tensorflow2.0学习笔记:wide and deep 模型
wide and deep 模型,谷歌16年发布,用于回归和分类。
稀疏特征:离散值–>One-hot编码,比如词表。可叉乘,类似笛卡尔乘积(组合)。
密集特征:向量表达,可计算距离。 Word2vec,带有语义信息,兼容没出现过的特征。
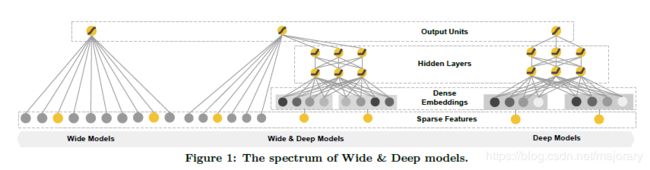
wide model 与 deep model 的结合,从下(输入层)往上(输出层)看,左边输入通过wide model , 右边输入通过 deep model , 之后拼接,输出。左边可以输入密集特征,右边可以是稀疏特征,这也是wide and deep 的优势。
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
import sklearn
import pandas as pd
import os
import sys
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
print(tf.__version__)
2.0.0
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
housing = fetch_california_housing()
# print(housing.DESCR)
# print(housing.data.shape)
# print(housing.target.shape)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x_train_all, x_test, y_train_all, y_test = train_test_split(
housing.data, housing.target, random_state = 7)
x_train, x_valid, y_train, y_valid, = train_test_split(
x_train_all, y_train_all, random_state = 11)
print(x_train.shape, y_train.shape)
print(x_valid.shape, y_valid.shape)
print(x_test.shape, y_test.shape)
(11610, 8) (11610,)
(3870, 8) (3870,)
(5160, 8) (5160,)
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
x_train_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(x_train)
x_valid_scaled = scaler.transform(x_valid)
x_test_scaked = scaler.transform(x_test)
x_train.shape
(11610, 8)
wide and deep 模型的两种实现方式
- 函数式API
- 子类API
1. 函数式API实现
# wide and deep中间有连接的部分,Sequence不再适用了,使用函数式API
# 函数式API,就像一个复合函数:f(x) = h(g(x))
input = keras.layers.Input(shape=x_train.shape[1:])
hidden1 = keras.layers.Dense(30,activation='relu')(input)
hidden2 = keras.layers.Dense(30,activation='relu')(hidden1)
concat = keras.layers.concatenate([input,hidden2]) # 拼接,合并,输入和隐藏层
output = keras.layers.Dense(1)(concat)
model = keras.models.Model(inputs = [input],outputs = [output]) # 函数API,需要固化一个model
model.summary()
model.compile(loss="mean_squared_error", optimizer="adam")
callbacks = [keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(
patience=5, min_delta=1e-2)]
2. 子类API实现
# 使用子类API,定义个一个model,即通过承父类keras.models.Model,定义WideDeepModel子类。
class WideDeepModel(keras.models.Model):
'''初始化函数(承载父类)'''
def __init__(self):
super(WideDeepModel,self).__init__()
'''定义模型的层次'''
self.hidden1_layer = keras.layers.Dense(30,activation='relu')
self.hidden2_layer = keras.layers.Dense(30,activation='relu')
self.output_layer = keras.layers.Dense(1)
def call(self,input):
'''完成模型的正向计算'''
hidden1 = self.hidden1_layer(input)
hidden2 = self.hidden2_layer(hidden1)
concat = keras.layers.concatenate([input,hidden2])
output = self.output_layer(concat)
return output
#创建WideDeepModel对象
model = WideDeepModel()
model.build(input_shape=(None,8)) #调用build函数,建立模型
'''
# 除了使用创建对象,也可以使用Sequential,构建模型。
model = keras.models.Sequential([
WideDeepModel(),
])
model.build(input_shape=(None,8))
'''
model.summary()
model.compile(loss="mean_squared_error", optimizer="adam")
callbacks = [keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(
patience=5, min_delta=1e-2)]
history = model.fit(x_train_scaled, y_train,
validation_data = (x_valid_scaled, y_valid),
epochs = 100,
callbacks = callbacks)
def plot_learning_curves(history):
pd.DataFrame(history.history).plot(figsize=(8, 5))
plt.grid(True)
plt.gca().set_ylim(0, 1)
plt.show()
plot_learning_curves(history)
model.evaluate(x_test_scaled,y_test)