数据结构实验——树与二叉树(哈夫曼树)
希望可以帮助到大家,同时希望帮助大家能够关注+收藏,会持续更新后面的内容
这一次就简单的分享一下以往写的代码,就不详细的介绍定义了。对于树和二叉树大家可以详细的看一看书中介绍。这里推荐王卓老师的课。
1.实验目的
通过上机实践,掌握二叉树的结构特性,以及各种存储结构的特点及适用范围,掌握用指针类型描述、访问和处理二叉树的运算。
2.实验内容
选题1: 哈夫曼树在通信编码中的应用
哈夫曼树的实际用途非常广泛,其中在通信编码中的应用是其最重要的应用之一。利用哈夫曼编码进行通信可以大大提高信道利用率,缩短信息传输时间,降低传输成本。这要求在发送端通过一个编码系统对待传输的数据事先编码,在接收端将传来的数据进行译码(复原)。对于双工信道(即可以双向传输信息的信道),每端都需要一个完整的编/译码系统。试为这样的信息收发站定一个哈夫曼编/译码系统。
输入一串字符串,根据给定的字符串中字符出现的频率建立相应的哈夫曼树,构造哈夫曼编码,在此基础上可以对文件进行压缩(即编码),同时可对压缩的二进制编码文件进行译码。
选题2: 层次遍历二叉树
已知二叉树以二叉链表作为存储结构,写一个算法按层次遍历它,通过程序在终端屏幕上打印出它的遍历序列。
选题3: 交换二叉树的所有结点的左右子树
已知二叉树以二叉链表作为存储结构,设计一算法实现交换该二叉树的所有结点的左右子树。
四、数据类型定义及功能模块声明
选题1: 哈夫曼树在通信编码中的应用
//定义数据
struct Element {
int weight;
int parent, Lchild, Rchild;
};
//查询左右子树中较小的数
void Select(Element hufftree[], int& i1, int& i2)
//哈夫曼树的创建函数
void HuffManTree(Element hufftree[], int n, int w[])
//找出字符串中的不同字符,并计算其权重
int findelementNum(char code[], char p[], int w[])
//编码函数
void makecode(int q[][10], int road[], Element huffTree[], int n)
//解码函数
void decode(int code2[], Element Hufftree[], char p[], int n)
//打印二叉树
void print(int q[][10], char p[], int n)选题2: 层次遍历二叉树
#define MAX 50 //二叉树层节点数最大值
#define N 100 //二叉树中编号的最大值
typedef char Etype;
typedef struct BiTNode {
Etype data;
BiTNode* Lchild, * Rchild;
}BiTNode, * BiTree;
BiTree Queue[MAX];
int front = 0, rear = 0;
//按完全二叉树形式建立二叉树
void CreatBT(BiTree& BT)
//按自右至左中序遍历二叉树
void WriteBT(BiTree BT, int level)
//数据入队
void EnQueue(BiTree BT)
//数据出队
BiTree OutQueue()
//层序遍历二叉树
void LeverBT(BiTree BT) 选题3: 交换二叉树的所有结点的左右子树
#define MAXSIZE 100
//定义变量
typedef struct BTNode
{
char data;
BTNode* Lchild;
BTNode* rchild;
}BiTNode, *BiTree;
//创建二叉树链表
void CreateBitTree(BiTree *T, char str[])
//交换算法,交换左右子树
void SwapSubTree(BiTree* T)
//打印二叉树
void TreePrint(BiTree T, int level)五、主要算法
选题1: 哈夫曼树在通信编码中的应用
//判断是否为空,并进行比较
while (hufftree[i].weight != -1)
{
if (min1 > hufftree[i].weight && hufftree[i].parent == -1)
{
min1 = hufftree[i].weight;
i1 = i;
}
i++;
}
i = 0;
while (hufftree[i].weight != -1)
{
if (min2 > hufftree[i].weight && hufftree[i].parent == -1 && i != i1)
{
min2 = hufftree[i].weight;
i2 = i;
}
i++;
}选题2: 层次遍历二叉树
//判断对头和队尾是否相同
while (front != rear)
{
p = OutQueue();
cout << " " << p->data;
if (p->Lchild != NULL) EnQueue(p->Lchild);
if (p->Rchild != NULL) EnQueue(p->Rchild);
}选题3: 交换二叉树的所有结点的左右子树
if ((*T))
{
//交换算法
temp = (*T)->Lchild;
(*T)->Lchild = (*T)->rchild;
(*T)->rchild = temp;
//递归调用
SwapSubTree(&((*T)->Lchild));
SwapSubTree(&((*T)->rchild));
}六、源程序
选题1: 哈夫曼树在通信编码中的应用
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int SIZE = 100;
//定义数据
struct Element {
int weight;
int parent, Lchild, Rchild;
};
//查询左右子树中较小的数
void Select(Element hufftree[], int& i1, int& i2)
{
int min1 = 10000, min2 = 10000;//定义两个较小的数
int i = 0;//计数
//判断是否为空,并进行比较
while (hufftree[i].weight != -1)
{
if (min1 > hufftree[i].weight && hufftree[i].parent == -1)
{
min1 = hufftree[i].weight;
i1 = i;
}
i++;
}
i = 0;
while (hufftree[i].weight != -1)
{
if (min2 > hufftree[i].weight && hufftree[i].parent == -1 && i != i1)
{
min2 = hufftree[i].weight;
i2 = i;
}
i++;
}
}
//哈夫曼树的创建函数
void HuffManTree(Element hufftree[], int n, int w[])
{
int i1 = 0, i2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
hufftree[i].weight = w[i];
}
cout << endl;
for (int i = n; i < 2 * n - 1; i++)
{
Select(hufftree, i1, i2);
hufftree[i].weight = hufftree[i1].weight + hufftree[i2].weight;
hufftree[i].Lchild = i1; hufftree[i].Rchild = i2;
hufftree[i1].parent = i; hufftree[i2].parent = i;
}
}
//找出字符串中的不同字符,并计算其权重
int findelementNum(char code[], char p[], int w[])
{
if (strlen(code) == 0)return 0;
int num = 1;//记录code中不同的字符个数
p[0] = code[0];
w[0]++;
for (int i = 1; i < strlen(code); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < num; j++)
{
if (code[i] == p[j] &&code[i] != 0)//code[i]已经出现过,则其权值加1,并退出内循环
{
w[j]++;
break;
}
if (j == num - 1)//code[i]未出现过,则录入p中,其权值变为1
{
p[num] = code[i];
w[num]++;
num++;
break;
}
}
}
return num;
}
//编码函数
void makecode(int q[][10], int road[], Element huffTree[], int n)
{
int bianma[10];//储存字符的编码
int parent = 0, current = 0;
memset(bianma, 0, sizeof(bianma));
int x = 0;//bianma字符串数组的指针
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
current = i; //current保存当前节点下标
parent = huffTree[current].parent;
while (parent != -1)
{
if (huffTree[parent].Lchild == current)//当前节点为其双亲的左孩子,编码为0
{
bianma[x] = 0;
road[i]++;
}
else if (huffTree[parent].Rchild == current)//当前节点为其双亲的右孩子,编码为1
{
bianma[x] = 1;
road[i]++;
}
x++;
current = parent;
parent = huffTree[parent].parent;//向上寻找双亲节点
}
for (int y = 0; y < x; y++)
{
q[i][y] = bianma[x - y - 1];
}
x = 0;
}
}
//解码函数
void decode(int code2[], Element Hufftree[], char p[], int n)
{
int i = 0, j = 2 * n - 2, x = 0, count = 0;//j为根节点下标
while (code2[i] == 1 || code2[i] == 0)
{
if (code2[i] == 1)
{
count++;
x = Hufftree[j].Rchild;
j = x;//更新根节点
if (Hufftree[x].Rchild == -1)//当前节点没有右孩子,即找到对应解码
{
cout << p[x];
j = 2 * n - 2;
count = 0;
}
else if (code2[i + 1] == -1 && Hufftree[x].Rchild != -1)//判断编码是否有误
{
cout << "(第" << i - count + 1 << "到第" << i << "号编码有误)";
j = 2 * n - 2;
count = 0;
}
}
else if (code2[i] == 0)
{
count++;
x = Hufftree[j].Lchild;
j = x;
if (Hufftree[x].Rchild == -1)
{
cout << p[x];
j = 2 * n - 2;
count = 0;
}
else if (code2[i + 1] == -1 && Hufftree[x].Rchild != -1)
{
cout << "(第" << i - count + 1 << "到第" << i << "号编码有误)";
j = 2 * n - 2;
count = 0;
}
}
i++;
}
}
//打印二叉树
void print(int q[][10], char p[], int n)
{
int w[SIZE];
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cout << p[i] << ":";
while (q[i][j] != -1)
{
cout << q[i][j];
j++;
}
j = 0;
cout << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
Element huffTree[SIZE];
int n;//叶子节点的个数
int w[SIZE];//储存叶子节点的权重
int road[SIZE];//储存叶子节点到根节点的路径长度
int q[SIZE][10];//储存不同字符的编码
char code[50];//待编码的字符串
char p[27] = { -1 };//储存字符串中不同的字符
memset(huffTree, -1, sizeof(huffTree));
memset(w, 0, sizeof(w));
memset(road, 0, sizeof(road));
memset(q, -1, sizeof(q));
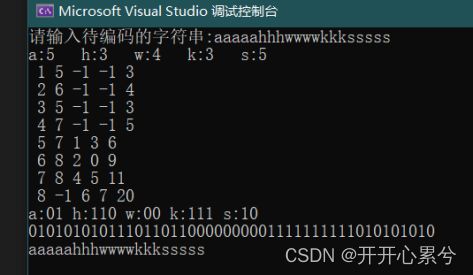
cout << "请输入待编码的字符串:";
cin >> code;
n = findelementNum(code, p, w);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cout << p[i] << ":" << w[i] << " ";
}
HuffManTree(huffTree, n, w);
for (int i = 1; i < 2 * n - 1; i++)
{
cout << " " << i;
cout << " " << huffTree[i].parent;
cout << " " << huffTree[i].Lchild;
cout << " " << huffTree[i].Rchild;
cout << " " << huffTree[i].weight << endl;
}
makecode(q, road, huffTree, n);
print(q, p, n);
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int x = 0; x < w[i]; x++)
{
while (q[i][j] != -1)
{
cout << q[i][j];
j++;
}
j = 0;
}
}
cout << endl;
cout << code << endl;
}
选题2: 层次遍历二叉树
#include
using namespace std;
#define MAX 50 //二叉树层节点数最大值
#define N 100 //二叉树中编号的最大值
typedef char Etype;
typedef struct BiTNode {
Etype data;
BiTNode* Lchild, * Rchild;
}BiTNode, * BiTree;
BiTree Queue[MAX];
int front = 0, rear = 0;
//按完全二叉树形式建立二叉树
void CreatBT(BiTree& BT)
{
BiTree p, v[N];
int i, j;
Etype e;
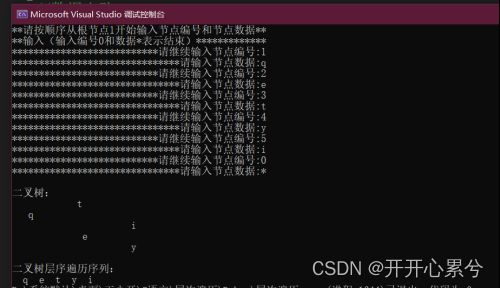
cout << "**请按顺序从根节点1开始输入节点编号和节点数据**" << endl;
cout << "**输入(输入编号0和数据*表示结束)*************" << endl;
cout << "***************************请继续输入节点编号:";
cin >> i;
cout << "*******************************请输入节点数据:";
cin >> e;
while (i != 0&& e != '*')
{
p=(BiTNode *)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
p->data = e;
p->Lchild = NULL;
p->Rchild = NULL;
v[i] = p;
if (i == 1) BT = p;
else if (i != 0)
{
j = i / 2;
if (i % 2 == 0) v[j]->Lchild = p;
else v[j]->Rchild = p;
}
else break;
cout << "***************************请继续输入节点编号:";
cin >> i;
cout << "*******************************请输入节点数据:";
cin >> e;
}
return;
}
//按自右至左中序遍历二叉树
void WriteBT(BiTree BT, int level)
{
int j;
if (BT)
{
WriteBT(BT->Rchild, level + 1); //先输出右子树
for (j = 0; j <= 5 * level; j++) //每个节点输出占据的位数
cout << " ";
cout<< BT->data <Lchild, level + 1);
cout << " ";
}
}
//数据入队
void EnQueue(BiTree BT)
{
if (front != (rear + 1) % MAX)
{
rear = (rear + 1) % MAX;
Queue[rear] = BT;
}
}
//数据出队
BiTree OutQueue()
{
if (front == rear)
return NULL;
front = (front + 1) % MAX;
return Queue[front];
}
//层序遍历二叉树
void LeverBT(BiTree BT)
{
BiTree p;
if (BT)
{
EnQueue(BT);
//判断对头和队尾是否相同
while (front != rear)
{
p = OutQueue();
cout << " " << p->data;
if (p->Lchild != NULL) EnQueue(p->Lchild);
if (p->Rchild != NULL) EnQueue(p->Rchild);
}
}
}
int main()
{
char ch;
int k;
BiTree BT;
CreatBT(BT);
cout << endl << "二叉树:" << endl;
WriteBT(BT, 0);
cout << endl << "二叉树层序遍历序列:" << endl;
LeverBT(BT);
return 0;
} 选题3: 交换二叉树的所有结点的左右子树
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define MAXSIZE 100
//定义变量
typedef struct BTNode
{
char data;
BTNode* Lchild;
BTNode* rchild;
}BiTNode, *BiTree;
//创建二叉树链表
void CreateBitTree(BiTree *T, char str[])
{
//初始化变量
char ch;
BiTree stack[MAXSIZE];
int top = -1;
int flag, k;
BiTNode* p=NULL;
*T = NULL, k = 0;
ch = str[k];
while (ch != '\0')
{
switch (ch)
{
case '(':
stack[++top] = p;
flag = 1;
break;
case ')':
top--;
break;
case ',':
flag = 2;
break;
default:
p = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiTNode));
p->data = ch;
p->Lchild = NULL;
p->rchild = NULL;
if (*T == NULL)
{
*T = p;
}
else
{
switch (flag)
{
case 1:
stack[top]->Lchild = p;
break;
case 2:
stack[top]->rchild = p;
}
}
}
ch = str[++k];
}
}
//交换算法,交换左右子树
void SwapSubTree(BiTree* T)
{
BiTNode* temp;
if ((*T))
{
//交换算法
temp = (*T)->Lchild;
(*T)->Lchild = (*T)->rchild;
(*T)->rchild = temp;
//递归调用
SwapSubTree(&((*T)->Lchild));
SwapSubTree(&((*T)->rchild));
}
}void TreePrint(BiTree T, int level)
{
int i;
//判空
if (T == NULL)
{
return;
}
TreePrint(T->rchild, level + 1);
//循环打印
for (i = 0; i < level; i++)
{
cout << " ";
}
cout<< T->data<Lchild, level + 1);
}
//主函数
void main()
{
BiTree T;
char str[MAXSIZE];
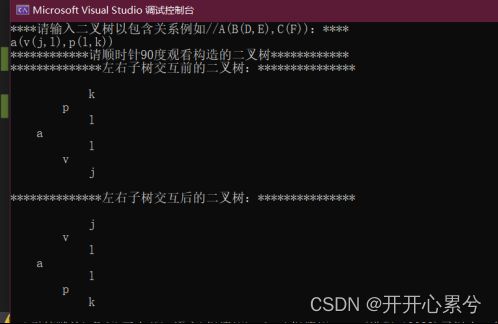
cout << "****请输入二叉树以包含关系例如//A(B(D,E),C(F)):****" << endl;
cin >> str;
cout << "************请顺时针90度观看构造的二叉树************" << endl;
CreateBitTree(&T, str);
cout << "**************左右子树交互前的二叉树:***************" << endl;
cout << endl;
TreePrint(T, 1);
cout << endl;
SwapSubTree(&T);
cout << "**************左右子树交互后的二叉树:***************" << endl;
cout << endl;
TreePrint(T, 1);
}