React Native通讯原理
之前写过一篇文章 ReactNative Android源码分析,在此文章的基础上分析和总结下RN与Native的通讯流程。
本文基于Android代码分析,iOS实现原理类似。
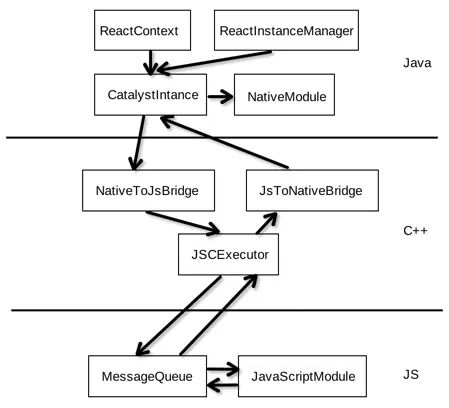
1. 通讯框架图
先来解析下各个模块的角色与作用:
Java层,这块的实现在ReactAndroid中
- ReactContext : Android上下文子类,包含一个CatalystInstance实例,用于获取NativeModule,JSModule、添加各种回调、处理异常等
- ReactInstanceManager : 管理CatalystInstance的实例,处理RN Root View,启动JS页面,管理生命周期
- CatalystInstance : 通讯的关键类,提供调用JS Module也支持JS调用Native Module,与Bridge进行交互,对开发者不可见
C++层,这块实现在ReactCommon中,供Android与iOS使用
- NativeToJsBridge : native与JS的桥接,负责调用JS Module、回调Native(调用JsToNativeBridge)、加载JS代码(调用JavaScriptCore)
- JsToNativeBridge : 调用Native Module的方法
- JSCExecutor : 加载/执行JS代码(调用JavaScriptCore)、调用JS Module、回调native、性能统计等,都是比较核心的功能
JS层,实现在Libraries中,RN JS相关的实现在都这个文件夹中
- MessageQueue : 管理JS的调用队列、调用Native/JS Module的方法、执行callback、管理JS Module等
- JavaScriptModule : 代指所有的JSModule实现,在java层中也有对应的代码(都是interface),使用动态代理调用,统一入口在CatalystInstance中
2. C++与JS间通讯
Native与JS通讯无非就是Java/OC与JS跨语言间的调用,在分析Native与JS通讯前先来了解下Java/OC与JS跨语言间的调用。
在ReactNative中使用JavaScriptCore来执行JS,这部分的关键就是如何利用JavaScriptCore。
看一下Android编译脚本:
- ReactAndroid/build.gradle
compile 'org.webkit:android-jsc:r174650'
task downloadJSCHeaders(type: Download) {
def jscAPIBaseURL = 'https://svn.webkit.org/repository/webkit/ !svn/bc/174650/trunk/Source/JavaScriptCore/API/'
def jscHeaderFiles = ['JavaScript.h', 'JSBase.h', 'JSContextRef.h', 'JSObjectRef.h', 'JSRetainPtr.h', 'JSStringRef.h', 'JSValueRef.h', 'WebKitAvailability.h']
def output = new File(downloadsDir, 'jsc')
output.mkdirs()
src(jscHeaderFiles.collect { headerName -> "$jscAPIBaseURL$headerName" })
onlyIfNewer true
overwrite false
dest output
}
// Create Android.mk library module based on so files from mvn + include headers fetched from webkit .org
task prepareJSC(dependsOn: downloadJSCHeaders) << {
copy {
from zipTree(configurations.compile.fileCollection { dep -> dep.name == 'android-jsc' }. singleFile)
from {downloadJSCHeaders.dest}
from 'src/main/jni/third-party/jsc/Android.mk'
include 'jni/**/*.so', '*.h', 'Android.mk'
filesMatching('*.h', { fname -> fname.path = "JavaScriptCore/${fname.path}"})
into "$thirdPartyNdkDir/jsc";
}
}
- ReactAndroid/src/main/jni/third-party/jsc/Android.mk
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := jni/$(TARGET_ARCH_ABI)/libjsc.so从这里可以看出RN并没有用系统自带的webkit,WebKit主要包括WebCore排版引擎和JSCore引擎,这里主要使用了JSCore引擎,排版交给Native去做。
在RN中通过下面的方法设置native方法和属性:
JSObjectSetProperty(m_context, globalObject, jsPropertyName, valueToInject, 0, NULL);这个方法正是上面gradle脚本下载的JSObjectRef.h中,实现在libjsc.so中。这样就可以在Native设置,然后在JS中取出执行,反过来也是同样的。
3. Native与JS通讯
#####加载bundle文件
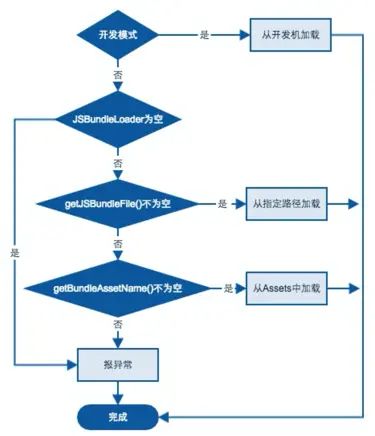
Native与JS的通讯首先需要加载Bundle文件,是在native初始化完成的时候,而Bundle文件的位置是可配置的。
public abstract class ReactNativeHost {
...
/**
* Returns the name of the main module. Determines the URL used to fetch the JS bundle
* from the packager server. It is only used when dev support is enabled.
* This is the first file to be executed once the {@link ReactInstanceManager} is created.
* e.g. "index.android"
*/
protected String getJSMainModuleName() {
return "index.android";
}
/**
* Returns a custom path of the bundle file. This is used in cases the bundle should be loaded
* from a custom path. By default it is loaded from Android assets, from a path specified
* by {@link getBundleAssetName}.
* e.g. "file://sdcard/myapp_cache/index.android.bundle"
*/
protected @Nullable String getJSBundleFile() {
return null;
}
/**
* Returns the name of the bundle in assets. If this is null, and no file path is specified for
* the bundle, the app will only work with {@code getUseDeveloperSupport} enabled and will
* always try to load the JS bundle from the packager server.
* e.g. "index.android.bundle"
*/
protected @Nullable String getBundleAssetName() {
return "index.android.bundle";
}
/**
* Returns whether dev mode should be enabled. This enables e.g. the dev menu.
*/
protected abstract boolean getUseDeveloperSupport();
...
}ReactNativeHost中的这些方法会根据需要在Application中重载,这些方法决定了从哪里加载Bundle,方法的注释写的非常清晰,不再介绍了,先看一下流程图:
JSBundleLoader从哪里加载,也是根据文件的位置,可以看看其loadScript方法,最终都会调用CatalystIntance去加载,有三个实现
/* package */ native void loadScriptFromAssets(AssetManager assetManager, String assetURL);
/* package */ native void loadScriptFromFile(String fileName, String sourceURL);
/* package */ native void loadScriptFromOptimizedBundle(String path, String sourceURL, int flags);最后一个支持加载优化后的Bundle,目前没有用到。这些方法都是c++实现,主要看一下前两个
void CatalystInstanceImpl::loadScriptFromAssets(jobject assetManager,
const std::string& assetURL) {
const int kAssetsLength = 9; // strlen("assets://");
auto sourceURL = assetURL.substr(kAssetsLength);
auto manager = react::extractAssetManager(assetManager);
auto script = react::loadScriptFromAssets(manager, sourceURL);
if (JniJSModulesUnbundle::isUnbundle(manager, sourceURL)) {
instance_->loadUnbundle(
folly::make_unique从assets中加载就是先读取bundle的内容,当作一个字符串,这里有一个UnBundle,是RN打包的一种方式,除了生成整合JS文件index.android.bundle外,还会生成各个单独的未整合JS文件(但会被优化),全部放在js-modules目录下,同时会生成一个名为UNBUNDLE的标识文件,一并放在其中。UNBUNDLE标识文件的前4个字节固定为0xFB0BD1E5,用于加载前的校验。需要注意的是,js-modules目录会一并打包到apk的assets文件夹中,这里就是处理这种情况的,后面具体的加载暂不分析,可以参考这篇文章。
对于开发模式有点特殊,在创建ReactInstanceManager之前会从server下载Bundle文件,然后保存起来,demo程序的路径为:
/data/user/0/com.awesomeproject/files/ReactNativeDevBundle.js
下载完成后调用CatalystInstance.loadScriptFromFile(),传递缓存后的径路,这个方法也是先读取文件内容,存为字符串&#