JAVA实现对已有数据库的插入、删除、更改、查询操作详细解释
摘要:
本文将详细讲述,java如何对sqlite数据库进行插入,删除,更改和查询,本文附有详细的代码和代码的注释,也有对应代码的运行结果图,以便大家理解此处的代码!
注:
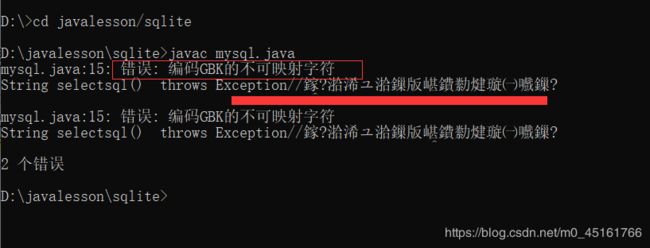
- 由于部分人个人电脑的设置问题,运行代码是不能出现中文,所以当出现如下报错时,请删除代码中的注释文字!
- 如需绿色版 SQlite数据库安装包,请参见博主上一篇文章:JAVA对SQlite数据库的安装配置和一些基本操作指令
一、java实现对已有数据库数据的查询
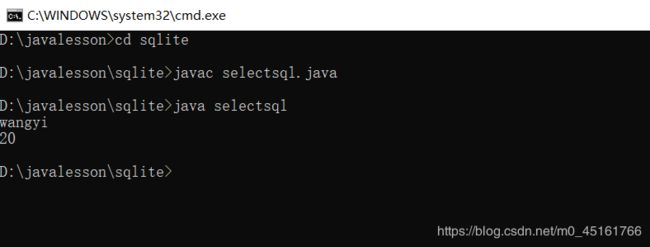
1、面向过程的查询方式
(1)实现代码
import java.sql.*;//对于任何数据库操作都要添加sql这个包
class selectsql
{
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception//应为要加载驱动文件,涉及到文件的iO,所以要抛出异常
{
Class.forName("org.sqlite.JDBC");//加载一个驱动文档,文档名叫org.sqlite.JDBC
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:sqlite:testdb.db");
//与数据进行连接,"jdbc:sqlite:testdb.db"中的意义是,jdbc的java数据库桥式连接到sqlite,sqlite连接到testdb.db数据库上
Statement st=con.createStatement();//Statement报表
ResultSet rs=st.executeQuery("select*from student");//对报表执行查询操作,赋值给结果集ResultSet
while(rs.next())
{
System.out.println(rs.getString(1));//打印第一个字段名---name
System.out.println(rs.getString(2));//打印第二个字段名---age
}
rs.close();//结果对象及关闭
st.close();//报表关闭
con.close();//连接对象关闭
}
}
1. 实现简单全部数据的查询
(1)实现代码
import java.sql.*;
class mysql
{
Connection con;
Statement st;
ResultSet rs;
mysql()
{
try{
Class.forName("org.sqlite.JDBC");//加载驱动
con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:sqlite:testdb.db");//创建连接对象
st=con.createStatement();//创建报表对象,通过连接对象的createStatement方法实现
}catch(Exception e){}
}
String selectsql() throws Exception
{
String str="";
String sql="select * from student";
rs=st.executeQuery(sql);
while (rs.next())
{
str+=rs.getString(1)+":"+rs.getString(2)+"\n";
}
return str;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
mysql m=new mysql();
System.out.println(m.selectsql());
}
}
2. 按照给定条件进行的高级查询方式
(1)实现代码
import java.sql.*;
class mysql
{
Connection con;
Statement st;
ResultSet rs;
mysql()
{
try{
Class.forName("org.sqlite.JDBC");
con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:sqlite:testdb.db");
st=con.createStatement();
}catch(Exception e){}
}
String selectsql(String name) throws Exception//定义查询函数
{
String str="";
String sql="select*from student where name=?";
//因为student表中都是常量,如何给这里加一个变量,这里就用‘?’来占位,之后对?进行处理
PreparedStatement ps=con.prepareStatement(sql);//创建报表对象,通过连接对象的prepareStatement方法实现
ps.setString(1, name);//设置的参数类型是字符型,给的是第一个问号,赋给的变量是name
rs=ps.executeQuery();
while (rs.next())
{
str+=rs.getString(1)+":"+rs.getString(2)+"\n";
}
return str;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
mysql m=new mysql();
System.out.println(m.selectsql("lier"));
}
}
二、java实现对已有数据库数据的更新
1、面向过程的更新数据方式
(1)实现代码
import java.sql.*;
class sqlall
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
Class.forName("org.sqlite.JDBC");
Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:sqlite:testdb.db");
Statement st=con.createStatement();
String sql="update student set age=30 where name='lier'";
st.execute(sql);
st.close();
con.close();
}
}
2、面向对象的数据更新方式
(1)实现代码
import java.sql.*;
class mysql
{
Connection con;
Statement st;
ResultSet rs;
mysql()
{
try{
Class.forName("org.sqlite.JDBC");
con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:sqlite:testdb.db");
st=con.createStatement();
}catch(Exception e){}
}
String selectsql() throws Exception
{
String str="";
String sql="select * from student";
rs=st.executeQuery(sql);
while (rs.next())
{
str+=rs.getString(1)+":"+rs.getString(2)+"\n";
}
return str;
}
void updatesql(String name,int age) throws Exception
{
String sql="update student set age=? where name=?";
PreparedStatement pstmt=con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setInt(1,age);
pstmt.setString(2,name);
pstmt.executeUpdate();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
mysql m=new mysql();
m.updatesql("zhaoqi",26);
System.out.println(m.selectsql());
}
}
三、java实现对已有数据库数据的插入
1、面向过程的插入数据
(1)实现代码
import java.sql.*;
class sqlall
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
Class.forName("org.sqlite.JDBC");
Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:sqlite:testdb.db");
Statement st=con.createStatement();
String sql="insert into student(name,age) values('lier',25)";
st.execute(sql);
st.close();
con.close();
}
}
## 2、面向对象的插入数据方式
(1)实现代码
import java.sql.*;
class mysql
{
Connection con;
Statement st;
ResultSet rs;
mysql()
{
try{
Class.forName("org.sqlite.JDBC");
con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:sqlite:testdb.db");
st=con.createStatement();
}catch(Exception e){}
}
String selectsql() throws Exception//查询方法
{
String str="";
String sql="select * from student";
rs=st.executeQuery(sql);
while (rs.next())
{
str+=rs.getString(1)+":"+rs.getString(2)+"\n";
}
return str;
}
void insertnewsql(String name,int age) throws Exception//插入方法
{
String sql="insert into student (name,age) values(?,?)";
PreparedStatement pstmt=con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1,name);//设置第一个问号为字符型,赋值给name
pstmt.setInt(2,age);//设置第二个问号为整型,赋值给age
pstmt.executeUpdate();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
mysql m=new mysql();
m.insertnewsql("zhaoqi",69);//插入数据
System.out.println(m.selectsql());//调用查询方法
}
}
(2)执行结果

3、面向对象的高级插入方式,实现插入时若已有数据则更新,没有数据则插入
(1)实现代码
import java.sql.*;
class mysql
{
Connection con;
Statement st;
ResultSet rs;
mysql()
{
try{
Class.forName("org.sqlite.JDBC");
con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:sqlite:testdb.db");
st=con.createStatement();
}catch(Exception e){}
}
void insertnewsql(String name,int age) throws Exception//插入函数
{
String sql="insert into student (name,age) values(?,?)";
PreparedStatement pstmt=con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1,name);
pstmt.setInt(2,age);
pstmt.executeUpdate();
}
String selectsql() throws Exception//所有以有数据的查询函数
{
String str="";
String sql="select * from student";
rs=st.executeQuery(sql);
while (rs.next())
{
str+=rs.getString(1)+":"+rs.getString(2)+"\n";
}
return str;
}
String selectsql(String name) throws SQLException//变量查询函数
{
String sql="select * from student where name=?";
PreparedStatement pstmt=con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1,name);
String str="";
rs=pstmt.executeQuery();
if(rs.next())
str=rs.getString(1)+":"+rs.getString(2)+"\n";
return str;
}
void updatesql(String name,int age) throws Exception//更新函数
{
String sql="update student set age=? where name=?";
PreparedStatement pstmt=con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setInt(1,age);
pstmt.setString(2,name);
pstmt.executeUpdate();
}
void insertsql(String name,int age) throws Exception
{
if (selectsql(name).equals(""))
insertnewsql(name,age);
else
updatesql(name,age);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
mysql m=new mysql();
m.insertsql("wangyi",47);
System.out.println(m.selectsql());
}
}
四、java实现对已有数据库数据的删除
1、面向过程的数据删除方式
(1)实现代码
import java.sql.*;
class sqlall
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
Class.forName("org.sqlite.JDBC");
Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:sqlite:testdb.db");
Statement st=con.createStatement();
String sql="delete from student where name='zhaoqi'";
st.execute(sql);
st.close();
con.close();
}
}
2、面向对象的数据删除方式
(1)实现代码
import java.sql.*;
class mysql
{
Connection con;
Statement st;
ResultSet rs;
mysql()
{
try{
Class.forName("org.sqlite.JDBC");
con=DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:sqlite:testdb.db");
st=con.createStatement();
}catch(Exception e){}
}
String selectsql() throws Exception//所有以有数据的查询函数
{
String str="";
String sql="select * from student";
rs=st.executeQuery(sql);
while (rs.next())
{
str+=rs.getString(1)+":"+rs.getString(2)+"\n";
}
return str;
}
void deletesql(String name) throws Exception//删除函数
{
String sql="delete from student where name=?";
PreparedStatement pstmt=con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1,name);
pstmt.execute();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
mysql m=new mysql();
m.deletesql("wangyi");
System.out.println(m.selectsql());
}
}