沙盒 SandBox
什么是沙盒:应用程序安装过程中,系统会为每一个应用程序创建一个文件存储空间(文件夹),在这个文件夹中包含沙盒根文件和沙盒子目录。
沙盒机制:是一种安全机制,每个应用程序只能在自己的沙盒中读取文件,不能访问其他区域的内容。非代码性的文件都保存在沙盒中,比如图片、音频、视频、属性列表(偏好设置)、文本文件等。
如何查看iOS应用程序沙盒?
1.打开终端输入命令:
显示Mac隐藏文件的命令:
defaults write com.apple.finder AppleShowAllFiles -bool true
隐藏Mac隐藏文件的命令:
defaults write com.apple.finder AppleShowAllFiles -bool false
2.强制退出—Finder——重新打开
3.前往文件夹 电脑 —硬盘—用户—小房子—资源库(浅灰色)—右键打开—ApplicationSupport—iPhone Slimulator—
进入沙盒:7.1对应3.5英寸的模拟器 7.1-64 对应64位的模拟器
进入之后选择Applications文件夹,即可进入沙盒,然后可以看到Applications下面存放的就是模拟器中所装的开发的应用程序
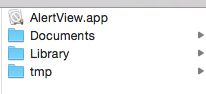
沙盒内部有4个文件夹:Documents、library、tmp、xxx.app
① Documents:(苹果建议将程序创建产生的文件以及应用浏览产生的文件数据保存在该目录下)应用中用户的数据保存在这里,比如下载的资源、创建的文件夹,对于开发者来说,最常用的就是这个文件夹
② Library:存储应用的默认设置或配置的相关信息
Library/Caches:存放缓存文件,保存应用的持久化数据,保存应用程序再次启动时所需要的信息
Library/Preferences:存储应用程序的偏好设置文件
③ tmp:临时文件夹,用来存储一些临时文件,保存应用程序再次启动时不需要的信息
④ xxx.app:应用程序的资源文件,这个文件夹存储应用程序所需要的所有资源,只读文件
//1.获取沙盒路径
//NSHomeDirectory获取沙盒路径
NSString *sandBox = NSHomeDirectory();
NSLog(@"%@",sandBox);
//2.获取documents文件路径
//方式一:字符串拼接
//stringByAppendingPathComponent字符串拼接的方法
NSString *document1 = [NSHomeDirectory() stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Documents"];
NSLog(@"document1_%@",document1);
//方式二:在根目录中搜索文件
//NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains 在根目录中搜索文件夹 search 搜索 directory 文件夹
//参数:1.要搜索的文件 NSDocumentDirectory:documents文件 2.文件搜索的范围NSUserDomainMask 用户的根目录搜索 3.是否展开绝对路径(是否展开波浪线)
NSArray *array = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES);
//在手机文件中沙盒路径是唯一的,所以数组中只有一个元素
NSString *document2 = [array objectAtIndex:0];
NSLog(@"document2__%@",document2);
//3.找library文件 和找documents 文件一致
NSString *library1 = [NSHomeDirectory() stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Library"];
NSLog(@"library1__%@",library1);
NSString *library2 = [NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSLibraryDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES) objectAtIndex:0];
NSLog(@"library2__%@",library2);
//3.获取caches
NSString *cache1 = [NSHomeDirectory() stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Library/Caches"];
NSLog(@"cache1__%@",cache1);
NSString *cache2 = [NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSCachesDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES) objectAtIndex:0];
NSLog(@"cache2__%@",cache2);
//获取tmp文件
NSString *tmp = NSTemporaryDirectory();
NSLog(@"tmp__%@",tmp);
//获取xxx.app应用程序资源
//[NSBundle mainBundle] 获取应用程序资源束
//resourcePath资源路径
NSString*app=[[NSBundle mainBundle] resourcePath];
NSLog(@"app__%@",app);
//6.获取资源路径
//参数1.资源的名字2.资源的类型
NSString *imgPath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"1" ofType:@"jpg"];
NSLog(@"imgPath__%@",imgPath);
沙盒下的存入取出
#pragma mark---存储
- (IBAction)userDeafultSave:(id)sender
{
//NSUserDefaults 是一个单例类,创建对象时,在应用程序中只用一个对象
//standardUserDefaults 是NSUserDefaults的单例方法
NSUserDefaults *user = [NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults];
//存储对象 和字典类似,但是比字典强大
[user setObject:_nameTF.text forKey:@"name"];
[user setObject:_ageTF.text forKey:@"age"];
//存储整形
[user setInteger:_sexSegment.selectedSegmentIndex forKey:@"sex"];
删除
//[user removeObjectForKey:@"name"];
//如果不调用synchronize方法,当你存储数据是,系统会把数据不定时的写入文件,如果想要立刻存入文件就要调用synchronize方法,否则,当存入数据时,程序突然崩溃,就有可能造成数据丢失
[user synchronize];
//NSUserDefaults 存储的文件放在沙盒Library/preference文件夹下的片plist文件中
//NSUserDefaults 可以存储的数据类型 数组 字符串 字典 数据类(NSData) NSNumber int float double BOOL
}
#pragma mark--读取
- (IBAction)userDeafultRead:(id)sender
{
NSUserDefaults *user = [NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults];
//读取对象
_nameTF.text = [user objectForKey:@"name"];
_ageTF.text = [user objectForKey:@"age"];
_sexSegment.selectedSegmentIndex = [user integerForKey:@"sex"];
}
沙盒 文件写入
//writetofile 文件写入
//能够进行文件写入的有字符串 数组 字典 数据类(NSData)
//进行文件写入时,自定义类存入字典 数组不能直接写入
#pragma mark --字符串
#pragma mark --字符串存入
//文件写入的路径
NSString *filePath = [NSHomeDirectory() stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Documents/string.text"];
//错误信息
NSError *error = nil;
//writeToFile 文件写入
//参数 1.要写入的文件路径
//2.atomically是否原子性写入(与线程相关);yes 原子性写入:进行文件写入时先把数据写入一个临时文件,当数据写入完毕,再吧数据放到目标文件;no:非原子性写入:进行文件 写入时直接把文件写入目标文件
//3.encoding 编码方式:NSUTF8StringEncoding 把字符串转化成二进制数据
//4.error 错误信息 当写入失败的时候 返回错误信息
//返回值表示是否写入成功
BOOL result =[string writeToFile:filePath atomically:YES encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:&error];
if (result == YES)
{
NSLog(@"字符串存储成功");
}
else
{
NSLog(@"字符串存储失败:%@",error);
}
#pragma mark --字符串取出
NSString *filePath = [NSHomeDirectory()stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Documents/string.text"];
//参数1.字符串的路径2.编码方式3.错误信息
NSString *string = [NSString stringWithContentsOfFile:filePath encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil];
#pragma mark -- 数组、字典和数据类(图片等)
//写入
[array writeToFile:filePath atomically:YES]
[dic writeToFile:filePath atomically:YES]
[data writeToFile:filePath atomically:YES]
//取出
//arrayWithContentsOfFile根据路径初始化数组
NSArray *array = [NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:filePath];
//根据路径初始化字典
NSDictionary *dic = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithContentsOfFile:filePath];
//数据类
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:dataPath];
NSFileManager 对沙盒下文件的管理的类
#define FILE_M [NSFileManager defaultManager]
#pragma mark - 创建一个文件
- (IBAction)createFile:(id)sender
{
//NSFileManager 文件管理类,单例类
//defaultManager 文件管理类的单例方法
NSFileManager *manager = [NSFileManager defaultManager];
//文件路径
NSString *filePath = [NSHomeDirectory() stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Documents/123.text"];
NSString *name = @"张三";
//NSUTF8StringEncoding 把字符串转化成二进制数据
NSData *data = [name dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
//createFile 创建文件的方法
//参数1.创建文件的路径 参数2.文件的内容 参数3.文件的属性
BOOL result = [manager createFileAtPath:filePath contents:data attributes:nil];
if (result == YES)
{
NSLog(@"文件创建成功");
}
}
#pragma mark - 删除文件
- (IBAction)deleteFile:(id)sender
{
NSString *filePath = [NSHomeDirectory() stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Documents/123.text"];
//删除文件 参数1.文件路径 参数2.错误信息
if ([FILE_M removeItemAtPath:filePath error:nil])
{
NSLog(@"文件删除成功");
}
}
#pragma mark -- 创建文件夹
- (IBAction)createDirectory:(id)sender
{
NSString *directoryPath = [NSHomeDirectory()stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Documents/Music/Rock"];
NSError *error = nil;
//createDirectory 创建文件夹
//参数1.创建文件夹的路径2.withIntermediateDirectories是否自动创建路径中不存在的文件夹3.文件夹得属性4.错误信息
if ([FILE_M createDirectoryAtPath:directoryPath withIntermediateDirectories:YES attributes:nil error:&error]) {
NSLog(@"文件夹创建成功");
}
else
{
NSLog(@"创建文件夹失败:%@",error);
}
}
#pragma mark -- 删除文件夹
- (IBAction)deleteDirectory:(id)sender
{
NSString *directoryPath = [NSHomeDirectory()stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Documents/Music/Rock"];
if ([FILE_M removeItemAtPath:directoryPath error:nil])
{
NSLog(@"文件夹删除成功");
}
}
#pragma mark --复制文件
- (IBAction)copyFile:(id)sender
{
//源文件的路径
NSString *atPath = [NSHomeDirectory() stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Documents/123.text"];
//目标文件路径
NSString *toPath =[NSHomeDirectory()stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Documents/Music/copy123.text"];
//复制文件: 1.源文件的路径 2.目标文件的路径 3.错误信息
if ([FILE_M copyItemAtPath:atPath toPath:toPath error:nil])
{
NSLog(@"文件复制成功");
}
}
#pragma mark -- 移动文件
- (IBAction)moveFile:(id)sender
{
//源文件的路径
NSString *atPath = [NSHomeDirectory() stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Documents/123.text"];
//目标文件路径
NSString *toPath = [NSHomeDirectory()stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Documents/Music/Rock/move123.text"];
if ([FILE_M moveItemAtPath:atPath toPath:toPath error:nil])
{
NSLog(@"文件移动成功");
}
}
#pragma mark -- 判断文件/文件夹是否存在
- (IBAction)fileExist:(id)sender
{
//1.判断文件是否存在
NSString *filePath = [NSHomeDirectory() stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Documents/123.text"];
//fileExists判断文件是否存在
if (![FILE_M fileExistsAtPath:filePath])
{
NSLog(@"文件不存在");
//当文件不存在的时候再去创建
[FILE_M createFileAtPath:filePath contents:[@"张三 "dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding] attributes:nil];
}
else
{
NSLog(@"文件存在");
}
//2.判断文件夹是否存在
NSString *directoryPath = [NSHomeDirectory()stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Documents/Music/Rock"];
if (![FILE_M fileExistsAtPath:directoryPath])
{
NSLog(@"文件夹不存在");
//当文件夹不存在的时候再去创建
[FILE_M createDirectoryAtPath:directoryPath withIntermediateDirectories:YES attributes:nil error:nil];
}
else
{
NSLog(@"文件夹存在");
}
BOOL isDirectory;
if ([FILE_M fileExistsAtPath:filePath isDirectory:&isDirectory])
{
NSLog(@"存在");
if (isDirectory == YES)
{
NSLog(@"是一个文件夹");
}
else
{
NSLog(@"是一个文件");
}
}
else
{
NSLog(@"不存在");
}
}
#pragma mark -- 获取文件属性
- (IBAction)attributesOfFile:(id)sender
{
NSString *filePath = [NSHomeDirectory() stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Documents/123.text"];
//attributesOfItemAtPath 获取文件的属性
NSDictionary *dic = [FILE_M attributesOfItemAtPath:filePath error:nil];
//fileSize文件的大小
unsigned long long size = [dic fileSize];
NSLog(@"%lld",size);
}
@end