Flume原理初探:基本执行原理概述
Flume
Flume是一款在数据收集领域使用较多的一个apache的开源工具,是一款分布式、可靠和高可用的系统,能够高效的从不同的源中收集、聚合上传大量的日志数据到结构化的存储模块中,Flume的使用不仅限于日志数据聚合, 由于数据源是可定制的,因此Flume可用于传输大量事件数据,包括但不限于网络流量数据,社交媒体生成的数据,电子邮件消息以及几乎所有可能的数据源。在实际的应用场景中Flume再大数据领域应用较为广泛,本文主要是简单的概述一下Flume的基本的架构流程,本通过官网的配置文件来大致分析一下Flume的工作流程。
Flume架构
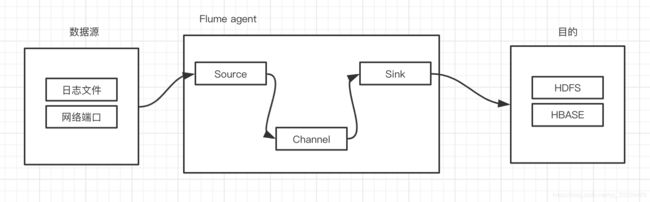
Flume在使用方面比较简单易用,主要通过配置文件来进行上传的数据源的配置、上传到哪里去,并且通过配置不同的通道策略来实现在不同场景下所要求的上传的数据的安全性的问题。这三个方面其实就是对应到Flume中的Source、Sink和Channel三个概念。首先可以查看一下架构图。
首先需要定义需要上传的数据源是什么,监控的数据源可以是文件也可以是监听的一个端口来接受数据,然后通过Flume中定义的Source来抓取对应的数据,获取数据之后就可以通过定义好的Channel来进行数据的转发,一个Source可以往多个Channel中发送这样可以通过对不同Channel将数据发送到不同的远端,并且可以再Channel中定义转发数据的策略,可选择将数据保存在内存中也可以选择将获取的数据保存在文件中,最后达到一定的阈值之后将数据发送到Sink中,Sink中就对应时发送到HDFS还是HABSE或者其他的消费者中,这样就达到了将数据进行消费发送的目的。
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = node1
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
这个配置就是Flume提供的例子,定义了a1的agent信息,a1的sources为r1,即netcat命令监听在44444端口,获取这个端口中传入的数据,a1的sink就是logger即日志的控制台输出,定义的channels就是内存类型,然后将该管道依次绑定到r1和k1上面。
Flume示例流程分析
初始化与配置解析流程
大家可通过官网提供的启动命令启动该配置文件,通过查看bin/flume-ng文件可知启动的入口类为flume-ng-node/src/main/java/org/apache/flume/node/Application.java类;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
SSLUtil.initGlobalSSLParameters();
Options options = new Options();
Option option = new Option("n", "name", true, "the name of this agent"); // 通过命令行启动设置ageent name
option.setRequired(true); // 设置为必须输入
options.addOption(option); // 添加到命令行输入解析选项中
option = new Option("f", "conf-file", true,
"specify a config file (required if -z missing)"); // 获取配置文件
option.setRequired(false);
options.addOption(option);
option = new Option(null, "no-reload-conf", false,
"do not reload config file if changed");
options.addOption(option); // 是否重新加载配置
// Options for Zookeeper
option = new Option("z", "zkConnString", true,
"specify the ZooKeeper connection to use (required if -f missing)"); // 是否连接zk
option.setRequired(false);
options.addOption(option);
option = new Option("p", "zkBasePath", true,
"specify the base path in ZooKeeper for agent configs"); // 配置的zk路径
option.setRequired(false);
options.addOption(option);
option = new Option("h", "help", false, "display help text"); // 展示帮助信息
options.addOption(option);
CommandLineParser parser = new GnuParser();
CommandLine commandLine = parser.parse(options, args); // 解析命令行传入的数据
if (commandLine.hasOption('h')) {
new HelpFormatter().printHelp("flume-ng agent", options, true);
return;
}
String agentName = commandLine.getOptionValue('n'); // 获取agnent名称
boolean reload = !commandLine.hasOption("no-reload-conf"); // 是否在修改完配置文件后自动加载
boolean isZkConfigured = false;
if (commandLine.hasOption('z') || commandLine.hasOption("zkConnString")) {
isZkConfigured = true;
}
Application application;
if (isZkConfigured) {
// get options
String zkConnectionStr = commandLine.getOptionValue('z');
String baseZkPath = commandLine.getOptionValue('p');
if (reload) {
EventBus eventBus = new EventBus(agentName + "-event-bus");
List<LifecycleAware> components = Lists.newArrayList();
PollingZooKeeperConfigurationProvider zookeeperConfigurationProvider =
new PollingZooKeeperConfigurationProvider(
agentName, zkConnectionStr, baseZkPath, eventBus);
components.add(zookeeperConfigurationProvider);
application = new Application(components);
eventBus.register(application);
} else {
StaticZooKeeperConfigurationProvider zookeeperConfigurationProvider =
new StaticZooKeeperConfigurationProvider(
agentName, zkConnectionStr, baseZkPath);
application = new Application();
application.handleConfigurationEvent(zookeeperConfigurationProvider.getConfiguration());
}
} else {
File configurationFile = new File(commandLine.getOptionValue('f')); // 获取配置文件
/*
* The following is to ensure that by default the agent will fail on
* startup if the file does not exist.
*/
if (!configurationFile.exists()) { // 检查配置文件是否存在
// If command line invocation, then need to fail fast
if (System.getProperty(Constants.SYSPROP_CALLED_FROM_SERVICE) ==
null) {
String path = configurationFile.getPath(); // 获取文件路径
try {
path = configurationFile.getCanonicalPath();
} catch (IOException ex) {
logger.error("Failed to read canonical path for file: " + path,
ex);
}
throw new ParseException(
"The specified configuration file does not exist: " + path);
}
}
List<LifecycleAware> components = Lists.newArrayList(); // 生成保存所有组件的数组
if (reload) {
EventBus eventBus = new EventBus(agentName + "-event-bus"); // 是否监控配置文件自动重载
PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider configurationProvider =
new PollingPropertiesFileConfigurationProvider(
agentName, configurationFile, eventBus, 30); // 每三十秒检查一下文件是否修改
components.add(configurationProvider);
application = new Application(components);
eventBus.register(application); // 如果重载则重新启动组件
} else {
PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider configurationProvider =
new PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider(agentName, configurationFile); // 解析配置文件
application = new Application();
application.handleConfigurationEvent(configurationProvider.getConfiguration()); // 加载配置相关信息
}
}
application.start(); // 开始执行
final Application appReference = application;
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread("agent-shutdown-hook") { // 主要是在退出时 停止所有组件
@Override
public void run() {
appReference.stop();
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("A fatal error occurred while running. Exception follows.", e);
}
}
主要就是完成了一些配置的加载的工作,加载完成之后再来进行启动运行,在此我们查看PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider相关的配置的加载流程,主要通过getConfiguration来进行。
public class PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider extends
AbstractConfigurationProvider {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory
.getLogger(PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider.class);
private static final String DEFAULT_PROPERTIES_IMPLEMENTATION = "java.util.Properties";
private final File file;
public PropertiesFileConfigurationProvider(String agentName, File file) {
super(agentName);
this.file = file;
}
@Override
public FlumeConfiguration getFlumeConfiguration() {
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); // 获取配置文件
String resolverClassName = System.getProperty("propertiesImplementation",
DEFAULT_PROPERTIES_IMPLEMENTATION);
Class propsclass = Class.forName(resolverClassName)
.asSubclass(Properties.class); // 获取解析配置文件的类
Properties properties = propsclass.newInstance(); // 生成属性类
properties.load(reader); // 加载解析的属性
return new FlumeConfiguration(toMap(properties)); // 实例化换一个配置类
} catch (IOException ex) {
LOGGER.error("Unable to load file:" + file
+ " (I/O failure) - Exception follows.", ex);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
LOGGER.error("Configuration resolver class not found", e);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
LOGGER.error("Instantiation exception", e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
LOGGER.error("Illegal access exception", e);
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
LOGGER.warn(
"Unable to close file reader for file: " + file, ex);
}
}
}
return new FlumeConfiguration(new HashMap()); // 如果解析出错则返回一个空的实例
}
}
由于该类继承自AbstractConfigurationProvider,所以调用的是AbstractConfigurationProvider类的getConfiguration()方法。
public AbstractConfigurationProvider(String agentName) {
super();
this.agentName = agentName; // 保存agent名称
this.sourceFactory = new DefaultSourceFactory(); // source的工厂类
this.sinkFactory = new DefaultSinkFactory(); // sink的工厂类
this.channelFactory = new DefaultChannelFactory(); // channel的工厂类
channelCache = new HashMap<Class<? extends Channel>, Map<String, Channel>>();
}
protected abstract FlumeConfiguration getFlumeConfiguration();
public MaterializedConfiguration getConfiguration() {
MaterializedConfiguration conf = new SimpleMaterializedConfiguration(); // 生成一个配置实例
FlumeConfiguration fconfig = getFlumeConfiguration(); // 获取配置信息,从配置文件中获取
AgentConfiguration agentConf = fconfig.getConfigurationFor(getAgentName()); // 获取对应agent的配置信息
if (agentConf != null) {
Map<String, ChannelComponent> channelComponentMap = Maps.newHashMap(); // 生成channel的字典
Map<String, SourceRunner> sourceRunnerMap = Maps.newHashMap(); // source的字典
Map<String, SinkRunner> sinkRunnerMap = Maps.newHashMap(); // sink的字典
try {
loadChannels(agentConf, channelComponentMap); // 加载配置文件中配置的channel类
loadSources(agentConf, channelComponentMap, sourceRunnerMap); // 加载配置中的source和channel的字典 完成映射关系
loadSinks(agentConf, channelComponentMap, sinkRunnerMap); // 加载channel到sink两个通道的字典 完成映射关系
Set<String> channelNames = new HashSet<String>(channelComponentMap.keySet());
for (String channelName : channelNames) {
ChannelComponent channelComponent = channelComponentMap.get(channelName); // 遍历获取的channel
if (channelComponent.components.isEmpty()) {
LOGGER.warn(String.format("Channel %s has no components connected" +
" and has been removed.", channelName));
channelComponentMap.remove(channelName);
Map<String, Channel> nameChannelMap =
channelCache.get(channelComponent.channel.getClass());
if (nameChannelMap != null) {
nameChannelMap.remove(channelName);
}
} else {
LOGGER.info(String.format("Channel %s connected to %s",
channelName, channelComponent.components.toString()));
conf.addChannel(channelName, channelComponent.channel); // 添加到配置中
}
}
for (Map.Entry<String, SourceRunner> entry : sourceRunnerMap.entrySet()) { // 遍历所有的source 并添加到配置中
conf.addSourceRunner(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
for (Map.Entry<String, SinkRunner> entry : sinkRunnerMap.entrySet()) { // 遍历所有的sink并添加到配置中
conf.addSinkRunner(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
LOGGER.error("Failed to instantiate component", ex);
} finally {
channelComponentMap.clear();
sourceRunnerMap.clear();
sinkRunnerMap.clear();
}
} else {
LOGGER.warn("No configuration found for this host:{}", getAgentName());
}
return conf;
}
public String getAgentName() {
return agentName;
}
private void loadChannels(AgentConfiguration agentConf,
Map<String, ChannelComponent> channelComponentMap)
throws InstantiationException {
LOGGER.info("Creating channels");
/*
* Some channels will be reused across re-configurations. To handle this,
* we store all the names of current channels, perform the reconfiguration,
* and then if a channel was not used, we delete our reference to it.
* This supports the scenario where you enable channel "ch0" then remove it
* and add it back. Without this, channels like memory channel would cause
* the first instances data to show up in the seconds.
*/
ListMultimap<Class<? extends Channel>, String> channelsNotReused =
ArrayListMultimap.create();
// assume all channels will not be re-used
for (Map.Entry<Class<? extends Channel>, Map<String, Channel>> entry :
channelCache.entrySet()) {
Class<? extends Channel> channelKlass = entry.getKey();
Set<String> channelNames = entry.getValue().keySet();
channelsNotReused.get(channelKlass).addAll(channelNames);
}
Set<String> channelNames = agentConf.getChannelSet();
Map<String, ComponentConfiguration> compMap = agentConf.getChannelConfigMap(); // 获取配置好的channel
/*
* Components which have a ComponentConfiguration object
*/
for (String chName : channelNames) {
ComponentConfiguration comp = compMap.get(chName); // 获取名称
if (comp != null) {
Channel channel = getOrCreateChannel(channelsNotReused,
comp.getComponentName(), comp.getType()); // 如果该类没有则创建该channel实例
try {
Configurables.configure(channel, comp); // 初始化该实例配置
channelComponentMap.put(comp.getComponentName(),
new ChannelComponent(channel)); // 生成一个该channel的实例
LOGGER.info("Created channel " + chName);
} catch (Exception e) {
String msg = String.format("Channel %s has been removed due to an " +
"error during configuration", chName);
LOGGER.error(msg, e);
}
}
}
/*
* Components which DO NOT have a ComponentConfiguration object
* and use only Context
*/
for (String chName : channelNames) {
Context context = agentConf.getChannelContext().get(chName);
if (context != null) {
Channel channel = getOrCreateChannel(channelsNotReused, chName,
context.getString(BasicConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_TYPE));
try {
Configurables.configure(channel, context);
channelComponentMap.put(chName, new ChannelComponent(channel));
LOGGER.info("Created channel " + chName);
} catch (Exception e) {
String msg = String.format("Channel %s has been removed due to an " +
"error during configuration", chName);
LOGGER.error(msg, e);
}
}
}
/*
* Any channel which was not re-used, will have it's reference removed
*/
for (Class<? extends Channel> channelKlass : channelsNotReused.keySet()) { // 移除未使用到的channel
Map<String, Channel> channelMap = channelCache.get(channelKlass);
if (channelMap != null) {
for (String channelName : channelsNotReused.get(channelKlass)) {
if (channelMap.remove(channelName) != null) {
LOGGER.info("Removed {} of type {}", channelName, channelKlass);
}
}
if (channelMap.isEmpty()) {
channelCache.remove(channelKlass);
}
}
}
}
private Channel getOrCreateChannel(
ListMultimap<Class<? extends Channel>, String> channelsNotReused,
String name, String type)
throws FlumeException {
Class<? extends Channel> channelClass = channelFactory.getClass(type); // 通过工厂类来获取指定类型的channel类
/*
* Channel has requested a new instance on each re-configuration
*/
if (channelClass.isAnnotationPresent(Disposable.class)) {
Channel channel = channelFactory.create(name, type);
channel.setName(name);
return channel;
}
Map<String, Channel> channelMap = channelCache.get(channelClass); // 检查是否缓存该类
if (channelMap == null) {
channelMap = new HashMap<String, Channel>();
channelCache.put(channelClass, channelMap);
}
Channel channel = channelMap.get(name);
if (channel == null) {
channel = channelFactory.create(name, type); // 创建一个该类实例并保存
channel.setName(name);
channelMap.put(name, channel);
}
channelsNotReused.get(channelClass).remove(name);
return channel;
}
private void loadSources(AgentConfiguration agentConf,
Map<String, ChannelComponent> channelComponentMap,
Map<String, SourceRunner> sourceRunnerMap)
throws InstantiationException {
Set<String> sourceNames = agentConf.getSourceSet(); // 获取source配置的信息
Map<String, ComponentConfiguration> compMap =
agentConf.getSourceConfigMap();
/*
* Components which have a ComponentConfiguration object
*/
for (String sourceName : sourceNames) {
ComponentConfiguration comp = compMap.get(sourceName);
if (comp != null) {
SourceConfiguration config = (SourceConfiguration) comp;
Source source = sourceFactory.create(comp.getComponentName(),
comp.getType()); // 通过工厂类生成一个source
try {
Configurables.configure(source, config);
Set<String> channelNames = config.getChannels(); // 获取channels
List<Channel> sourceChannels =
getSourceChannels(channelComponentMap, source, channelNames); // 查找对应的source下面所有的sourceChannels 列表
if (sourceChannels.isEmpty()) {
String msg = String.format("Source %s is not connected to a " +
"channel", sourceName);
throw new IllegalStateException(msg);
}
ChannelSelectorConfiguration selectorConfig =
config.getSelectorConfiguration(); // 获取配置的驱动事件
ChannelSelector selector = ChannelSelectorFactory.create(
sourceChannels, selectorConfig); // 生成该channel的selector
ChannelProcessor channelProcessor = new ChannelProcessor(selector); // 实例化该ChannelProcessor
Configurables.configure(channelProcessor, config); // 配置该channelProcessor
source.setChannelProcessor(channelProcessor); // 设置source的通道处理实例
sourceRunnerMap.put(comp.getComponentName(),
SourceRunner.forSource(source)); // 保存字典中
for (Channel channel : sourceChannels) {
ChannelComponent channelComponent =
Preconditions.checkNotNull(channelComponentMap.get(channel.getName()),
String.format("Channel %s", channel.getName()));
channelComponent.components.add(sourceName);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
String msg = String.format("Source %s has been removed due to an " +
"error during configuration", sourceName);
LOGGER.error(msg, e);
}
}
}
/*
* Components which DO NOT have a ComponentConfiguration object
* and use only Context
*/
Map<String, Context> sourceContexts = agentConf.getSourceContext(); // 获取上下文
for (String sourceName : sourceNames) {
Context context = sourceContexts.get(sourceName);
if (context != null) {
Source source =
sourceFactory.create(sourceName,
context.getString(BasicConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_TYPE)); // 创建配置的source
try {
Configurables.configure(source, context);
String[] channelNames = context.getString(
BasicConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_CHANNELS).split("\\s+");
List<Channel> sourceChannels =
getSourceChannels(channelComponentMap, source, Arrays.asList(channelNames)); // 获取channel列表
if (sourceChannels.isEmpty()) {
String msg = String.format("Source %s is not connected to a " +
"channel", sourceName);
throw new IllegalStateException(msg);
}
Map<String, String> selectorConfig = context.getSubProperties(
BasicConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_SOURCE_CHANNELSELECTOR_PREFIX);
ChannelSelector selector = ChannelSelectorFactory.create(
sourceChannels, selectorConfig); // 生成一个channelSelector
ChannelProcessor channelProcessor = new ChannelProcessor(selector);
Configurables.configure(channelProcessor, context); // 初始化并添加到字典中
source.setChannelProcessor(channelProcessor);
sourceRunnerMap.put(sourceName,
SourceRunner.forSource(source));
for (Channel channel : sourceChannels) {
ChannelComponent channelComponent =
Preconditions.checkNotNull(channelComponentMap.get(channel.getName()),
String.format("Channel %s", channel.getName()));
channelComponent.components.add(sourceName);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
String msg = String.format("Source %s has been removed due to an " +
"error during configuration", sourceName);
LOGGER.error(msg, e);
}
}
}
}
private List<Channel> getSourceChannels(Map<String, ChannelComponent> channelComponentMap,
Source source, Collection<String> channelNames) throws InstantiationException {
List<Channel> sourceChannels = new ArrayList<Channel>();
for (String chName : channelNames) { // 遍历所有的channel
ChannelComponent channelComponent = channelComponentMap.get(chName); // 获取加载完成的channel
if (channelComponent != null) {
checkSourceChannelCompatibility(source, channelComponent.channel);
sourceChannels.add(channelComponent.channel); // 添加该channel
}
}
return sourceChannels;
}
private void checkSourceChannelCompatibility(Source source, Channel channel)
throws InstantiationException {
if (source instanceof BatchSizeSupported && channel instanceof TransactionCapacitySupported) {
long transCap = ((TransactionCapacitySupported) channel).getTransactionCapacity();
long batchSize = ((BatchSizeSupported) source).getBatchSize();
if (transCap < batchSize) {
String msg = String.format(
"Incompatible source and channel settings defined. " +
"source's batch size is greater than the channels transaction capacity. " +
"Source: %s, batch size = %d, channel %s, transaction capacity = %d",
source.getName(), batchSize,
channel.getName(), transCap);
throw new InstantiationException(msg);
}
}
}
private void checkSinkChannelCompatibility(Sink sink, Channel channel)
throws InstantiationException {
if (sink instanceof BatchSizeSupported && channel instanceof TransactionCapacitySupported) {
long transCap = ((TransactionCapacitySupported) channel).getTransactionCapacity();
long batchSize = ((BatchSizeSupported) sink).getBatchSize();
if (transCap < batchSize) {
String msg = String.format(
"Incompatible sink and channel settings defined. " +
"sink's batch size is greater than the channels transaction capacity. " +
"Sink: %s, batch size = %d, channel %s, transaction capacity = %d",
sink.getName(), batchSize,
channel.getName(), transCap);
throw new InstantiationException(msg);
}
}
}
private void loadSinks(AgentConfiguration agentConf,
Map<String, ChannelComponent> channelComponentMap, Map<String, SinkRunner> sinkRunnerMap)
throws InstantiationException {
Set<String> sinkNames = agentConf.getSinkSet(); // 获取sink的配置信息
Map<String, ComponentConfiguration> compMap =
agentConf.getSinkConfigMap();
Map<String, Sink> sinks = new HashMap<String, Sink>();
/*
* Components which have a ComponentConfiguration object
*/
for (String sinkName : sinkNames) {
ComponentConfiguration comp = compMap.get(sinkName); // 获取对应的sick配置
if (comp != null) {
SinkConfiguration config = (SinkConfiguration) comp;
Sink sink = sinkFactory.create(comp.getComponentName(), comp.getType()); // 通过该工程方法生成一个类实例
try {
Configurables.configure(sink, config); // 添加配置
ChannelComponent channelComponent = channelComponentMap.get(config.getChannel()); // 获取channel
if (channelComponent == null) {
String msg = String.format("Sink %s is not connected to a " +
"channel", sinkName);
throw new IllegalStateException(msg);
}
checkSinkChannelCompatibility(sink, channelComponent.channel);
sink.setChannel(channelComponent.channel); // 设置该sink的channel
sinks.put(comp.getComponentName(), sink); // 保存该sink
channelComponent.components.add(sinkName); // 添加该sink名称
} catch (Exception e) {
String msg = String.format("Sink %s has been removed due to an " +
"error during configuration", sinkName);
LOGGER.error(msg, e);
}
}
}
/*
* Components which DO NOT have a ComponentConfiguration object
* and use only Context
*/
Map<String, Context> sinkContexts = agentConf.getSinkContext(); // 加载不在配置信息中的sink
for (String sinkName : sinkNames) {
Context context = sinkContexts.get(sinkName);
if (context != null) {
Sink sink = sinkFactory.create(sinkName, context.getString(
BasicConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_TYPE));
try {
Configurables.configure(sink, context);
ChannelComponent channelComponent =
channelComponentMap.get(
context.getString(BasicConfigurationConstants.CONFIG_CHANNEL));
if (channelComponent == null) {
String msg = String.format("Sink %s is not connected to a " +
"channel", sinkName);
throw new IllegalStateException(msg);
}
checkSinkChannelCompatibility(sink, channelComponent.channel);
sink.setChannel(channelComponent.channel);
sinks.put(sinkName, sink);
channelComponent.components.add(sinkName);
} catch (Exception e) {
String msg = String.format("Sink %s has been removed due to an " +
"error during configuration", sinkName);
LOGGER.error(msg, e);
}
}
}
loadSinkGroups(agentConf, sinks, sinkRunnerMap); // 加载分组信息
}
private void loadSinkGroups(AgentConfiguration agentConf,
Map<String, Sink> sinks, Map<String, SinkRunner> sinkRunnerMap)
throws InstantiationException {
Set<String> sinkGroupNames = agentConf.getSinkgroupSet();
Map<String, ComponentConfiguration> compMap =
agentConf.getSinkGroupConfigMap();
Map<String, String> usedSinks = new HashMap<String, String>();
for (String groupName: sinkGroupNames) {
ComponentConfiguration comp = compMap.get(groupName);
if (comp != null) {
SinkGroupConfiguration groupConf = (SinkGroupConfiguration) comp;
List<Sink> groupSinks = new ArrayList<Sink>();
for (String sink : groupConf.getSinks()) {
Sink s = sinks.remove(sink);
if (s == null) {
String sinkUser = usedSinks.get(sink);
if (sinkUser != null) {
throw new InstantiationException(String.format(
"Sink %s of group %s already " +
"in use by group %s", sink, groupName, sinkUser));
} else {
throw new InstantiationException(String.format(
"Sink %s of group %s does "
+ "not exist or is not properly configured", sink,
groupName));
}
}
groupSinks.add(s);
usedSinks.put(sink, groupName);
}
try {
SinkGroup group = new SinkGroup(groupSinks);
Configurables.configure(group, groupConf);
sinkRunnerMap.put(comp.getComponentName(),
new SinkRunner(group.getProcessor()));
} catch (Exception e) {
String msg = String.format("SinkGroup %s has been removed due to " +
"an error during configuration", groupName);
LOGGER.error(msg, e);
}
}
}
// add any unassigned sinks to solo collectors
for (Entry<String, Sink> entry : sinks.entrySet()) {
if (!usedSinks.containsValue(entry.getKey())) {
try {
SinkProcessor pr = new DefaultSinkProcessor();
List<Sink> sinkMap = new ArrayList<Sink>();
sinkMap.add(entry.getValue());
pr.setSinks(sinkMap);
Configurables.configure(pr, new Context());
sinkRunnerMap.put(entry.getKey(), new SinkRunner(pr));
} catch (Exception e) {
String msg = String.format("SinkGroup %s has been removed due to " +
"an error during configuration", entry.getKey());
LOGGER.error(msg, e);
}
}
}
}
private static class ChannelComponent {
final Channel channel;
final List<String> components;
ChannelComponent(Channel channel) {
this.channel = channel;
components = Lists.newArrayList();
}
}
protected Map<String, String> toMap(Properties properties) {
Map<String, String> result = Maps.newHashMap();
Enumeration<?> propertyNames = properties.propertyNames();
while (propertyNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String name = (String) propertyNames.nextElement();
String value = properties.getProperty(name);
result.put(name, value);
}
return result;
}
该类的主要方法就是通过配置文件来加载对应的channel、source和sink配置信息,从实例配置中配置的channel配置为memory,source的type为netcat,sink的type为logger,其对应的工作类的信息如下;
memory --> flume-ng-core/src/java/org/apache/flume/channel/MemoryChannel.java
netcat --> flume-ng-core/src/java/org/apache/flume/source/NetcatSource.java
logger --> flume-ng-core/src/java/org/apache/flume/sink/LoggerSink.java
此时配置文件加载完成,接着就需要启动所有的加载的source,channel和sink实例,此时就回到Application中的
handleConfigurationEvent进行加载完成的组件的运行。
@Subscribe
public void handleConfigurationEvent(MaterializedConfiguration conf) {
try {
lifecycleLock.lockInterruptibly();
stopAllComponents(); // 先停止已经在运行的组件
startAllComponents(conf); // 开启组件启动
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
logger.info("Interrupted while trying to handle configuration event");
return;
} finally {
// If interrupted while trying to lock, we don't own the lock, so must not attempt to unlock
if (lifecycleLock.isHeldByCurrentThread()) {
lifecycleLock.unlock();
}
}
}
private void startAllComponents(MaterializedConfiguration materializedConfiguration) {
logger.info("Starting new configuration:{}", materializedConfiguration);
this.materializedConfiguration = materializedConfiguration;
for (Entry<String, Channel> entry :
materializedConfiguration.getChannels().entrySet()) { // 先获取所有从配置文件中实例化的channel
try {
logger.info("Starting Channel " + entry.getKey());
supervisor.supervise(entry.getValue(),
new SupervisorPolicy.AlwaysRestartPolicy(), LifecycleState.START); // 加入到supervisor中运行
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error while starting {}", entry.getValue(), e);
}
}
/*
* Wait for all channels to start.
*/
for (Channel ch : materializedConfiguration.getChannels().values()) { // 检查所有的channel为运行状态 需要等待所有的channel状态为开始
while (ch.getLifecycleState() != LifecycleState.START
&& !supervisor.isComponentInErrorState(ch)) {
try {
logger.info("Waiting for channel: " + ch.getName() +
" to start. Sleeping for 500 ms");
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
logger.error("Interrupted while waiting for channel to start.", e);
Throwables.propagate(e);
}
}
}
for (Entry<String, SinkRunner> entry : materializedConfiguration.getSinkRunners().entrySet()) { // 获取所有的SinkRunner
try {
logger.info("Starting Sink " + entry.getKey());
supervisor.supervise(entry.getValue(),
new SupervisorPolicy.AlwaysRestartPolicy(), LifecycleState.START); // 开启sinkRunner
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error while starting {}", entry.getValue(), e);
}
}
for (Entry<String, SourceRunner> entry :
materializedConfiguration.getSourceRunners().entrySet()) { // 获取所有的source 并且开启source运行
try {
logger.info("Starting Source " + entry.getKey());
supervisor.supervise(entry.getValue(),
new SupervisorPolicy.AlwaysRestartPolicy(), LifecycleState.START);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error while starting {}", entry.getValue(), e);
}
}
this.loadMonitoring(); // 启动监控
}
主要j就是再前面初始化完成之后,依次先启动channel然后再启动sink最后启动source,依次运行通过supervisor.supervise来运行;
public synchronized void supervise(LifecycleAware lifecycleAware,
SupervisorPolicy policy, LifecycleState desiredState) {
if (this.monitorService.isShutdown()
|| this.monitorService.isTerminated()
|| this.monitorService.isTerminating()) {
throw new FlumeException("Supervise called on " + lifecycleAware + " " +
"after shutdown has been initiated. " + lifecycleAware + " will not" +
" be started");
} // 检查执行器是否终止
Preconditions.checkState(!supervisedProcesses.containsKey(lifecycleAware),
"Refusing to supervise " + lifecycleAware + " more than once");
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Supervising service:{} policy:{} desiredState:{}",
new Object[] { lifecycleAware, policy, desiredState });
}
Supervisoree process = new Supervisoree(); // 生成一个Process
process.status = new Status(); // 生成一个状态
process.policy = policy;
process.status.desiredState = desiredState;
process.status.error = false;
MonitorRunnable monitorRunnable = new MonitorRunnable(); // 生成一个运行的实例
monitorRunnable.lifecycleAware = lifecycleAware; // 配置执行的组件
monitorRunnable.supervisoree = process;
monitorRunnable.monitorService = monitorService; // 设置服务
supervisedProcesses.put(lifecycleAware, process); // 保存
ScheduledFuture<?> future = monitorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(
monitorRunnable, 0, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 添加到等待执行
monitorFutures.put(lifecycleAware, future);
}
@Override
public void run() {
logger.debug("checking process:{} supervisoree:{}", lifecycleAware,
supervisoree);
long now = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 获取当前时间
try {
if (supervisoree.status.firstSeen == null) {
logger.debug("first time seeing {}", lifecycleAware);
supervisoree.status.firstSeen = now;
}
supervisoree.status.lastSeen = now;
synchronized (lifecycleAware) {
if (supervisoree.status.discard) {
// Unsupervise has already been called on this.
logger.info("Component has already been stopped {}", lifecycleAware);
return;
} else if (supervisoree.status.error) {
logger.info("Component {} is in error state, and Flume will not"
+ "attempt to change its state", lifecycleAware);
return;
}
supervisoree.status.lastSeenState = lifecycleAware.getLifecycleState(); // 获取当前的状态
if (!lifecycleAware.getLifecycleState().equals(
supervisoree.status.desiredState)) {
logger.debug("Want to transition {} from {} to {} (failures:{})",
new Object[] { lifecycleAware, supervisoree.status.lastSeenState,
supervisoree.status.desiredState,
supervisoree.status.failures });
switch (supervisoree.status.desiredState) { // 获取当前需要的状态
case START:
try {
lifecycleAware.start(); // 如果是开始则开始执行
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("Unable to start " + lifecycleAware
+ " - Exception follows.", e);
if (e instanceof Error) {
// This component can never recover, shut it down.
supervisoree.status.desiredState = LifecycleState.STOP; // 出错则设置为停止
try {
lifecycleAware.stop(); // 调用停止
logger.warn("Component {} stopped, since it could not be"
+ "successfully started due to missing dependencies",
lifecycleAware);
} catch (Throwable e1) {
logger.error("Unsuccessful attempt to "
+ "shutdown component: {} due to missing dependencies."
+ " Please shutdown the agent"
+ "or disable this component, or the agent will be"
+ "in an undefined state.", e1);
supervisoree.status.error = true;
if (e1 instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) e1;
}
// Set the state to stop, so that the conf poller can
// proceed.
}
}
supervisoree.status.failures++;
}
break;
case STOP:
try {
lifecycleAware.stop(); // 如果是停止信号则停止
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("Unable to stop " + lifecycleAware
+ " - Exception follows.", e);
if (e instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) e;
}
supervisoree.status.failures++;
}
break;
default:
logger.warn("I refuse to acknowledge {} as a desired state",
supervisoree.status.desiredState);
}
if (!supervisoree.policy.isValid(lifecycleAware, supervisoree.status)) {
logger.error(
"Policy {} of {} has been violated - supervisor should exit!",
supervisoree.policy, lifecycleAware);
}
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Unexpected error", t);
}
logger.debug("Status check complete");
}
}
主要就是通过线程池来执行每个组件,每个组件都是被包裹在MonitorRunnable中运行,最后会调用组件实例的start方法。
NetcatSource的启动流程
@Override
public void start() {
logger.info("Source starting");
counterGroup.incrementAndGet("open.attempts");
try {
SocketAddress bindPoint = new InetSocketAddress(hostName, port); // 绑定ip和端口
serverSocket = ServerSocketChannel.open(); // 打开端口
serverSocket.socket().setReuseAddress(true); // 设置端口可重用
serverSocket.socket().bind(bindPoint);
logger.info("Created serverSocket:{}", serverSocket);
} catch (IOException e) {
counterGroup.incrementAndGet("open.errors");
logger.error("Unable to bind to socket. Exception follows.", e);
stop();
throw new FlumeException(e);
}
handlerService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(new ThreadFactoryBuilder()
.setNameFormat("netcat-handler-%d").build()); // 初始化一个线程池来处理请求
AcceptHandler acceptRunnable = new AcceptHandler(maxLineLength); // 设置一个接受处理handler
acceptThreadShouldStop.set(false); // 设置参数
acceptRunnable.counterGroup = counterGroup;
acceptRunnable.handlerService = handlerService;
acceptRunnable.shouldStop = acceptThreadShouldStop;
acceptRunnable.ackEveryEvent = ackEveryEvent;
acceptRunnable.source = this;
acceptRunnable.serverSocket = serverSocket;
acceptRunnable.sourceEncoding = sourceEncoding;
acceptThread = new Thread(acceptRunnable); // 开启线程接受数据
acceptThread.start(); // 运行该接受线程
logger.debug("Source started");
super.start(); // 调用父类设置状态为开始状态
}
可知调用了start方法其实就是开启了一个线程并用线程池来处理接入进来的请求。
private static class AcceptHandler implements Runnable {
private ServerSocketChannel serverSocket;
private CounterGroup counterGroup;
private ExecutorService handlerService;
private EventDrivenSource source;
private AtomicBoolean shouldStop;
private boolean ackEveryEvent;
private String sourceEncoding;
private final int maxLineLength;
public AcceptHandler(int maxLineLength) {
this.maxLineLength = maxLineLength;
}
@Override
public void run() {
logger.debug("Starting accept handler");
while (!shouldStop.get()) { // 检查是否是停止状态
try {
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocket.accept(); // 接受连接
NetcatSocketHandler request = new NetcatSocketHandler(maxLineLength);
request.socketChannel = socketChannel;
request.counterGroup = counterGroup;
request.source = source;
request.ackEveryEvent = ackEveryEvent;
request.sourceEncoding = sourceEncoding;
handlerService.submit(request); // 提交获取的数据
counterGroup.incrementAndGet("accept.succeeded"); // 计数加1
} catch (ClosedByInterruptException e) {
// Parent is canceling us.
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error("Unable to accept connection. Exception follows.", e);
counterGroup.incrementAndGet("accept.failed");
}
}
logger.debug("Accept handler exiting");
}
}
通过该端口接受到的数据都通过NetcatSocketHandler的线程来进行处理接受的数据;
@Override
public void run() {
logger.debug("Starting connection handler");
Event event = null;
try {
Reader reader = Channels.newReader(socketChannel, sourceEncoding); // 获取读
Writer writer = Channels.newWriter(socketChannel, sourceEncoding); // 获取写
CharBuffer buffer = CharBuffer.allocate(maxLineLength); // 获取缓存
buffer.flip(); // flip() so fill() sees buffer as initially empty
while (true) {
// this method blocks until new data is available in the socket
int charsRead = fill(buffer, reader);
logger.debug("Chars read = {}", charsRead); // 阻塞直到可读
// attempt to process all the events in the buffer
int eventsProcessed = processEvents(buffer, writer); // 处理读事件
logger.debug("Events processed = {}", eventsProcessed);
if (charsRead == -1) { // 如果为-1则读出错
// if we received EOF before last event processing attempt, then we
// have done everything we can
break;
} else if (charsRead == 0 && eventsProcessed == 0) {
if (buffer.remaining() == buffer.capacity()) { // 检查缓存是否有剩余
// If we get here it means:
// 1. Last time we called fill(), no new chars were buffered
// 2. After that, we failed to process any events => no newlines
// 3. The unread data in the buffer == the size of the buffer
// Therefore, we are stuck because the client sent a line longer
// than the size of the buffer. Response: Drop the connection.
logger.warn("Client sent event exceeding the maximum length");
counterGroup.incrementAndGet("events.failed");
writer.write("FAILED: Event exceeds the maximum length (" +
buffer.capacity() + " chars, including newline)\n");
writer.flush();
break;
}
}
}
socketChannel.close(); // 关闭连接
counterGroup.incrementAndGet("sessions.completed"); // 连接加1
} catch (IOException e) {
counterGroup.incrementAndGet("sessions.broken");
try {
socketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
logger.error("Unable to close socket channel. Exception follows.", ex);
}
}
logger.debug("Connection handler exiting");
}
/**
* Consume some number of events from the buffer into the system.
*
* Invariants (pre- and post-conditions):
* buffer should have position @ beginning of unprocessed data.
* buffer should have limit @ end of unprocessed data.
*
* @param buffer The buffer containing data to process
* @param writer The channel back to the client
* @return number of events successfully processed
* @throws IOException
*/
private int processEvents(CharBuffer buffer, Writer writer)
throws IOException {
int numProcessed = 0;
boolean foundNewLine = true;
while (foundNewLine) {
foundNewLine = false;
int limit = buffer.limit(); // 获取缓存限制
for (int pos = buffer.position(); pos < limit; pos++) { // 获取缓存位置
if (buffer.get(pos) == '\n') {
// parse event body bytes out of CharBuffer
buffer.limit(pos); // temporary limit
ByteBuffer bytes = Charsets.UTF_8.encode(buffer);
buffer.limit(limit); // restore limit
// build event object
byte[] body = new byte[bytes.remaining()];
bytes.get(body);
Event event = EventBuilder.withBody(body);
// process event
ChannelException ex = null;
try {
source.getChannelProcessor().processEvent(event); // 调用getChannelProcessor来处理该数据
} catch (ChannelException chEx) {
ex = chEx;
}
if (ex == null) {
counterGroup.incrementAndGet("events.processed"); // 处理成功计数加
numProcessed++;
if (true == ackEveryEvent) {
writer.write("OK\n");
}
} else {
counterGroup.incrementAndGet("events.failed"); // 失败计数加
logger.warn("Error processing event. Exception follows.", ex);
writer.write("FAILED: " + ex.getMessage() + "\n");
}
writer.flush(); // 刷新
// advance position after data is consumed
buffer.position(pos + 1); // skip newline 处理新的数据
foundNewLine = true;
break;
}
}
}
return numProcessed;
}
该处理线程主要是接受从端口接受到的数据,然后将接受到的数据通过设置的channelProcessor来处理接受的数据,该类的处理如下;
public void processEvent(Event event) {
event = interceptorChain.intercept(event); // 看是否添加了过滤链
if (event == null) {
return;
}
// Process required channels
List<Channel> requiredChannels = selector.getRequiredChannels(event); // 获取需要的channels
for (Channel reqChannel : requiredChannels) { // 遍历channels
Transaction tx = reqChannel.getTransaction(); // 获取channel的事务
Preconditions.checkNotNull(tx, "Transaction object must not be null");
try {
tx.begin(); // 开启事务
reqChannel.put(event); // 向channel中添加数据
tx.commit(); // 提交
} catch (Throwable t) {
tx.rollback(); // 如果出错则回滚
if (t instanceof Error) {
LOG.error("Error while writing to required channel: " + reqChannel, t);
throw (Error) t;
} else if (t instanceof ChannelException) {
throw (ChannelException) t;
} else {
throw new ChannelException("Unable to put event on required " +
"channel: " + reqChannel, t);
}
} finally {
if (tx != null) {
tx.close();
}
}
}
// Process optional channels
List<Channel> optionalChannels = selector.getOptionalChannels(event); // 获取optional的channel
for (Channel optChannel : optionalChannels) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
tx = optChannel.getTransaction(); // 开启事务
tx.begin();
optChannel.put(event); // 添加数据
tx.commit(); // 提交
} catch (Throwable t) {
tx.rollback(); // 如果出错则回滚
LOG.error("Unable to put event on optional channel: " + optChannel, t);
if (t instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) t;
}
} finally {
if (tx != null) {
tx.close();
}
}
}
}
其中selector默认是ReplicatingChannelSelector类,该类就把所有需要将数据发送出去的channel放在了
requiredChannels列表中,至此,Source的数据已经发送到了channel中。
MemoryChannel执行流程
@Override
public synchronized void start() {
channelCounter.start(); // 启动counter
channelCounter.setChannelSize(queue.size()); // 设置队列大小
channelCounter.setChannelCapacity(Long.valueOf(
queue.size() + queue.remainingCapacity())); // 设置队列的容量
super.start(); // 启动
}
这是channel在启动的时候进行了队列的设置等操作,当Source调用事务来提交数据的时候执行的是如下的代码;
public abstract class BasicTransactionSemantics implements Transaction {
private State state;
private long initialThreadId;
protected void doBegin() throws InterruptedException {}
protected abstract void doPut(Event event) throws InterruptedException;
protected abstract Event doTake() throws InterruptedException;
protected abstract void doCommit() throws InterruptedException;
protected abstract void doRollback() throws InterruptedException;
protected void doClose() {}
protected BasicTransactionSemantics() {
state = State.NEW;
initialThreadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
}
/**
*
* The method to which {@link BasicChannelSemantics} delegates calls
* to put.
*
*/
protected void put(Event event) {
Preconditions.checkState(Thread.currentThread().getId() == initialThreadId,
"put() called from different thread than getTransaction()!");
Preconditions.checkState(state.equals(State.OPEN),
"put() called when transaction is %s!", state);
Preconditions.checkArgument(event != null,
"put() called with null event!");
try {
doPut(event);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new ChannelException(e.toString(), e);
}
}
/**
*
* The method to which {@link BasicChannelSemantics} delegates calls
* to take.
*
*/
protected Event take() {
Preconditions.checkState(Thread.currentThread().getId() == initialThreadId,
"take() called from different thread than getTransaction()!");
Preconditions.checkState(state.equals(State.OPEN),
"take() called when transaction is %s!", state);
try {
return doTake(); // 调用doTake
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
return null;
}
}
/**
* @return the current state of the transaction
*/
protected State getState() {
return state;
}
@Override
public void begin() {
Preconditions.checkState(Thread.currentThread().getId() == initialThreadId,
"begin() called from different thread than getTransaction()!");
Preconditions.checkState(state.equals(State.NEW),
"begin() called when transaction is " + state + "!");
try {
doBegin(); // 调用doBegin 并设置状态为OPEN
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new ChannelException(e.toString(), e);
}
state = State.OPEN;
}
@Override
public void commit() {
Preconditions.checkState(Thread.currentThread().getId() == initialThreadId,
"commit() called from different thread than getTransaction()!");
Preconditions.checkState(state.equals(State.OPEN),
"commit() called when transaction is %s!", state);
try {
doCommit(); // 提交并设置状态为COMPLETED
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new ChannelException(e.toString(), e);
}
state = State.COMPLETED;
}
@Override
public void rollback() {
Preconditions.checkState(Thread.currentThread().getId() == initialThreadId,
"rollback() called from different thread than getTransaction()!");
Preconditions.checkState(state.equals(State.OPEN),
"rollback() called when transaction is %s!", state);
state = State.COMPLETED;
try {
doRollback(); // 回滚并设置为完成
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new ChannelException(e.toString(), e);
}
}
@Override
public void close() {
Preconditions.checkState(Thread.currentThread().getId() == initialThreadId,
"close() called from different thread than getTransaction()!");
Preconditions.checkState(
state.equals(State.NEW) || state.equals(State.COMPLETED),
"close() called when transaction is %s"
+ " - you must either commit or rollback first", state);
state = State.CLOSED; // 设置为关闭
doClose();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("BasicTransactionSemantics: {");
builder.append(" state:").append(state);
builder.append(" initialThreadId:").append(initialThreadId);
builder.append(" }");
return builder.toString();
}
/**
*
* The state of the {@link Transaction} to which it belongs.
*
*
* - NEW
* - A newly created transaction that has not yet begun.
* - OPEN
* - A transaction that is open. It is permissible to commit or rollback.
*
* - COMPLETED
* - This transaction has been committed or rolled back. It is illegal to
* perform any further operations beyond closing it.
* - CLOSED
* - A closed transaction. No further operations are permitted.
*
*/
protected static enum State {
NEW, OPEN, COMPLETED, CLOSED
}
}
此时的MemoryTransaction实现如下;
public class MemoryChannel extends BasicChannelSemantics implements TransactionCapacitySupported {
private static Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MemoryChannel.class);
private static final Integer defaultCapacity = 100;
private static final Integer defaultTransCapacity = 100;
private static final double byteCapacitySlotSize = 100;
private static final Long defaultByteCapacity = (long)(Runtime.getRuntime().maxMemory() * .80);
private static final Integer defaultByteCapacityBufferPercentage = 20;
private static final Integer defaultKeepAlive = 3;
private class MemoryTransaction extends BasicTransactionSemantics {
private LinkedBlockingDeque<Event> takeList;
private LinkedBlockingDeque<Event> putList;
private final ChannelCounter channelCounter;
private int putByteCounter = 0;
private int takeByteCounter = 0;
public MemoryTransaction(int transCapacity, ChannelCounter counter) {
putList = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Event>(transCapacity); // 设置一个put的阻塞队列
takeList = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Event>(transCapacity); // 设置一个拿的阻塞队列
channelCounter = counter;
}
@Override
protected void doPut(Event event) throws InterruptedException {
channelCounter.incrementEventPutAttemptCount();
int eventByteSize = (int) Math.ceil(estimateEventSize(event) / byteCapacitySlotSize);
if (!putList.offer(event)) { // 检查队列是否满了 满了则报错
throw new ChannelException(
"Put queue for MemoryTransaction of capacity " +
putList.size() + " full, consider committing more frequently, " +
"increasing capacity or increasing thread count");
}
putByteCounter += eventByteSize;
}
@Override
protected Event doTake() throws InterruptedException {
channelCounter.incrementEventTakeAttemptCount();
if (takeList.remainingCapacity() == 0) { // 检查takeList是否为空 如果为空则报错
throw new ChannelException("Take list for MemoryTransaction, capacity " +
takeList.size() + " full, consider committing more frequently, " +
"increasing capacity, or increasing thread count");
}
if (!queueStored.tryAcquire(keepAlive, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
return null;
}
Event event;
synchronized (queueLock) {
event = queue.poll(); // 取出队列头部的数据
}
Preconditions.checkNotNull(event, "Queue.poll returned NULL despite semaphore " +
"signalling existence of entry");
takeList.put(event); // 在takeList中加入该数据
int eventByteSize = (int) Math.ceil(estimateEventSize(event) / byteCapacitySlotSize);
takeByteCounter += eventByteSize;
return event; // 返回该事件
}
@Override
protected void doCommit() throws InterruptedException {
int remainingChange = takeList.size() - putList.size(); // 获取当前的变化值
if (remainingChange < 0) {
if (!bytesRemaining.tryAcquire(putByteCounter, keepAlive, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
throw new ChannelException("Cannot commit transaction. Byte capacity " +
"allocated to store event body " + byteCapacity * byteCapacitySlotSize +
"reached. Please increase heap space/byte capacity allocated to " +
"the channel as the sinks may not be keeping up with the sources");
}
if (!queueRemaining.tryAcquire(-remainingChange, keepAlive, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
bytesRemaining.release(putByteCounter);
throw new ChannelFullException("Space for commit to queue couldn't be acquired." +
" Sinks are likely not keeping up with sources, or the buffer size is too tight");
}
}
int puts = putList.size(); // 获取当前的put的列表大小
int takes = takeList.size(); // 获取take的列表大小
synchronized (queueLock) {
if (puts > 0) {
while (!putList.isEmpty()) { // 如果putList不为空
if (!queue.offer(putList.removeFirst())) { // 是否可以将putList中的数据移动到queue中
throw new RuntimeException("Queue add failed, this shouldn't be able to happen");
}
}
}
putList.clear(); // 如果都可以移动则清空
takeList.clear();
}
bytesRemaining.release(takeByteCounter);
takeByteCounter = 0;
putByteCounter = 0;
queueStored.release(puts);
if (remainingChange > 0) {
queueRemaining.release(remainingChange);
}
if (puts > 0) {
channelCounter.addToEventPutSuccessCount(puts); // 添加计数
}
if (takes > 0) {
channelCounter.addToEventTakeSuccessCount(takes); // 添加计数
}
channelCounter.setChannelSize(queue.size());
}
@Override
protected void doRollback() {
int takes = takeList.size(); // 回滚获取到的值
synchronized (queueLock) {
Preconditions.checkState(queue.remainingCapacity() >= takeList.size(),
"Not enough space in memory channel " +
"queue to rollback takes. This should never happen, please report");
while (!takeList.isEmpty()) { // 如果不为空
queue.addFirst(takeList.removeLast()); // 将takeList中的数据都移动到queue中
}
putList.clear(); // putList 清空
}
putByteCounter = 0;
takeByteCounter = 0;
queueStored.release(takes);
channelCounter.setChannelSize(queue.size());
}
}
// lock to guard queue, mainly needed to keep it locked down during resizes
// it should never be held through a blocking operation
private Object queueLock = new Object();
@GuardedBy(value = "queueLock")
private LinkedBlockingDeque<Event> queue;
// invariant that tracks the amount of space remaining in the queue(with all uncommitted takeLists deducted)
// we maintain the remaining permits = queue.remaining - takeList.size()
// this allows local threads waiting for space in the queue to commit without denying access to the
// shared lock to threads that would make more space on the queue
private Semaphore queueRemaining;
// used to make "reservations" to grab data from the queue.
// by using this we can block for a while to get data without locking all other threads out
// like we would if we tried to use a blocking call on queue
private Semaphore queueStored;
// maximum items in a transaction queue
private volatile Integer transCapacity;
private volatile int keepAlive;
private volatile int byteCapacity;
private volatile int lastByteCapacity;
private volatile int byteCapacityBufferPercentage;
private Semaphore bytesRemaining;
private ChannelCounter channelCounter;
public MemoryChannel() {
super();
}
/**
* Read parameters from context
* capacity = type long that defines the total number of events allowed at one time in the queue.
* transactionCapacity = type long that defines the total number of events allowed in one transaction.
* byteCapacity = type long that defines the max number of bytes used for events in the queue.
* byteCapacityBufferPercentage = type int that defines the percent of buffer between byteCapacity and the estimated event size.
* keep-alive = type int that defines the number of second to wait for a queue permit
*/
@Override
public void configure(Context context) { // 根据配置设置channel的相关配置信息
Integer capacity = null;
try {
capacity = context.getInteger("capacity", defaultCapacity); // 获取容量大小
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
capacity = defaultCapacity; // 如果没有配置则使用默认
LOGGER.warn("Invalid capacity specified, initializing channel to "
+ "default capacity of {}", defaultCapacity);
}
if (capacity <= 0) {
capacity = defaultCapacity;
LOGGER.warn("Invalid capacity specified, initializing channel to "
+ "default capacity of {}", defaultCapacity);
}
try {
transCapacity = context.getInteger("transactionCapacity", defaultTransCapacity); // 获取开启的事务的默认值
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
transCapacity = defaultTransCapacity; // 如果出错则设置为默认的事务值
LOGGER.warn("Invalid transation capacity specified, initializing channel"
+ " to default capacity of {}", defaultTransCapacity);
}
if (transCapacity <= 0) {
transCapacity = defaultTransCapacity;
LOGGER.warn("Invalid transation capacity specified, initializing channel"
+ " to default capacity of {}", defaultTransCapacity);
}
Preconditions.checkState(transCapacity <= capacity,
"Transaction Capacity of Memory Channel cannot be higher than " +
"the capacity."); // 容量必须要大于事务容量
try {
byteCapacityBufferPercentage = context.getInteger("byteCapacityBufferPercentage",
defaultByteCapacityBufferPercentage); // 获取容量的内存占用比
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
byteCapacityBufferPercentage = defaultByteCapacityBufferPercentage;
}
try {
byteCapacity = (int) ((context.getLong("byteCapacity", defaultByteCapacity).longValue() *
(1 - byteCapacityBufferPercentage * .01)) / byteCapacitySlotSize); // 计算容量的占用比率值
if (byteCapacity < 1) {
byteCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // 如果计算小于1则使用最大值
}
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
byteCapacity = (int) ((defaultByteCapacity * (1 - byteCapacityBufferPercentage * .01)) /
byteCapacitySlotSize);
}
try {
keepAlive = context.getInteger("keep-alive", defaultKeepAlive); // 是否keep-alive
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
keepAlive = defaultKeepAlive;
}
if (queue != null) {
try {
resizeQueue(capacity); // 队列如果不为空 重新设置队列大小
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
} else {
synchronized (queueLock) {
queue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Event>(capacity); // 生成一个阻塞队列
queueRemaining = new Semaphore(capacity);
queueStored = new Semaphore(0);
}
}
if (bytesRemaining == null) {
bytesRemaining = new Semaphore(byteCapacity);
lastByteCapacity = byteCapacity;
} else {
if (byteCapacity > lastByteCapacity) {
bytesRemaining.release(byteCapacity - lastByteCapacity);
lastByteCapacity = byteCapacity;
} else {
try {
if (!bytesRemaining.tryAcquire(lastByteCapacity - byteCapacity, keepAlive,
TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
LOGGER.warn("Couldn't acquire permits to downsize the byte capacity, resizing has been aborted");
} else {
lastByteCapacity = byteCapacity;
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}
if (channelCounter == null) {
channelCounter = new ChannelCounter(getName()); // 生成一个channelCounter实例
}
}
private void resizeQueue(int capacity) throws InterruptedException {
int oldCapacity;
synchronized (queueLock) {
oldCapacity = queue.size() + queue.remainingCapacity(); // 获取旧的容量大小
}
if (oldCapacity == capacity) { // 如果旧值与新值相同则返回
return;
} else if (oldCapacity > capacity) {
if (!queueRemaining.tryAcquire(oldCapacity - capacity, keepAlive, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
LOGGER.warn("Couldn't acquire permits to downsize the queue, resizing has been aborted");
} else {
synchronized (queueLock) {
LinkedBlockingDeque<Event> newQueue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Event>(capacity); // 否则重新生成一个队列 并将旧值放入
newQueue.addAll(queue);
queue = newQueue;
}
}
} else {
synchronized (queueLock) {
LinkedBlockingDeque<Event> newQueue = new LinkedBlockingDeque<Event>(capacity);
newQueue.addAll(queue);
queue = newQueue;
}
queueRemaining.release(capacity - oldCapacity); // 重新调用剩余的值
}
}
@Override
public synchronized void start() {
channelCounter.start(); // 启动counter
channelCounter.setChannelSize(queue.size()); // 设置队列大小
channelCounter.setChannelCapacity(Long.valueOf(
queue.size() + queue.remainingCapacity())); // 设置队列的容量
super.start(); // 启动
}
@Override
public synchronized void stop() {
channelCounter.setChannelSize(queue.size());
channelCounter.stop();
super.stop();
}
@Override
protected BasicTransactionSemantics createTransaction() {
return new MemoryTransaction(transCapacity, channelCounter); // 创建一个事务
}
private long estimateEventSize(Event event) { // 获取body的长度
byte[] body = event.getBody();
if (body != null && body.length != 0) {
return body.length;
}
//Each event occupies at least 1 slot, so return 1.
return 1;
}
@VisibleForTesting
int getBytesRemainingValue() {
return bytesRemaining.availablePermits();
}
public long getTransactionCapacity() {
return transCapacity;
}
}
通过两个put和take队列来模拟实现当前的数据是否可以提交到队列中去,将数据提交到队列中。
sinkRuner执行流程
在sink的解析过程中,会将sink对应的处理函数放入到SinkRunner进行包装,此时LoggerSink的同样被包装进入了SinkRunner类中;
@Override
public void start() {
SinkProcessor policy = getPolicy(); // 获取policy
policy.start(); // 运行policy
runner = new PollingRunner(); // 初始化一个policy
runner.policy = policy;
runner.counterGroup = counterGroup;
runner.shouldStop = new AtomicBoolean(); // 原子bool值 是否停止
runnerThread = new Thread(runner);
runnerThread.setName("SinkRunner-PollingRunner-" +
policy.getClass().getSimpleName());
runnerThread.start(); // 线程运行runner
lifecycleState = LifecycleState.START;
}
public static class PollingRunner implements Runnable {
private SinkProcessor policy;
private AtomicBoolean shouldStop;
private CounterGroup counterGroup;
@Override
public void run() {
logger.debug("Polling sink runner starting");
while (!shouldStop.get()) { // 是否停止
try {
if (policy.process().equals(Sink.Status.BACKOFF)) { // 调用policy的process来处理
counterGroup.incrementAndGet("runner.backoffs");
Thread.sleep(Math.min(
counterGroup.incrementAndGet("runner.backoffs.consecutive")
* backoffSleepIncrement, maxBackoffSleep));
} else {
counterGroup.set("runner.backoffs.consecutive", 0L);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
logger.debug("Interrupted while processing an event. Exiting.");
counterGroup.incrementAndGet("runner.interruptions");
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Unable to deliver event. Exception follows.", e);
if (e instanceof EventDeliveryException) {
counterGroup.incrementAndGet("runner.deliveryErrors");
} else {
counterGroup.incrementAndGet("runner.errors");
}
try {
Thread.sleep(maxBackoffSleep);
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}
logger.debug("Polling runner exiting. Metrics:{}", counterGroup);
}
}
java在配置文件加载的过程中;如果没有配置group则会默认生成一个SinkRunner类来包装;
// loadSinks --> loadSinkGroups
// add any unassigned sinks to solo collectors
for (Entry<String, Sink> entry : sinks.entrySet()) {
if (!usedSinks.containsValue(entry.getKey())) {
try {
SinkProcessor pr = new DefaultSinkProcessor();
List<Sink> sinkMap = new ArrayList<Sink>();
sinkMap.add(entry.getValue());
pr.setSinks(sinkMap);
Configurables.configure(pr, new Context());
sinkRunnerMap.put(entry.getKey(), new SinkRunner(pr));
} catch (Exception e) {
String msg = String.format("SinkGroup %s has been removed due to " +
"an error during configuration", entry.getKey());
LOGGER.error(msg, e);
}
}
此时就是通过policy的process方法来监听是否有数据传入;
public class LoggerSink extends AbstractSink implements Configurable {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory
.getLogger(LoggerSink.class);
// Default Max bytes to dump
public static final int DEFAULT_MAX_BYTE_DUMP = 16;
// Max number of bytes to be dumped
private int maxBytesToLog = DEFAULT_MAX_BYTE_DUMP;
public static final String MAX_BYTES_DUMP_KEY = "maxBytesToLog";
@Override
public void configure(Context context) {
String strMaxBytes = context.getString(MAX_BYTES_DUMP_KEY);
if (!Strings.isNullOrEmpty(strMaxBytes)) {
try {
maxBytesToLog = Integer.parseInt(strMaxBytes);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
logger.warn(String.format(
"Unable to convert %s to integer, using default value(%d) for maxByteToDump",
strMaxBytes, DEFAULT_MAX_BYTE_DUMP));
maxBytesToLog = DEFAULT_MAX_BYTE_DUMP;
}
}
}
@Override
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {
Status result = Status.READY;
Channel channel = getChannel();
Transaction transaction = channel.getTransaction(); // 获取事务
Event event = null;
try {
transaction.begin(); // 开启事务
event = channel.take(); // 从通道中获取数据
if (event != null) { // 如果不为空并且可以打应信息
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Event: " + EventHelper.dumpEvent(event, maxBytesToLog)); // 输出打印信息
}
} else {
// No event found, request back-off semantics from the sink runner
result = Status.BACKOFF; // 否则没有数据停止
}
transaction.commit(); // 提交事务
} catch (Exception ex) {
transaction.rollback();
throw new EventDeliveryException("Failed to log event: " + event, ex);
} finally {
transaction.close();
}
return result;
}
}
至此,结果的输出层的流程也执行完成。
总结
Flume分布式可靠的传输的主要流程如上所述,根据最简单的配置文件进行了基本流程的梳理,通过梳理可知,channel与source、sink的数据交互通过队列来完成,并且通过类似于事务的形式来确保数据能够被正确的传递,并控制数据的正常消费,如果sink出问题则不会提交数据消费,或者如果channel中还好数据没有被消费也不会被消费掉。由于本人才疏学浅,如有错误请批评指正。