Deep Leaning 学习笔记之改善神经网络的超参数(2.2)——优化算法的运行速度(实例)
1 mini-batch Gradient Descent
1.1 步骤概念
-
将样本随机打乱(确保X和Y一起打乱,保证X与lableY仍然相对应)
-
permutation = list(np.random.permutation(m))
shuffled_X = X[:, permutation]
shuffled_Y = Y[:, permutation].reshape((1,m)) -
划分小批量
# Step 2: Partition (shuffled_X, shuffled_Y). Minus the end case.
num_complete_minibatches = math.floor(m/mini_batch_size) # number of mini batches of size mini_batch_size in your partitionning
for k in range(0, num_complete_minibatches):
### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines)
mini_batch_X = shuffled_X[:,(k)*mini_batch_size:(k+1)*mini_batch_size]
mini_batch_Y = shuffled_Y[:,(k)*mini_batch_size:(k+1)*mini_batch_size]
### END CODE HERE ###
mini_batch = (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y)
mini_batches.append(mini_batch)
# Handling the end case (last mini-batch < mini_batch_size)
if m % mini_batch_size != 0:
### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines)
mini_batch_X = shuffled_X[:,mini_batch_size*(math.floor(m/mini_batch_size)):m]
mini_batch_Y = shuffled_Y[:,mini_batch_size*(math.floor(m/mini_batch_size)):m]
### END CODE HERE ###
mini_batch = (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y)
mini_batches.append(mini_batch)
- 洗牌和分区是构建小型批所需的两个步骤
2的幂通常选择为小批大小,例如,16、32、64、128。
2. 动量Momentum
也就是V值等等的一系列操作
2.1 初始化initialize_velocity
# GRADED FUNCTION: initialize_velocity
def initialize_velocity(parameters):
"""
Initializes the velocity as a python dictionary with:
- keys: "dW1", "db1", ..., "dWL", "dbL"
- values: numpy arrays of zeros of the same shape as the corresponding gradients/parameters.
Arguments:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters.
parameters['W' + str(l)] = Wl
parameters['b' + str(l)] = bl
Returns:
v -- python dictionary containing the current velocity.
v['dW' + str(l)] = velocity of dWl
v['db' + str(l)] = velocity of dbl
"""
L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural networks
v = {}
# Initialize velocity
for l in range(L):
### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines)
v["dW" + str(l+1)] = np.zeros((parameters['W'+str(l+1)].shape[0],parameters['W'+str(l+1)].shape[1]))
v["db" + str(l+1)] = np.zeros((parameters['b'+str(l+1)].shape[0],parameters['b'+str(l+1)].shape[1]))
### END CODE HERE ###
return v
2.2 更新参数with动量
# GRADED FUNCTION: update_parameters_with_momentum
def update_parameters_with_momentum(parameters, grads, v, beta, learning_rate):
"""
Update parameters using Momentum
Arguments:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters:
parameters['W' + str(l)] = Wl
parameters['b' + str(l)] = bl
grads -- python dictionary containing your gradients for each parameters:
grads['dW' + str(l)] = dWl
grads['db' + str(l)] = dbl
v -- python dictionary containing the current velocity:
v['dW' + str(l)] = ...
v['db' + str(l)] = ...
beta -- the momentum hyperparameter, scalar
learning_rate -- the learning rate, scalar
Returns:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your updated parameters
v -- python dictionary containing your updated velocities
"""
L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural networks
# Momentum update for each parameter
for l in range(L):
### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 4 lines)
# compute velocities
v["dW" + str(l+1)] = beta*v["dW" + str(l)]+(1-beta*v["dW" + str(l+1)])
v["db" + str(l+1)] = beta*v["db" + str(l)]+(1-beta*v["db" + str(l+1)])
# update parameters
parameters["W" + str(l+1)] = parameters["W" + str(l+1)] - learning_rate*v["dW" + str(l+1)]
parameters["b" + str(l+1)] = parameters["b" + str(l+1)] - learning_rate*v["db" + str(l+1)]
### END CODE HERE ###
return parameters, v
3.Adam算法
Adam算法是训练神经网络最有效的优化算法之一。它结合了RMSProp(在讲座中描述)和Momentum的思想。
How does Adam work?
- 它计算过去梯度的指数加权平均值,并将其存储在变量 v v v(偏差校正前)和 v c o r r e c t e d v^{corrected} vcorrected(偏差校正后)中。
- 它计算过去梯度的平方的指数加权平均值,并将其存储在变量 s s s(偏差校正前)和 s c o r r e c t e d s^{corrected} scorrected{纠正后)中。
- 它根据来自“1”和“2”的信息组合的方向更新参数。
The update rule is, for l = 1 , . . . , L l = 1, ..., L l=1,...,L:
{ v d W [ l ] = β 1 v d W [ l ] + ( 1 − β 1 ) ∂ J ∂ W [ l ] v d W [ l ] c o r r e c t e d = v d W [ l ] 1 − ( β 1 ) t s d W [ l ] = β 2 s d W [ l ] + ( 1 − β 2 ) ( ∂ J ∂ W [ l ] ) 2 s d W [ l ] c o r r e c t e d = s d W [ l ] 1 − ( β 2 ) t W [ l ] = W [ l ] − α v d W [ l ] c o r r e c t e d s d W [ l ] c o r r e c t e d + ε \begin{cases} v_{dW^{[l]}} = \beta_1 v_{dW^{[l]}} + (1 - \beta_1) \frac{\partial \mathcal{J} }{ \partial W^{[l]} } \\ v^{corrected}_{dW^{[l]}} = \frac{v_{dW^{[l]}}}{1 - (\beta_1)^t} \\ s_{dW^{[l]}} = \beta_2 s_{dW^{[l]}} + (1 - \beta_2) (\frac{\partial \mathcal{J} }{\partial W^{[l]} })^2 \\ s^{corrected}_{dW^{[l]}} = \frac{s_{dW^{[l]}}}{1 - (\beta_2)^t} \\ W^{[l]} = W^{[l]} - \alpha \frac{v^{corrected}_{dW^{[l]}}}{\sqrt{s^{corrected}_{dW^{[l]}}} + \varepsilon} \end{cases} ⎩⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎧vdW[l]=β1vdW[l]+(1−β1)∂W[l]∂JvdW[l]corrected=1−(β1)tvdW[l]sdW[l]=β2sdW[l]+(1−β2)(∂W[l]∂J)2sdW[l]corrected=1−(β2)tsdW[l]W[l]=W[l]−αsdW[l]corrected+εvdW[l]corrected
where:
- t 计算了 Adam 的步数
- L 是神经网络的层数
- β 1 \beta_1 β1 and β 2 \beta_2 β2 是控制两个指数加权平均的超参数。
- α \alpha α is the learning rate
- ε \varepsilon ε 防止除数为0 的非常小的数
As usual, we will store all parameters in the parameters dictionary
3.1 初始化参数
# GRADED FUNCTION: initialize_adam
def initialize_adam(parameters) :
"""
Initializes v and s as two python dictionaries with:
- keys: "dW1", "db1", ..., "dWL", "dbL"
- values: numpy arrays of zeros of the same shape as the corresponding gradients/parameters.
Arguments:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters.
parameters["W" + str(l)] = Wl
parameters["b" + str(l)] = bl
Returns:
v -- python dictionary that will contain the exponentially weighted average of the gradient.
v["dW" + str(l)] = ...
v["db" + str(l)] = ...
s -- python dictionary that will contain the exponentially weighted average of the squared gradient.
s["dW" + str(l)] = ...
s["db" + str(l)] = ...
"""
L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural networks
v = {}
s = {}
# Initialize v, s. Input: "parameters". Outputs: "v, s".
for l in range(L):
### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 4 lines)
v["dW" + str(l+1)] = np.zeros((parameters["W" + str(l+1)].shape[0],parameters["W" + str(l+1)].shape[1]))
v["db" + str(l+1)] = np.zeros((parameters["b" + str(l+1)].shape[0],parameters["b" + str(l+1)].shape[1]))
s["dW" + str(l+1)] = np.zeros((parameters["W" + str(l+1)].shape[0],parameters["W" + str(l+1)].shape[1]))
s["db" + str(l+1)] = np.zeros((parameters["b" + str(l+1)].shape[0],parameters["b" + str(l+1)].shape[1]))
### END CODE HERE ###
return v, s
3.2 更新参数
# GRADED FUNCTION: update_parameters_with_adam
def update_parameters_with_adam(parameters, grads, v, s, t, learning_rate = 0.01,
beta1 = 0.9, beta2 = 0.999, epsilon = 1e-8):
"""
Update parameters using Adam
Arguments:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters:
parameters['W' + str(l)] = Wl
parameters['b' + str(l)] = bl
grads -- python dictionary containing your gradients for each parameters:
grads['dW' + str(l)] = dWl
grads['db' + str(l)] = dbl
v -- Adam variable, moving average of the first gradient, python dictionary
s -- Adam variable, moving average of the squared gradient, python dictionary
learning_rate -- the learning rate, scalar.
beta1 -- Exponential decay hyperparameter for the first moment estimates
beta2 -- Exponential decay hyperparameter for the second moment estimates
epsilon -- hyperparameter preventing division by zero in Adam updates
Returns:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your updated parameters
v -- Adam variable, moving average of the first gradient, python dictionary
s -- Adam variable, moving average of the squared gradient, python dictionary
"""
L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layers in the neural networks
v_corrected = {} # Initializing first moment estimate, python dictionary
s_corrected = {} # Initializing second moment estimate, python dictionary
# Perform Adam update on all parameters
for l in range(L):
# Moving average of the gradients. Inputs: "v, grads, beta1". Output: "v".
### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines)
v["dW" + str(l+1)] = beta1*v["dW" + str(l+1)]+(1-beta1)*grads["dW" + str(l+1)]
v["db" + str(l+1)] = beta1*v["db" + str(l+1)]+(1-beta1)*grads["db" + str(l+1)]
### END CODE HERE ###
# Compute bias-corrected first moment estimate. Inputs: "v, beta1, t". Output: "v_corrected".
### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines)
v_corrected["dW" + str(l+1)] = v["dW" + str(l+1)]/(1-beta1**t)
v_corrected["db" + str(l+1)] = v["db" + str(l+1)]/(1-beta1**t)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Moving average of the squared gradients. Inputs: "s, grads, beta2". Output: "s".
### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines)
s["dW" + str(l+1)] = beta2*s["dW" + str(l+1)]+(1-beta2)*np.square(grads["dW" + str(l+1)])
s["db" + str(l+1)] = beta2*s["db" + str(l+1)]+(1-beta2)*np.square(grads["db" + str(l+1)])
### END CODE HERE ###
# Compute bias-corrected second raw moment estimate. Inputs: "s, beta2, t". Output: "s_corrected".
### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines)
s_corrected["dW" + str(l+1)] = s["dW" + str(l+1)]/(1-beta2**t)
s_corrected["db" + str(l+1)] = s["db" + str(l+1)]/(1-beta2**t)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Update parameters. Inputs: "parameters, learning_rate, v_corrected, s_corrected, epsilon". Output: "parameters".
### START CODE HERE ### (approx. 2 lines)
parameters["W" + str(l+1)] = parameters["W" + str(l+1)] - learning_rate*(v_corrected["dW" + str(l+1)]/(np.sqrt(s_corrected["dW" + str(l+1)])+epsilon))
parameters["b" + str(l+1)] = parameters["b" + str(l+1)] - learning_rate*(v_corrected["db" + str(l+1)]/(np.sqrt(s_corrected["db" + str(l+1)])+epsilon))
### END CODE HERE ###
return parameters, v, s
4.总体模型对比(gd,mini-batch,Adam)
4.1 Model
def model(X, Y, layers_dims, optimizer, learning_rate = 0.0007, mini_batch_size = 64, beta = 0.9,
beta1 = 0.9, beta2 = 0.999, epsilon = 1e-8, num_epochs = 10000, print_cost = True):
"""
3-layer neural network model which can be run in different optimizer modes.
Arguments:
X -- input data, of shape (2, number of examples)
Y -- true "label" vector (1 for blue dot / 0 for red dot), of shape (1, number of examples)
layers_dims -- python list, containing the size of each layer
learning_rate -- the learning rate, scalar.
mini_batch_size -- the size of a mini batch
beta -- Momentum hyperparameter
beta1 -- Exponential decay hyperparameter for the past gradients estimates
beta2 -- Exponential decay hyperparameter for the past squared gradients estimates
epsilon -- hyperparameter preventing division by zero in Adam updates
num_epochs -- number of epochs
print_cost -- True to print the cost every 1000 epochs
Returns:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your updated parameters
"""
L = len(layers_dims) # number of layers in the neural networks
costs = [] # to keep track of the cost
t = 0 # initializing the counter required for Adam update
seed = 10 # For grading purposes, so that your "random" minibatches are the same as ours
# Initialize parameters
parameters = initialize_parameters(layers_dims)
# Initialize the optimizer
if optimizer == "gd":
pass # no initialization required for gradient descent
elif optimizer == "momentum":
v = initialize_velocity(parameters)
elif optimizer == "adam":
v, s = initialize_adam(parameters)
# Optimization loop
for i in range(num_epochs):
# Define the random minibatches. We increment the seed to reshuffle differently the dataset after each epoch
seed = seed + 1
minibatches = random_mini_batches(X, Y, mini_batch_size, seed)
cost = 0
for minibatch in minibatches:
# Select a minibatch
(minibatch_X, minibatch_Y) = minibatch
# Forward propagation
a3, caches = forward_propagation(minibatch_X, parameters)
# Compute cost
cost += compute_cost(a3, minibatch_Y)
# Backward propagation
grads = backward_propagation(minibatch_X, minibatch_Y, caches)
# Update parameters
if optimizer == "gd":
parameters = update_parameters_with_gd(parameters, grads, learning_rate)
elif optimizer == "momentum":
parameters, v = update_parameters_with_momentum(parameters, grads, v, beta, learning_rate)
elif optimizer == "adam":
t = t + 1 # Adam counter
parameters, v, s = update_parameters_with_adam(parameters, grads, v, s,
t, learning_rate, beta1, beta2, epsilon)
# Print the cost every 1000 epoch
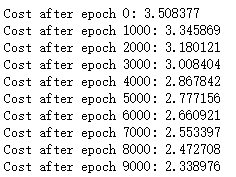
if print_cost and i % 1000 == 0:
print ("Cost after epoch %i: %f" %(i, cost))
if print_cost and i % 100 == 0:
costs.append(cost)
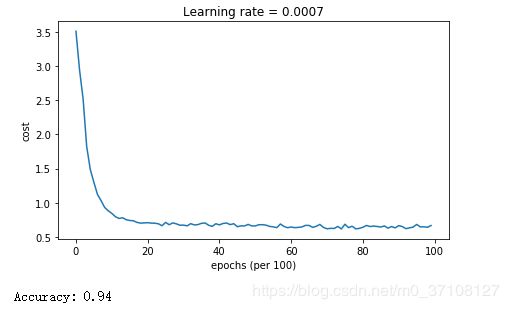
# plot the cost
plt.plot(costs)
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('epochs (per 100)')
plt.title("Learning rate = " + str(learning_rate))
plt.show()
return parameters
4.2 Compare——GD
4.3 mini-batch GD with momentum
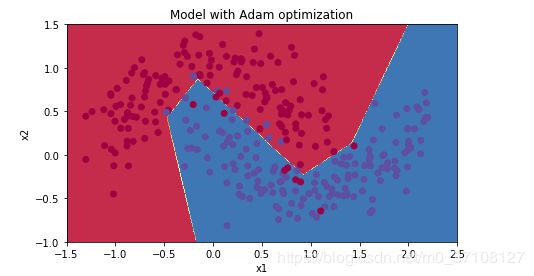
4.4 - Mini-batch with Adam mode
5.总结
| optimization method | accuracy | cost shape |
| Gradient descent | 79.7% | oscillations |
| Momentum | 79.7% | oscillations |
| Adam | 94% | smoother |
- 动量通常是有帮助的,但是考虑到较小的学习速度和简单的数据集,它的影响几乎是可以忽略的。
- 此外,您在成本中看到的巨大振荡来自于这样一个事实,即一些小批量比其他优化算法更困难。另一方面,Adam明显优于小批量梯度下降和动量。如果您在这个简单的数据集中运行模型更长的时间,那么这三种方法都将带来非常好的结果。不过,你已经看到Adam收敛得更快了。
- Adam的一些优势包括:内存需求相对较低(尽管高于动量梯度下降法和梯度下降)通常可以用的调优很hyperparameters(除了α)