Leetcode刷题之二叉树(一)
一、二叉树的最大深度(104)
1、问题
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
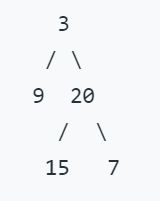
返回它的最大深度 3 。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree
2、解答
解法一:递归方法:树的前序遍历(类比于图的深度优先搜索算法DFS)。
官方示例

二叉树遍历(前序、中序、后序、层次、深度优先、广度优先遍历)
图的广度优先搜索(BFS)和深度优先搜索(DFS)算法解析
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
import java.lang.Math;
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return 0;//递归头
}else{ //递归体
int left = maxDepth(root.left);
int right = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(left,right)+1; //每次向下成功搜索加1
}
}
}
解法二:迭代方法,利用栈
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
import javafx.util.Pair; //相当于python中的二元组
import java.lang.Math;
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
//迭代法
Stack> stack = new Stack<>();
if(root!=null){
stack.push(new Pair(root,1));
}
int depth = 0;
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
Pair current = stack.pop();
root = current.getKey();
int current_depth = current.getValue();
if (root != null) {
depth = Math.max(depth, current_depth);
stack.push(new Pair(root.left, current_depth + 1));
stack.push(new Pair(root.right, current_depth + 1));
}
}
return depth;
}
}
二、二叉树的最小深度(111)
1、问题
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
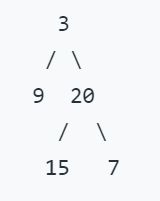
返回它的最小深度 2.
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree
2、解答
递归方法:
递归终止的条件:空节点,返回0;当 root 节点左右子树都为空时(叶子),返回 1;左右子树有一个为空时,返回不为空的子树的深度;左右子树都存在时,返回左右子树深度较小的节点的
这和求最大深度有点不同,最大深度不用考虑有一个子树为空的情况,max(m1,m2)+1已经包括了这个情况。
求最小深度,要考虑这种特殊情况,这里应该考虑的是非空子树的深度,用min(m1,m2)取得的是0,它忽略了非空子树的深度,这里应该返回m1+m2+1;
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return 0;
}else{
int m1 = minDepth(root.left);
int m2 = minDepth(root.right);
return root.left==null||root.right==null?m1+m2+1:Math.min(m1,m2)+1;
}
}
}