槽机制,可以让PeerConnection对象接收低层次对象所发射的信号,以获知某个事态的发生、状态的改变,并在自己的方法中对信号进行响应处理。比如后续将要提到的JsepTransportController对象会发射一些列的连接状态,ICE状态相关的信号SignalXxx,PeerConnection将以OnXxx的方法予以绑定信号,响应并处理。
这些功能大致可以从两方面简要说明(正如PeerConnection英文注释告知的那样):
一方面PeerConnection单独提供如下功能:
- 管理WebRTC的会话状态(信令状态);
- 创建和初始化WebRTC内部的低层次对象,比如PortAllocator、BaseChannels;
- 持有RtpSender/RtpReceiver、track对象,并管理它们的生命周期;
- 跟踪当前的local/remote sdp。
一方面PeerConnection与其他对象一起提供如下功能:
- 解析sdp;
- 根据当前状态生成offer sdp和answer sdp;
- 管理ICE状态机;
- 产生统计数据。
3.1 PeerConnection构造
源码如下:
PeerConnection::PeerConnection(PeerConnectionFactory* factory,
std::unique_ptr<RtcEventLog> event_log,
std::unique_ptr<Call> call)
: factory_(factory),
event_log_(std::move(event_log)),
event_log_ptr_(event_log_.get()),
operations_chain_(rtc::OperationsChain::Create()),
datagram_transport_config_(
field_trial::FindFullName(kDatagramTransportFieldTrial)),
datagram_transport_data_channel_config_(
field_trial::FindFullName(kDatagramTransportDataChannelFieldTrial)),
rtcp_cname_(GenerateRtcpCname()),
local_streams_(StreamCollection::Create()),
remote_streams_(StreamCollection::Create()),
call_(std::move(call)),
call_ptr_(call_.get()),
local_ice_credentials_to_replace_(new LocalIceCredentialsToReplace()),
data_channel_controller_(this),
weak_ptr_factory_(this) {}
PeerConnection的构造无非就是给成员赋值,虽然简单,但也给我们提供了一些值得注意的信息,其中想要重点说明的是rtcp_cname_这个成员,接下来的一小节对RTCP CNAME进行比较详细的介绍。
3.1.1 CNAME
一个PeerConnection仅有一个RTCP CNAME成员rtcp_cname_,该成员是一个长达16字符的随机字符串,随着PeerConnection的创建,由GenerateRtcpCname()方法创建这个字符串。ietf的RTC规范中详细的描述了RTCP CNAME的作用:https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-rtcweb-rtp-usage-26#section-4.9
以下是对规范中关于RTCP CNAME介绍的一个翻译,有可能解释的不够清楚,请查看上述英文原文:
RTCP规范名称(CNAME) 为一个RTP端点提供了持久的传输层次的唯一标识。RTP端点的SSRC标识可能会因为检测到和其他RTP端点的SSRC冲突 或者 当RTP应用重启时发生更改,但是CNAME是不会更改的,只要RTCPeerConnection对象没有更改。因此,RTP端点可以很容易的在相关RTP会话集合中识别出与其相关流的RTP包
一个RTP端点必须至少有一个CNAME,并且在RTCPeerConnection中是唯一的。CNAME可以标识一个特别的同步上下文,所有与这个CNAME关联的SSRCs共享同一个参考时钟。如果一个端点有多个SSRCs,它们关联多个不同步的参考时钟,因此,是不同的同步上下文。那么就需要不同的CNAMEs,每个同步上下文一个CNAME。
一个WebRTC端点在单个RTCPeerConnection中有且仅有一个CNAME用于属于RTCPeerConnection的多个RTP会话(因为一个RTCPeerConnection就是一个同步上下文)。 RTP middleboxes可能会产生关联不同CANME的多个流,这样就可以避免来自不同端点的多方RTP会话对这些流进行媒体时钟重新同步。
3.2 PeerConnection初始化
源码及分析如下:
bool PeerConnection::Initialize(
const PeerConnectionInterface::RTCConfiguration& configuration,
PeerConnectionDependencies dependencies) {
// 1. 确保初始化是在信令线程中
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(signaling_thread());
TRACE_EVENT0("webrtc", "PeerConnection::Initialize");
// 2. 检查全局参数配置的有效性
RTCError config_error = ValidateConfiguration(configuration);
if (!config_error.ok()) {
RTC_LOG(LS_ERROR) << "Invalid configuration: " << config_error.message();
return false;
}
// 3. 依赖参数——PortAllocator和PeerConnectionObserver不可为空
if (!dependencies.allocator) {
RTC_LOG(LS_ERROR)
<< "PeerConnection initialized without a PortAllocator? "
"This shouldn't happen if using PeerConnectionFactory.";
return false;
}
if (!dependencies.observer) {
// TODO(deadbeef): Why do we do this?
RTC_LOG(LS_ERROR) << "PeerConnection initialized without a "
"PeerConnectionObserver";
return false;
}
// 4. 成员赋值
observer_ = dependencies.observer;
async_resolver_factory_ = std::move(dependencies.async_resolver_factory);
port_allocator_ = std::move(dependencies.allocator);
ice_transport_factory_ = std::move(dependencies.ice_transport_factory);
tls_cert_verifier_ = std::move(dependencies.tls_cert_verifier);
// 5. 处理STUN server和TURN server
// 5.1 解析并获取stun_servers和turn_servers
cricket::ServerAddresses stun_servers;
std::vector<cricket::RelayServerConfig> turn_servers;
RTCErrorType parse_error =
ParseIceServers(configuration.servers, &stun_servers, &turn_servers);
if (parse_error != RTCErrorType::NONE) {
return false;
}
// 5.2 给所有的turn_server配置日志id
// Add the turn logging id to all turn servers
for (cricket::RelayServerConfig& turn_server : turn_servers) {
turn_server.turn_logging_id = configuration.turn_logging_id;
}
// 5.3 给stun_servers和turn_servers进行端口分配器的初始化
// The port allocator lives on the network thread and should be initialized
// there.
const auto pa_result =
network_thread()->Invoke<InitializePortAllocatorResult>(
RTC_FROM_HERE,
rtc::Bind(&PeerConnection::InitializePortAllocator_n, this,
stun_servers, turn_servers, configuration));
// 5.4 通知STUN_SERVER和TURN_SERVER被使用
// If initialization was successful, note if STUN or TURN servers
// were supplied.
if (!stun_servers.empty()) {
NoteUsageEvent(UsageEvent::STUN_SERVER_ADDED);
}
if (!turn_servers.empty()) {
NoteUsageEvent(UsageEvent::TURN_SERVER_ADDED);
}
// 6. 发送IPV4/IPv6状态
// Send information about IPv4/IPv6 status.
PeerConnectionAddressFamilyCounter address_family;
if (pa_result.enable_ipv6) {
address_family = kPeerConnection_IPv6;
} else {
address_family = kPeerConnection_IPv4;
}
RTC_HISTOGRAM_ENUMERATION("WebRTC.PeerConnection.IPMetrics", address_family,
kPeerConnectionAddressFamilyCounter_Max);
const PeerConnectionFactoryInterface::Options& options = factory_->options();
// 7. 创建64位有符号整型会话id
// RFC 3264: The numeric value of the session id and version in the
// o line MUST be representable with a "64 bit signed integer".
// Due to this constraint session id |session_id_| is max limited to
// LLONG_MAX.
session_id_ = rtc::ToString(rtc::CreateRandomId64() & LLONG_MAX);
// 8. 1) 填充JSEP传输控制的参数
// 2) 并创建JsepTransportController,
// 3) 关联JsepTransportController的信号与PeerConnection的槽方法
// 8.1.1 创建JSEP的参数结构体JsepTransportController::Config
JsepTransportController::Config config;
// 8.1.2 用应用层传入的全局配置参数来填充JSEP传输控制的参数
config.redetermine_role_on_ice_restart =
configuration.redetermine_role_on_ice_restart;
config.ssl_max_version = factory_->options().ssl_max_version;
config.disable_encryption = options.disable_encryption;
config.bundle_policy = configuration.bundle_policy;
config.rtcp_mux_policy = configuration.rtcp_mux_policy;
// TODO(bugs.webrtc.org/9891) - Remove options.crypto_options then remove this
// stub.
config.crypto_options = configuration.crypto_options.has_value()
? *configuration.crypto_options
: options.crypto_options;
config.transport_observer = this;
// It's safe to pass |this| and using |rtcp_invoker_| and the |call_| pointer
// since the JsepTransportController instance is owned by this PeerConnection
// instance and is destroyed before both |rtcp_invoker_| and the |call_|
// pointer.
config.rtcp_handler = [this](const rtc::CopyOnWriteBuffer& packet,
int64_t packet_time_us) {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(network_thread());
rtcp_invoker_.AsyncInvoke<void>(
RTC_FROM_HERE, worker_thread(), [this, packet, packet_time_us] {
RTC_DCHECK_RUN_ON(worker_thread());
// |call_| is reset on the worker thread in the PeerConnection
// destructor, so we check that it's still valid before propagating
// the packet.
if (call_) {
call_->Receiver()->DeliverPacket(MediaType::ANY, packet,
packet_time_us);
}
});
};
config.event_log = event_log_ptr_;
#if defined(ENABLE_EXTERNAL_AUTH)
config.enable_external_auth = true;
#endif
config.active_reset_srtp_params = configuration.active_reset_srtp_params;
// 8.1.3 外部应该提供MediaTransportFactory时,WebRTC内部应该使用使用DatagramTransport接口取代dtls。
// 此处填充相关的4个参数。
use_datagram_transport_ = datagram_transport_config_.enabled &&
configuration.use_datagram_transport.value_or(
datagram_transport_config_.default_value);
use_datagram_transport_for_data_channels_ =
datagram_transport_data_channel_config_.enabled &&
configuration.use_datagram_transport_for_data_channels.value_or(
datagram_transport_data_channel_config_.default_value);
use_datagram_transport_for_data_channels_receive_only_ =
configuration.use_datagram_transport_for_data_channels_receive_only
.value_or(datagram_transport_data_channel_config_.receive_only);
if (use_datagram_transport_ || use_datagram_transport_for_data_channels_) {
if (!factory_->media_transport_factory()) {
RTC_DCHECK(false)
<< "PeerConnecton is initialized with use_datagram_transport = true "
"or use_datagram_transport_for_data_channels = true "
<< "but media transport factory is not set in PeerConnectionFactory";
return false;
}
config.use_datagram_transport = use_datagram_transport_;
config.use_datagram_transport_for_data_channels =
use_datagram_transport_for_data_channels_;
config.use_datagram_transport_for_data_channels_receive_only =
use_datagram_transport_for_data_channels_receive_only_;
config.media_transport_factory = factory_->media_transport_factory();
}
// 8.1.4 判断DataChannel传输方式,使用SCTP则填充sctp_factory
// 首先,根据根据证书是否存在,证书生成器是否存在,是否允许加密来判断是不是dtls使能
// 然后,确定datachannel传输数据的协议:
// DCT_DATA_CHANNEL_TRANSPORT:使用UDP传输,无dtls
// DCT_DATA_CHANNEL_TRANSPORT_SCTP:使用UDP传输,失败可以回退到使用SCTP
// DCT_RTP:使用RTP传输
// DCT_SCTP:使用SCTP传输
// 最后,在DCT_DATA_CHANNEL_TRANSPORT_SCTP和DCT_SCTP情况下需要填充sctp_factory
// Obtain a certificate from RTCConfiguration if any were provided (optional).
rtc::scoped_refptr<rtc::RTCCertificate> certificate;
if (!configuration.certificates.empty()) {
// TODO(hbos,torbjorng): Decide on certificate-selection strategy instead of
// just picking the first one. The decision should be made based on the DTLS
// handshake. The DTLS negotiations need to know about all certificates.
certificate = configuration.certificates[0];
}
if (options.disable_encryption) {
dtls_enabled_ = false;
} else {
// Enable DTLS by default if we have an identity store or a certificate.
dtls_enabled_ = (dependencies.cert_generator || certificate);
// |configuration| can override the default |dtls_enabled_| value.
if (configuration.enable_dtls_srtp) {
dtls_enabled_ = *(configuration.enable_dtls_srtp);
}
}
sctp_factory_ = factory_->CreateSctpTransportInternalFactory();
if (use_datagram_transport_for_data_channels_) {
if (configuration.enable_rtp_data_channel) {
RTC_LOG(LS_ERROR) << "enable_rtp_data_channel and "
"use_datagram_transport_for_data_channels are "
"incompatible and cannot both be set to true";
return false;
}
if (configuration.enable_dtls_srtp && !*configuration.enable_dtls_srtp) {
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Using data channel transport with no fallback";
data_channel_controller_.set_data_channel_type(
cricket::DCT_DATA_CHANNEL_TRANSPORT);
} else {
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Using data channel transport with fallback to SCTP";
data_channel_controller_.set_data_channel_type(
cricket::DCT_DATA_CHANNEL_TRANSPORT_SCTP);
config.sctp_factory = sctp_factory_.get();
}
} else if (configuration.enable_rtp_data_channel) {
// Enable creation of RTP data channels if the kEnableRtpDataChannels is
// set. It takes precendence over the disable_sctp_data_channels
// PeerConnectionFactoryInterface::Options.
data_channel_controller_.set_data_channel_type(cricket::DCT_RTP);
} else {
// DTLS has to be enabled to use SCTP.
if (!options.disable_sctp_data_channels && dtls_enabled_) {
data_channel_controller_.set_data_channel_type(cricket::DCT_SCTP);
config.sctp_factory = sctp_factory_.get();
}
}
// 8.1.5 填充ICE传输工厂
config.ice_transport_factory = ice_transport_factory_.get();
// 8.2 创建JsepTransportController
transport_controller_.reset(new JsepTransportController(
signaling_thread(), network_thread(), port_allocator_.get(),
async_resolver_factory_.get(), config));
// 8.3 绑定JsepTransportController的信号与PeerConnection相应的槽函数
// 让PeerConnection能够响应JsepTransportController状态的改变
transport_controller_->SignalIceConnectionState.connect(
this, &PeerConnection::OnTransportControllerConnectionState);
transport_controller_->SignalStandardizedIceConnectionState.connect(
this, &PeerConnection::SetStandardizedIceConnectionState);
transport_controller_->SignalConnectionState.connect(
this, &PeerConnection::SetConnectionState);
transport_controller_->SignalIceGatheringState.connect(
this, &PeerConnection::OnTransportControllerGatheringState);
transport_controller_->SignalIceCandidatesGathered.connect(
this, &PeerConnection::OnTransportControllerCandidatesGathered);
transport_controller_->SignalIceCandidateError.connect(
this, &PeerConnection::OnTransportControllerCandidateError);
transport_controller_->SignalIceCandidatesRemoved.connect(
this, &PeerConnection::OnTransportControllerCandidatesRemoved);
transport_controller_->SignalDtlsHandshakeError.connect(
this, &PeerConnection::OnTransportControllerDtlsHandshakeError);
transport_controller_->SignalIceCandidatePairChanged.connect(
this, &PeerConnection::OnTransportControllerCandidateChanged);
// 9. 初始化两个数据统计收集器
stats_.reset(new StatsCollector(this));
stats_collector_ = RTCStatsCollector::Create(this);
// 10. 保存全局的配置参数
configuration_ = configuration;
// 11. 从全局配置参数中抽取ICE相关的参数,并设置到JsepTransportController中
transport_controller_->SetIceConfig(ParseIceConfig(configuration));
// 12. 设置音视频相关的网络传输相关参数
video_options_.screencast_min_bitrate_kbps =
configuration.screencast_min_bitrate;
audio_options_.combined_audio_video_bwe =
configuration.combined_audio_video_bwe;
audio_options_.audio_jitter_buffer_max_packets =
configuration.audio_jitter_buffer_max_packets;
audio_options_.audio_jitter_buffer_fast_accelerate =
configuration.audio_jitter_buffer_fast_accelerate;
audio_options_.audio_jitter_buffer_min_delay_ms =
configuration.audio_jitter_buffer_min_delay_ms;
audio_options_.audio_jitter_buffer_enable_rtx_handling =
configuration.audio_jitter_buffer_enable_rtx_handling;
// 13. 1)创建WebRtcSessionDescriptionFactory对象
// 2)绑定WebRtcSessionDescriptionFactory信号与PeerConnection的槽
// 3)WebRtcSessionDescriptionFactory参数赋值
// 13.1 创建WebRtcSessionDescriptionFactory对象
// Whether the certificate generator/certificate is null or not determines
// what PeerConnectionDescriptionFactory will do, so make sure that we give it
// the right instructions by clearing the variables if needed.
if (!dtls_enabled_) {
dependencies.cert_generator.reset();
certificate = nullptr;
} else if (certificate) {
// Favor generated certificate over the certificate generator.
dependencies.cert_generator.reset();
}
webrtc_session_desc_factory_.reset(new WebRtcSessionDescriptionFactory(
signaling_thread(), channel_manager(), this, session_id(),
std::move(dependencies.cert_generator), certificate, &ssrc_generator_));
// 13.2 绑定WebRtcSessionDescriptionFactory信号与PeerConnection的槽
webrtc_session_desc_factory_->SignalCertificateReady.connect(
this, &PeerConnection::OnCertificateReady);
// 13.3 WebRtcSessionDescriptionFactory参数赋值
if (options.disable_encryption) {
webrtc_session_desc_factory_->SetSdesPolicy(cricket::SEC_DISABLED);
}
webrtc_session_desc_factory_->set_enable_encrypted_rtp_header_extensions(
GetCryptoOptions().srtp.enable_encrypted_rtp_header_extensions);
webrtc_session_desc_factory_->set_is_unified_plan(IsUnifiedPlan());
// 14 Plan B SDP下,添加默认的音视频transceivers
// Add default audio/video transceivers for Plan B SDP.
if (!IsUnifiedPlan()) {
transceivers_.push_back(
RtpTransceiverProxyWithInternal<RtpTransceiver>::Create(
signaling_thread(), new RtpTransceiver(cricket::MEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO)));
transceivers_.push_back(
RtpTransceiverProxyWithInternal<RtpTransceiver>::Create(
signaling_thread(), new RtpTransceiver(cricket::MEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO)));
}
int delay_ms =
return_histogram_very_quickly_ ? 0 : REPORT_USAGE_PATTERN_DELAY_MS;
signaling_thread()->PostDelayed(RTC_FROM_HERE, delay_ms, this,
MSG_REPORT_USAGE_PATTERN, nullptr);
// 15 创建视频比特分配器工厂
if (dependencies.video_bitrate_allocator_factory) {
video_bitrate_allocator_factory_ =
std::move(dependencies.video_bitrate_allocator_factory);
} else {
video_bitrate_allocator_factory_ =
CreateBuiltinVideoBitrateAllocatorFactory();
}
return true;
}
关于PeerConnection初始化过程如源码注释,分了15个部分进行分割阐述。其中比较重要或者复杂的是
- 处理STUN server和TURN server;
- 64位有符号整型会话id的创建;
- JsepTransportController会话传输控制器的创建、信号-槽绑定。这个过程中比较重要的是:外部是否提供MediaTransportFactory,这个会影响到媒体传输方式;DataChannel传输方式的确定,可以是直接的UDP传输,带fallback的UDP传输(fallback到stcp),RTP传输,SCTP传输;JsepTransportController——PeerConnection的信号-槽绑定。
- SDP工厂类WebRtcSessionDescriptionFactory的创建,信号-槽绑定,参数设置等。
3.2.1 会话ID——Session ID
如上对PeerConnection.Initialize方法的分析过程得知:此处会创建 “64位有符号整型"的Session ID。使用的是rtc_base/helpers.cc中随机数生成函数CreateRandomId64()来产生。WebRTC中的随机值生成系统的分析可见另外的文章——WebRTC源码分析——随机值(数、字符串)生成模块。
会话id将会出现在SDP的o line中,如下一个简单的Offser SDP:
v=0
o=alice 2890844526 2890844526 IN IP4 host.anywhere.com
s=
c=IN IP4 host.anywhere.com
t=0 0
m=audio 49170 RTP/AVP 0
a=rtpmap:0 PCMU/8000
m=video 51372 RTP/AVP 31
a=rtpmap:31 H261/90000
m=video 53000 RTP/AVP 32
a=rtpmap:32 MPV/90000
o line格式如下
o=
各字段含义如下:
- username:发起者的用户名,不允许存在空格,如果应用不支持用户名,则为-。
- sess-id:会话id,由应用自行定义,规范的建议是NTP(Network Time Protocol)时间戳。
- sess-version:会话版本,用途由应用自行定义,只要会话数据发生变化时(比如编码),sess-version随着递增就行。同样的,规范的建议是NTP时间戳。
- nettype:网络类型,比如IN表示Internet。
- addrtype:地址类型,比如IP4、IV6
- unicast-address:域名,或者IP地址。
示例中的2890844526就是取得Session ID值。
4 总结
至此,PeerConnection对象的创建过程已经阐述完毕,也对PeerConnection对象提供的能力也做了基本的介绍。简单回顾下整个源码分析过程,有这么几点提炼出来以作最后的总结:
- PeerConnection的创建需要两方面的数据:依赖项参数 和 全局配置项参数
- 依赖项参数PeerConnectionDependencies是应用层提供的源码级别的内容,要么作为某个功能模块提供给WebRTC内部调用来影响WebRTC的行为,比如PortAllocator;要么是作为PeerConnection的事件回调,监听PeerConnection的状态,在应用层来做出某些响应,比如PeerConnectionObserver。
- 全局配置项参数RTCConfiguration是应用层提供给WebRTC全局参数,WebRTC内部通过检查这些参数值做出不同的行为。其中比较重要的参数为SdpSemantics 、IceServers 、IceTransportsType 、BundlePolicy 、RtcpMuxPolicy 、ice_candidate_pool_size等。
- 与PeerConnectionFactory的创建一样,对于应用层,返回的并非是PeerConnection实体对象,而是PeerConnectionProxy。通过代理方式使得应用层可以安全、方便的使用PeerConnection所带来的功能
- 注意CNAME的概念与作用。