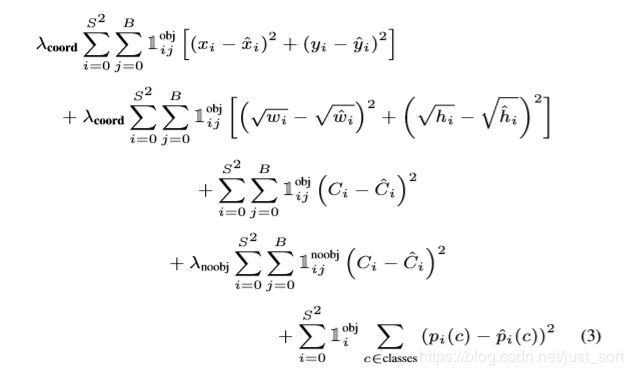【AlexeyAB DarkNet框架解析】七,YOLOV1损失函数代码详解(detection_layer.c)
前言
灵魂拷问,你真的懂YOLOV1的损失函数吗?进一步,懂了损失函数,你清楚它的反向求导过程吗?为了解决这俩问题,本文就结合DarkNet中的YOLOV1的损失函数代码实现(在src/detection_layer.c中)来帮助你理解,相信我,看完你真的能理解。关于YOLOV1就不做过多介绍了,之前写过一篇详细的推文介绍,地址为:目标检测算法之YOLOv1
损失函数公式
YOLOV1的损失函数就是这样,不做过多解释了。需要注意的一个点是,在反向传播求导的时候,各个变量的梯度其实应该都有一个系数2的,但是代码中全部都省掉了,这对整个优化过程其实是没有影响的。
代码详细解析
/**
* 构建detection层,yolov1中最后一层
* @param batch 一个batch包含图片的张数
* @param inputs detection层一张输入图片元素个数
* @param n yolov1一个grid cell预测bbox的数量 2
* @param side // grid cell的大小 7
* @param classes yolov1 预测类的个数
* @param coords 一个bbox包含的坐标数量 4
* @param rescore
* @return
*/
detection_layer make_detection_layer(int batch, int inputs, int n, int side, int classes, int coords, int rescore)
{
detection_layer l = { (LAYER_TYPE)0 };
l.type = DETECTION;
// 这些变量都可以参考darknet.h中的注释
l.n = n; //一个cell中预测多少个box
l.batch = batch; //一个batch中包含图片的张数
l.inputs = inputs; //detection层一张输入图片的元素个数
l.classes = classes; //类别数
l.coords = coords; //一个bbox包含的坐标数量
l.rescore = rescore;
l.side = side; //grid cell的大小 7
l.w = side; //grid cell的宽度
l.h = side; //grid cell的高度
assert(side*side*((1 + l.coords)*l.n + l.classes) == inputs); //7*7*(1 + 4) * 2 + 30 ) = 7*7*30
l.cost = (float*)xcalloc(1, sizeof(float)); //detection层的总损失
l.outputs = l.inputs; //detection层对应输入图片的输出元素个数,detection层不改变输入输出大小
l.truths = l.side*l.side*(1+l.coords+l.classes); //GT:7*7*(1+4+20) 只有一个bbox和置信度
l.output = (float*)xcalloc(batch * l.outputs, sizeof(float)); // detection层所有输出(包含整个batch的)
l.delta = (float*)xcalloc(batch * l.outputs, sizeof(float)); //detection层误差项(包含整个batch的)
l.forward = forward_detection_layer; //前向传播
l.backward = backward_detection_layer; //反向传播
#ifdef GPU
l.forward_gpu = forward_detection_layer_gpu;
l.backward_gpu = backward_detection_layer_gpu;
l.output_gpu = cuda_make_array(l.output, batch*l.outputs);
l.delta_gpu = cuda_make_array(l.delta, batch*l.outputs);
#endif
fprintf(stderr, "Detection Layer\n");
srand(time(0));
return l;
}
/**
* detection层前向传播函数
* @param l 当前detection层
* @param net 整个网络
*/
void forward_detection_layer(const detection_layer l, network_state state)
{
int locations = l.side*l.side; //grid cell的数量7*7=49
int i,j;
memcpy(l.output, state.input, l.outputs*l.batch*sizeof(float));
//if(l.reorg) reorg(l.output, l.w*l.h, size*l.n, l.batch, 1);
int b;
if (l.softmax){ //yolo v1这里为0,并没有使用
for(b = 0; b < l.batch; ++b){
int index = b*l.inputs;
for (i = 0; i < locations; ++i) {
int offset = i*l.classes;
softmax(l.output + index + offset, l.classes, 1,
l.output + index + offset, 1);
}
}
}
if(state.train){
float avg_iou = 0;
float avg_cat = 0;
float avg_allcat = 0;
float avg_obj = 0;
float avg_anyobj = 0;
int count = 0;
*(l.cost) = 0; //detection层的总损失
int size = l.inputs * l.batch; //误差项的个数
memset(l.delta, 0, size * sizeof(float)); //误差项初始化
for (b = 0; b < l.batch; ++b){
int index = b*l.inputs; //第b个batch的起始位置
for (i = 0; i < locations; ++i) { //第i个grid cell,一共有7*7个
int truth_index = (b*locations + i)*(1+l.coords+l.classes); //获取第i个grid cell的bbox的GT
int is_obj = state.truth[truth_index]; //获取第i个grid cell是否包含物体
for (j = 0; j < l.n; ++j) { // 获取yolov1 第i个grid cell预测的两个bbox,与GT比较
int p_index = index + locations*l.classes + i*l.n + j; // 获取第j个预测的bbox起始位置
l.delta[p_index] = l.noobject_scale*(0 - l.output[p_index]); // bbox中不含object的置信度误差项, noobject_scale=0.5 Loss 1-4(1-4指的是公式)
*(l.cost) += l.noobject_scale*pow(l.output[p_index], 2); //第i个grid cell中第j个预测bbox中,不含object的置信度损失计算,Loss 1-4
avg_anyobj += l.output[p_index]; //bbox中不含object的置信度求和
}
int best_index = -1;
float best_iou = 0;
float best_rmse = 20; //best bbox的rmse阈值
if (!is_obj){ // 当前第i个grid cell, 第j个bbox不含object, 则loss计算完成
continue;
}
// 当前第i个grid cell, 第j个bbox含有object,继续计算坐标预测损失Loss 1-1,1-2,confidence预测损失Loss 1-3,类别预测损失Loss 1-5
int class_index = index + i*l.classes;// 获取第i个grid cell的classes起始位置
for(j = 0; j < l.classes; ++j) {
//第i个grid cell预测分类误差项
l.delta[class_index+j] = l.class_scale * (state.truth[truth_index+1+j] - l.output[class_index+j]); // 第i个grid cell预测分类误差项
*(l.cost) += l.class_scale * pow(state.truth[truth_index+1+j] - l.output[class_index+j], 2); // 类别预测损失计算, Loss 1-5
if(state.truth[truth_index + 1 + j]) avg_cat += l.output[class_index+j]; // GT对应的grid cell预测分类值求和
avg_allcat += l.output[class_index+j]; // 所有grid cell预测分类值求和
}
// 获取第i个grid cell, GT BBOX的[x, y, w, h], float_to_box 第一个参数是bbox起始位置
box truth = float_to_box(state.truth + truth_index + 1 + l.classes);
truth.x /= l.side;
truth.y /= l.side;
//坐标预测损失计算 Loss 1-1, 1-2
// 找到第i个grid cell的best bbox
for(j = 0; j < l.n; ++j){
//第i个grid cell预测第j个bbox的起始位置
int box_index = index + locations*(l.classes + l.n) + (i*l.n + j) * l.coords;
box out = float_to_box(l.output + box_index); // 获取预测bbox的[x,y,w,h]
//yolo v1 直接回归的是 7*x, 所以与GT bbox 计算IOU, 需要先除以7
out.x /= l.side;
out.y /= l.side;
if (l.sqrt){
//yolo v1直接回归的sqrt(w), 所以与GT bbox 计算IOU前,需要pow一下
out.w = out.w*out.w;
out.h = out.h*out.h;
}
//计算预测bbox与 GT bbox之间的IOU
float iou = box_iou(out, truth);
//iou = 0;
//计算预测bbox的[x,y]与GT bbox的[x,y]之间的均方差损失 Loss 1-1
float rmse = box_rmse(out, truth);
// 找到第i个grid cell预测最大的那个bbox
if(best_iou > 0 || iou > 0){
if(iou > best_iou){
best_iou = iou;
best_index = j;
}
}else{ // 均方差最小的
if(rmse < best_rmse){
best_rmse = rmse;
best_index = j;
}
}
}
// 强制指定一个bbox
if(l.forced){
// GT bbox w*h < 0.1,强制最好的bbox index是1
if(truth.w*truth.h < .1){
best_index = 1;
}else{
best_index = 0;
}
}
//随机选择最佳bbox
if(l.random && *(state.net.seen) < 64000){
best_index = rand()%l.n;
}
// 模型预测的bbox起始位置
int box_index = index + locations*(l.classes + l.n) + (i*l.n + best_index) * l.coords;
int tbox_index = truth_index + 1 + l.classes;
// 获取最佳bbox的[x, y, w, h]
box out = float_to_box(l.output + box_index);
out.x /= l.side; // 归一化x
out.y /= l.side;
if (l.sqrt) { // yolo v1直接回归的sqrt(w), 所以与GT bbox 计算IOU前,需要pow一下
out.w = out.w*out.w;
out.h = out.h*out.h;
}
float iou = box_iou(out, truth); // 计算二者IOU
//printf("%d,", best_index);
// 获取第i个grid cell,best bbox的起始位置
int p_index = index + locations*l.classes + i*l.n + best_index;
// 减去之前计算不含object的confidence预测损失
*(l.cost) -= l.noobject_scale * pow(l.output[p_index], 2);
// 含有object的confidence的预测损失
*(l.cost) += l.object_scale * pow(1-l.output[p_index], 2);
// bbox中含object的置信度求和
avg_obj += l.output[p_index];
// 第i个含有object的那个best bbox,grid cell预测分类误差项
l.delta[p_index] = l.object_scale * (1.-l.output[p_index]);
//yolo v1这里为0,并没有使用
if(l.rescore){
l.delta[p_index] = l.object_scale * (iou - l.output[p_index]);
}
// 第i个grid cell的x对应误差项计算
l.delta[box_index+0] = l.coord_scale*(state.truth[tbox_index + 0] - l.output[box_index + 0]);
// 第i个grid cell的y对应误差项计算
l.delta[box_index+1] = l.coord_scale*(state.truth[tbox_index + 1] - l.output[box_index + 1]);
// 第i个grid cell的w对应误差项计算
l.delta[box_index+2] = l.coord_scale*(state.truth[tbox_index + 2] - l.output[box_index + 2]);
// 第i个grid cell的h对应误差项计算
l.delta[box_index+3] = l.coord_scale*(state.truth[tbox_index + 3] - l.output[box_index + 3]);
if(l.sqrt){
// Loss 1-2计算, GT bbox需要开根号
l.delta[box_index+2] = l.coord_scale*(sqrt(state.truth[tbox_index + 2]) - l.output[box_index + 2]);
l.delta[box_index+3] = l.coord_scale*(sqrt(state.truth[tbox_index + 3]) - l.output[box_index + 3]);
}
*(l.cost) += pow(1-iou, 2);
avg_iou += iou; // 包含object的grid cell,best bbox 与 GT bbox的IOU求和
++count; // 训练阶段,截止到本batch的训练完,包含object总数量
}
} // 一个batch中所有图片处理完
if(0){
float* costs = (float*)xcalloc(l.batch * locations * l.n, sizeof(float));
for (b = 0; b < l.batch; ++b) {
int index = b*l.inputs;
for (i = 0; i < locations; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < l.n; ++j) {
int p_index = index + locations*l.classes + i*l.n + j;
costs[b*locations*l.n + i*l.n + j] = l.delta[p_index]*l.delta[p_index];
}
}
}
int indexes[100];
top_k(costs, l.batch*locations*l.n, 100, indexes);
float cutoff = costs[indexes[99]];
for (b = 0; b < l.batch; ++b) {
int index = b*l.inputs;
for (i = 0; i < locations; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < l.n; ++j) {
int p_index = index + locations*l.classes + i*l.n + j;
if (l.delta[p_index]*l.delta[p_index] < cutoff) l.delta[p_index] = 0;
}
}
}
free(costs);
}
//一个batch的总损失计算
*(l.cost) = pow(mag_array(l.delta, l.outputs * l.batch), 2); // 一个batch的总损失计算
printf("Detection Avg IOU: %f, Pos Cat: %f, All Cat: %f, Pos Obj: %f, Any Obj: %f, count: %d\n", avg_iou/count, avg_cat/count, avg_allcat/(count*l.classes), avg_obj/count, avg_anyobj/(l.batch*locations*l.n), count);
//if(l.reorg) reorg(l.delta, l.w*l.h, size*l.n, l.batch, 0);
}
}
/**
* detection层反向传播函数
* @param l 当前detection层
* @param net 整个网络
*/
void backward_detection_layer(const detection_layer l, network_state state)
{
axpy_cpu(l.batch*l.inputs, 1, l.delta, 1, state.delta, 1);
}
/**
* yolo v1 Infence 阶段,解析7*7*30
* @param l 当前detection层
* @param w 输入图片的宽度
* @param h 输入图片的高度
* @param thresh confidence阈值
* @param dets 用于保存结果
*/
void get_detection_detections(layer l, int w, int h, float thresh, detection *dets)
{
int i, j, n;
float *predictions = l.output;
//int per_cell = 5*num+classes;
for (i = 0; i < l.side*l.side; ++i) {
int row = i / l.side; //获取grid cell的行号
int col = i % l.side; //获取grid cell的列号
for (n = 0; n < l.n; ++n) { //遍历两个box
int index = i*l.n + n;
int p_index = l.side*l.side*l.classes + i*l.n + n;
float scale = predictions[p_index];
int box_index = l.side*l.side*(l.classes + l.n) + (i*l.n + n) * 4;
box b;
b.x = (predictions[box_index + 0] + col) / l.side * w; // 坐标转换为真实值
b.y = (predictions[box_index + 1] + row) / l.side * h;
b.w = pow(predictions[box_index + 2], (l.sqrt ? 2 : 1)) * w;
b.h = pow(predictions[box_index + 3], (l.sqrt ? 2 : 1)) * h;
dets[index].bbox = b;
dets[index].objectness = scale; // 保存框置信度得分
for (j = 0; j < l.classes; ++j) {
int class_index = i*l.classes;
float prob = scale*predictions[class_index + j]; // 类别置信度得分=条件类别概率×框置信度得分
dets[index].prob[j] = (prob > thresh) ? prob : 0; // 低于阈值一律置为0
}
}
}
}
有了这个详细的代码注释结合上面的公式就应该可以完全理解YOLOV1的损失函数和反向求导,有任何问题可以加我微信hellotopython一起交流。
后记
本文介绍了YOLOV1的损失函数实现,也即是src/detection_layer.c文件的内容,希望看完这篇你能彻底理解YOLOV1的损失函数,后面我会继续更新YOLOV2/YOLOV3的DarkNet代码解释,请继续关注。
同期文章
- 【翻译】手把手教你用AlexeyAB版Darknet
- 【AlexeyAB DarkNet框架解析】一,框架总览
- 【AlexeyAB DarkNet框架解析】二,数据结构解析
- 【AlexeyAB DarkNet框架解析】三,加载数据进行训练
- 【AlexeyAB DarkNet框架解析】四,网络的前向传播和反向传播介绍以及layer的详细解析
- 【AlexeyAB DarkNet框架解析】五,卷积层的前向传播解析
- 【AlexeyAB DarkNet框架解析】六,卷积层的反向传播解析
欢迎关注GiantPandaCV, 在这里你将看到独家的深度学习分享,坚持原创,每天分享我们学习到的新鲜知识。( • ̀ω•́ )✧
有对文章相关的问题,或者想要加入交流群,欢迎添加BBuf微信:
![]()