自己实现一个 ping 命令
目录
- 基础
- 协议基础
- 套接字基础
- 传输层 Stream 和 Datagram Socket
- 网络层 Raw Socket
- 数据链接层 Packet Socket
- 模拟实现 Ping
- ICMP 协议
- 实现
- 参考
为了加深自己对计算机网络的理解, 想自己实现一些操作系统提供的网络工具, 于是先从 ping 开始
首先, ping 命令的作用是检测两个网络设备在 TCP/IP 网络下是否能连通. 其底层基于 ICMP 协议, 而 ICMP 协议位于 TCP/IP 协议栈的网络层. 模拟 ping 命令则需要模拟发送 ICMP 报文的过程.
基础
万丈高楼平地起
协议基础
先简单回顾下 TCP/IP 协议栈. 如下图, TCP/IP 栈分为4层, 每一层包括一些协议, 这些协议又主要分为两个类别, 基于流的协议和基于数据包的协议:

- 基于流的协议, 主要就是基于 TCP, 基于流的协议提供双向、有序、可靠、非重复数据通信
- 基于数据包的协议则主要有 UDP, IP, ICMP 等, 基于数据包的协议也提供双向数据流通信, 但是不保证数据的可靠性
- 流和数据包的区别也主要在传输层, 等到了下面的网络层和网络接口层, 它们都会封装为数据报和帧
再用 HTTP 请求回顾下数据从应用层走到网卡的过程:

每经过一层, 其对应的 Header 就会被添加到上层传下来的数据包的头部, 为什么是添加到头部呢?因为每个协议的头部数据大小是有规则的, 而应用层的数据大小是不确定的, 而且像 TCP 还会对超过 MWS(max window size) 的数据进行分片传递, 每层协议头都追加到头部就能够方便接收方由下而上的对原始数据包进行头部剥离, 而不用关心其后面的实际数据到底有多少.
既然这里是通过发送 ICMP 报文模拟 ping 命令, 那么 ICMP 报文又是如何封装的呢?

如上图所示, 由于 ICMP 协议位于网络层, 所以实现它并不需要它上面的传输层和应用层的协议(这也是一种分层设计思想, 分层设计里应该只有一个方向的依赖. 比如 TCP/IP 栈中只会上层协议依赖下层协议, 不会出现下层协议依赖上层协议). 因此整个数据包中其实只有3个 Header: 以太网 Header, Ip Header 和 ICMP Header.
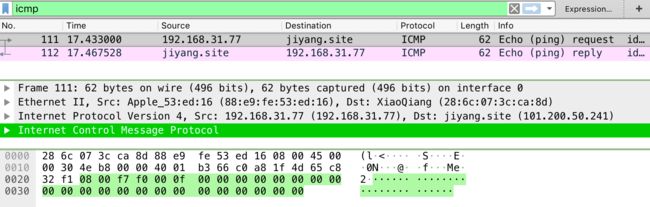
通过 Wireshark 也可以看下 ICMP 数据包的封装过程:
| ICMP | IP | Ethernet | Frame |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
最下面的十六进制是原始数据流的二进制的缩写, 绿色高亮的部分对应于某一层的数据部分.
套接字基础
上面回顾了网络协议, 那说了这么多, 我们到底怎样才能真正在操作系统上面用到或者实现上面所说的那些协议呢?
答案就是套接字: Sokcet, Socket 最初由 Unix 系统发明, 由于其功能强大, 后来几乎所有操作系统都实现了它.

创建一个 Socket 的方法为:
int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol);
调用此系统方法, 你就能够创建一个 Socket, 该方法将返回一个指向 socket 的文件描述符. 这个方法创建的套接字, 可以访问 TCP/IP 栈中不同层上的协议, 可谓很强大了. 根据能影响到 TCP/IP 栈中的哪一层, 套接字分为不同的种类.
传输层 Stream 和 Datagram Socket
为了获得对传输层的访问, type 参数必须是 SOCK_STREAM(使用TCP) 或者 SOCK_DGRAM(使用UDP), 这样创建的套接字被称为 stream 或者 datagram socket.
domain 参数则可以为:
PF_UNIX,PF_LOCAL: 面向本地的 SocketPF_INET: 基于 IPv4PF_INET6: 基于 IPv6- …
传递的 protocol 参数为协议编号, 这里创建 Stream 和 Datagram Socket 应该传递 0
sd = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
sd = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
大多数的应用层协议都创建的这种 socket, 但这类 socket 有很大的限制, 只能访问和修改应用层传递的数据, 传输层及以下层协议的 header 在使用这类 socket 将访问不到. 因为在发送数据时下层协议的 header 将会由系统追加;在接收数据时, 下层协议的 header 信息会先被操作系统剥离, 到了应用时就只剩数据部分了.

man 2 socket 可以看 socket 的一些详细解释.
网络层 Raw Socket
为了突破 Stream Socket 和 Datagram Socket 的限制, 触达网络层, 于是出现了名为 Raw Socket 的狠角色.
要创建这种狠角色, 首先只有 super 用户有权限. type 参数要为 SOCK_RAW, domain 参数规则和上面 Stream Socket 一样, protocol 可以为 0 或者任何你想要由自己组装数据包的协议, 比如:
/* 由自己填充 TCP 头 */
s = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_TCP);
/* 由自己填充 UDP 头 */
s = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_UDP);
/* 由自己填充 ICMP 头 */
s = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_ICMP);
/* 由自己填充任何协议头 */
s = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_RAW);
经过上面方法创建的 socket, 我们就能自己填充对应协议的 header 了, 但是 IP 数据包的 header 还是会被操作系统的 TCP/IP 栈实现去填充.

如果我们想自己填充 IP 数据包, 还需要设置 socket 的 option 参数打开 IP_HDRINCL:
int on = 1;
if ((setsockopt(s, IPPROTO_IP, IP_HDRINCL, &on, sizeof(on))) == -1)
{
LOG_D(TAG, "[setsockopt] IP_HDRINCL errno: %d", errno);
}
数据链接层 Packet Socket
Pakcet Socket 只有 Linux 支持: http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man7/packet.7.html
Mac OS 等基于 BSD 的系统则要使用 Berkeley Packet Filter 实现对原始链路层封包的收发
通过 Raw Socket, 我们已经能够自由定制网络层及以上各层的数据包了, 这时如果还想自己定制更底层网络接口层的数据包, domain 参数就需要使用 PF_PACKET. 使用这种 Socket 就能够访问底层的网卡数据了.只有 SOCK_RAW 和 SOCK_DGRAM 两种 type 参数支持 Packet Socket.
SOCK_RAW
当使用 SOCK_RAW 参数时: 操作系统将从网卡拿到的数据包, 原封不动的传递给我们的程序, 各层协议的数据都都将保持在数据包中; 同时发送数据时, 各个协议数据包都要我们自己组装
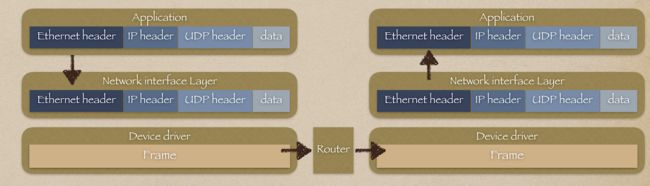
SOCK_DGRAM
当使用 SOCK_DGRAM 参数时: 操作系统在将网卡的数据传递给我们的程序时, 会先去除网络接口层的 header 数据; 发送数据时, 除开网络接口层的 header 不用我们自己组装, 上层的各个协议数据包也要我们自己组装
模拟实现 Ping
接下来利用 Raw Socket 发送网络层上的 ICMP 报文到目标主机, 从而模拟实现 ping 命令
ICMP 协议
https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc792
ICMP 消息有多种类型, 因此其数据结构中定义了几种共用体.
在数据中位于第一个字节的是 Type, ping 中则是发送发送 Echo Request 消息, 响应方回复 Echo Reply 消息. 他俩的结构一样, 只是 Type 的值不同:
Echo or Echo Reply Message 0 1 2 3 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ | Type | Code | Checksum | +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ | Identifier | Sequence Number | +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ | Data ... +-+-+-+-+-
- Type: Type 和 Code 是一种组合的关系, 通过 Type 和 Code 可以组合多种不同的消息类型
- Type 0 且 Code 0: 表示 Echo Reply
- Type 8 且 Code 0: 表示 Echo Request
- Checksum: 根据 ICMP Header 和 Data 计算的校验和
- Identifier: 一个标识符, 发起请求方可以设置一个标识符, 用来筛选 ICMP 响应
下面是 MacOS(BSD base OS) 中 icmp 数据结构的定义:
sysroot/usr/include/netinet/ip_icmp.h
/*
* Structure of an icmp header.
*/
struct icmp {
uint8_t icmp_type; /* type of message */
uint8_t icmp_code; /* type sub code */
uint16_t icmp_cksum; /* ones complement cksum of struct */
union {
uint8_t ih_pptr; /* ICMP_PARAMPROB */
struct in_addr ih_gwaddr; /* ICMP_REDIRECT */
struct ih_idseq {
uint16_t icd_id;
uint16_t icd_seq;
} ih_idseq;
int32_t ih_void;
/* ICMP_UNREACH_NEEDFRAG -- Path MTU Discovery (RFC1191) */
struct ih_pmtu {
uint16_t ipm_void;
uint16_t ipm_nextmtu;
} ih_pmtu;
struct ih_rtradv {
uint8_t irt_num_addrs;
uint8_t irt_wpa;
uint16_t irt_lifetime;
} ih_rtradv;
} icmp_hun;
// 定义了一些结构体区域内的宏, 方便调用
// 比如 sturct icmp *pk = new icmp();
// 要设置 sequence number, 则需要设置 pk->icmp_hun.ih_idseq.icd_seq = 0;
// 可以利用宏 icmp_seq, 等效简写为 pk->icmp_seq = 0;
#define icmp_pptr icmp_hun.ih_pptr
#define icmp_gwaddr icmp_hun.ih_gwaddr
#define icmp_id icmp_hun.ih_idseq.icd_id
#define icmp_seq icmp_hun.ih_idseq.icd_seq
#define icmp_void icmp_hun.ih_void
#define icmp_pmvoid icmp_hun.ih_pmtu.ipm_void
#define icmp_nextmtu icmp_hun.ih_pmtu.ipm_nextmtu
#define icmp_num_addrs icmp_hun.ih_rtradv.irt_num_addrs
#define icmp_wpa icmp_hun.ih_rtradv.irt_wpa
#define icmp_lifetime icmp_hun.ih_rtradv.irt_lifetime
union {
struct id_ts {
uint32_t its_otime;
uint32_t its_rtime;
uint32_t its_ttime;
} id_ts;
struct id_ip {
struct ip idi_ip;
/* options and then 64 bits of data */
} id_ip;
uint32_t id_mask;
int8_t id_data[1];
} icmp_dun;
#define icmp_otime icmp_dun.id_ts.its_otime
#define icmp_rtime icmp_dun.id_ts.its_rtime
#define icmp_ttime icmp_dun.id_ts.its_ttime
#define icmp_ip icmp_dun.id_ip.idi_ip
#define icmp_mask icmp_dun.id_mask
#define icmp_data icmp_dun.id_data
};
实现
以下是在 MacOS 上的实现, Linux 上头文件和一些数据结构会有所差别
通过一个定时器每隔 1 秒向本博客发送一个 ICMP Echo Request
#include "log.h"
#include void doping(int signal)
{
if (signal != SIGALRM || step >= max)
{
exit(1);
}
int icmplen;
struct icmp *icmp;
char sendbuf[BUFFER_SIZE];
icmp = reinterpret_cast<struct icmp *>(sendbuf);
/* Fill all filed of the ICMP message */
icmp->icmp_type = ICMP_ECHO;
icmp->icmp_code = 0;
icmp->icmp_id = getpid();
icmp->icmp_seq = step;
gettimeofday((struct timeval *)icmp->icmp_data, NULL);
icmplen = 8 + 56;
icmp->icmp_cksum = 0;
icmp->icmp_cksum = checksum(reinterpret_cast<unsigned short *>(icmp), icmplen);
if (sendto(
s,
sendbuf,
icmplen,
0,
reinterpret_cast<sockaddr *>(&serveraddr),
sizeof(sockaddr)) < 0)
{
LOG_D(TAG, "[send to] error: %d", errno);
}
if (step == 0)
{
LOG_D(TAG, "PING %s (%s): %d data bytes", hostname, ipadrr, icmplen);
}
step++;
}
}; // namespace NetUtility
int main()
{
NetUtility::ping("jiyang.site", 6);
return 0;
}
参考
- 伯克利套接字
- https://medium.com/@c_bata_/how-to-write-cross-platform-packet-capture-using-raw-socket-and-bpf-bab3b614bc03