深度学习手记(七)之MNIST实现CNN模型
手写字体识别是一个很好练习CNN框架搭建的数据集。下面简单讲述一下整个模型构建的思路:
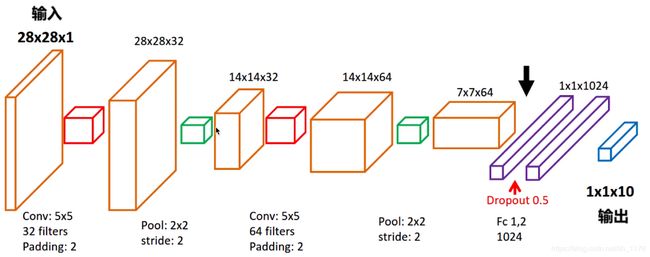 整个模型通过两次卷积、两次亚采样以及两次全连接层,整个结构比较简单,也易理解。其中,两次卷积层的大小都为5x5,过滤器分别为32和64个,为了不改变图片的大小,设置padding参数为“same”,步长为1,激活函数为Relu;两次亚采样层(Pool)的大小都为2x2,步长设为2,以至于图片尺寸缩小一倍。通过两次卷积两次亚采样之后,图像的维度就变为了7x7x64,再经过两次全连接层以及通过softmax激活函数之后与十种类别相匹配,预测手写字体的数字。
整个模型通过两次卷积、两次亚采样以及两次全连接层,整个结构比较简单,也易理解。其中,两次卷积层的大小都为5x5,过滤器分别为32和64个,为了不改变图片的大小,设置padding参数为“same”,步长为1,激活函数为Relu;两次亚采样层(Pool)的大小都为2x2,步长设为2,以至于图片尺寸缩小一倍。通过两次卷积两次亚采样之后,图像的维度就变为了7x7x64,再经过两次全连接层以及通过softmax激活函数之后与十种类别相匹配,预测手写字体的数字。
分别使用TensorFlow和Keras实现代码
**
1. TensorFlow
**
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
# 下载MNIST数据
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("mnist_data", one_hot=True)
# 使用占位符创建输入变量
# None 表示张量(Tensor)的第一个维度可以是任何长度
# 除以 255 是为了做 归一化(Normalization),把灰度值从 [0, 255] 变成 [0, 1] 区间
# 归一话可以让之后的优化器(optimizer)更快更好地找到误差最小值
input_x = tf.placeholder("float32", [None, 28*28]) / 255.
output_y = tf.placeholder("int32", [None, 10])
# -1 表示自动推导维度大小。让计算机根据其他维度的值
# 和总的元素大小来推导出 -1 的地方的维度应该是多少
input_x_images = tf.reshape(input_x, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
# MNIST测试数据集(选取其中3000张)
test_x = mnist.test.images[:3000]
test_y = mnist.test.labels[:3000]
# 构建卷积神经网络
# # 第一层卷积
conv1 = tf.layers.conv2d(
inputs=input_x_images, # 形状 [28, 28, 1]
filters=32, # 32 个过滤器,输出的深度(depth)是32
kernel_size=[5, 5], # 过滤器在二维的大小是 (5 * 5)
strides=1, # 步长是 1
padding='same', # same 表示输出的大小不变,因此需要在外围补零 2 圈
activation=tf.nn.relu # 激活函数是 Relu
) # 形状 [28, 28, 32]
# # 第一层池化层(亚采样)
pool1 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(
inputs=conv1, # 形状 [28, 28, 32]
pool_size=[2, 2], # 过滤器在二维的大小是(2 * 2)
strides=2 # 步长是 2
) # 形状 [14, 14, 32]
# # 第 2 层卷积
conv2 = tf.layers.conv2d(
inputs=pool1, # 形状 [14, 14, 32]
filters=64, # 64 个过滤器,输出的深度(depth)是64
kernel_size=[5, 5], # 过滤器在二维的大小是 (5 * 5)
strides=1, # 步长是 1
padding='same', # same 表示输出的大小不变,因此需要在外围补零 2 圈
activation=tf.nn.relu # 激活函数是 Relu
) # 形状 [14, 14, 64]
# # 第 2 层池化(亚采样)
pool2 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(
inputs=conv2, # 形状 [14, 14, 64]
pool_size=[2, 2], # 过滤器在二维的大小是(2 * 2)
strides=2 # 步长是 2
) # 形状 [7, 7, 64]
# # 平坦化(flat)。降维
flat = tf.reshape(pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64]) # 形状 [7 * 7 * 64, ]
# # 1024 个神经元的全连接层
dense = tf.layers.dense(inputs=flat, units=1024, activation=tf.nn.relu)
# # Dropout : 丢弃 50%(rate=0.5)
dropout = tf.layers.dropout(inputs=dense, rate=0.5)
# 10 个神经元的全连接层,这里不用激活函数来做非线性化了
logits = tf.layers.dense(inputs=dropout, units=10) # 输出。形状 [1, 1, 10]
# 卷积神经网络的优化过程
# # 计算误差(先用 Softmax 计算百分比概率,再用 Cross entropy(交叉熵)来计算百分比概率和对应的独热码之间的误差)
loss = tf.losses.softmax_cross_entropy(onehot_labels=output_y, logits=logits)
# # Adam 优化器来最小化误差,学习率 0.001
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.001).minimize(loss)
# # 精度。计算 预测值 和 实际标签 的匹配程度
# # 返回 (accuracy, update_op), 会创建两个局部变量
accuracy = tf.metrics.accuracy(
labels=tf.argmax(output_y, axis=1),
predictions=tf.argmax(logits, axis=1))[1]
# # 创建会话
sess = tf.Session()
# # 初始化变量:全局和局部
init = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.local_variables_initializer())
# # 变量生效
sess.run(init)
# 训练过程
# # 训练 5000 步。这个步数可以调节
for i in range(5000):
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(50) # 从 Train(训练)数据集里取 “下一个” 50 个样本
train_loss, train_op_ = sess.run([loss, train_op], {input_x: batch[0], output_y: batch[1]})
if i % 100 == 0:
test_accuracy = sess.run(accuracy, {input_x: test_x, output_y: test_y})
print("第 {} 步的训练损失={:.4f}, 测试精度={:.2f}".format(i, train_loss, test_accuracy))
# 测试过程
# # 测试:打印 20 个预测值 和 真实值
test_output = sess.run(logits, {input_x: test_x[:20]})
inferred_y = np.argmax(test_output, 1)
print(inferred_y, '推测的数字') # 推测的数字
print(np.argmax(test_y[:20], 1), '真实的数字') # 真实的数字
# # 关闭会话
sess.close()
**
2. Keras
**
import numpy as np
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.utils import np_utils
from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Convolution2D, MaxPooling2D, Flatten
from keras.optimizers import Adam
# 载入数据
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
# (60000, 28, 28) -> (60000, 28, 28, 1)
x_train = x_train.reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1)/255.0
x_test = x_test.reshape(-1, 28, 28, 1)/255.0
# 换one hot格式
y_train = np_utils.to_categorical(y_train, num_classes=10)
y_test = np_utils.to_categorical(y_test, num_classes=10)
# 定义顺序模型
model = Sequential()
# 第一个卷积层
# input_shape 输入平面
# filters卷积核/滤波器个数
# kernel_size卷积窗口大小
# strides步长
# padding方式
# activation激活函数
model.add(Convolution2D(
input_shape = (28, 28, 1),
filters = 32,
kernel_size = 5,
strides = 1,
padding = "same",
activation = "relu"))
# 第一个池化层
model.add(MaxPooling2D(
pool_size = 2,
strides = 2,
padding = 'same',
))
# 第二个卷积层
model.add(Convolution2D(64,5,strides=1,padding='same',activation = 'relu'))
# 第二个池化层
model.add(MaxPooling2D(2,2,'same'))
# 把第二个池化层的输出扁平化为1维
model.add(Flatten())
# 第一个全连接层
model.add(Dense(1024,activation = 'relu'))
# Dropout
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
# 第二个全连接层
model.add(Dense(10,activation='softmax'))
# 定义优化器
adam = Adam(lr=1e-4)
# 定义优化器,loss function,训练过程中计算准确率
model.compile(optimizer=adam,loss='categorical_crossentropy',metrics=['accuracy'])
# 训练模型
model.fit(x_train,y_train,batch_size=64,epochs=10)
# 评估模型
loss,accuracy = model.evaluate(x_test,y_test)
print('test loss',loss)
print('test accuracy',accuracy)