一、复习知识点
第一章复习题
1.复习Internet描述中涉及到的基本术语。特别注意速率单位bps中存在的K和M的转换关系。
2.协议的定义
3.网络edge中的end system的工作模式。
4.常见的physical media有哪些,分别用在什么场合。
5.congestion control和flow control 的差别:重点要注意发生的地方,产生的原因
6.缩写:RFC,ISP,ISDN,ADSL
1、bit=8*byte,1M=1000K(做题的时候)
2、协议:一个协议定义了在两个或多个通信实体之间交换的报文格式和次序,以及报文发送、接收报文和其他事件所采取的动作。
3、end ststem的两种工作模式:C/S model 和 peer/peer model。
4、常见的物理介质有:双绞铜线,经常用于住宅因特网接入;
同轴电缆又被称为共享介质(shared medium),多用于电缆电视系统
光纤多用于长途电话网络和因特网主干。
陆地无线电信道分为三类:一类运行在很短距离(例如1m~2m),一类用于局域(几十米~百米),一类用于广域(无线耳机,无线键盘,医疗设备等)
卫星无线电信道,还未用于因特网。
5、拥塞控制产生原因:由于网络中的负载太大,出现拥塞情况。
流量控制产生原因:发送端发送速度大于接收端接收速度,导致丢包现象。
6、RFC:请求评论
ISP:因特网服务提供商
ISDN:综合业务数字网
ADSL:非对称数字用户线路
1.R1. What is the difference between a host and an end system? List several different types of end systems. Is a Web server an end system?
2.List six access technologies. Classify each one as home access, enterprise access, or wide-area wireless access.
3.It has been said that flow control and congestion control are equivalent. Is this true for the Internet's connection-oriented service? Are the objectives of flow control and congestion control the same?
4.What are the two types of services that the Internet provides to its applications? What are some of characteristics of each of these services?
1、没有区别。PC、工作站、Web服务器。Web服务器属于端系统。
2、略
3、不是的,拥塞控制跟流量控制在TCP中是不一样的。拥塞控制和流量控制是不相同的,详见上一篇。
4、面向对象连接服务和无连接服务(不能答TCP和UDP,这两个是协议不是服务。)面向对象连接服务是可靠的。
而无连接服务是不可靠的
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1.掌握circuit switching 和packet switching 的工作原理,主要从差异性进行对比。
2.packet switching的两种模式的基本原理
3.一个nodal delay 包含哪些时延,分别是什么?
4,Transmission delay和propagation delay的差别和计算公式
5.end to end 的时延如何计算
6.end to end的average Throughput的计算方法
7.网络为什么分层?
8,实体,对等实体,layer ,protocol stack,的基本概念
9,缩写:FDM,TDM,PDU
1、详见上一篇。
2、数据报网络(datagram network)和虚电路网路(virtual circuit network)
3、包含:处理时延,传输时延,传播时延,队列时延。
4、详见上一篇
5、假设链路上有N台路由器,则d=(N+1)*(传播时延+传输时延+队列时延)
6、假设主机A接收的报文长度为L,接收的总时间为T,则平均带宽为L/T。
7、利用分层的体系结构我们可以实现一个定义良好、大而复杂系统的特定部分。且某一层服务改变不影响到其它层。
8、详见上一章。
9、FDM:频分复用
TDM:时分复用
PDU:协议数据单元
1、Suppose there is exactly one packet switch between a sending host and a receiving host. The transmission rates between the sending host and the switch and between the switch and the receiving host are R1 and R2, respectively.
Assuming that the switch uses store-and-forward packet switching,what is the total end-to end delay to send a packet of length L? (Ignore queuing, propagation delay, and processing delay.)
2、
Consider sending a packet from a source host to a destination host over afixed route. List the delay components in the end-to-end delay. Which of these delays are constant and which are variable?
3、
How long does it take a packet of length 1,000 bytes to propagate over a link
of distance 2,500 km, propagation speed 2.5 · 108 m/s, and transmission rate
2 Mbps? More generally, how long does it take a packet of length L to propagate
over a link of distance d, propagation speed s, and transmission rate R
bps? Does this delay depend on packet length? Does this delay depend on
transmission rate?
4、
Suppose Host A wants to send a large file to Host B. The path from Host A to
Host B has three links, of rates R1 = 500 kbps, R2 = 2 Mbps, and R3 = 1 Mbps.
a. Assuming no other traffic in the network, what is the throughput for the
file transfer?
b. Suppose the file is 4 million bytes. Dividing the file size by the throughput,
roughly how long will it take to transfer the file to Host B?
c. Repeat (a) and (b), but now with R2 reduced to 100 kbps.
1、L/R1+L/R2
2、结点时延、队列时延、传输时延、传播时延。
可变时延:队列时延和传输时延
3、1000Bytes=8000bits
8k/2000kbps=0.004s
2500km/2.5*10^8(m/s)=0.01s
t=0.005s
L/S+R/D
传输时延取决于报文长度和传输速率。
传播时延取决于传播速率和链路长度。
4、
(a)500kbps<1Mbps<2Mbps
所以吞吐量为500kbps
(b)4 million bytes= 32 million bits
32million bits/500kbps=64s
(c)100kbs<500kbps<1Mbps
所以吞吐量为100kbps
32million bytes/100kbps=320s
1、
(a)电路交换较适合,因为在这个应用中,传输速率稳定,在电路交换中带宽不会被浪费。
(b)不需要拥塞控制,因为数据传输塑料布小于链路的容量,不会出现拥塞。
2、
(a)d1=m/s
(b)d2=L/R
(c)d=d1+d2
(d)刚从主机A上出发
(e)在主机A和主机B之间的链路上
(f)在主机B上
(g)m/2.5*10^8=120/56kbps
m=536km
3、
dp1=5000km/2.5*10^8=0.02s
dp2=4000km/2.5*10^8=0.016s
dp3=1000km/2.5*10^8=0.004s
1500bytes=12000bits
dt=12000bits/2Mbps=0.006s
d=dp1+dp2+dp2+dp3+3*dt+0.003+0.003=0.064s=64ms
4、
d=(1+2+3+...+(N-1))*(L/R)/N=((N-1)*L)/2R
5、
(a)d=20000km/2.5*10^8=0.08s
R*d=160000bits
(b)链路带宽为160000bits,所以在任意时刻链路上最大长度为160000bits
(c)任意时刻在链路上的最大容量
(d)m/(R*d)=125m,比足球场大
(e)m/(R*d)=m/(R*m/s)=S/R
6、
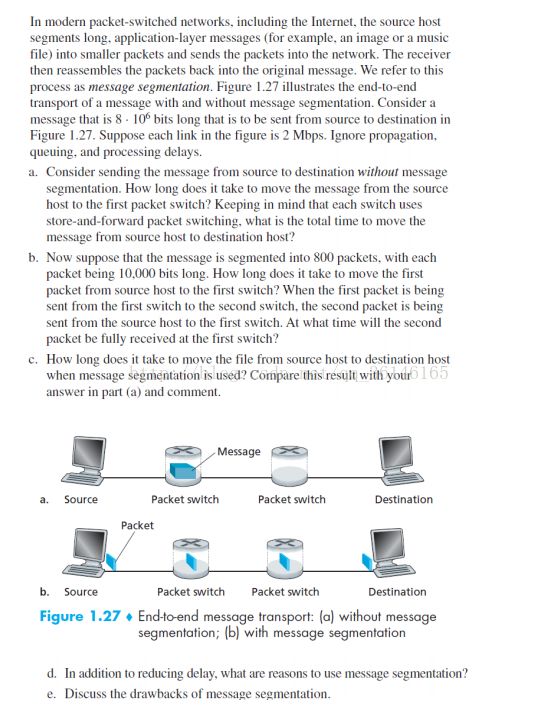
(a)d1=8*10^6bits/2Mbps=4s
d=d1*3=12s
(b)t=10000/2Mbps=0.005s
0.005秒时第一个分组传送到第一个分组交换机
0.01秒时第二个分组传送到第一个分组交换机
(c)3*t+799*t=4.01s,比(a)快
7、
(a)