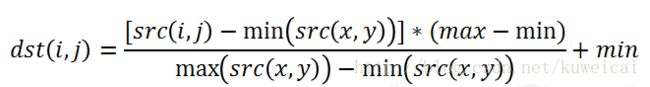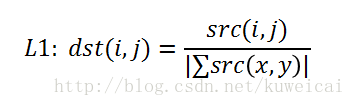- 霍夫变换(Hough Transform)算法原来详解和纯C++代码实现以及OpenCV中的使用示例
点云SLAM
算法图形图像处理算法opencv图像处理与计算机视觉算法直线提取检测目标检测霍夫变换算法
霍夫变换(HoughTransform)是一种经典的图像处理与计算机视觉算法,广泛用于检测图像中的几何形状,例如直线、圆、椭圆等。其核心思想是将图像空间中的“点”映射到参数空间中的“曲线”,从而将形状检测问题转化为参数空间中的峰值检测问题。一、霍夫变换基本思想输入:边缘图像(如经过Canny边缘检测)输出:一组满足几何模型的形状(如直线、圆)关键思想:图像空间中的一个点→参数空间中的一个曲线参数空
- 用OpenCV标定相机内参应用示例(C++和Python)
下面是一个完整的使用OpenCV进行相机内参标定(CameraCalibration)的示例,包括C++和Python两个版本,基于棋盘格图案标定。一、目标:相机标定通过拍摄多张带有棋盘格图案的图像,估计相机的内参:相机矩阵(内参)K畸变系数distCoeffs可选外参(R,T)标定精度指标(如重投影误差)二、棋盘格参数设置(根据自己的棋盘格设置):棋盘格角点数:9x6(内角点,9列×6行);每个
- OpenCV图像数据处理:convertTo,normalize和scaleAdd
luofeiju
OpenCV函数实战opencv
在OpenCV图像处理的世界里,有几个函数进行一些基本数据变换:cv::convertTo():类型转换与线性缩放;cv::normalize():归一化处理;cv::scaleAdd():加权叠加运算。cv::addWeighted():与scaleAdd相似,进行加权叠加运算;一、cv::convertTo():线性变换+数据类型转换voidcv::Mat::convertTo(OutputA
- 用Python和OpenCV从零搭建一个完整的双目视觉系统(三)
presenttttt
双目立体视觉数码相机
本系列文章旨在系统性地阐述如何利用Python与OpenCV库,从零开始构建一个完整的双目立体视觉系统。本项目github地址:https://github.com/present-cjn/stereo-vision-python.git在上一篇文章中,我们为项目设计了清晰的架构。现在,我们将深入第一个,也是整个双目视觉系统最关键的模块——相机标定(CameraCalibration)。如果说双目
- (一)OpenCV——噪声去除(降噪)
高斯滤波器(针对高斯噪声)高斯噪声是指它的概率密度函数服从高斯分布(即正态分布)的一类噪声。常见的高斯噪声包括起伏噪声、宇宙噪声、热噪声和散粒噪声等等。高斯滤波(Gaussianfilter)包含许多种,包括低通、带通和高通等,我们通常图像上说的高斯滤波,指的是高斯模糊(GaussianBlur),是一种高斯低通滤波,其过滤调图像高频成分(图像细节部分),保留图像低频成分(图像平滑区域),所以对图
- OpenCV图片操作100例:从入门到精通指南(1)
总有刁民想爱朕ha
opencv计算机视觉人工智能
OpenCV图片操作100例:从入门到精通指南本文整理了100个OpenCV实用技巧,涵盖图像处理各个领域,助你轻松掌握计算机视觉核心技能!一、入门必备:基础操作1.图像读写与显示importcv2#读取图像(BGR格式)img=cv2.imread('image.jpg')#显示图像cv2.imshow('示例图片',img)cv2.waitKey(0)#按任意键退出cv2.destroyAll
- OpenCV图片操作100例:从入门到精通指南(3)
总有刁民想爱朕ha
opencv人工智能计算机视觉
高效学习路径:1️⃣分阶段学习:入门:1-20例(基础操作)进阶:21-50例(图像处理)高级:51-100例(计算机视觉)2️⃣项目驱动学习:证件照背景替换(1-15例)停车场车位检测(30-45例)视频运动追踪(70-85例)3️⃣性能优化技巧:#使用UMat加速图像处理umat_img=cv2.UMat(img)processed=cv2.GaussianBlur(umat_img,(5,5
- Python OpenCV教程从入门到精通的全面指南【文末送书】
一键难忘
pythonopencv开发语言
文章目录PythonOpenCV从入门到精通1.安装OpenCV2.基本操作2.1读取和显示图像2.2图像基本操作3.图像处理3.1图像转换3.2图像阈值处理3.3图像平滑4.边缘检测和轮廓4.1Canny边缘检测4.2轮廓检测5.高级操作5.1特征检测5.2目标跟踪5.3深度学习与OpenCVPythonOpenCV从入门到精通【文末送书】PythonOpenCV从入门到精通OpenCV(Ope
- OpenCV入门到精通:AI视觉处理的完整指南
AI云原生与云计算技术学院
人工智能opencv计算机视觉ai
OpenCV入门到精通:AI视觉处理的完整指南关键词:OpenCV、计算机视觉、图像预处理、目标检测、AI视觉应用摘要:本文是一份面向AI视觉爱好者的OpenCV完整学习指南。从OpenCV的核心概念讲起,结合生活案例、代码示例和项目实战,逐步拆解图像读取/显示、灰度化、边缘检测、目标检测等关键技术。无论你是想入门计算机视觉的新手,还是希望用OpenCV解决实际问题的开发者,都能通过本文掌握从理论
- OpenCV入门到精通:从基础到实战的全面指南
摘要:本文旨在为初学者和有一定经验的开发者提供OpenCV从入门到精通的全面指南。文章首先介绍了OpenCV的基本概念和安装方法,然后深入讲解了图像处理基础、特征检测与匹配、视频处理与分析等核心内容,最后通过实战案例展示了OpenCV在计算机视觉任务中的应用。关键词:OpenCV;图像处理;特征检测;视频分析;实战案例引言OpenCV(OpenSourceComputerVisionLibrary
- libjpeg-turbo图片解码 VS opencv
momomo_mocs
opencv人工智能计算机视觉
#include#include#includestd::pairJpegTurboDecode(conststd::string&raw_jpeg_data,std::vector*result_data){if(nullptr==result_data){LOG(INFO)(const_cast(raw_jpeg_data.data())),raw_jpeg_data.size(),&widt
- OpenCV探索之旅:多尺度视觉与形状的灵魂--图像金字塔与轮廓分析
在我们学会用Canny算法勾勒处世界的轮廓之后,一个更深层次的问题摆在了面前:这些由像素组成的线条,如何才能被赋予“生命”,成为我们能够理解和分析的“形状”?如果一个物体在图像中时大时小,我们又该如何稳定地识别它?欢迎来到本次的探索之旅。我们将建造两种强大的“金字塔”,赋予我们跨越尺度的“鹰之眼”;然后,我们将不仅仅是找到轮廓,更要深入其内部,测量它的面积、周长,找到它的重心,甚至量化它的“形状”
- 【零基础学AI】第31讲:目标检测 - YOLO算法
1989
0基础学AI人工智能目标检测YOLOrnnlstmtensorflow
本节课你将学到YOLO算法的核心思想和工作原理如何使用YOLO进行物体检测构建一个简单的物体检测系统开始之前环境要求Python3.8+需要安装的包:opencv-python,numpy,matplotlib硬件要求:推荐使用GPU(非必须)前置知识基本Python编程能力了解卷积神经网络(CNN)的基本概念(第24讲内容)核心概念什么是目标检测?目标检测就像教计算机"看"图片中的物体。它不仅要
- OpenCV颜色矩哈希算法------cv::img_hash::ColorMomentHash
操作系统:ubuntu22.04OpenCV版本:OpenCV4.9IDE:VisualStudioCode编程语言:C++11算法描述该类实现了颜色矩哈希算法(ColorMomentHash),用于图像相似性比较。它基于图像在HSV颜色空间中的颜色矩统计特征来生成哈希值,对颜色分布的变化具有较好的鲁棒性。适用于以下场景:图像检索图像去重水印检测色彩变化较大的图像匹配公共成员函数compute(I
- OpenCV哈希算法------Marr-Hildreth 边缘检测哈希算法
村北头的码农
OpenCVopencv哈希算法人工智能
操作系统:ubuntu22.04OpenCV版本:OpenCV4.9IDE:VisualStudioCode编程语言:C++11算法描述该类实现了Marr-Hildreth边缘检测哈希算法(Marr-HildrethHash),用于图像相似性比较。它基于Marr-Hildreth边缘检测器(也称为LaplacianofGaussian,LoG)提取图像边缘信息,并生成二进制哈希值。这种哈希方法对图
- OpenCV 图像哈希类cv::img_hash::AverageHash
村北头的码农
OpenCVopencv哈希算法人工智能
操作系统:ubuntu22.04OpenCV版本:OpenCV4.9IDE:VisualStudioCode编程语言:C++11算法描述cv::img_hash::AverageHash是OpenCV中用于图像哈希(ImageHashing)的一个类,属于opencv_img_hash模块。它实现了平均哈希算法(AverageHash,aHash),可以快速计算图像的“指纹”或“感知哈希值”,用于
- 【图像处理基石】如何检测到画面中的ppt并对其进行增强?
1.入门版ppt检测增强工具我们介绍一个使用Python进行PPT检测并校正画面的实现方案。这个方案主要利用OpenCV进行图像处理,通过边缘检测和透视变换技术来识别并校正PPT画面。importcv2importnumpyasnpfromPILimportImageimportmatplotlib.pyplotaspltclassPPTDetector:def__init__(self):#初始
- OpenCvSharp 实现环形文字识别OCR实例(C#)
XisVisual_Basic
ocrc#计算机视觉C#
近年来,随着计算机视觉和图像处理的不断发展,光学字符识别(OCR)技术也变得愈发成熟。OCR技术可以将图像中的文字转换为可编辑和可搜索的文本,为人们带来了极大的便利。在本篇文章中,我们将介绍如何使用OpenCvSharp库来实现环形文字的识别。首先,在使用OpenCvSharp之前,我们需要确保已经在项目中引用了该库,并添加相应的命名空间。usingOpenCvSharp;接下来,我们需要准备一张
- 环形文字识别实例:使用OpenCV和OCR的C/C++实现
TechPr
opencvocrc语言C/C++
环形文字识别实例:使用OpenCV和OCR的C/C++实现在本篇文章中,我们将介绍如何使用OpenCV和OCR技术来实现环形文字的识别。我们将使用C/C++语言编写源代码,并通过一步一步的解释来帮助您理解实现的过程。导入必要的库首先,我们需要导入所需的库。我们将使用OpenCV来处理图像,以及OCR库来进行文字识别。以下是所需的头文件:#include#include#
- Python|OpenCV-实现识别弧形文字(17)
写python的鑫哥
OpenCV入门与进阶pythonopencv人工智能计算机视觉弧形文字环形文字识别
前言本文是该专栏的第19篇,后面将持续分享OpenCV计算机视觉的干货知识,记得关注。我们知道,OCR可以识别文字方面的需求,但是如果遇到那些目标文字是“弧形文字”,需要怎么去识别呢?遇到想要识别“弧形文字”的需求,这个时候你可以借助于Opencv+OCR技术来实现。而本文,笔者将针对上述问题需求,利用OpenCV结合OCR来实现“弧形文字”的识别。废话不多说,具体的细节部分以及详细的解决方案,跟
- OpenCV实战之二 | 基于哈希算法比较图像的相似性
w94ghz
OpenCV实战笔记opencv哈希算法人工智能
前言☘️本章节主要介绍常用的图像相似性评价算法:图像哈希算法。图像哈希算法通过获取图像的哈希值并比较两幅图像的哈希值的汉明距离来衡量两幅图像是否相似。两幅图像越相似,其哈希值的汉明距离越小。图像哈希算法可以用于图片检索,重复图片剔除,以图搜图以及图片相似度比较。目录一、汉明距离二、img_hash模块三、哈希算法哈希算法实现步骤:代码实现一、汉明距离汉明距离(HammingDistance)是用于
- OpenCV CUDA模块设备层-----高效地计算两个 uint 类型值的带权重平均值
村北头的码农
OpenCVopencv人工智能计算机视觉
操作系统:ubuntu22.04OpenCV版本:OpenCV4.9IDE:VisualStudioCode编程语言:C++11算法描述OpenCV的CUDA模块(cudev)中的一个设备端内联函数,用于高效地计算两个uint类型值的带权重平均值。该函数返回两个无符号整数a和b的加权平均值,权重为:return(a*3+b)/4;函数原型__device____forceinline__uintc
- 【解决方案】Building wheel for opencv-python:安装卡顿的原因与解决方案。
当你pipinstallopencv-python或pipinstallopencv-contrib-python时,命令行停在Buildingwheelforopencv-python(PEP517)...-似乎卡住了。其实,这并非程序假死,而是OpenCV这个庞大的C++library在进行compile,这个过程非常耗时。为何安装过程如此漫长?这是因为OpenCV是一个庞大的C++libra
- Python在人工智能领域的实际应用:示例代码解析
辣条yyds
pythonpython人工智能开发语言
摘要:本文将通过几个典型的人工智能应用场景,展示Python在图像识别、自然语言处理、推荐系统等方面的高级用法。通过示例代码,带大家深入理解Python在人工智能领域的实际应用。正文:Python作为一门流行的编程语言,凭借其简洁的语法、丰富的库和框架,成为了人工智能(AI)领域的主流开发语言。下面,我们将通过几个示例,探讨Python在人工智能方向的实际应用。示例一:图像识别-使用OpenCV进
- Hough变换
先上代码,c++1.hough检测线//LineFinder.h#include"opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"#include"opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"#include"opencv2/core/core.hpp"#include//#include//#includeusingnamespacestd;usingnamespacecv;
- opencv初步学习——图像处理2
这一部分主要讲解如何初步地创建一个图像,以及彩色图像我们的一些基本处理方法一、创建一个灰度图像1-1、zeros()函数[NumPy库]要用到这一个函数,首先我们需要调用我们的NumPy库,这一个函数的作用是可以帮助我们生成一个元素值都是0的二维数组,如果我们把这些数据放到一张图片里面去,那么就对应着我们的一个黑色图像。当然我们也可以通过修改数组中的数字大小来改变图像的颜色(但还是灰度图像)(1)
- OpenCV 人脸分析------面部关键点检测类cv::face::FacemarkLBF
村北头的码农
OpenCVopencv人工智能计算机视觉
操作系统:ubuntu22.04OpenCV版本:OpenCV4.9IDE:VisualStudioCode编程语言:C++11算法描述使用LocalBinaryFeatures(LBF)算法进行面部关键点检测(faciallandmarkdetection)。该算法通过级联回归树预测人脸的68个关键点,具有较高的精度和速度。公共成员函数staticPtrcreate(constParams&pa
- RK3588 源码编译 opencv
hitsz_syl
opencv人工智能计算机视觉
从你的输出信息来看,系统已经安装了libpng1.6.37(最新版本),但OpenCV4.8.1在编译时仍然找不到png_set_longjmp_fn和png_get_eXIf_1等符号。这表明CMake可能没有正确链接到系统的libpng库,或者OpenCV的编译配置存在问题。解决方案1.检查libpng是否包含所需符号运行以下命令,确认libpng.so是否包含OpenCV需要的符号:nm-D
- opencv-python与opencv-contrib-python的区别联系
剑心缘
零碎小知识pythonopencv
opencv-python包含基本的opencvopencv-contrib-python是高配版,带一些收费或者专利的算法,还有一些比较新的算法的高级版本,这些算法稳定之后会加入上面那个。官网对contrib模块的简介(点击链接跳转)参考链接
- OpenCV 图像操作:颜色识别、替换与水印添加
目录引言代码实现1.导入必要的库2.图像加法3.图像直接相加4.颜色加权加法5.HSV颜色空间转换概念作用6.查找颜色范围对应的像素点7.与运算-生成掩膜8.添加水印9.主函数总结引言在计算机视觉领域,OpenCV是一个强大的库,提供了丰富的图像操作功能。本文将详细介绍如何使用OpenCV进行图像加法、颜色加权加法、HSV颜色空间转换、颜色范围查找、与运算生成掩膜以及添加水印等操作,并给出相应的P
- ios内付费
374016526
ios内付费
近年来写了很多IOS的程序,内付费也用到不少,使用IOS的内付费实现起来比较麻烦,这里我写了一个简单的内付费包,希望对大家有帮助。
具体使用如下:
这里的sender其实就是调用者,这里主要是为了回调使用。
[KuroStoreApi kuroStoreProductId:@"产品ID" storeSender:self storeFinishCallBa
- 20 款优秀的 Linux 终端仿真器
brotherlamp
linuxlinux视频linux资料linux自学linux教程
终端仿真器是一款用其它显示架构重现可视终端的计算机程序。换句话说就是终端仿真器能使哑终端看似像一台连接上了服务器的客户机。终端仿真器允许最终用户用文本用户界面和命令行来访问控制台和应用程序。(LCTT 译注:终端仿真器原意指对大型机-哑终端方式的模拟,不过在当今的 Linux 环境中,常指通过远程或本地方式连接的伪终端,俗称“终端”。)
你能从开源世界中找到大量的终端仿真器,它们
- Solr Deep Paging(solr 深分页)
eksliang
solr深分页solr分页性能问题
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2148370
作者:eksliang(ickes) blg:http://eksliang.iteye.com/ 概述
长期以来,我们一直有一个深分页问题。如果直接跳到很靠后的页数,查询速度会比较慢。这是因为Solr的需要为查询从开始遍历所有数据。直到Solr的4.7这个问题一直没有一个很好的解决方案。直到solr
- 数据库面试题
18289753290
面试题 数据库
1.union ,union all
网络搜索出的最佳答案:
union和union all的区别是,union会自动压缩多个结果集合中的重复结果,而union all则将所有的结果全部显示出来,不管是不是重复。
Union:对两个结果集进行并集操作,不包括重复行,同时进行默认规则的排序;
Union All:对两个结果集进行并集操作,包括重复行,不进行排序;
2.索引有哪些分类?作用是
- Android TV屏幕适配
酷的飞上天空
android
先说下现在市面上TV分辨率的大概情况
两种分辨率为主
1.720标清,分辨率为1280x720.
屏幕尺寸以32寸为主,部分电视为42寸
2.1080p全高清,分辨率为1920x1080
屏幕尺寸以42寸为主,此分辨率电视屏幕从32寸到50寸都有
适配遇到问题,已1080p尺寸为例:
分辨率固定不变,屏幕尺寸变化较大。
如:效果图尺寸为1920x1080,如果使用d
- Timer定时器与ActionListener联合应用
永夜-极光
java
功能:在控制台每秒输出一次
代码:
package Main;
import javax.swing.Timer;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class T {
private static int count = 0;
public static void main(String[] args){
- Ubuntu14.04系统Tab键不能自动补全问题解决
随便小屋
Ubuntu 14.04
Unbuntu 14.4安装之后就在终端中使用Tab键不能自动补全,解决办法如下:
1、利用vi编辑器打开/etc/bash.bashrc文件(需要root权限)
sudo vi /etc/bash.bashrc
接下来会提示输入密码
2、找到文件中的下列代码
#enable bash completion in interactive shells
#if
- 学会人际关系三招 轻松走职场
aijuans
职场
要想成功,仅有专业能力是不够的,处理好与老板、同事及下属的人际关系也是门大学问。如何才能在职场如鱼得水、游刃有余呢?在此,教您简单实用的三个窍门。
第一,多汇报
最近,管理学又提出了一个新名词“追随力”。它告诉我们,做下属最关键的就是要多请示汇报,让上司随时了解你的工作进度,有了新想法也要及时建议。不知不觉,你就有了“追随力”,上司会越来越了解和信任你。
第二,勤沟通
团队的力
- 《O2O:移动互联网时代的商业革命》读书笔记
aoyouzi
读书笔记
移动互联网的未来:碎片化内容+碎片化渠道=各式精准、互动的新型社会化营销。
O2O:Online to OffLine 线上线下活动
O2O就是在移动互联网时代,生活消费领域通过线上和线下互动的一种新型商业模式。
手机二维码本质:O2O商务行为从线下现实世界到线上虚拟世界的入口。
线上虚拟世界创造的本意是打破信息鸿沟,让不同地域、不同需求的人
- js实现图片随鼠标滚动的效果
百合不是茶
JavaScript滚动属性的获取图片滚动属性获取页面加载
1,获取样式属性值
top 与顶部的距离
left 与左边的距离
right 与右边的距离
bottom 与下边的距离
zIndex 层叠层次
例子:获取左边的宽度,当css写在body标签中时
<div id="adver" style="position:absolute;top:50px;left:1000p
- ajax同步异步参数async
bijian1013
jqueryAjaxasync
开发项目开发过程中,需要将ajax的返回值赋到全局变量中,然后在该页面其他地方引用,因为ajax异步的原因一直无法成功,需将async:false,使其变成同步的。
格式:
$.ajax({ type: 'POST', ur
- Webx3框架(1)
Bill_chen
eclipsespringmaven框架ibatis
Webx是淘宝开发的一套Web开发框架,Webx3是其第三个升级版本;采用Eclipse的开发环境,现在支持java开发;
采用turbine原型的MVC框架,扩展了Spring容器,利用Maven进行项目的构建管理,灵活的ibatis持久层支持,总的来说,还是一套很不错的Web框架。
Webx3遵循turbine风格,velocity的模板被分为layout/screen/control三部
- 【MongoDB学习笔记五】MongoDB概述
bit1129
mongodb
MongoDB是面向文档的NoSQL数据库,尽量业界还对MongoDB存在一些质疑的声音,比如性能尤其是查询性能、数据一致性的支持没有想象的那么好,但是MongoDB用户群确实已经够多。MongoDB的亮点不在于它的性能,而是它处理非结构化数据的能力以及内置对分布式的支持(复制、分片达到的高可用、高可伸缩),同时它提供的近似于SQL的查询能力,也是在做NoSQL技术选型时,考虑的一个重要因素。Mo
- spring/hibernate/struts2常见异常总结
白糖_
Hibernate
Spring
①ClassNotFoundException: org.aspectj.weaver.reflect.ReflectionWorld$ReflectionWorldException
缺少aspectjweaver.jar,该jar包常用于spring aop中
②java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.sprin
- jquery easyui表单重置(reset)扩展思路
bozch
formjquery easyuireset
在jquery easyui表单中 尚未提供表单重置的功能,这就需要自己对其进行扩展。
扩展的时候要考虑的控件有:
combo,combobox,combogrid,combotree,datebox,datetimebox
需要对其添加reset方法,reset方法就是把初始化的值赋值给当前的组件,这就需要在组件的初始化时将值保存下来。
在所有的reset方法添加完毕之后,就需要对fo
- 编程之美-烙饼排序
bylijinnan
编程之美
package beautyOfCoding;
import java.util.Arrays;
/*
*《编程之美》的思路是:搜索+剪枝。有点像是写下棋程序:当前情况下,把所有可能的下一步都做一遍;在这每一遍操作里面,计算出如果按这一步走的话,能不能赢(得出最优结果)。
*《编程之美》上代码有很多错误,且每个变量的含义令人费解。因此我按我的理解写了以下代码:
*/
- Struts1.X 源码分析之ActionForm赋值原理
chenbowen00
struts
struts1在处理请求参数之前,首先会根据配置文件action节点的name属性创建对应的ActionForm。如果配置了name属性,却找不到对应的ActionForm类也不会报错,只是不会处理本次请求的请求参数。
如果找到了对应的ActionForm类,则先判断是否已经存在ActionForm的实例,如果不存在则创建实例,并将其存放在对应的作用域中。作用域由配置文件action节点的s
- [空天防御与经济]在获得充足的外部资源之前,太空投资需有限度
comsci
资源
这里有一个常识性的问题:
地球的资源,人类的资金是有限的,而太空是无限的.....
就算全人类联合起来,要在太空中修建大型空间站,也不一定能够成功,因为资源和资金,技术有客观的限制....
&
- ORACLE临时表—ON COMMIT PRESERVE ROWS
daizj
oracle临时表
ORACLE临时表 转
临时表:像普通表一样,有结构,但是对数据的管理上不一样,临时表存储事务或会话的中间结果集,临时表中保存的数据只对当前
会话可见,所有会话都看不到其他会话的数据,即使其他会话提交了,也看不到。临时表不存在并发行为,因为他们对于当前会话都是独立的。
创建临时表时,ORACLE只创建了表的结构(在数据字典中定义),并没有初始化内存空间,当某一会话使用临时表时,ORALCE会
- 基于Nginx XSendfile+SpringMVC进行文件下载
denger
应用服务器Webnginx网络应用lighttpd
在平常我们实现文件下载通常是通过普通 read-write方式,如下代码所示。
@RequestMapping("/courseware/{id}")
public void download(@PathVariable("id") String courseID, HttpServletResp
- scanf接受char类型的字符
dcj3sjt126com
c
/*
2013年3月11日22:35:54
目的:学习char只接受一个字符
*/
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i;
char ch;
scanf("%d", &i);
printf("i = %d\n", i);
scanf("%
- 学编程的价值
dcj3sjt126com
编程
发一个人会编程, 想想以后可以教儿女, 是多么美好的事啊, 不管儿女将来从事什么样的职业, 教一教, 对他思维的开拓大有帮助
像这位朋友学习:
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/articlelist_2584320772_0_1.html
VirtualGS教程 (By @林泰前): 几十年的老程序员,资深的
- 二维数组(矩阵)对角线输出
飞天奔月
二维数组
今天在BBS里面看到这样的面试题目,
1,二维数组(N*N),沿对角线方向,从右上角打印到左下角如N=4: 4*4二维数组
{ 1 2 3 4 }
{ 5 6 7 8 }
{ 9 10 11 12 }
{13 14 15 16 }
打印顺序
4
3 8
2 7 12
1 6 11 16
5 10 15
9 14
13
要
- Ehcache(08)——可阻塞的Cache——BlockingCache
234390216
并发ehcacheBlockingCache阻塞
可阻塞的Cache—BlockingCache
在上一节我们提到了显示使用Ehcache锁的问题,其实我们还可以隐式的来使用Ehcache的锁,那就是通过BlockingCache。BlockingCache是Ehcache的一个封装类,可以让我们对Ehcache进行并发操作。其内部的锁机制是使用的net.
- mysqldiff对数据库间进行差异比较
jackyrong
mysqld
mysqldiff该工具是官方mysql-utilities工具集的一个脚本,可以用来对比不同数据库之间的表结构,或者同个数据库间的表结构
如果在windows下,直接下载mysql-utilities安装就可以了,然后运行后,会跑到命令行下:
1) 基本用法
mysqldiff --server1=admin:12345
- spring data jpa 方法中可用的关键字
lawrence.li
javaspring
spring data jpa 支持以方法名进行查询/删除/统计。
查询的关键字为find
删除的关键字为delete/remove (>=1.7.x)
统计的关键字为count (>=1.7.x)
修改需要使用@Modifying注解
@Modifying
@Query("update User u set u.firstna
- Spring的ModelAndView类
nicegege
spring
项目中controller的方法跳转的到ModelAndView类,一直很好奇spring怎么实现的?
/*
* Copyright 2002-2010 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* yo
- 搭建 CentOS 6 服务器(13) - rsync、Amanda
rensanning
centos
(一)rsync
Server端
# yum install rsync
# vi /etc/xinetd.d/rsync
service rsync
{
disable = no
flags = IPv6
socket_type = stream
wait
- Learn Nodejs 02
toknowme
nodejs
(1)npm是什么
npm is the package manager for node
官方网站:https://www.npmjs.com/
npm上有很多优秀的nodejs包,来解决常见的一些问题,比如用node-mysql,就可以方便通过nodejs链接到mysql,进行数据库的操作
在开发过程往往会需要用到其他的包,使用npm就可以下载这些包来供程序调用
&nb
- Spring MVC 拦截器
xp9802
spring mvc
Controller层的拦截器继承于HandlerInterceptorAdapter
HandlerInterceptorAdapter.java 1 public abstract class HandlerInterceptorAdapter implements HandlerIntercep
![]()
![]()