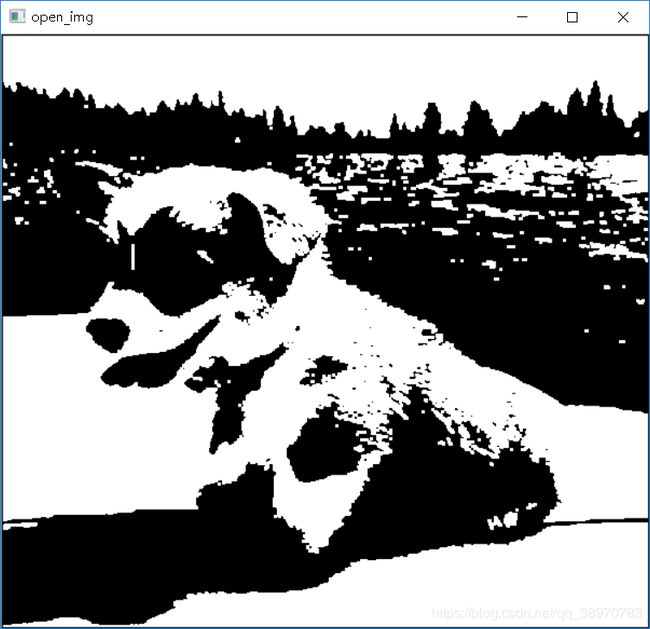
(自己编写函数)Python + Opencv 图像形态学处理(腐蚀、膨胀、开运算、闭运算)
原理:
形态学运算是结构元素与图像进行逻辑运算,产生新的图像的图像处理方法。二值图像B和结构元素S是定义在笛卡儿网格上的集合,网格中值为1的点是集合的元素。
-
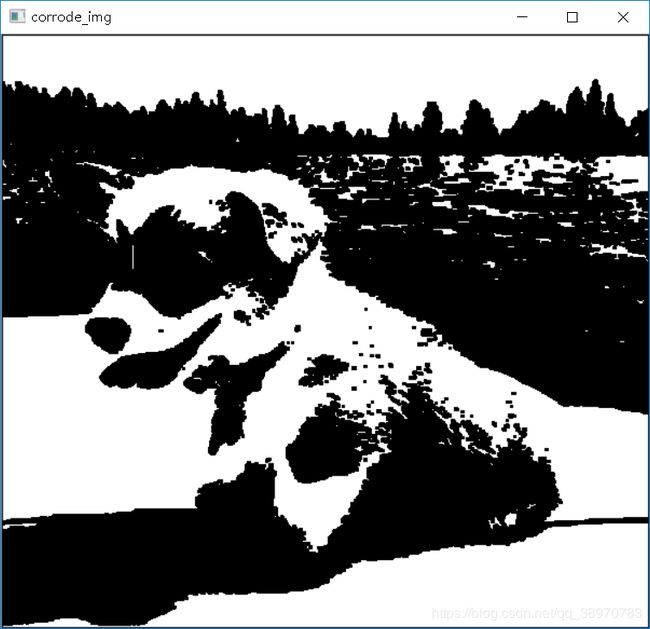
腐蚀
定义:
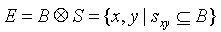
算法:
a) 用3x3的结构元素,扫描图像的每一个像素。
b) 用结构元素与其覆盖的二值图像做“与”操作。
c) 如果都为1,结果图像的该像素为1,否则为0。 -
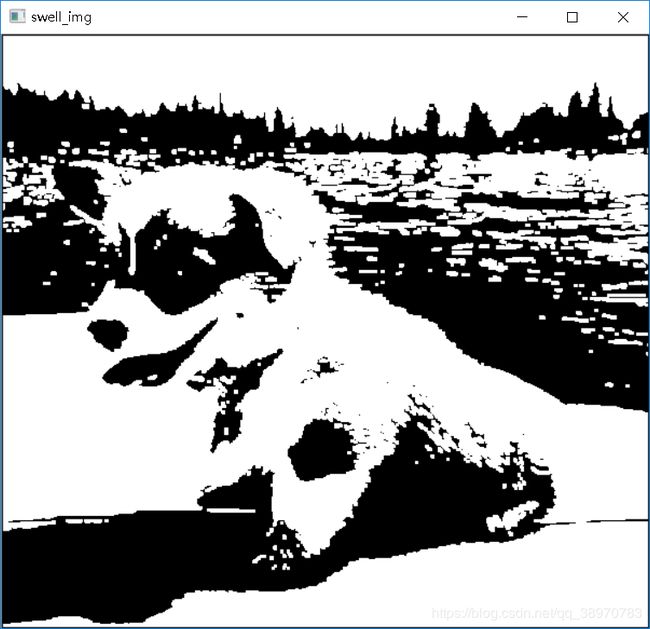
膨胀
定义:
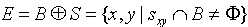
算法:
a) 用3x3的结构元素,扫描图像的每一个像素。
b) 用结构元素与其覆盖的二值图像做“与”操作。
c) 如果都为0,结果图像的该像素为0,否则为1。 -
开运算
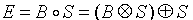
定义: 即先腐蚀,再膨胀。
算法:
a) 用3x3的结构元素,对图像做腐蚀操作。
b) 再用3x3的结构元素,对图像做膨胀操作。 -
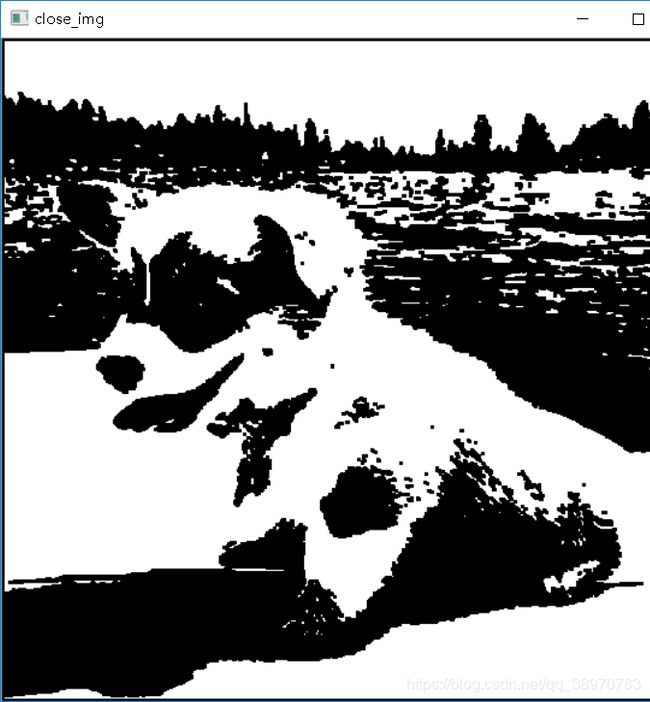
闭运算
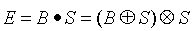
定义: 即先膨胀,再腐蚀。
算法:
a) 用3x3的结构元素,对图像做膨胀操作。
b) 再用3x3的结构元素,对图像做腐蚀操作。
代码以及算法设计:
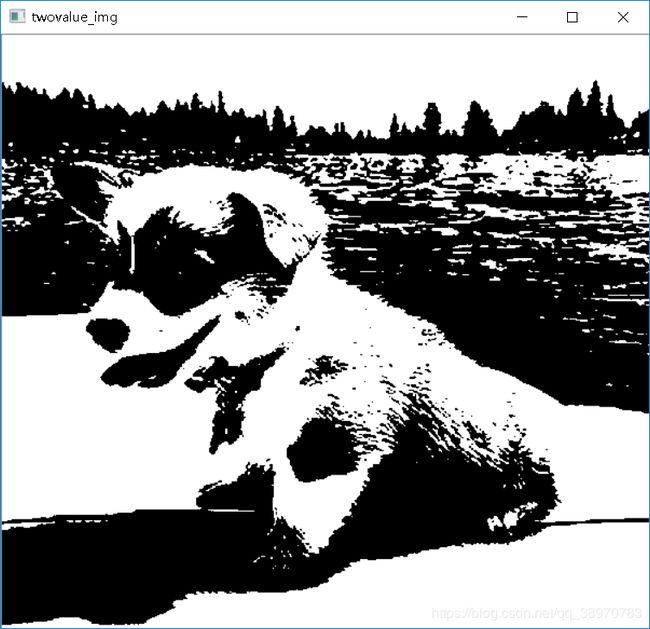
一、首先使用OSTU算法进行计算最适合的阈值,ostu算法的原理如下:
- 先计算图像的直方图,即将图像所有的像素点按照0~255共256个bin,统计落在每个bin的像素点数量
- 归一化直方图,也即将每个bin中像素点数量除以总的像素点
- i表示分类的阈值,也即一个灰度级,从0开始迭代
- 通过归一化的直方图,统计0~i 灰度级的像素(假设像素值在此范围的像素叫做前景像素) 所占整幅图像的比例w0,并统计前景像素的平均灰度u0;统计i~255灰度级的像素(假设像素值在此范围的像素叫做背景像素) 所占整幅图像的比例w1,并统计背景像素的平均灰度u1;
- 计算前景像素和背景像素的方差 g = w0w1(u0-u1) (u0-u1)
- i++;转到 4 ,直到i为256时结束迭代
- 将最大g相应的i值作为图像的全局阈值
#使用otsu算法思维求出阈值并对图像进行二值化处理
def myotsu(gray):
countdown = 0
countup = 0
hist_new = []
num = []
hist_countresult = []
hist_key = []
hist_proresult = []
#处理后最终输出矩阵将齐大小设置为与原图一样
gray2=np.array([[0 for i in range(gray.shape[1])] for i in range(gray.shape[0])], dtype='float')
#gray1 用于统计每哥灰度级所有的个数 ,因为是列表不是矩阵,
#所以要先将gray的灰度级矩阵变成一维列表
gray1 = list(gray.ravel())
#以字典的形式保存,统计出来的灰度级及其个数
obj = dict(collections.Counter(gray1))
obj = sorted(obj.items(),key=lambda item:item[0])
#将统计出来的灰度级的值与他的个数分开用列表保存
for each in obj :
key = list(each)[0]
num =list(each)[1]
hist_key.append(key)
hist_new.append(num)
#检查从0-255每个灰度级是否都有个数,没有的话添加并将值设为0
for i in range (0,256) :
if i in hist_key :
num = hist_key.index(i)
hist_countresult.append(hist_new[num])
else :
hist_countresult.append(0)
if len(hist_countresult) < 256 :
for i in range (0,256-len(hist_countresult)) :
hist_new.append(0)
#计算整幅图的像素数目
hist_sum = gray.shape[0] * gray.shape[1]
#计算每个灰度级的像素数目占整个数目的比重
for each in hist_countresult :
result = float(each / hist_sum)
hist_proresult.append(result)
#遍历灰度级[0,255],寻找合适的threshold
w0 = w1 = u0tmp = u1tmp = u0 = u1 = deltaTmp = deltaMax = float(0)
for i in range (256) :
w0 = w1 = u0tmp = u1tmp = u0 = u1 = deltaTmp = float(0)
for j in range (256) :
if j <= i : #背景部分
w0 = float(w0 + hist_proresult[j])
u0tmp += j * hist_proresult[j]
else : #前景部分
w1 += float(hist_proresult[j])
u1tmp += j * hist_proresult[j]
if w0 == 0.0 or w1 == 0.0:
pass
else :
u0 = float(u0tmp / w0)
u1 = float(u1tmp / w1)
deltaTmp = (float)(w0 *w1* pow((u0 - u1), 2))
if deltaTmp > deltaMax :
deltaMax = deltaTmp
threshold = i
#用ostu大津算法得出最适当的阈值后,将图片进行二值化
for i in range(gray.shape[0]) :
for j in range(gray.shape[1]) :
#对大于阈值的显示为255白色,小于阈值的显示为0黑色
if gray[i][j] <= threshold :
gray2[i][j] = 0
countdown += 1
else :
gray2[i][j] = 255
countup += 1
return gray2
二、使用numpy模块的函数生成一个3 * 3 的矩阵
三、腐蚀:
- a) 用3x3的结构元素,扫描图像的每一个像素。
- b) 用结构元素与其覆盖的二值图像做“与”操作。
- c) 如果都为1,结果图像的该像素为1,否则为0。
#腐蚀
def corrode(twovalue_img) :
#处理后最终输出矩阵将齐大小设置为与原图一样
gray2=np.array([[0 for i in range(twovalue_img.shape[1])] for i in range(twovalue_img.shape[0])], dtype='float')
#生成 3*3的结构元素
structuralelement = np.array([[1 for i in range (3)]for i in range (3)],dtype='int')
#使用结构元素去与原二值图像中为1的值进行与操作
for i in range (1,twovalue_img.shape[0]-1) :
for j in range (1,twovalue_img.shape[1]-1) :
#添加每次处理后的元素到集合中
list1 = []
count1 = 0 #保存进行于操作后图中到底有几个1
list1.append(twovalue_img[i-1][j-1] and structuralelement[0][0])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i-1][j] and structuralelement[0][1])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i-1][j+1] and structuralelement[0][2])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i][j-1] and structuralelement[1][0])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i][j] and structuralelement[1][1])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i][j+1] and structuralelement[1][2])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i+1][j-1] and structuralelement[2][0])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i+1][j] and structuralelement[2][1])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i+1][j+1] and structuralelement[2][2])
#如果都为1,结果图像的该像素为1,否则为0。
for each in list1 :
if each == 1 :
count1 += 1
if count1 == 9 :
gray2[i][j] = 255
else :
gray2[i][j] = 0
return gray2
四、膨胀:
- a) 用3x3的结构元素,扫描图像的每一个像素。
- b) 用结构元素与其覆盖的二值图像做“与”操作。
- c) 如果都为0,结果图像的该像素为0,否则为1。
#膨胀
def swell(twovalue_img):
#处理后最终输出矩阵将齐大小设置为与原图一样
gray2=np.array([[0 for i in range(twovalue_img.shape[1])] for i in range(twovalue_img.shape[0])], dtype='float')
#生成 3*3的结构元素
structuralelement = np.array([[1 for i in range (3)]for i in range (3)],dtype='int')
#使用结构元素去与原二值图像中为1的值进行与操作
for i in range (1,twovalue_img.shape[0]-1) :
for j in range (1,twovalue_img.shape[1]-1) :
#添加每次处理后的元素到集合中
list1 = []
count1 = 0 #保存进行于操作后图中到底有几个1
list1.append(twovalue_img[i-1][j-1] and structuralelement[0][0])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i-1][j] and structuralelement[0][1])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i-1][j+1] and structuralelement[0][2])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i][j-1] and structuralelement[1][0])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i][j] and structuralelement[1][1])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i][j+1] and structuralelement[1][2])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i+1][j-1] and structuralelement[2][0])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i+1][j] and structuralelement[2][1])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i+1][j+1] and structuralelement[2][2])
#如果都为0,结果图像的该像素为0,否则为1。
for each in list1 :
if each == 1 :
count1 += 1
if count1 > 0 :
gray2[i][j] = 255
else :
gray2[i][j] = 0
return gray2
五、开运算:先腐蚀,后膨胀(直接调用两次函数即可)
- a) 用3x3的结构元素,对图像做腐蚀操作。
- b) 再用3x3的结构元素,对图像做膨胀操作。
#开运算
def opencalc(twovalue_img) :
#先腐蚀,再膨胀
corrode_pic = corrode(twovalue_img)
open_img = swell(corrode_pic)
return open_img
六、闭运算:先膨胀,后腐蚀(直接调用两次函数即可)
- a) 用3x3的结构元素,对图像做膨胀操作。
- b) 再用3x3的结构元素,对图像做腐蚀操作。
#闭运算
def closecalc(twovalue_img) :
#先膨胀,再腐蚀
swell_pic = swell(twovalue_img)
close_img = corrode(swell_pic)
return close_img
完整代码:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import signal
import numpy as np
import copy as cp
import random
import math
import cv2
import collections
#使用otsu算法思维求出阈值并对图像进行二值化处理
def myotsu(gray):
countdown = 0
countup = 0
hist_new = []
num = []
hist_countresult = []
hist_key = []
hist_proresult = []
#处理后最终输出矩阵将齐大小设置为与原图一样
gray2=np.array([[0 for i in range(gray.shape[1])] for i in range(gray.shape[0])], dtype='float')
#gray1 用于统计每哥灰度级所有的个数 ,因为是列表不是矩阵,
#所以要先将gray的灰度级矩阵变成一维列表
gray1 = list(gray.ravel())
#以字典的形式保存,统计出来的灰度级及其个数
obj = dict(collections.Counter(gray1))
obj = sorted(obj.items(),key=lambda item:item[0])
#将统计出来的灰度级的值与他的个数分开用列表保存
for each in obj :
key = list(each)[0]
num =list(each)[1]
hist_key.append(key)
hist_new.append(num)
#检查从0-255每个灰度级是否都有个数,没有的话添加并将值设为0
for i in range (0,256) :
if i in hist_key :
num = hist_key.index(i)
hist_countresult.append(hist_new[num])
else :
hist_countresult.append(0)
if len(hist_countresult) < 256 :
for i in range (0,256-len(hist_countresult)) :
hist_new.append(0)
#计算整幅图的像素数目
hist_sum = gray.shape[0] * gray.shape[1]
#计算每个灰度级的像素数目占整个数目的比重
for each in hist_countresult :
result = float(each / hist_sum)
hist_proresult.append(result)
#遍历灰度级[0,255],寻找合适的threshold
w0 = w1 = u0tmp = u1tmp = u0 = u1 = deltaTmp = deltaMax = float(0)
for i in range (256) :
w0 = w1 = u0tmp = u1tmp = u0 = u1 = deltaTmp = float(0)
for j in range (256) :
if j <= i : #背景部分
w0 = float(w0 + hist_proresult[j])
u0tmp += j * hist_proresult[j]
else : #前景部分
w1 += float(hist_proresult[j])
u1tmp += j * hist_proresult[j]
if w0 == 0.0 or w1 == 0.0:
pass
else :
u0 = float(u0tmp / w0)
u1 = float(u1tmp / w1)
deltaTmp = (float)(w0 *w1* pow((u0 - u1), 2))
if deltaTmp > deltaMax :
deltaMax = deltaTmp
threshold = i
#用ostu大津算法得出最适当的阈值后,将图片进行二值化
for i in range(gray.shape[0]) :
for j in range(gray.shape[1]) :
#对大于阈值的显示为255白色,小于阈值的显示为0黑色
if gray[i][j] <= threshold :
gray2[i][j] = 0
countdown += 1
else :
gray2[i][j] = 255
countup += 1
return gray2
#腐蚀
def corrode(twovalue_img) :
#处理后最终输出矩阵将齐大小设置为与原图一样
gray2=np.array([[0 for i in range(twovalue_img.shape[1])] for i in range(twovalue_img.shape[0])], dtype='float')
#生成 3*3的结构元素
structuralelement = np.array([[1 for i in range (3)]for i in range (3)],dtype='int')
#使用结构元素去与原二值图像中为1的值进行与操作
for i in range (1,twovalue_img.shape[0]-1) :
for j in range (1,twovalue_img.shape[1]-1) :
#添加每次处理后的元素到集合中
list1 = []
count1 = 0 #保存进行于操作后图中到底有几个1
list1.append(twovalue_img[i-1][j-1] and structuralelement[0][0])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i-1][j] and structuralelement[0][1])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i-1][j+1] and structuralelement[0][2])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i][j-1] and structuralelement[1][0])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i][j] and structuralelement[1][1])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i][j+1] and structuralelement[1][2])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i+1][j-1] and structuralelement[2][0])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i+1][j] and structuralelement[2][1])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i+1][j+1] and structuralelement[2][2])
#如果都为1,结果图像的该像素为1,否则为0。
for each in list1 :
if each == 1 :
count1 += 1
if count1 == 9 :
gray2[i][j] = 255
else :
gray2[i][j] = 0
return gray2
#膨胀
def swell(twovalue_img):
#处理后最终输出矩阵将齐大小设置为与原图一样
gray2=np.array([[0 for i in range(twovalue_img.shape[1])] for i in range(twovalue_img.shape[0])], dtype='float')
#生成 3*3的结构元素
structuralelement = np.array([[1 for i in range (3)]for i in range (3)],dtype='int')
#使用结构元素去与原二值图像中为1的值进行与操作
for i in range (1,twovalue_img.shape[0]-1) :
for j in range (1,twovalue_img.shape[1]-1) :
#添加每次处理后的元素到集合中
list1 = []
count1 = 0 #保存进行于操作后图中到底有几个1
list1.append(twovalue_img[i-1][j-1] and structuralelement[0][0])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i-1][j] and structuralelement[0][1])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i-1][j+1] and structuralelement[0][2])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i][j-1] and structuralelement[1][0])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i][j] and structuralelement[1][1])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i][j+1] and structuralelement[1][2])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i+1][j-1] and structuralelement[2][0])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i+1][j] and structuralelement[2][1])
list1.append(twovalue_img[i+1][j+1] and structuralelement[2][2])
#如果都为0,结果图像的该像素为0,否则为1。
for each in list1 :
if each == 1 :
count1 += 1
if count1 > 0 :
gray2[i][j] = 255
else :
gray2[i][j] = 0
return gray2
#开运算
def opencalc(twovalue_img) :
#先腐蚀,再膨胀
corrode_pic = corrode(twovalue_img)
open_img = swell(corrode_pic)
return open_img
#闭运算
def closecalc(twovalue_img) :
#先膨胀,再腐蚀
swell_pic = swell(twovalue_img)
close_img = corrode(swell_pic)
return close_img
def MAIN():
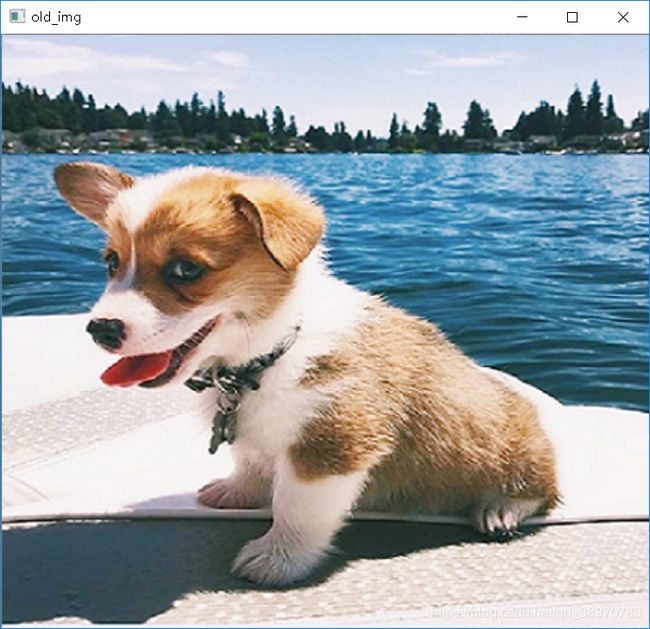
image = cv2.imread(r"D:/Code/Python/2.png")
cv2.imshow("old_img",image)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
#调用自己写的otsu算法,并将处理后的二值化图像输出
twovalue_img = myotsu(gray)
cv2.imshow("twovalue_img",twovalue_img)
#腐蚀操作
corrode_img = corrode(twovalue_img)
cv2.imshow("corrode_img",corrode_img)
#膨胀操作
swell_img = swell(twovalue_img)
cv2.imshow("swell_img",swell_img)
#开运算
open_img = opencalc(twovalue_img)
cv2.imshow("open_img",open_img)
#闭运算
close_img = closecalc(twovalue_img)
cv2.imshow("close_img",close_img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
if __name__ == "__main__":
MAIN()