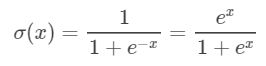Word2Vec 源码
之前微信暑期实习面试有问过word2vec的底层实现,之前只掌握了原理和掉包,现在补补Word2Vec的C源码吧。
文末附源码。
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/jeryjeryjery/article/details/80245924
流程:
训练:
![]()
(一)部分全局变量参数:
size: 对应代码中layer1_size, 表示词向量的维度,默认值是100。
train: 对应代码中train_file, 表示语料库文件路径。
save-vocab: 对应代码中save_vocab_file, 词汇表保存路径。
read-vocab: 对应代码中read_vocab_file, 表示已有的词汇表文件路径,直接读取,不用从语料库学习得来。
debug: 对应代码中debug_mode, 表示是否选择debug模型,值大于1表示开启,默认是2。开启debug会打印一些信息。
binary: 对应代码中全局变量binary,表示文件保存方式,1表示按二进制保存,0表示按文本保存,默认是0.
cbow: 对应代码中cbow, 1表示按cbow模型训练, 0表示按skip模式训练,默认是1。
alpha: 对应代码中alpha,表示学习率。skip模式下默认为0.025, cbow模式下默认是0.05。
output: 对应代码中output_file, 表示词向量保存路径。
window: 对应代码中window,表示训练窗口大小。默认是5
sample: 对应代码中sample,表示下采样阀值。
hs: 对应代码中hs, 表示按huffman softmax模式训练。默认是0, 表示不使用hs。
negative: 对应代码中negative, 表示按负采样模式训练, 默认是5。值为0表示不采用负采样训练;如果使用,值一般为3到10。
threads: 对应代码中num_threads,训练线程数,一般为12。
iter: 对应代码中iter,训练迭代次数,默认是5.
min-count: 对应代码中min_count,表示最小出现频率,低于这个频率的词会被移除词汇表。默认值是5
classes: 对应代码中classes,表示聚类中心数, 默认是0, 表示不启用聚类。
min-count: read(二)近似exp简化计算
word2vec计算过程中用上下文预测中心词或者用中心词预测上下文,都需要进行预测;而word2vec中采用的预测方式是逻辑回归分类,需要用到sigmoid函数。
在训练过程中需要用到大量的sigmoid值计算,如果每次都临时去算![]() 的值,将会影响性能;当对精度的要求不是很严格的时候,我们可以采用近似的运算。在word2vec中,将区间[-MAX_EXP, MAX_EXP](代码中MAX_EXP默认值为6)等距划分为EXP_TABLE_SIZE等份,并将每个区间的sigmoid值计算好存入到expTable中。在需要使用时,只需要确定所属的区间,属于哪一份,然后直接去数组中查找。expTable初始化代码如下:
的值,将会影响性能;当对精度的要求不是很严格的时候,我们可以采用近似的运算。在word2vec中,将区间[-MAX_EXP, MAX_EXP](代码中MAX_EXP默认值为6)等距划分为EXP_TABLE_SIZE等份,并将每个区间的sigmoid值计算好存入到expTable中。在需要使用时,只需要确定所属的区间,属于哪一份,然后直接去数组中查找。expTable初始化代码如下:
expTable = (real *)malloc((EXP_TABLE_SIZE + 1) * sizeof(real)); //初始化expTable,近似逼近sigmoid(x)值,x区间为[-MAX_EXP, MAX_EXP],分成EXP_TABLE_SIZE份
//将[-MAX_EXP, MAX_EXP]分成EXP_TABLE_SIZE份 产生e^-6 到 e^6 之间的f值
for (i = 0; i < EXP_TABLE_SIZE; i++) {
expTable[i] = exp((i / (real)EXP_TABLE_SIZE * 2 - 1) * MAX_EXP); // Precompute the exp() table
expTable[i] = expTable[i] / (expTable[i] + 1); // Precompute f(x) = x / (x + 1)
}
(三)构建词汇库
构建词汇库过程中,先判断是否已经有处理好现成的词汇库,有的话直接读取,没有的话再进行训练。
词汇表训练过程分为以下几个步骤:1.读取一个单词,2.计算单词对应hash值,3.通过hash值得到单词在词汇表中索引,4.将单词加入到词汇表, 5.对词汇表根据词频进行降序排序, 6.保存训练好的词汇表。依次介绍以上几个步骤。
首先给出词汇表中每个词对应的结构体:
//词汇中每个word对应的结构体
struct vocab_word {
long long cn; //词频
int *point; //记录huffman树中父节点索引, 自顶向下
char *word, *code, codelen; //word表示该单词; code表示Huffman编码表,记录父节点是左节点还是右节点;codelen表示码值表长度
};1.读一个单词
// Reads a single word from a file, assuming space + tab + EOL to be word boundaries
//从文件中读取单个单词,假设单词之间通过空格或者tab键或者EOL键进行分割的
void ReadWord(char *word, FILE *fin) {
int a = 0, ch;
while (!feof(fin)) {
ch = fgetc(fin); //读一个词
if (ch == 13) continue; //如果是换行符
if ((ch == ' ') || (ch == '\t') || (ch == '\n')) { //代表一个单词结束的边界
if (a > 0) { //如果读到了单词但是遇到了换行符,
if (ch == '\n') ungetc(ch, fin); //退回到流中
break;
}
if (ch == '\n') { //仅仅读到了换行符
strcpy(word, (char *)""); //将赋予给word
return;
} else continue;
}
word[a] = ch;
a++;
if (a >= MAX_STRING - 1) a--; // Truncate too long words //截断
}
word[a] = 0; //最后一个字符是'\0'
}2.计算单词对应的hash值
// Returns hash value of a word
//返回一个词对应的hash值
int GetWordHash(char *word) {
unsigned long long a, hash = 0;
for (a = 0; a < strlen(word); a++) hash = hash * 257 + word[a];
hash = hash % vocab_hash_size;
return hash;
}3.通过hash值得到word在词汇表中索引
使用到了开放定址法,关于开放地址法,参考这里。
//开放地址发得到词的位置
int SearchVocab(char *word) {
unsigned int hash = GetWordHash(word); //获得索引
while (1) {
if (vocab_hash[hash] == -1) return -1;
if (!strcmp(word, vocab[vocab_hash[hash]].word)) return vocab_hash[hash];
hash = (hash + 1) % vocab_hash_size; //开放定址法
}
return -1;
}wrod2vec中使用ReadWordIndex()函数直接整合了步骤1、步骤2和步骤3,代码如下:
// Reads a word and returns its index in the vocabulary
int ReadWordIndex(FILE *fin) {
char word[MAX_STRING];
ReadWord(word, fin); //从文件流中读取一个单词
if (feof(fin)) return -1;
return SearchVocab(word); //返回对应的词汇表中索引
}4.将word加入到词汇表
// Adds a word to the vocabulary
//将word加入到词汇表
int AddWordToVocab(char *word) {
unsigned int hash, length = strlen(word) + 1;
if (length > MAX_STRING) length = MAX_STRING; //规定每个word不超过MAX_STRING个字符
vocab[vocab_size].word = (char *)calloc(length, sizeof(char));
strcpy(vocab[vocab_size].word, word); //结构体的word词
vocab[vocab_size].cn = 0;
vocab_size++;
// Reallocate memory if needed //动态扩展内存
if (vocab_size + 2 >= vocab_max_size) {
vocab_max_size += 1000; //词汇量加上1000
vocab = (struct vocab_word *)realloc(vocab, vocab_max_size * sizeof(struct vocab_word));
}
hash = GetWordHash(word);
while (vocab_hash[hash] != -1) hash = (hash + 1) % vocab_hash_size; //得到word实际对应的hash值
vocab_hash[hash] = vocab_size - 1; //通过hash值获得word在vocab中索引
return vocab_size - 1; //返回单词对应索引
}5.对词汇表进行排序 (按词频)
排序需要先建立一个比较器,这里构造了一个降序排列的比较器,代码如下:
// Used later for sorting by word counts
//构造一个比较器,用来排序,降序
int VocabCompare(const void *a, const void *b) {
return ((struct vocab_word *)b)->cn - ((struct vocab_word *)a)->cn;
}
// Sorts the vocabulary by frequency using word counts
void SortVocab() {
int a, size;
unsigned int hash;
// Sort the vocabulary and keep at the first position
qsort(&vocab[1], vocab_size - 1, sizeof(struct vocab_word), VocabCompare);
for (a = 0; a < vocab_hash_size; a++) vocab_hash[a] = -1;
size = vocab_size;
train_words = 0;
for (a = 0; a < size; a++) {
// Words occuring less than min_count times will be discarded from the vocab
//频率低于一定程度的词会被抛弃掉
if ((vocab[a].cn < min_count) && (a != 0)) {
vocab_size--;
free(vocab[a].word);
} else {
// Hash will be re-computed, as after the sorting it is not actual
//因为排序之后顺序打乱,会重新计算一次hash值
hash=GetWordHash(vocab[a].word);
while (vocab_hash[hash] != -1) hash = (hash + 1) % vocab_hash_size;
vocab_hash[hash] = a;
train_words += vocab[a].cn;
}
}
//重新规划内存大小
vocab = (struct vocab_word *)realloc(vocab, (vocab_size + 1) * sizeof(struct vocab_word));
// Allocate memory for the binary tree construction
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) {
vocab[a].code = (char *)calloc(MAX_CODE_LENGTH, sizeof(char));
vocab[a].point = (int *)calloc(MAX_CODE_LENGTH, sizeof(int));
}
}6.保存训练好的词汇表
//保存学习到的词汇文件表
void SaveVocab() {
long long i;
FILE *fo = fopen(save_vocab_file, "wb");
for (i = 0; i < vocab_size; i++) fprintf(fo, "%s %lld\n", vocab[i].word, vocab[i].cn); //保存单词和词频
fclose(fo);
}代码中还有一个词汇表裁剪函数, 当词汇表中词汇量大于一定值时,会进行裁剪,先裁掉频率低的词,然后再裁剪掉频率高的词,直到词汇量满足要求,代码如下:
// Reduces the vocabulary by removing infrequent tokens
//对于频率小于min_reduce的词将会被裁剪掉
void ReduceVocab() {
int a, b = 0;
unsigned int hash;
//仅仅一个数组就实现了裁剪过程
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) if (vocab[a].cn > min_reduce) {
vocab[b].cn = vocab[a].cn;
vocab[b].word = vocab[a].word;
b++;
} else free(vocab[a].word);
vocab_size = b;
//重新设置hash值
for (a = 0; a < vocab_hash_size; a++) vocab_hash[a] = -1;
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) {
// Hash will be re-computed, as it is not actual
hash = GetWordHash(vocab[a].word);
while (vocab_hash[hash] != -1) hash = (hash + 1) % vocab_hash_size;
vocab_hash[hash] = a;
}
fflush(stdout);
min_reduce++; //每次裁剪之后都会提高最低频率数
}如果已经有训练好的词汇表,可以直接读取,不需要通过语料库进行训练,代码如下:
//从已有的词汇文件中直接读取,不用临时去学习
void ReadVocab() {
long long a, i = 0;
char c;
char word[MAX_STRING];
FILE *fin = fopen(read_vocab_file, "rb");
if (fin == NULL) { //判断文件是否存在
printf("Vocabulary file not found\n");
exit(1);
}
for (a = 0; a < vocab_hash_size; a++) vocab_hash[a] = -1; //vocab_hash值默认为-1
vocab_size = 0;
while (1) { //不停读取,直到文件末尾
ReadWord(word, fin); //从文件流中读取一个单词到word中
if (feof(fin)) break;
a = AddWordToVocab(word); //将单词加入到词汇表
fscanf(fin, "%lld%c", &vocab[a].cn, &c); //读取词频到vocav.cn中,换行符
i++;
}
SortVocab();
if (debug_mode > 0) {
printf("Vocab size: %lld\n", vocab_size);
printf("Words in train file: %lld\n", train_words);
}
fin = fopen(train_file, "rb");
if (fin == NULL) {
printf("ERROR: training data file not found!\n");
exit(1);
}
fseek(fin, 0, SEEK_END); //将读取指针定位到文件尾部
file_size = ftell(fin); //得到离头部偏离值,获取文件大小
fclose(fin);
}词汇库生成过程由LearnVocabFromTrainFile()函数组合以上步骤来完成,代码如下:
//整合上面的文件操作
void LearnVocabFromTrainFile() {
char word[MAX_STRING];
FILE *fin;
long long a, i;
for (a = 0; a < vocab_hash_size; a++) vocab_hash[a] = -1; //hash值初始为-1
fin = fopen(train_file, "rb");
if (fin == NULL) {
printf("ERROR: training data file not found!\n");
exit(1);
}
vocab_size = 0;
AddWordToVocab((char *)""); //将''添加到词汇表,换行符就是用这个表示
while (1) {
ReadWord(word, fin);
if (feof(fin)) break;
train_words++;
if ((debug_mode > 1) && (train_words % 100000 == 0)) {
printf("%lldK%c", train_words / 1000, 13);
fflush(stdout);
}
i = SearchVocab(word); //查找该词的位置
if (i == -1) { //还未加入到词汇表
a = AddWordToVocab(word);
vocab[a].cn = 1;
} else vocab[i].cn++; //已经加入到词汇表
if (vocab_size > vocab_hash_size * 0.7) ReduceVocab(); //裁剪词操作
}
SortVocab(); //排序
if (debug_mode > 0) {
printf("Vocab size: %lld\n", vocab_size);
printf("Words in train file: %lld\n", train_words);
}
file_size = ftell(fin);
fclose(fin);
}(四)初始化网络
初始化网络包括以下几个过程:1.初始化网络参数, 2.构建哈夫曼树, 3,初始化负采样概率表。
1.初始化网络参数
网络中的参数主要包括syn0,syn1和syn1neg。
syn0: 我们需要得到的词向量,源码中使用一个real(float)类型的一维数组表示,注意是一个一维数组!
容量大小为vocab_size * layer1_size,即 词汇量 * 词向量维度。
syn1: huffman树中,包括叶子节点和非叶子节点。叶子节点是对应的是词汇表中的单词,而非叶子节点是在构造huffman树过程中
生成的路径节点。syn1表示的就是huffman树中的非叶子节点向量,其维度和词向量维度是一样的,共有(n-1)个非叶子节点,
n表示词汇表中单词量。注意,syn1也是一个一维real(float)数组,容量为 vocab_size * layer1_size
syn1neg: 这是单词的另一个向量表示,之前看斯坦福自然语言处理视频中有提到过每个单词会训练出两个向量,现在看来的确是这
样,不过是通过negative方式训练才有。这个向量是用于负采样模式优化时需要的变量。也是一个一维的float数组,
大小是 vocab_size * layer1_size。初始化代码如下:
//初始化网络
void InitNet() {
long long a, b;
unsigned long long next_random = 1;
//为syn0分配内存,对齐的内存,大小为vocab_size * layer1_size * sizeof(real),也就是每个词汇对应一个layer1_size的向量
a = posix_memalign((void **)&syn0, 128, (long long)vocab_size * layer1_size * sizeof(real));
if (syn0 == NULL) {printf("Memory allocation failed\n"); exit(1);}
//如果采用huffman softmax构造,那么需要初始化syn1,大小为vocab_size * layer1_size * sizeof(real),每个词对应一个
if (hs) {
a = posix_memalign((void **)&syn1, 128, (long long)vocab_size * layer1_size * sizeof(real));
if (syn1 == NULL) {printf("Memory allocation failed\n"); exit(1);}
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) for (b = 0; b < layer1_size; b++)
syn1[a * layer1_size + b] = 0;
}
//如果采用负采样进行训练,那么久初始化syn1neg,大小为vocab_size * layer1_size * sizeof(real),每个词对应一个
if (negative>0) {
a = posix_memalign((void **)&syn1neg, 128, (long long)vocab_size * layer1_size * sizeof(real));
if (syn1neg == NULL) {printf("Memory allocation failed\n"); exit(1);}
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) for (b = 0; b < layer1_size; b++)
syn1neg[a * layer1_size + b] = 0;
}
//对syn0中每个词对应的词向量进行初始化
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) for (b = 0; b < layer1_size; b++) {
next_random = next_random * (unsigned long long)25214903917 + 11; //生成一个很大的数
syn0[a * layer1_size + b] = (((next_random & 0xFFFF) / (real)65536) - 0.5) / layer1_size;//& 0xFFFF表示截断为[0, 65536]
}
//构建huffman softmax需要的哈夫曼树
CreateBinaryTree();
}syn0的每个值的范围为:![]() ,m表示向量维度;syn1初始化为0;syn1neg也初始化为0.
,m表示向量维度;syn1初始化为0;syn1neg也初始化为0.
2.构建哈夫曼树
// Create binary Huffman tree using the word counts
// Frequent words will have short uniqe binary codes
void CreateBinaryTree() {
long long a, b, i, min1i, min2i, pos1, pos2, point[MAX_CODE_LENGTH];
char code[MAX_CODE_LENGTH];
//分配的空间大小为,(vocab_size * 2 + 1) * sizeof(long long),因为hufuman树的特性,所以总结点数是2 * n + 1, 其中n是节点数, 此处应该有错误,是2 * n - 1才对
long long *count = (long long *)calloc(vocab_size * 2 + 1, sizeof(long long)); //节点对应频率
long long *binary = (long long *)calloc(vocab_size * 2 + 1, sizeof(long long)); //记录每个节点是左节点还是右节点
long long *parent_node = (long long *)calloc(vocab_size * 2 + 1, sizeof(long long)); //父节点位置
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) count[a] = vocab[a].cn;
//后面的设为无穷
for (a = vocab_size; a < vocab_size * 2; a++) count[a] = 1e15;
pos1 = vocab_size - 1;
pos2 = vocab_size;
// Following algorithm constructs the Huffman tree by adding one node at a time
//如同天才般的代码,一次遍历就构造好了huffuman树, ##注意,这个a还代表了一种顺序,所有count值由小到大的顺序##
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size - 1; a++) {
// First, find two smallest nodes 'min1, min2',注意vocab中的词是已经按照cn排好序的了,是按照降序排列的
//pos1表示取最原始的词对应的词频,而pos2表示取合并最小值形成的词频
//连续两次取,两次取的时候代码操作时一模一样的
if (pos1 >= 0) {
if (count[pos1] < count[pos2]) {
min1i = pos1;
pos1--;
} else {
min1i = pos2;
pos2++;
}
} else {
min1i = pos2;
pos2++;
}
if (pos1 >= 0) {
if (count[pos1] < count[pos2]) {
min2i = pos1;
pos1--;
} else {
min2i = pos2;
pos2++;
}
} else {
min2i = pos2;
pos2++;
}
count[vocab_size + a] = count[min1i] + count[min2i];
parent_node[min1i] = vocab_size + a; //记录好合并形成的父节点的位置
parent_node[min2i] = vocab_size + a;
binary[min2i] = 1; //左为0,右为1
}
// Now assign binary code to each vocabulary word
// 建好了hufuman树之后,就需要分配code了,注意这个hufuman树是用一个数组来存储的,并不是我们常用的指针式链表
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) {
b = a;
i = 0;
while (1) {
code[i] = binary[b]; //对于每个节点,自底向上得到code值,通过每个节点的binary来实现
point[i] = b; //point记录节点到根节点经过的节点的路径
i++;
b = parent_node[b];
if (b == vocab_size * 2 - 2) break;
}
vocab[a].codelen = i; //记录词对应的码值的长度
vocab[a].point[0] = vocab_size - 2; //最大值作为根节点
for (b = 0; b < i; b++) {
vocab[a].code[i - b - 1] = code[b]; //倒序过来,自顶向下
vocab[a].point[i - b] = point[b] - vocab_size; //注意这个索引对应的是huffman树中的非叶子节点,对应syn1中的索引, 因为非叶子节点都是在vocab_size * 2 + 1 的后(vocab_size + 1)个
}
}
free(count);
free(binary);
free(parent_node);
}多么简洁而亮眼的代码。它主要利用了词汇表的有序性,是降序排列。所以刚开始 pos1 = vocab_size - 1 是原始词汇表中词频最小的那个单词。每次合并两个最小值,我们将新生成的节点放到后vocab-size + 1个位置,并且也是有序的往后填充,所以最终代表huffman数的count数组有一个特性,都是中心往两头在递增值。所以,我们每次取最小值,只需要比较两头中哪一头的当前值最小,就能取到两个最小值。
3.初始化负采样概率表
如果是采用负采样的方法,此时还需要初始化每个词被选中的概率。在所有的词构成的词典中,每一个词出现的频率有高有低,我们希望,对于那些高频的词,被选中成为负样本的概率要大点,同时,对于那些出现频率比较低的词,我们希望其被选中成为负样本的频率低点。
//生成负采样的概率表
void InitUnigramTable() {
int a, i;
double train_words_pow = 0;
double d1, power = 0.75;
table = (int *)malloc(table_size * sizeof(int));
//pow(x, y)计算x的y次方;train_words_pow表示总的词的概率,不是直接用每个词的频率,而是频率的0.75次方幂
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) train_words_pow += pow(vocab[a].cn, power);
i = 0;
d1 = pow(vocab[i].cn, power) / train_words_pow;
//每个词在table中占的小格子数是不一样的,频率高的词,占的格子数显然多
for (a = 0; a < table_size; a++) {
table[a] = i;
if (a / (double)table_size > d1) {
i++;
d1 += pow(vocab[i].cn, power) / train_words_pow;
}
if (i >= vocab_size) i = vocab_size - 1;
}
}(五)模型训练
关于word2vec的CBOW和SKIP模型原理,强力推荐大神的博客讲解,虽然有错误细节,但是大体思想都是正确的。
首先定义了几个重要的变量,变量解释如下:
last_word: 当前窗口正在训练的词的索引。
sentence_length: 当前训练的句子的长度
sentence_position: 当前中心词在句子中的位置
sen: 数组,存的是句子中每个词在词汇表中的索引
neu1: 是cbow模式下映射层对应的上下文向量表示,为上下文中所有词向量的平均值
neu1e: 因为skip模式下,映射层向量就是输入层向量的复制,所以neu1e仅仅用来记录上下文词对输入层的梯度。每次读取一条句子,记录好句子中每个词在词汇表中对应的索引。如果启用了下采样,则会随机的跳过一些词,会随机的丢弃频繁的单词,同时保持顺序不变。代码如下:
if (sentence_length == 0) {
while (1) {
word = ReadWordIndex(fi); //得到词在词汇表中对应的索引
if (feof(fi)) break; //
if (word == -1) continue;
word_count++; //句子总的次数
if (word == 0) break; //遇到换行符,则直接跳出来,第一个词''代表换行符
// The subsampling randomly discards frequent words while keeping the ranking same
//下采样随机丢弃频繁的单词,同时保持排名相同,随机跳过一些词的训练
if (sample > 0) {
real ran = (sqrt(vocab[word].cn / (sample * train_words)) + 1) * (sample * train_words) / vocab[word].cn;
next_random = next_random * (unsigned long long)25214903917 + 11;
//频率越大的词,对应的ran就越小,越容易被抛弃,被跳过
if (ran < (next_random & 0xFFFF) / (real)65536) continue;
}
sen[sentence_length] = word; //当前句子包含的词,存的是索引
sentence_length++; //句子实际长度,减去跳过的词
if (sentence_length >= MAX_SENTENCE_LENGTH) break;
}
sentence_position = 0;
} 然后就开始训练了,先初始化了neu1和neu1e的值。并且确定了窗口的起始位置,通过b = next_random % window来确定,理论上,我们在中心词左右都是取大小为window个上下文词,但是在代码中,并不是保证左右都是window个,而是左边为(window - b)个, 右边为(window + b)个,总数仍然是2 * window个。训练的时候,有两种训练模型,分别是CBOW模型和SKIP模型;对于每种模型,又有两种训练模式,分别为huffman softmax模式(hs)和negative模式(负采样),下面分别讲解。
1.CBOW模型
在CBOW模型中,总共有三层,分别是输入层,映射层和输出层。如下图所示: ![]()
hs模式和negative模式中,输入层到映射层的处理是一样的,仅仅是映射层到输出层的处理不一致。输入层到映射层的具体操作是:将上下文窗口中的每个词向量求和,然后再平均,得到一个和词向量一样维度的向量,假设叫上下文向量,这个向量就是映射层的向量。代码如下:
if (cbow) { //train the cbow architecture
// in -> hidden
cw = 0;
//随机取一个词word,然后计算该词上下文词对应的向量的各维度之和
for (a = b; a < window * 2 + 1 - b; a++) if (a != window) {
c = sentence_position - window + a;
if (c < 0) continue;
if (c >= sentence_length) continue;
last_word = sen[c]; //获得senten中第c个词的索引
if (last_word == -1) continue;
//注意syn0是一维数组,不是二维的,所以通过last_word * layer1_size来定位某个词对应的向量位置, last_word表示上下文中上一个词
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) neu1[c] += syn0[c + last_word * layer1_size]; //neu1表示映射层向量,上下文累加平均
cw++;
}
if (cw) {
//上下文表示是所有词对应词向量的平均值
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) neu1[c] /= cw;
......
}
......
}1.1 hs模式
huffman softmax中,计算上下文向量到中心词的概率,是一连串的二分类问题,因为从根节点到中心词对应的叶子节点,需要多次决定沿左节点还是右节点到叶子节点。详细介绍请参考word2vec数学原理详解。对于中心词w,从根节点到中心词节点的总概率为
再对应代码实现:
if (hs) for (d = 0; d < vocab[word].codelen; d++) {
f = 0;
l2 = vocab[word].point[d] * layer1_size; //索引到该词在数组偏移量
// Propagate hidden -> output, 传播过程
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) f += neu1[c] * syn1[c + l2]; //注意syn1也是一维数组,不同词对应的位置需要偏移量l2确定
if (f <= -MAX_EXP) continue; //当f值不属于[-MAX_EXP, MAX_EXP]
else if (f >= MAX_EXP) continue;
else f = expTable[(int)((f + MAX_EXP) * (EXP_TABLE_SIZE / MAX_EXP / 2))]; //查看f属于第几份,((f + MAX_EXP) / (2 * MAX_EXP)) * EXP_TABLE_SIZE
// 'g' is the gradient multiplied by the learning rate
g = (1 - vocab[word].code[d] - f) * alpha; //需要推导,得到这个梯度比例
// Propagate errors output -> hidden
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) neu1e[c] += g * syn1[c + l2]; //这个部分才是最终梯度值
// Learn weights hidden -> output
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) syn1[c + l2] += g * neu1[c]; //加上梯度值,更新syn1
}更新词向量代码如下:
// hidden -> in
//更新输入层的词向量
for (a = b; a < window * 2 + 1 - b; a++) if (a != window) {
c = sentence_position - window + a;
if (c < 0) continue;
if (c >= sentence_length) continue;
last_word = sen[c];
if (last_word == -1) continue;
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) syn0[c + last_word * layer1_size] += neu1e[c];
}1.2 negative模式
导数就能够进行梯度上升求最大值。实现代码如下:
// NEGATIVE SAMPLING
if (negative > 0) for (d = 0; d < negative + 1; d++) {
if (d == 0) { //一个正样本
target = word;
label = 1;
} else {
next_random = next_random * (unsigned long long)25214903917 + 11; //随机挑选一个负样本,负样本就是除中心词以外的所有词
target = table[(next_random >> 16) % table_size];
if (target == 0) target = next_random % (vocab_size - 1) + 1; //如果target为0,这个等式保证不为0
if (target == word) continue; //正样本则跳过
label = 0;
}
l2 = target * layer1_size; //syn1neg是一维数组,某个词需要先计算偏移量
f = 0;
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) f += neu1[c] * syn1neg[c + l2]; //负采样实际会为每个词生成两个向量
if (f > MAX_EXP) g = (label - 1) * alpha;
else if (f < -MAX_EXP) g = (label - 0) * alpha;
else g = (label - expTable[(int)((f + MAX_EXP) * (EXP_TABLE_SIZE / MAX_EXP / 2))]) * alpha;
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) neu1e[c] += g * syn1neg[c + l2];
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) syn1neg[c + l2] += g * neu1[c];
}更新词向量代码如下:
// hidden -> in
//更新输入层的词向量
for (a = b; a < window * 2 + 1 - b; a++) if (a != window) {
c = sentence_position - window + a;
if (c < 0) continue;
if (c >= sentence_length) continue;
last_word = sen[c];
if (last_word == -1) continue;
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) syn0[c + last_word * layer1_size] += neu1e[c];
}2. SKIP模型
skip模型中,也是三层,输入层、映射层和输出层。结构如下: ![]()
skip模型和cbow模型优化类似,主要是输入层到映射层之间不同,cbow中是上下文词向量平均求和,而skip模型中是直接复制中心词向量。skip模型中,优化过程是逐个计算中心词和上下文词之间的概率,使其最大化,所以和cbow中的优化计算基本类似,代码如下:
else { //train skip-gram
//还是保证一个2 * window大小上下文,但是中心词左右并不一定刚好都是window个,根据b确定
for (a = b; a < window * 2 + 1 - b; a++) if (a != window) {
c = sentence_position - window + a; //c表示上下文的当前遍历位置
if (c < 0) continue;
if (c >= sentence_length) continue;
last_word = sen[c]; //用来记录上一个词
if (last_word == -1) continue; //如果词不在词汇表中,则直接跳过
l1 = last_word * layer1_size; //偏移量,因为syn0是一维数组,每个词对应的向量需要先偏移前面的词对应向量
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) neu1e[c] = 0;
// HIERARCHICAL SOFTMAX
//不需要像cbow一样求平均
if (hs) for (d = 0; d < vocab[word].codelen; d++) {
f = 0;
l2 = vocab[word].point[d] * layer1_size; //
// Propagate hidden -> output
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) f += syn0[c + l1] * syn1[c + l2];
if (f <= -MAX_EXP) continue;
else if (f >= MAX_EXP) continue;
else f = expTable[(int)((f + MAX_EXP) * (EXP_TABLE_SIZE / MAX_EXP / 2))];
// 'g' is the gradient multiplied by the learning rate
g = (1 - vocab[word].code[d] - f) * alpha;
// Propagate errors output -> hidden
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) neu1e[c] += g * syn1[c + l2];
// Learn weights hidden -> output
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) syn1[c + l2] += g * syn0[c + l1];
}
// NEGATIVE SAMPLING
if (negative > 0) for (d = 0; d < negative + 1; d++) {
if (d == 0) { //正样本
target = word;
label = 1;
} else { //负样本
next_random = next_random * (unsigned long long)25214903917 + 11;
target = table[(next_random >> 16) % table_size];
if (target == 0) target = next_random % (vocab_size - 1) + 1;
if (target == word) continue;
label = 0;
}
l2 = target * layer1_size; //偏移量
f = 0;
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) f += syn0[c + l1] * syn1neg[c + l2];//
if (f > MAX_EXP) g = (label - 1) * alpha; //计算梯度
else if (f < -MAX_EXP) g = (label - 0) * alpha;
else g = (label - expTable[(int)((f + MAX_EXP) * (EXP_TABLE_SIZE / MAX_EXP / 2))]) * alpha;
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) neu1e[c] += g * syn1neg[c + l2]; //完整梯度
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) syn1neg[c + l2] += g * syn0[c + l1];//更新
}
// Learn weights input -> hidden
//更新输入层权重
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) syn0[c + l1] += neu1e[c];
}
}(六)结果处理
可以直接保存结果或者用k-means聚类算法分析结果,代码如下:
//训练模型
void TrainModel() {
long a, b, c, d;
FILE *fo;
pthread_t *pt = (pthread_t *)malloc(num_threads * sizeof(pthread_t));
printf("Starting training using file %s\n", train_file);
starting_alpha = alpha; //设置学习率
if (read_vocab_file[0] != 0) ReadVocab(); else LearnVocabFromTrainFile(); //获得词汇表,如果已经有直接读,否则学
if (save_vocab_file[0] != 0) SaveVocab();
if (output_file[0] == 0) return; //必须有输出文件参数
InitNet(); //初始化网络参数
if (negative > 0) InitUnigramTable(); //如果是使用负采样,那么需要负采样概率表
start = clock(); //计时器
for (a = 0; a < num_threads; a++) pthread_create(&pt[a], NULL, TrainModelThread, (void *)a);
for (a = 0; a < num_threads; a++) pthread_join(pt[a], NULL);
fo = fopen(output_file, "wb");
if (classes == 0) { //classes判断是否使用kmean聚类,为0表示否
// Save the word vectors
fprintf(fo, "%lld %lld\n", vocab_size, layer1_size);
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) {
fprintf(fo, "%s ", vocab[a].word);
if (binary) for (b = 0; b < layer1_size; b++) fwrite(&syn0[a * layer1_size + b], sizeof(real), 1, fo);
else for (b = 0; b < layer1_size; b++) fprintf(fo, "%lf ", syn0[a * layer1_size + b]);
fprintf(fo, "\n");
}
} else {
// Run K-means on the word vectors
//类别中心数,迭代次数,
int clcn = classes, iter = 10, closeid;
int *centcn = (int *)malloc(classes * sizeof(int)); //每个中心点拥有的词数量
int *cl = (int *)calloc(vocab_size, sizeof(int)); //每个词所属类别标签
real closev, x;
real *cent = (real *)calloc(classes * layer1_size, sizeof(real)); //聚类中心,注意是用一维数组表示,每个中心需要通过偏移量来定位
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) cl[a] = a % clcn; //初始化每个词所属类别
for (a = 0; a < iter; a++) { //开始训练
for (b = 0; b < clcn * layer1_size; b++) cent[b] = 0; //初始化中心点位置
for (b = 0; b < clcn; b++) centcn[b] = 1; //初始化每个中心点拥有的词的数量
//求每个中心点每个维度值的总和,等于所有属于这个类别的词向量的相应维度相加
for (c = 0; c < vocab_size; c++) {
for (d = 0; d < layer1_size; d++) cent[layer1_size * cl[c] + d] += syn0[c * layer1_size + d];
centcn[cl[c]]++; //所包含词的数量+1
}
//对于每一个类别,需要更新中心点各维度值,就是总和平均
for (b = 0; b < clcn; b++) {
closev = 0;
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) { //遍历每个维度
cent[layer1_size * b + c] /= centcn[b]; //每个词每个维度平均
closev += cent[layer1_size * b + c] * cent[layer1_size * b + c]; //求每个中心点的模的平方
}
closev = sqrt(closev); //每个中心点模
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) cent[layer1_size * b + c] /= closev; //归一化处理
}
//更新每个词所属的类别,看离哪个中心点最近就归为相应的类别
for (c = 0; c < vocab_size; c++) {
closev = -10; //记录离最近中心点距离
closeid = 0; //记录最近的类别id
for (d = 0; d < clcn; d++) {
x = 0;
for (b = 0; b < layer1_size; b++) x += cent[layer1_size * d + b] * syn0[c * layer1_size + b];
if (x > closev) {
closev = x;
closeid = d;
}
}
cl[c] = closeid;
}
}
// Save the K-means classes
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) fprintf(fo, "%s %d\n", vocab[a].word, cl[a]);
free(centcn);
free(cent);
free(cl);
}
fclose(fo);
}
int ArgPos(char *str, int argc, char **argv) {
int a;
for (a = 1; a < argc; a++) if (!strcmp(str, argv[a])) {
if (a == argc - 1) {
printf("Argument missing for %s\n", str);
exit(1);
}
return a;
}
return -1;
}
源码:
// Copyright 2013 Google Inc. All Rights Reserved.
//
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
// You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
// limitations under the License.
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define MAX_STRING 100 // 一个word的最大长度
#define EXP_TABLE_SIZE 1000 // 对sigmoid的运算结果进行缓存,存储1000个,需要用的时候查表
#define MAX_EXP 6 // 最大计算到6 (exp^6 / (exp^6 + 1)),最小计算到-6 (exp^-6 / (exp^-6 + 1))
#define MAX_SENTENCE_LENGTH 1000 // 定义最大的句子长度
#define MAX_CODE_LENGTH 40 //point域和code域大小 // 定义最长的霍夫曼编码长度
// 哈希,线性探测,开放定址法,装填系数0.7
const int vocab_hash_size = 30000000; // Maximum 30 * 0.7 = 21M words in the vocabulary
typedef float real; // Precision of float numbers
//2.1构建词库的过程:词的结构体
struct vocab_word {
long long cn; //词频,,来自于vocab file或者从训练模型中来计算
int *point; // 霍夫曼树中从根节点到该词的路径,存放路径上每个非叶结点的索引
char *word, *code, codelen; // 分别对应着:词,Huffman编码,编码长度
};
// 训练文件、输出文件名称定义
char train_file[MAX_STRING], output_file[MAX_STRING];
// 词汇表输出文件和词汇表读入文件名称定义
char save_vocab_file[MAX_STRING], read_vocab_file[MAX_STRING];
// 声明词汇表结构体,//输入文件中每个基本词的结构体数组
struct vocab_word *vocab;
// binary 0则vectors.bin输出为二进制(默认),1则为文本形式
// cbow 1使用cbow框架,0使用skip-gram框架
// debug_mode 大于0,加载完毕后输出汇总信息,大于1,加载训练词汇的时候输出信息,训练过程中输出信息
// window 窗口大小,在cbow中表示了word vector的最大的sum范围,在skip-gram中表示了max space between words(w1,w2,p(w1 | w2))
// min_count 设置最低频率,默认是5,如果一个词语在文档中出现的次数小于5,那么就会丢弃
// num_threads 线程数
// min_reduce ReduceVocab删除词频小于这个值的词,因为哈希表总共可以装填的词汇数是有限的
//如果词典的大小N>0.7*vocab_hash_size,则从词典中删除所有词频小于min_reduce的词。
int binary = 0, cbow = 1, debug_mode = 2, window = 5, min_count = 5, num_threads = 12, min_reduce = 1;
// 词汇表的hash存储,下标是词的hash,内容是词在vocab中的位置,a[word_hash] = word index in vocab
int *vocab_hash;
// vocab_max_size 词汇表的最大长度,可以扩增,每次扩1000
// vocab_size 词汇表的现有长度,接近vocab_max_size的时候会扩容
// layer1_size 隐层的节点数
long long vocab_max_size = 1000, vocab_size = 0, layer1_size = 100;
// train_words 训练的单词总数(词频累加)
// word_count_actual 已经训练完的word个数
// file_size 训练文件大小,ftell得到
// classes 输出word clusters的类别数(聚类的数目)
long long train_words = 0, word_count_actual = 0, iter = 5, file_size = 0, classes = 0;
// alpha BP算法的学习速率,过程中自动调整
// starting_alpha 初始alpha值
// sample 亚采样概率的参数,亚采样的目的是以一定概率拒绝高频词,使得低频词有更多出镜率,默认为0,即不进行亚采样
//(采样的阈值,如果一个词语在训练样本中出现的频率越大,那么就越会被采样)
real alpha = 0.025, starting_alpha, sample = 1e-3;
// syn0 表示: 存储词典中每个词的词向量
// syn1 表示: hs(hierarchical softmax)算法中霍夫曼编码树非叶结点的权重
// syn1neg 表示: ns(negative sampling)负采样时,存储每个词对应的辅助向量(可以参考https://blog.csdn.net/itplus/article/details/37998797)
// expTable 预先存储sigmod函数结果,算法执行中查表,提前计算好,提高效率
real *syn0, *syn1, *syn1neg, *expTable;
// start 算法运行的起始时间,会用于计算平均每秒钟处理多少词
clock_t start;
// hs 采用hs还是ns的标志位,默认采用ng
int hs = 0, negative = 5;
// table_size 静态采样表的规模
// table 采样表
const int table_size = 1e8;
int *table;
// 根据词频生成采样表,也就是每个单词的能量分布表,table在负采样中用到
//3.网络模型初始化:负采样初始化,生成负采样概率表
void InitUnigramTable() {
int a, i;
double train_words_pow = 0;
double d1, power = 0.75; // 概率与词频的power次方成正比
table = (int *)malloc(table_size * sizeof(int));
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) train_words_pow += pow(vocab[a].cn, power); //遍历词汇表,统计词的能量总值train_words_pow
i = 0;
d1 = pow(vocab[i].cn, power) / train_words_pow; //表示已遍历词的能量值占总能量的比
//a - table表的索引
//i - 词汇表的索引
for (a = 0; a < table_size; a++) {
table[a] = i;//单词i占用table的a位置 //table反映的是一个单词能量的分布,一个单词能量越大,所占用的table的位置越多
if (a / (double)table_size > d1) {
i++; //移到下个词
d1 += pow(vocab[i].cn, power) / train_words_pow;
}
if (i >= vocab_size) i = vocab_size - 1; // 处理最后一段概率,所有落在最后一个概率区间的,都选中最后一个词
}
}
// Reads a single word from a file, assuming space + tab + EOL to be word boundaries
// 每次从fin中读取一个单词
//2.1构建词库的过程:NO.2 开始读取文件中的每一个词
void ReadWord(char *word, FILE *fin) {
int a = 0, ch; //a - 用于向word中插入字符的索引;ch - 从fin中读取的每个字符
while (!feof(fin)) {
ch = fgetc(fin);
if (ch == 13) continue; //回车,开始新的一行,重新开始while循环读取下一个字符
//当遇到space(' ') + tab(\t) + EOL(\n)时,认为word结束,UNIX/Linux中‘\n’为一行的结束符号,windows中为:“<回车><换行>”,即“\r\n”;Mac系统里,每行结尾是“<回车>”,即“\r”。
if ((ch == ' ') || (ch == '\t') || (ch == '\n')) {
if (a > 0) {
if (ch == '\n') ungetc(ch, fin); //跳出while循环,这里的特例是‘\n’,我们需要将‘\n’回退给fin,词汇表中'\n'用来表示。
break;
}
if (ch == '\n') {
strcpy(word, (char *)""); //此时word还为空(a=0),直接将赋给word
return;
} else continue; //此时a=0,且遇到的为\t or ' ',直接跳过取得下一个字符
}
word[a] = ch;
a++;
if (a >= MAX_STRING - 1) a--; // Truncate too long words
}
word[a] = 0; //字符串末尾以/0作为结束符
}
// Returns hash value of a word
//2.1构建词库的过程:返回一个词的hash值,,一个词跟hash值一一对应(可能冲突,采用顺序查找法解决)
int GetWordHash(char *word) {
unsigned long long a, hash = 0;
for (a = 0; a < strlen(word); a++) hash = hash * 257 + word[a]; //int和char相加,相当于加了char的ansii值
hash = hash % vocab_hash_size;
return hash;
}
// Returns position of a word in the vocabulary; if the word is not found, returns -1
// 线性探索,开放定址法
//2.1构建词库的过程:NO.4 查找词在词库中位置,检索词是否存在。如不存在则返回-1,否则,返回该词在词库中的索引
int SearchVocab(char *word) {
unsigned int hash = GetWordHash(word);
while (1) {
if (vocab_hash[hash] == -1) return -1; // 没有这个词
if (!strcmp(word, vocab[vocab_hash[hash]].word)) return vocab_hash[hash]; // 返回单词在词汇表中的索引
hash = (hash + 1) % vocab_hash_size; //继续顺序往下查找,因为前面存储的时候,遇到冲突就是顺序往下查找存储位置的
}
return -1;
}
// Reads a word and returns its index in the vocabulary
//2.1构建词库的过程:// 从文件流中读取一个词,并返回这个词在词汇表中的位置
int ReadWordIndex(FILE *fin) {
char word[MAX_STRING];
ReadWord(word, fin);
if (feof(fin)) return -1; //当文件只有一个EOF字符时,当将EOF读入word后,_IOEOF被设置,达到文件尾。
return SearchVocab(word);
}
// Adds a word to the vocabulary
// 将一个词添加到一个词汇中,返回该词在词汇表中的位置
//2.1构建词库的过程:NO.6 词不存在,把它添加到词库中,通过hash表存储。否则:词频+1
int AddWordToVocab(char *word) {
unsigned int hash, length = strlen(word) + 1;
if (length > MAX_STRING) length = MAX_STRING;
vocab[vocab_size].word = (char *)calloc(length, sizeof(char)); // 单词存储,//在当前词汇表末尾添加word
strcpy(vocab[vocab_size].word, word);
vocab[vocab_size].cn = 0; //词频记为0, 在调用函数之外赋值1
vocab_size++; // 词汇表现有单词数
// Reallocate memory if needed
if (vocab_size + 2 >= vocab_max_size) {
vocab_max_size += 1000; // 每次增加1000个词位
vocab = (struct vocab_word *)realloc(vocab, vocab_max_size * sizeof(struct vocab_word));
}
hash = GetWordHash(word); // 获得hash表示
while (vocab_hash[hash] != -1) hash = (hash + 1) % vocab_hash_size; // 线性探索hash
vocab_hash[hash] = vocab_size - 1; // 记录在词汇表中的存储位置
return vocab_size - 1; // 返回添加的单词在词汇表中的存储位置
}
// Used later for sorting by word counts
//2.1构建词库的过程:NO.8 按词频排序,关键结构体比较函数
// 比较函数,词汇表需使用词频进行排序(qsort),从大到小进行排序
int VocabCompare(const void *a, const void *b) {
return ((struct vocab_word *)b)->cn - ((struct vocab_word *)a)->cn;
}
// Sorts the vocabulary by frequency using word counts
//2.1构建词库的过程:NO.8 按词频排序
// 根据词频排序
// 通过排序把出现数量少的word排在vocab数组的后面
//同时,给霍夫曼编码和路径的词汇表索引分配空间
void SortVocab() {
int a, size;
unsigned int hash;
// Sort the vocabulary and keep at the first position // 保留回车在首位
qsort(&vocab[1], vocab_size - 1, sizeof(struct vocab_word), VocabCompare); // 对词汇表进行快速排序
for (a = 0; a < vocab_hash_size; a++) vocab_hash[a] = -1; // 词汇重拍了,哈希记录的index也乱了,所有的hash记录清除,下面会重建
size = vocab_size;
train_words = 0; // 用于训练的词汇总数(词频累加)
for (a = 0; a < size; a++) {
// Words occuring less than min_count times will be discarded from the vocab
if ((vocab[a].cn < min_count) && (a != 0)) { // 清除长尾词,放在vocab的第
vocab_size--;
free(vocab[a].word);
} else {
// Hash will be re-computed, as after the sorting it is not actual
hash=GetWordHash(vocab[a].word);
while (vocab_hash[hash] != -1) hash = (hash + 1) % vocab_hash_size;//处理冲突
vocab_hash[hash] = a;
train_words += vocab[a].cn; // 词频累加
}
}
//重新指定vocab的内存大小,realloc 可重新指定vocab的内存大小,可大可小
//分配的多余空间收回
vocab = (struct vocab_word *)realloc(vocab, (vocab_size + 1) * sizeof(struct vocab_word));
// Allocate memory for the binary tree construction
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) { // 给霍夫曼编码和路径的词汇表索引分配空间
vocab[a].code = (char *)calloc(MAX_CODE_LENGTH, sizeof(char));
vocab[a].point = (int *)calloc(MAX_CODE_LENGTH, sizeof(int));
}
}
// Reduces the vocabulary by removing infrequent tokens
void ReduceVocab() {
int a, b = 0;
unsigned int hash;
//如果词典的大小N>0.7*vocab_hash_size,则从词典中删除所有词频小于min_reduce的词。
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) if (vocab[a].cn > min_reduce) {
vocab[b].cn = vocab[a].cn;
vocab[b].word = vocab[a].word;
b++;
} else free(vocab[a].word); //清理指针所指向的内存区域
vocab_size = b; // 最后剩下b个词,词频均大于min_reduce
// 重新分配hash索引
//在删除了低频词后,需要重新对词库中的词进行hash值的计算
for (a = 0; a < vocab_hash_size; a++) vocab_hash[a] = -1;
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) {
// Hash will be re-computed, as it is not actual
hash = GetWordHash(vocab[a].word);
while (vocab_hash[hash] != -1) hash = (hash + 1) % vocab_hash_size;
vocab_hash[hash] = a;
}
fflush(stdout);
min_reduce++;
}
//3.3.创建huffman树:CreateBinaryTree
// Create binary Huffman tree using the word counts
// Frequent words will have short uniqe binary codes
// 利用单词计数的频率 将会有很短的二元代码。
void CreateBinaryTree() {
long long a, b, i, min1i, min2i, pos1, pos2, point[MAX_CODE_LENGTH]; //MAX_CODE_LENGTH: 最长的编码值,point:记录从root到word的路径
char code[MAX_CODE_LENGTH];
// calloc initializes the memory to zeros
// SHOULD IT BE vocab_size * 2 - 1 - this is because
// it seems that is in part of construction, but vocab_size is
// actually len(vocab)-1, excluding
//count数组中前vocab_size存储的是每一个词的对应的词频,后面初始化的是很大的数,用来存储生成节点的频数
//binary数组中前vocab_size存储的是每一个词的对应的二进制编码,后面初始化的是0,用来存储生成节点的编码
//parent_node数组中前vocab_size存储的是每一个词的对应的父节点,后面初始化的是0,用来存储生成节点的父节点
long long *count = (long long *)calloc(vocab_size * 2 + 1, sizeof(long long));
long long *binary = (long long *)calloc(vocab_size * 2 + 1, sizeof(long long));
long long *parent_node = (long long *)calloc(vocab_size * 2 + 1, sizeof(long long));
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) count[a] = vocab[a].cn; // count - word counts of all words
// extend count as twice large
// SO ONLY vocab_size * 2 - 1 elements will BE NEEDED, EVEN FOR A COMPLETE TREE
for (a = vocab_size; a < vocab_size * 2; a++) count[a] = 1e15;
// initialize the node positions
pos1 = vocab_size - 1;
pos2 = vocab_size;
// Following algorithm constructs the Huffman tree by adding one node at a time
// the vocab should have been sorted IN DECREASING order
// pos1 and pos2 will be the two current smallest node
// they could be the original elements, they could be composed parent nodes
// the parents node will be constructed and placed along the array
// from [vocab_size to vocab_size * 2 - 1].
// THE GOOD THING IS: the elements on the left of pos1 are all SORTED,
// and the elements on the right of pos2 will also be SORTED.
// THE LAST WORD WILL ALSO BE INCLUDED IN THE TREE
// ONLY NEED TO CONSTRUCT vocab_size - 1 times, that is max number
// of parent nodes for a complete binary tree
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size - 1; a++) {
// First, find two smallest nodes 'min1, min2'
// 每次寻找两个最小的点做合并,最小的点为0,词小的点为1
if (pos1 >= 0) {
if (count[pos1] < count[pos2]) {
min1i = pos1;
pos1--;
} else {
min1i = pos2;
pos2++;
}
} else { // no choice, can move right ONLy now
min1i = pos2;
pos2++;
}
if (pos1 >= 0) {
if (count[pos1] < count[pos2]) { // move left via pos1
min2i = pos1;
pos1--;
} else { // move right via pos2
min2i = pos2;
pos2++;
}
} else {
min2i = pos2;
pos2++;
}
count[vocab_size + a] = count[min1i] + count[min2i]; // parent's count is the sum of children's counts //存储算法生成的中间节点的词频
// commmon parents
// level 2 parents will be from vocab_size to vocab_size * 2
parent_node[min1i] = vocab_size + a; //存储父节点的编号:为叶子节点数目+a,a表示当前生成第a个节点
parent_node[min2i] = vocab_size + a;
// binary code: min1i 0 min2i 1, for each leaf and internal node
binary[min2i] = 1; //存储两个节点中 词频大的节点定为1,代表负类
}
// Now assign binary code to each vocabulary word
// 顺着父子关系找回编码
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) {
b = a;
i = 0;
//找到一个word的huffman编码
while (1) {
code[i] = binary[b]; // 编码赋值
point[i] = b; // 路径赋值,第一个是自己
i++; // 码个数
b = parent_node[b];
if (b == vocab_size * 2 - 2) break; //到达根节点所在索引,结束
}
// 以下要注意的是,同样的位置,point总比code深一层
vocab[a].codelen = i; // 编码长度赋值,少1,没有算根节点
// point - relative index of parent from vocab_size+1,这个地方看了半天,一定要注意,这是个相对索引,但是并不影响后面的计算
// in reverse order - path from root to the current word (leaf node)
vocab[a].point[0] = vocab_size - 2; // //路径第一个节点为:根节点; 逆序,把第一个赋值为root(即2*vocab_size - 2 - vocab_size)
for (b = 0; b < i; b++) { // 逆序处理
vocab[a].code[i - b - 1] = code[b]; // 编码逆序,没有根节点,左子树0,右子树1,//下面存放每个基本词的路径,注意i - b - 1是距离叶子节点最近的父节点的编码
////生成的第i个节点,记录的是从根结点到叶子节点的路径
vocab[a].point[i - b] = point[b] - vocab_size; // 其实point数组最后一个是负的,用不到,point的长度是编码的真正长度,比code长1
}
}
free(count);
free(binary);
free(parent_node);
}
// 装载训练文件到词汇表数据结构
void LearnVocabFromTrainFile() {
char word[MAX_STRING];
FILE *fin;
long long a, i;
for (a = 0; a < vocab_hash_size; a++) vocab_hash[a] = -1;
fin = fopen(train_file, "rb");
if (fin == NULL) {
printf("ERROR: training data file not found!\n");
exit(1);
}
vocab_size = 0;
//2.1构建词库的过程:ON.1 在词库中第一个位置添加空格,
//该词代表语料中出现的换行符,它虽然也对应一个词向量
//但这个向量在训练过程中,并不参与运算.
//其主要作用是用来判别一个句子的结束。
AddWordToVocab((char *)""); //最初将添加到vocab的第一个位置,后续再读取word的时候,把“\N换成了”
//2.1构建词库的过程:NO.2-7循环读取每一个词
while (1) {
//2.1构建词库的过程:NO.2 开始读取文件中的每一个词
ReadWord(word, fin);
//2.1构建词库的过程:NO.3 判断文件是否结束
if (feof(fin)) break;
train_words++;
if ((debug_mode > 1) && (train_words % 100000 == 0)) {
printf("%lldK%c", train_words / 1000, 13);
fflush(stdout);
}
//2.1构建词库的过程:NO.4 查找词在词库中位置
i = SearchVocab(word);//SearchVocab返回word在vocab中的位置,如果不存在返回-1.
// no found in vocab - add to vocab and vocab_hash, set word.cn = 1
// found in vocab - update word.cn += 1
//2.1构建词库的过程:NO.5 词是否存在
if (i == -1) { // 如果这个单词不存在,我们将其加入hash表
//2.1构建词库的过程:NO.6 词不存在,把它添加到词库中,通过hash表存储。否则:词频+1
a = AddWordToVocab(word);
vocab[a].cn = 1;
} else vocab[i].cn++; // 否则词频加一
//2.1构建词库的过程:NO.7 对低频词进行处理。当词典的规模大到一定程度后,
//删除词典中出现次数小于min_reduce的词
if (vocab_size > vocab_hash_size * 0.7) ReduceVocab(); // 如果超出装填系数,将词汇表扩容
}
//2.1构建词库的过程:NO.8 按词频排序
SortVocab(); // 所有词汇加载完毕后进行排序,词频高的靠前
if (debug_mode > 0) {
printf("Vocab size: %lld\n", vocab_size);
printf("Words in train file: %lld\n", train_words);
}
file_size = ftell(fin); // 文件大小
fclose(fin);
}
// 输出单词和词频到文件
void SaveVocab() {
long long i;
FILE *fo = fopen(save_vocab_file, "wb");
for (i = 0; i < vocab_size; i++) fprintf(fo, "%s %lld\n", vocab[i].word, vocab[i].cn);
fclose(fo);
}
// 读入词汇表文件到词汇表数据结构
void ReadVocab() {
long long a, i = 0;
char c;
char word[MAX_STRING];
FILE *fin = fopen(read_vocab_file, "rb");
if (fin == NULL) {
printf("Vocabulary file not found\n");
exit(1);
}
for (a = 0; a < vocab_hash_size; a++) vocab_hash[a] = -1;
vocab_size = 0;
while (1) {
ReadWord(word, fin);
if (feof(fin)) break;
a = AddWordToVocab(word); //AddWordToVocab返回word在vocab的位置
fscanf(fin, "%lld%c", &vocab[a].cn, &c); //这里的c是什么???难道是空格吗
i++;
}
SortVocab(); /排序中删除词频小于min_count的词
if (debug_mode > 0) {
printf("Vocab size: %lld\n", vocab_size);
printf("Words in train file: %lld\n", train_words);
}
fin = fopen(train_file, "rb"); // 还得打开以下训练文件好知道文件大小是多少……
if (fin == NULL) {
printf("ERROR: training data file not found!\n");
exit(1);
}
fseek(fin, 0, SEEK_END);
file_size = ftell(fin);
fclose(fin);
}
//3.网络模型初始化
//3.1.词向量的初始化:syn0
//3.2.映射层到输出层权重初始化:hs(syn1)、negtive(syn1neg)
//3.3.创建huffman树:CreateBinaryTree
void InitNet() {
long long a, b;
// layer1_size will the the dimension of feature space
// syn0 and syn1/syn1neg are of size vocab_size * layer1_size
// syn0-词向量
unsigned long long next_random = 1;
// posix_memalign() 成功时会返回size字节的动态内存,并且这块内存的地址是alignment(这里是128)的倍数
// syn0 存储的是word vectors
//这里为syn0分配内存空间
//调用posiz_memalign来获取一块数量为vocab_size * layer1_size,128byte页对齐的内存
//其中layer1_size是词向量的长度
a = posix_memalign((void **)&syn0, 128, (long long)vocab_size * layer1_size * sizeof(real));
if (syn0 == NULL) {printf("Memory allocation failed\n"); exit(1);}
//3.2.映射层到输出层权重初始化:hs(syn1)
if (hs) {
//syn1存储的是Haffman树中每个非叶节点的向量
//这里为syn1分配内存空间
a = posix_memalign((void **)&syn1, 128, (long long)vocab_size * layer1_size * sizeof(real));
if (syn1 == NULL) {printf("Memory allocation failed\n"); exit(1);}
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) for (b = 0; b < layer1_size; b++) //将Huffman树的内节点初始化为0
syn1[a * layer1_size + b] = 0;
}
//如果要使用负采样,则需要为syn1neg分配内存空间
//syn1neg是负采样时每个词的辅助向量
//3.2.映射层到输出层权重初始化:negtive(syn1neg)
if (negative>0) {
a = posix_memalign((void **)&syn1neg, 128, (long long)vocab_size * layer1_size * sizeof(real));
if (syn1neg == NULL) {printf("Memory allocation failed\n"); exit(1);}
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) for (b = 0; b < layer1_size; b++) //将每个词的辅助向量初始化为0
syn1neg[a * layer1_size + b] = 0;
}
//3.1.词向量的初始化:首先,生成一个很大的next_random的数,
//通过与“0xFFFF”进行与运算截断,再除以65536得到[0,1]之间的数,
//最终,得到的初始化的向量的范围为:[-0.5/layer1_size,0.5/layer1_size],其中layer1_size为词向量的长度
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) for (b = 0; b < layer1_size; b++) {
next_random = next_random * (unsigned long long)25214903917 + 11;
syn0[a * layer1_size + b] = (((next_random & 0xFFFF) / (real)65536) - 0.5) / layer1_size; // 随机初始化word vectors
}
//3.3.创建huffman树:CreateBinaryTree
CreateBinaryTree();
}
//4.多线程模型训练://这个线程函数执行之前,已经做好了一些工作:已经完成词表排序、Haffman树的生成以及每个词的Haffman编码计算
void *TrainModelThread(void *id) {
// word: 在提取句子时用来表示当前词在词表中的索引,也就是说向sen中添加单词用,句子完成后表示句子中的当前单词
// last_word 上一个单词,辅助扫描窗口,记录当前扫描到的上下文单词
// sentence_length 当前处理的句子长度,当前句子的长度(单词数)
// sentence_position 当前处理的单词在当前句子中的位置(index)
//cw:窗口长度(中心词除外)
long long a, b, d, cw, word, last_word, sentence_length = 0, sentence_position = 0;
//word_count: 当前线程当前时刻已训练的语料的长度
//last_word_count: 当前线程上一次记录时已训练的语料长度
// last_word_count:保存值,以便在新训练语料长度超过某个值时输出信息
// sen 单词数组,表示句子,//sen:当前从文件中读取的待处理句子,存放的是每个词在词表中的索引
long long word_count = 0, last_word_count = 0, sen[MAX_SENTENCE_LENGTH + 1];
//l1:在skip-gram模型中,在syn0中定位当前词词向量的起始位置
//l2:在syn1或syn1neg中定位中间节点向量或负采样向量的起始位置
// l1 ns中表示word在concatenated word vectors中的起始位置,之后layer1_size是对应的word vector,因为把矩阵拉成长向量了 说的不太懂,不如上面的清晰
// l2 cbow或ns中权重向量的起始位置,之后layer1_size是对应的syn1或syn1neg,因为把矩阵拉成长向量了
// c 循环中的计数作用
//target:在负采样中存储当前样本
//label:在负采样中存储当前样本的标记
long long l1, l2, c, target, label, local_iter = iter;
// id 线程创建的时候传入,辅助随机数生成
unsigned long long next_random = (long long)id;
// f e^x / (1/e^x),fs中指当前编码为是0(父亲的左子节点为0,右为1)的概率,ns中指label是1的概率
// g 误差(f与真实值的偏离)与学习速率的乘积
real f, g;
// 当前时间,和start比较计算算法效率
clock_t now;
//neu1:输入词向量,在CBOW模型中是Context(x)中各个词的向量和,在skip-gram模型中是中心词的词向量
real *neu1 = (real *)calloc(layer1_size, sizeof(real)); // 隐层节点
real *neu1e = (real *)calloc(layer1_size, sizeof(real)); // 误差累计项,其实对应的是Gneu1
FILE *fi = fopen(train_file, "rb");
//4.1.多线程模型训练:利用多线程对训练文件划分,每个线程训练一部分的数据
//每个进程对应一段文本,根据当前线程的id找到该线程对应文本的初始位置
//file_size就是之前LearnVocabFromTrainFile和ReadVocab函数中获取的训练文件的大小
fseek(fi, file_size / (long long)num_threads * (long long)id, SEEK_SET); // 将文件内容分配给各个线程
//4.2 对每一个词,应用四种模型进行训练。
while (1) {
//每训练约10000词输出一次训练进度
if (word_count - last_word_count > 10000) {
//word_count_actual是所有线程总共当前处理的词数
word_count_actual += word_count - last_word_count;
last_word_count = word_count;
if ((debug_mode > 1)) {
now=clock();
//输出信息包括:
//当前的学习率alpha;
//训练总进度(当前训练的总词数/(迭代次数*训练样本总词数)+1);
//每个线程每秒处理的词数
printf("%cAlpha: %f Progress: %.2f%% Words/thread/sec: %.2fk ", 13, alpha,
word_count_actual / (real)(iter * train_words + 1) * 100,
word_count_actual / ((real)(now - start + 1) / (real)CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000));
fflush(stdout);
}
//在初始学习率的基础上,随着实际训练词数的上升,逐步降低当前学习率(自适应调整学习率)
alpha = starting_alpha * (1 - word_count_actual / (real)(iter * train_words + 1)); // 自动调整学习速率
if (alpha < starting_alpha * 0.0001) alpha = starting_alpha * 0.0001; // 学习速率有下限
}
if (sentence_length == 0) { // 如果当前句子长度为0 //从训练样本中取出一个句子,句子间以回车分割
while (1) {
word = ReadWordIndex(fi); //从文件中读入一个词,将该词在词汇表中的索引赋给word
if (feof(fi)) break; // 读到文件末尾
if (word == -1) continue; // 没有这个单词
word_count++; // 单词计数增加
if (word == 0) break; // 是个回车 //如果读到的时回车,表示句子结束
// The subsampling randomly discards frequent words while keeping the ranking same
// 这里的亚采样是指 Sub-Sampling,Mikolov 在论文指出这种亚采样能够带来 2 到 10 倍的性能提升,并能够提升低频词的表示精度。
// 低频词被丢弃概率低,高频词被丢弃概率高
//对高频词进行随机下采样,丢弃掉一些高频词,能够使低频词向量更加准确,同时加快训练速度
//可以看作是一种平滑方法
if (sample > 0) {
real ran = (sqrt(vocab[word].cn / (sample * train_words)) + 1) * (sample * train_words) / vocab[word].cn;
next_random = next_random * (unsigned long long)25214903917 + 11;
//以1-ran的概率舍弃高频词
if (ran < (next_random & 0xFFFF) / (real)65536) continue;
}
sen[sentence_length] = word; //sen存放的为该词在词典中的索引,并且sen[]中词的顺序与文本中词的顺序一致
sentence_length++;
//1000个单词视作一个句子
//如果句子长度超出最大长度则截断
if (sentence_length >= MAX_SENTENCE_LENGTH) break;
}
sentence_position = 0; // 定位到句子头,表示当前单词在当前句中的index,起始值为0
}
//如果当前线程处理的词数超过了它应该处理的最大值,那么开始新一轮迭代
//如果迭代数超过上限,则停止迭代
if (feof(fi) || (word_count > train_words / num_threads)) {
word_count_actual += word_count - last_word_count;
local_iter--;
if (local_iter == 0) break;
word_count = 0;
last_word_count = 0;
sentence_length = 0;
fseek(fi, file_size / (long long)num_threads * (long long)id, SEEK_SET);
continue;
}
word = sen[sentence_position]; // 取句子中的第一个单词,开始运行BP算法
if (word == -1) continue; // 如果没有这个单词,则继续
// 隐层节点值和隐层节点误差累计项清零
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) neu1[c] = 0;
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) neu1e[c] = 0;
next_random = next_random * (unsigned long long)25214903917 + 11;
//生成一个[0, window-1]的随机数,用来确定|context(w)|窗口的实际宽度(提高训练速率?)
b = next_random % window; // b是个随机数,0到window-1,指定了本次算法操作实际的窗口大小
/********如果使用的是CBOW模型:输入是某单词周围窗口单词的词向量,来预测该中心单词本身*********/
// cbow 框架
//4.2.1.CBOW模型:首先找到每个词对应的词向量,并将这些词的词向量相加
if (cbow) { //train the cbow architecture
// in -> hidden
cw = 0;
//一个词的窗口为[setence_position - window + b, sentence_position + window - b]
//因此窗口总长度为 2*window - 2*b + 1
// 将窗口内的word vectors累加到隐层节点上
for (a = b; a < window * 2 + 1 - b; a++) if (a != window) {//去除窗口的中心词,这是我们要预测的内容,仅仅提取上下文
c = sentence_position - window + a;//sentence_position表示的是当前的位置,c表示上下文词的具体位置
//判断c是否越界
if (c < 0) continue;
if (c >= sentence_length) continue;
//sen数组中存放的是句子中的每个词在词表中的索引
last_word = sen[c];
if (last_word == -1) continue; // 这个单词没有
//step1:传说中的向量和,layer1_size是词向量的维度,默认是100
//当累加完窗口内的所有的词向量的之后,存储在映射层neu1中
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) neu1[c] += syn0[c + last_word * layer1_size];
cw++;//统计实际窗口中的有效词数
}
if (cw) {
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) neu1[c] /= cw;//计算均值
//4.2.1.CBOW模型:-Hierarchical SOFTMAX
//如果采用分层softmax优化
//根据Haffman树上从根节点到当前词的叶节点的路径,遍历所有经过的中间节点
if (hs) for (d = 0; d < vocab[word].codelen; d++) { // 这里的codelen其实是少一个的,所以不会触及point里面最后一个负数
f = 0;
//l2为当前遍历到的中间节点的向量在syn1中的起始位置
l2 = vocab[word].point[d] * layer1_size; // 路径上的点 //找到第d个词对应的vector
//可以参考链接:http://www.hankcs.com/nlp/word2vec.html 里面有代码的对应关系
// Propagate hidden -> output // 准备计算f, f为输入向量neu1与中间结点向量的内积,也就是f为Xw和Theta的内积
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) f += neu1[c] * syn1[c + l2]; // 映射层到输出层
//检测f有没有超出Sigmoid函数表的范围
// 不在expTable内的舍弃掉,邮件问过作者,他说计算精度有限,怕有不好印象,但这里我改成太小的都是0,太大的都是1,运行结果还是有差别的
if (f <= -MAX_EXP) continue;
else if (f >= MAX_EXP) continue;
else f = expTable[(int)((f + MAX_EXP) * (EXP_TABLE_SIZE / MAX_EXP / 2))]; // 从expTable中查找,快速计算
// 'g' is the gradient multiplied by the learning rate
//g是梯度和学习率的乘积
//学习率越大,则错误分类的惩罚也越大,对中间向量的修正量也越大
//注意!word2vec中将Haffman编码为1的节点定义为负类,而将编码为0的节点定义为正类
//即一个节点的label = 1 - d
g = (1 - vocab[word].code[d] - f) * alpha;
// Propagate errors output -> hidden // 记录累积误差项 //可以参考链接:http://www.hankcs.com/nlp/word2vec.html 里面有代码的对应关系
//根据计算得到的修正量g和中间节点的向量更新累计误差
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) neu1e[c] += g * syn1[c + l2];
// Learn weights hidden -> output // 更新隐层到霍夫曼树非叶节点的权重
//根据计算得到的修正量g和输入向量更新中间节点的向量值(中间节点这个向量,不是词向量,只是一个参数)
//很好理解,假设vocab[word].code[d]编码为1,即负类,其节点label为1-1=0
//sigmoid函数得到的值为(0,1)范围内的数,大于label,很自然的,我们需要把这个中间节点的向量调小
//而此时的g = (label - f)*alpha是一个负值,作用在中间节点向量上时,刚好起到调小效果
//调小的幅度与sigmoid函数的计算值偏离label的幅度成正比
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) syn1[c + l2] += g * neu1[c];
}
//4.2.1.CBOW模型:-NEGATIVE SAMPLING 负采样
// NEGATIVE SAMPLING
//遍历所有正负样本(1个正样本+negative个负样本)
if (negative > 0) for (d = 0; d < negative + 1; d++) {
if (d == 0) { //第一次循环处理的是目标单词,即正样本
target = word; //正样本,也就是目标单词
label = 1; // 当前词的分类器应当输出1
} else { //// //从能量表中随机抽取负样本,选择出负样本, 采样使得与target不同,label为0,也即最多采样negative个negative sample
next_random = next_random * (unsigned long long)25214903917 + 11;
target = table[(next_random >> 16) % table_size]; //从table表中选择出负样本
if (target == 0) target = next_random % (vocab_size - 1) + 1; //负采样抽到回车,再重新采样
if (target == word) continue;
label = 0;
}
//在负采样优化中,每个词在syn1neg数组中对应一个辅助向量
//此时的l2为syn1neg中目标单词向量的起始位置
l2 = target * layer1_size;
f = 0;
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) f += neu1[c] * syn1neg[c + l2]; //f为输入向量neu1与辅助向量的内积,在负采样优化中,每个word都对应一个辅助向量Theta(syn1neg)
// 这里直接上0、1,没有考虑计算精度问题……
if (f > MAX_EXP) g = (label - 1) * alpha;
else if (f < -MAX_EXP) g = (label - 0) * alpha;
else g = (label - expTable[(int)((f + MAX_EXP) * (EXP_TABLE_SIZE / MAX_EXP / 2))]) * alpha;
//neu1e-累积误差,直到一轮抽样完了后才能更新输入层的词向量
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) neu1e[c] += g * syn1neg[c + l2]; //隐藏层的误差
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) syn1neg[c + l2] += g * neu1[c]; //update1:更新辅助变量Theta(syn1neg)
}
// hidden -> in
//4.2.1.更新syn0 所表示的词向量
// 根据隐层节点累积误差项,更新word vectors
for (a = b; a < window * 2 + 1 - b; a++) if (a != window) {
c = sentence_position - window + a;
if (c < 0) continue;
if (c >= sentence_length) continue;
last_word = sen[c];
if (last_word == -1) continue;
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) syn0[c + last_word * layer1_size] += neu1e[c];
}
}
}
else { //train skip-gram
//4.2.2.skip-gram模型:
for (a = b; a < window * 2 + 1 - b; a++) if (a != window) { // 预测非中心的单词(邻域内的单词)
c = sentence_position - window + a;
if (c < 0) continue;
if (c >= sentence_length) continue;
last_word = sen[c];
if (last_word == -1) continue;
l1 = last_word * layer1_size;
// 累计误差项清零
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) neu1e[c] = 0;
// HIERARCHICAL SOFTMAX
//4.2.2.skip-gram模型:HIERARCHICAL SOFTMAX
if (hs) for (d = 0; d < vocab[word].codelen; d++) {
f = 0;
l2 = vocab[word].point[d] * layer1_size;
// Propagate hidden -> output
// 待预测单词的 word vecotr 和 隐层-霍夫曼树非叶节点权重 的内积
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) f += syn0[c + l1] * syn1[c + l2];
// 同cbow中hs的讨论
if (f <= -MAX_EXP) continue;
else if (f >= MAX_EXP) continue;
// 以下内容同之前的cbow
else f = expTable[(int)((f + MAX_EXP) * (EXP_TABLE_SIZE / MAX_EXP / 2))];
// 'g' is the gradient multiplied by the learning rate
g = (1 - vocab[word].code[d] - f) * alpha; // 这里的code[d]其实是下一层的,code错位了,point和code是错位的!
// Propagate errors output -> hidden
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) neu1e[c] += g * syn1[c + l2];
// Learn weights hidden -> output
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) syn1[c + l2] += g * syn0[c + l1];
}
// NEGATIVE SAMPLING
//4.2.2.skip-gram模型:NEGATIVE SAMPLING
if (negative > 0) for (d = 0; d < negative + 1; d++) {
if (d == 0) {
target = word;
label = 1;
} else {
next_random = next_random * (unsigned long long)25214903917 + 11;
target = table[(next_random >> 16) % table_size];
if (target == 0) target = next_random % (vocab_size - 1) + 1;
if (target == word) continue;
label = 0;
}
l2 = target * layer1_size;
f = 0;
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) f += syn0[c + l1] * syn1neg[c + l2];
// 以下内容同之前的cbow
if (f > MAX_EXP) g = (label - 1) * alpha;
else if (f < -MAX_EXP) g = (label - 0) * alpha;
else g = (label - expTable[(int)((f + MAX_EXP) * (EXP_TABLE_SIZE / MAX_EXP / 2))]) * alpha;
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) neu1e[c] += g * syn1neg[c + l2];
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) syn1neg[c + l2] += g * syn0[c + l1];
}
// Learn weights input -> hidden
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) syn0[c + l1] += neu1e[c];
}
}
sentence_position++;
if (sentence_position >= sentence_length) {
sentence_length = 0;
continue;
}
}
fclose(fi);
free(neu1);
free(neu1e);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void TrainModel() {
long a, b, c, d;
FILE *fo;
// 创建多线程
pthread_t *pt = (pthread_t *)malloc(num_threads * sizeof(pthread_t));
printf("Starting training using file %s\n", train_file);
starting_alpha = alpha;
//2构建词库:way1:指定词库:ReadVocab()方法.way2:从词的文本构建词库:LearnVocabFromTrainFile()方法
//2.1构建词库的过程:
//2.2利用指定词库
// 优先从词汇表文件中加载,否则从训练文件中加载
if (read_vocab_file[0] != 0) ReadVocab(); else LearnVocabFromTrainFile();
// 输出词汇表文件,词+词频
if (save_vocab_file[0] != 0) SaveVocab();
if (output_file[0] == 0) return;
InitNet(); // 网络结构初始化
//3.网络模型初始化:负采样初始化,负采样表的生成。
if (negative > 0) InitUnigramTable(); // 根据词频生成采样映射
//4.多线程模型训练:
start = clock(); // 开始计时 //该程序从启动到函数调用占用CPU的时间
for (a = 0; a < num_threads; a++) pthread_create(&pt[a], NULL, TrainModelThread, (void *)a);
for (a = 0; a < num_threads; a++) pthread_join(pt[a], NULL);
// 训练结束,准备输出
fo = fopen(output_file, "wb");
if (classes == 0) { // 保存 word vectors
// Save the word vectors
fprintf(fo, "%lld %lld\n", vocab_size, layer1_size); // 词汇量,vector维数
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) {
fprintf(fo, "%s ", vocab[a].word);
if (binary) for (b = 0; b < layer1_size; b++) fwrite(&syn0[a * layer1_size + b], sizeof(real), 1, fo);
else for (b = 0; b < layer1_size; b++) fprintf(fo, "%lf ", syn0[a * layer1_size + b]);
fprintf(fo, "\n");
}
} else {
// Run K-means on the word vectors
// 运行K-means算法,详细的注释:https://blog.csdn.net/EnochX/article/details/52852271
int clcn = classes, iter = 10, closeid;
int *centcn = (int *)malloc(classes * sizeof(int));
int *cl = (int *)calloc(vocab_size, sizeof(int));
real closev, x;
real *cent = (real *)calloc(classes * layer1_size, sizeof(real));
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) cl[a] = a % clcn;
for (a = 0; a < iter; a++) {
for (b = 0; b < clcn * layer1_size; b++) cent[b] = 0;
for (b = 0; b < clcn; b++) centcn[b] = 1;
for (c = 0; c < vocab_size; c++) {
for (d = 0; d < layer1_size; d++) cent[layer1_size * cl[c] + d] += syn0[c * layer1_size + d];
centcn[cl[c]]++;
}
for (b = 0; b < clcn; b++) {
closev = 0;
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) {
cent[layer1_size * b + c] /= centcn[b];
closev += cent[layer1_size * b + c] * cent[layer1_size * b + c];
}
closev = sqrt(closev);
for (c = 0; c < layer1_size; c++) cent[layer1_size * b + c] /= closev;
}
for (c = 0; c < vocab_size; c++) {
closev = -10;
closeid = 0;
for (d = 0; d < clcn; d++) {
x = 0;
for (b = 0; b < layer1_size; b++) x += cent[layer1_size * d + b] * syn0[c * layer1_size + b];
if (x > closev) {
closev = x;
closeid = d;
}
}
cl[c] = closeid;
}
}
// Save the K-means classes
for (a = 0; a < vocab_size; a++) fprintf(fo, "%s %d\n", vocab[a].word, cl[a]);
free(centcn);
free(cent);
free(cl);
}
fclose(fo);
}
int ArgPos(char *str, int argc, char **argv) {
int a;
for (a = 1; a < argc; a++) if (!strcmp(str, argv[a])) {
if (a == argc - 1) {
printf("Argument missing for %s\n", str);
exit(1);
}
return a;
}
return -1;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int i;
if (argc == 1) {
printf("WORD VECTOR estimation toolkit v 0.1c\n\n");
printf("Options:\n");
printf("Parameters for training:\n");
printf("\t-train \n"); // 指定训练文件
printf("\t\tUse text data from to train the model\n");
printf("\t-output \n"); // 指定输出文件,以存储word vectors,或者单词类
printf("\t\tUse to save the resulting word vectors / word clusters\n");
printf("\t-size \n"); // word vector的维数,对应 layer1_size,默认是100
printf("\t\tSet size of word vectors; default is 100\n");
// 窗口大小,在cbow中表示了word vector的最大的叠加范围,在skip-gram中表示了max space between words(w1,w2,p(w1 | w2))
printf("\t-window \n");
printf("\t\tSet max skip length between words; default is 5\n");
printf("\t-sample \n"); // 亚采样拒绝概率的参数
printf("\t\tSet threshold for occurrence of words. Those that appear with higher frequency in the training data\n");
printf("\t\twill be randomly down-sampled; default is 1e-3, useful range is (0, 1e-5)\n");
printf("\t-hs \n"); // 使用hs求解,默认为0
printf("\t\tUse Hierarchical Softmax; default is 0 (not used)\n");
printf("\t-negative \n"); // 使用ns的时候采样的样本数
printf("\t\tNumber of negative examples; default is 5, common values are 3 - 10 (0 = not used)\n");
printf("\t-threads \n"); // 指定线程数
printf("\t\tUse threads (default 12)\n");
printf("\t-iter \n");
printf("\t\tRun more training iterations (default 5)\n");
printf("\t-min-count \n"); // 长尾词的词频阈值
printf("\t\tThis will discard words that appear less than times; default is 5\n");
printf("\t-alpha \n"); // 初始的学习速率,默认为0.025
printf("\t\tSet the starting learning rate; default is 0.025 for skip-gram and 0.05 for CBOW\n");
printf("\t-classes \n"); // 输出单词类别数,默认为0,也即不输出单词类
printf("\t\tOutput word classes rather than word vectors; default number of classes is 0 (vectors are written)\n");
printf("\t-debug \n"); // 调试等级,默认为2
printf("\t\tSet the debug mode (default = 2 = more info during training)\n");
printf("\t-binary \n"); // 是否将结果输出为二进制文件,默认为0,即不输出为二进制
printf("\t\tSave the resulting vectors in binary moded; default is 0 (off)\n");
printf("\t-save-vocab \n"); // 词汇表存储文件
printf("\t\tThe vocabulary will be saved to \n");
printf("\t-read-vocab \n"); // 词汇表加载文件,则可以不指定trainfile
printf("\t\tThe vocabulary will be read from , not constructed from the training data\n");
printf("\t-cbow \n"); // 使用cbow框架
printf("\t\tUse the continuous bag of words model; default is 1 (use 0 for skip-gram model)\n");
printf("\nExamples:\n"); // 使用示例
printf("./word2vec -train data.txt -output vec.txt -size 200 -window 5 -sample 1e-4 -negative 5 -hs 0 -binary 0 -cbow 1 -iter 3\n\n");
return 0;
}
// 文件名均空
output_file[0] = 0;
save_vocab_file[0] = 0;
read_vocab_file[0] = 0;
// 参数与变量的对应关系
if ((i = ArgPos((char *)"-size", argc, argv)) > 0) layer1_size = atoi(argv[i + 1]);
if ((i = ArgPos((char *)"-train", argc, argv)) > 0) strcpy(train_file, argv[i + 1]);
if ((i = ArgPos((char *)"-save-vocab", argc, argv)) > 0) strcpy(save_vocab_file, argv[i + 1]);
if ((i = ArgPos((char *)"-read-vocab", argc, argv)) > 0) strcpy(read_vocab_file, argv[i + 1]);
if ((i = ArgPos((char *)"-debug", argc, argv)) > 0) debug_mode = atoi(argv[i + 1]);
if ((i = ArgPos((char *)"-binary", argc, argv)) > 0) binary = atoi(argv[i + 1]);
if ((i = ArgPos((char *)"-cbow", argc, argv)) > 0) cbow = atoi(argv[i + 1]);
if (cbow) alpha = 0.05;
if ((i = ArgPos((char *)"-alpha", argc, argv)) > 0) alpha = atof(argv[i + 1]);
if ((i = ArgPos((char *)"-output", argc, argv)) > 0) strcpy(output_file, argv[i + 1]);
if ((i = ArgPos((char *)"-window", argc, argv)) > 0) window = atoi(argv[i + 1]);
if ((i = ArgPos((char *)"-sample", argc, argv)) > 0) sample = atof(argv[i + 1]);
if ((i = ArgPos((char *)"-hs", argc, argv)) > 0) hs = atoi(argv[i + 1]);
if ((i = ArgPos((char *)"-negative", argc, argv)) > 0) negative = atoi(argv[i + 1]);
if ((i = ArgPos((char *)"-threads", argc, argv)) > 0) num_threads = atoi(argv[i + 1]);
if ((i = ArgPos((char *)"-iter", argc, argv)) > 0) iter = atoi(argv[i + 1]);
if ((i = ArgPos((char *)"-min-count", argc, argv)) > 0) min_count = atoi(argv[i + 1]);
if ((i = ArgPos((char *)"-classes", argc, argv)) > 0) classes = atoi(argv[i + 1]);
vocab = (struct vocab_word *)calloc(vocab_max_size, sizeof(struct vocab_word));
vocab_hash = (int *)calloc(vocab_hash_size, sizeof(int));
//1.预处理:提前计算sigmod值,并保存起来
expTable = (real *)malloc((EXP_TABLE_SIZE + 1) * sizeof(real));
// 产生e^-6 到 e^6 之间的f值
for (i = 0; i < EXP_TABLE_SIZE; i++) {
expTable[i] = exp((i / (real)EXP_TABLE_SIZE * 2 - 1) * MAX_EXP); // Precompute the exp() table
expTable[i] = expTable[i] / (expTable[i] + 1); // Precompute f(x) = x / (x + 1)
}
TrainModel();
return 0;
}