DL with python(3)——神经网络优化涉及的损失函数
本文涉及到的是中国大学慕课《人工智能实践:Tensorflow笔记》第二讲的内容,主要是神经网络优化涉及的损失函数。
相关版本为Windows10系统,Python3.7,Tensorflow1.14.0,PyCharm2019.3.3
损失函数
损失函数(loss):预测值(y)与已知答案(y_)的差距
NN优化目标: loss最小,这里涉及三种损失函数:mse (Mean Squared Error),ce (Cross Entropy)和自定义函数。
均方误差MSE(Mean Squared Error)

预测酸奶日销量y,x1、x2是影响日销量的因素。
建模前,应预先采集的数据有:每日x1、x2和销量y_(即已知答案,最佳情况:产量=销量)
拟造数据集X,Y_: y_ = x1 + x2
噪声:-0.05 ~ +0.05
拟合可以预测销量的函数,实现代码如下
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
tf.enable_eager_execution()
SEED = 23455 #随机数种子
rdm = np.random.RandomState(seed=SEED) # 生成[0,1)之间的随机数
x = rdm.rand(32, 2) #生成32个x1和x2
y_ = [[x1 + x2 + (rdm.rand() / 10.0 - 0.05)] for (x1, x2) in x] # 生成随机的y=x1+x2+噪声[0,1)/10=[0,0.1); [0,0.1)-0.05=[-0.05,0.05)
x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) # 将x转换为float类型
w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([2, 1], stddev=1, seed=1)) # 用tf.Variable()标记两个可训练参数,对应x1和x2
epoch = 15000 #训练轮次
lr = 0.002 #学习率
for epoch in range(epoch):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape: # 计算损失函数在某一张量处的梯度
y = tf.matmul(x, w1) # 实现两个矩阵的相乘
loss_mse = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_ - y)) # 计算均方误差
grads = tape.gradient(loss_mse, w1)
w1.assign_sub(lr * grads) # 学习率乘以梯度
if epoch % 500 == 0: # 每500个轮次输出参数
print("After %d training steps,w1 is " % (epoch))
print(w1.numpy(), "\n")
print("Final w1 is: ", w1.numpy()) #输出最后的参数
运行结果
After 0 training steps,w1 is
[[-0.8096241]
[ 1.4855157]]
After 500 training steps,w1 is
[[-0.21934733]
[ 1.6984866 ]]
......
After 14500 training steps,w1 is
[[1.0002553 ]
[0.99838644]]
Final w1 is: [[1.0009792]
[0.9977485]]
自定义损失函数
如预测商品销量,预测多了,损失成本;预测少了,损失利润。利润和成本不相等的情况下,则mse产生的loss无法使得利益最大化。
如:预测酸奶销量,酸奶成本(COST)1元,酸奶利润(PROFIT)99元。
预测少了损失利润99元,大于预测多了损失成本1元。
预测少了损失大,希望生成的预测函数往多了预测。
实现代码
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
tf.compat.v1.enable_eager_execution()
SEED = 23455 # 随机数种子
COST = 1 # 成本
PROFIT = 99 # 利润
rdm = np.random.RandomState(SEED) # 随机数种子
x = rdm.rand(32, 2) # 生成32个x1和x2
y_ = [[x1 + x2 + (rdm.rand() / 10.0 - 0.05)] for (x1, x2) in x] # 生成真实值y = x1+x2+[0,1)/10=[0,0.1); [0,0.1)-0.05=[-0.05,0.05)
x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) # 将x转换为float类型
w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([2, 1], stddev=1, seed=1)) # 用tf.Variable()标记两个可训练参数,对应x1和x2
epoch = 10000 # 训练轮次
lr = 0.002 # 学习率
for epoch in range(epoch):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape: # 计算损失函数在某一张量处的梯度
y = tf.matmul(x, w1) # 实现两个矩阵的相乘,得到y的预测值
loss = tf.reduce_sum(tf.where(tf.greater(y, y_), (y - y_) * COST, (y_ - y) * PROFIT)) #计算自定义的损失函数
grads = tape.gradient(loss, w1) # 得到梯度值
w1.assign_sub(lr * grads) # 学习率乘以梯度
if epoch % 500 == 0: # 每500个轮次输出参数
print("After %d training steps,w1 is " % (epoch))
print(w1.numpy(), "\n")
print("Final w1 is: ", w1.numpy()) # 输出最后的参数
运行结果
成本很低,利润很高,人们希望多预测些,生成模型系数大于1,往多了预测
After 0 training steps,w1 is
[[2.0855923]
[3.8476257]]
After 500 training steps,w1 is
[[1.1830753]
[1.1627482]]
......
After 9500 training steps,w1 is
[[1.1611756]
[1.0651482]]
Final w1 is: [[1.1626335]
[1.1191947]]
如果将成本和利润换一下,成本99元,利润1元。运行结果如下,成本高于利润,生成模型系数小于1,往少了预测
......
Final w1 is: [[0.9205433]
[0.9186459]]
交叉熵损失函数CE (Cross Entropy)
Cross Entropy表征两个概率分布之间的距离,
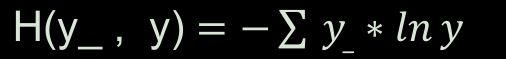
实例
二分类任务,已知答案y_=(1, 0),得到两个预测结果
y1 =(0.6, 0.4) ,y2 =(0.8, 0.2),哪个更接近标准答案?
交叉熵计算公式
H1 ((1,0),(0.6,0.4)) = -(1ln0.6 + 0ln0.4) ≈ -(-0.511 + 0) = 0.511
H2 ((1,0),(0.8,0.2)) = -(1ln0.8 + 0ln0.2) ≈ -(-0.223 + 0) = 0.223
因为H1 > H2 ,所以 ,所以y2 预测结果更准。
代码实现
import tensorflow as tf
# 计算代码,调用keras中的函数
loss_ce1 = tf.keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy([1, 0], [0.6, 0.4])
loss_ce2 = tf.keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy([1, 0], [0.8, 0.2])
# 输出结果
sess = tf.compat.v1.Session()
print(sess.run(loss_ce1))
print(sess.run(loss_ce2))