java使用递归,非递归方式实现二叉树的三种常见遍历方式
二叉树的定义:
二叉树(binary tree)是结点的有限集合,这个集合或者空,或者由一个根及两个互不相交的称为这个根的左子树或右子树构成.
从定义可以看出,二叉树包括:1.空树 2.只有一个根节点 3.只有左子树 4.只有右子树 5.左右子树都存在 有且仅有这5中表现形式 二叉树的特点:
- 性质1:在二叉树的第i层上至多有2^(i-1)个节点(i >= 1)
- 性质2:深度为k的二叉树至多有2^(k-1)个节点(k >=1)
- 性质3:对于任意一棵二叉树T而言,其叶子节点数目为N0,度为2的节点数目为N2,则有N0 = N2 + 1。
- 性质4:具有n个节点的完全二叉树的深度 。
二叉树的遍历
二叉树的遍历分为三种:前序遍历 中序遍历 后序遍历
- 前序遍历:按照“根左右”,先遍历根节点,再遍历左子树 ,再遍历右子树
- 中序遍历:按照“左根右“,先遍历左子树,再遍历根节点,最后遍历右子树
- 后续遍历:按照“左右根”,先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树,最后遍历根节点
其中前,后,中指的是每次遍历时候的根节点被遍历的顺序
============
特殊的二叉树:
(1)斜树:顾名思义,斜树一定是要斜的;所有的结点都只有左子树的二叉树叫左斜树,所有的结点都只有右子树的二叉树叫右斜树;其实,线性表就可以理解为树的一种特殊的表现形式;
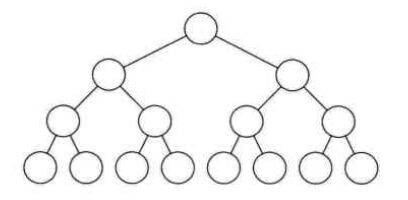
(2)满二叉树:在一棵二叉树中,如果所有分支结点都存在左子树和右子树,并且所有叶子都在同一层上,这样的二叉树称为满二叉树;如图:
(3)完全二叉树:对一棵具有n个结点的二叉树按层序编号,如果编号为i的结点与同样深度的满二叉树中编号为i的结点在二叉树中位置完全相同,那么这棵二叉树称为完全二叉树;或者这样理解:在一棵二叉树中,除最后一层外,若其余层都是满的,并且最后一层或者是满的,或者是右边缺少连续若干个结点,则称此树为完全二叉树;
所以我们可以这样判断完全二叉树:那就是看着树的示意图,心中默默给每个结点按照满二叉树的结构逐层顺序编号,如果编号出现空档,就说明不是完全二叉树,否则就是;
二叉树的实现:同样,二叉树也可以通过顺序存储和链式存储来实现;
二叉树的顺序存储就是用一维数组存储二叉树中的结点,并且结点的存储位置,也就是数组的下标要能体现结点之间的逻辑关系,比如父结点与子结点的逻辑关系,子结点 与子结点之间的关系;但顺序存储的实用性不强;
所以一般采用链式存储;
二叉树的遍历:是指从根结点出发,按照某种次序,依次访问二叉树中所有结点,使得每个结点被访问一次且仅被访问一次;
二叉树的遍历方式有好多种,如果我们限制了从左到右的习惯方式,那么主要就有以下几种:
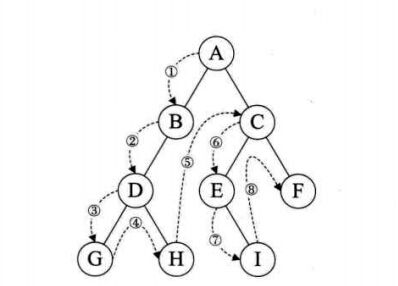
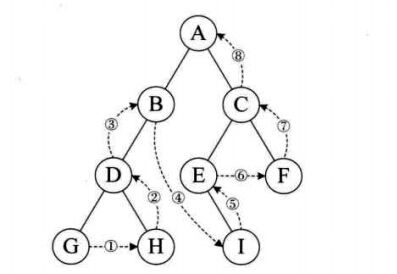
(1)前序遍历:先访问子结点,然后前序遍历左子树,再前序遍历右子树;如下图,遍历顺序是:ABDGHCEIF
(2)中序遍历:从根结点开始(但并不是先访问根结点),中序遍历根结点的左子树,然后方式根结点,最后中序遍历右树,如图,遍历的顺序是:GDHBAEICF
(3)后序遍历:从左到右先叶子后结点的方式遍历访问左右子树,最后是访问根结点;如图,遍历的顺序是:GHDBIEFCA
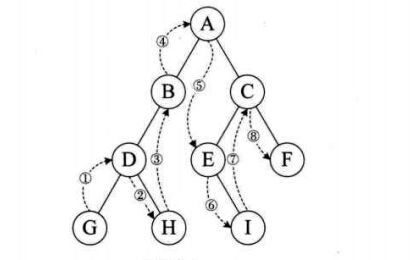
(4)层序遍历:从树的第一层,也就是根结点开始访问,从上而下逐层遍历,在同一层中,按从左到右的顺序对结点进行逐个访问;如图,遍历顺序为:ABCDEFGHI
二叉树遍历的java实现
package test.tree;
public class TreeNode {
public int key;
public String data;
public TreeNode leftChild;
public TreeNode rightChild;
public boolean isVisted=false;
public TreeNode() {
}
public TreeNode(int key, String data) {
this.key = key;
this.data = data;
}
public TreeNode(int key, String data, TreeNode leftChild,
TreeNode rightChild) {
this.key = key;
this.data = data;
this.leftChild = leftChild;
this.rightChild = rightChild;
}
}
package test.tree;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
public class BinaryTree {
private TreeNode root=null;
public BinaryTree(){
root=new TreeNode(1,"rootNode(A)");
}
/**
* 创建一棵二叉树
*
* A
* B C
* D E F
* X M N
*
* @param root
*/
public void createBinTree(TreeNode root){
TreeNode newNodeB = new TreeNode(2,"B");
TreeNode newNodeC = new TreeNode(3,"C");
TreeNode newNodeD = new TreeNode(4,"D");
TreeNode newNodeE = new TreeNode(5,"E");
TreeNode newNodeF = new TreeNode(6,"F");
root.leftChild=newNodeB;
root.rightChild=newNodeC;
root.leftChild.leftChild=newNodeD;
root.leftChild.rightChild=newNodeE;
root.rightChild.rightChild=newNodeF;
root.leftChild.rightChild.leftChild = new TreeNode(7, "M");
root.leftChild.rightChild.rightChild = new TreeNode(8,"N");
root.leftChild.leftChild.rightChild= new TreeNode(9,"X");
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return root==null;
}
//树的高度
public int height(){
return height(root);
}
//节点个数
public int size(){
return size(root);
}
private int height(TreeNode subTree){
if(subTree==null)
return 0;//递归结束:空树高度为0
else{
int i=height(subTree.leftChild);
int j=height(subTree.rightChild);
return (i stack=new Stack();
TreeNode node=p;
while(node!=null||stack.size()>0){
while(node!=null){
visted(node);
stack.push(node);
node=node.leftChild;
}
if(stack.size()>0){
node=stack.pop();
node=node.rightChild;
}
}
}
public void preTraversal(TreeNode p ){
Stack a = new Stack();
a.push(p);
TreeNode t;
while( !a.isEmpty() ){
t = a.pop();
while( t!=null){
System.out.println(t.data);
if(t.rightChild!=null)
{a.push(t.rightChild);}
t = t.leftChild;
}
}
}
//中序遍历的非递归实现
public void nonRecInOrder(TreeNode p){
Stack stack =new Stack();
TreeNode node =p;
while(node!=null||stack.size()>0){
//存在左子树
while(node!=null){
stack.push(node);
node=node.leftChild;
}
//栈非空
if(stack.size()>0){
node=stack.pop();
visted(node);
node=node.rightChild;
}
}
}
//后序遍历的非递归实现
public void noRecPostOrder(TreeNode p){
Stack stack=new Stack();
TreeNode node =p;
while(p!=null){
//左子树入栈
for(;p.leftChild!=null;p=p.leftChild){
stack.push(p);
}
//当前结点无右子树或右子树已经输出
while(p!=null&&(p.rightChild==null||p.rightChild==node)){
visted(p);
//纪录上一个已输出结点
node =p;
if(stack.empty())
return;
p=stack.pop();
}
//处理右子树
stack.push(p);
p=p.rightChild;
}
}
public void visted(TreeNode subTree){
subTree.isVisted=true;
System.out.println("key:"+subTree.key+"--name:"+subTree.data);;
}
//层次遍历
public void levelIterator(TreeNode n){
Queue queue = new LinkedList();
queue.offer(n);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode t = queue.poll();
if (t !=null) {
visted(t);
}
if (t.leftChild !=null) {
queue.offer(t.leftChild);
}
if (t.rightChild !=null) {
queue.offer(t.rightChild);
}
}
}
//测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree();
bt.createBinTree(bt.root);
System.out.println("the size of the tree is " + bt.size());
System.out.println("the height of the tree is " + bt.height());
System.out.println("*******(前序遍历)遍历*****************");
bt.preOrder(bt.root);
System.out.println("*******(中序遍历)遍历*****************");
bt.inOrder(bt.root);
System.out.println("*******(后序遍历)遍历*****************");
bt.postOrder(bt.root);
System.out.println("***非递归实现****(前序遍历)遍历*****************");
bt.nonRecPreOrder(bt.root);
bt.preTraversal(bt.root);
System.out.println("层次遍历*****************");
bt.levelIterator(bt.root);
System.out.println("***非递归实现****(中序遍历)遍历*****************");
bt.nonRecInOrder(bt.root);
System.out.println("***非递归实现****(后序遍历)遍历*****************");
bt.noRecPostOrder(bt.root);
}
}