spring-mvc底层实现-1
Spring MVC
Spring MVC是基于servlet功能实现的,通过实现Servlet接口的DispatcherServlet来封装其核心功能实现,通过将请求分派给处理程序,同时带有可配置的处理程序映射、视图解析、本地语言、主题解析以及上传下载文件支持。默认的处理程序是非常简单的Controller接口,只有一个ModelAndView hangleRequest(request, response)方法。Spring提供了一个控制器层次结构,可以派生子类。如果应用程序需要处理用户输入表单,那么可以继承AbstractFormController。如果应用程序需要处理用户输入表单,那么可以继承AbstractWizardFormController。
Web.xml
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0">
<display-name>spring_mvc01display-name>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xmlparam-value>
context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListenerlistener-class>
listener>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvcservlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServletservlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:mvc.xmlparam-value>
init-param>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvcservlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.dourl-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.htmlwelcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.htmwelcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.jspwelcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.htmlwelcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.htmwelcome-file>
<welcome-file>default.jspwelcome-file>
welcome-file-list>
web-app>
1、ContextLoaderListener
对于SpringMVC功能的实现分析。我们首先从web.xml开始,在web.xml文件中我们首先配置的就是ContextLoaderListener。
ContextLoaderListener的作用启动web容器时,自动装配ApplicationContext的配置信息(spring.xml)。因为他实现了ServletContextListener这个接口,在web.xml配置这个监听器,启动容器时,就会默认执行它实现的方法,使用ServletContextListener这个接口,开发者能够在为客户端请求提供服务之前向ServletContext中添加任意的对象。这个对象在ServletContext启动的时候被初始化,然后在ServletContext整个运行期间都是可见的。每一个Web应用都有一个ServletContext与之相关联。ServletContext对象在引用启动时被创建,在引用关闭时被销毁。ServletContext在全局范围内有效,类似于应用中的一个全局变量。
1.1、ServletContextListener
(1)自定义实现ServletContextListener,首先我们创建ServletContextListener,目标是在系统启动时添加自定义的属性,以便于在全局范围内可以随时调用。系统启动的时候会调用ServletContextListener实现类的contextInitialized方法,所以需要在这个方法中实现我们的初始化逻辑:
(2)注册监听器:在web.xml文件中需要注册自定义的监听器:
(3)启动tomcat服务器,我们就能在任意的servlet或者jsp中通过下面的方式来获取我们的初始化参数:
1.2、ContextLoaderListener
ContextLoaderListener实现了ServletContextListener接口,因此在ServletContext启动之后会调用ServletContextListener的contextInitialized方法,那么,我们就从这个函数开始进行分析:
这里涉及了一个常用类WebApplicationContext;在web应用中,我们会用到WebApplicationContext,WebApplicationContext继承自ApplicationContext,在ApplicationContext的基础上又追加了一些特定于Web的操作及属性。其主要实现如下:
(1)检验WebApplicationContext存在性,
(2)创建WebApplicationContext实例,
(3)将实例记录在serveltContext中,
(4)映射当前的类加载器与创建的实例到全局变量currentContextPerThread中。
2、DispatcherServlet
在Spring中,ContextLoaderListener只是辅助功能,用于创建WebApplicationContext类型实例,而真正的逻辑实现其实就是在DispatcherServlet中进行的,DispatcherServlet是实现servlet接口的实现类。servlet是一个java编写的程序,此程序是基于HTTP协议的,在服务器端运行的,是按照servelt规范编写的一个java类。servelt主要是处理客户端的请求并将其结果发送到客户端。Servelt的框架是由两个java包组成,javax.servelt和javax.servlet.http。javax.servlet定义了所有的servlet类都必须实现或扩展的通用接口和类,在javax.servle.http定义了采用HTTP通信协议的HttpServlet类。
2.1、DispatcherServlet的初始化(init() )
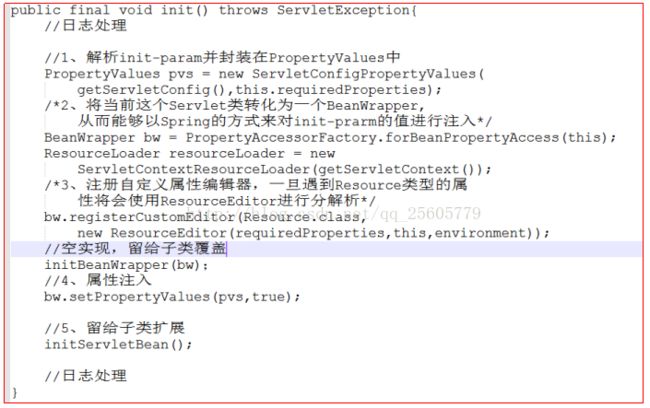
DispatcherServlet的初始化过程主要是通过将当前的servlet类型实例转换为BeanWrapper类型实例,以便使用Spring中提供的注入功能进行对应的属性的注入。属性注入包括:
1)封装及验证初始化参数,
2)将当前servlet实例转化成BeanWrapper实例,
3)注册相对于Resource的属性编辑器,
4)属性注入,
5)servletBean的初始化 。
在ContextLoaderListener加载的时候已经创建了WebApplicationContext实例,而在这个函数中最重要的就是对这个实例进一步的补充初始化:
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
Logger... //日志处理
//对WebApplication进行补充处理
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
Logger... //日志处理
}
2.2、WebApplicationContext的初始化
initWebApplicationContext函数的主要工作就是创建或刷新WebApplicationContext实例并对servlet功能所使用的变量进行初始化。其主要包括以下几个部分:
1)寻找或创建对应的WebApplicationContext实例
2)调用configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext方法来对已经创建的WebApplicationContext实例进行配置及刷新
3)刷新:onRefresh是FrameworkServlet类中提供的模板方法,在其子类DispathcerServlet中进行了重写,主要用于刷新Spring在web功能实现中所必须使用的全局变量。