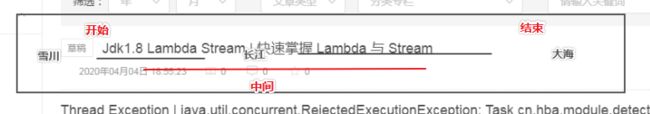
Jdk1.8 Lambda Stream | 快速掌握 Lambda 与 Stream
好久没写博客了,^_^。
目录
1.基本概念。
2. Stream
常用接口与操作
常用函数式接口
Stream 常用 api 操作
3.举个栗
3.1 首先准备一个数据源。
3.2 如何准备一个流呢?
3.3 对流进行操作
4. 结束
完整代码
1.基本概念。
jdk1.8 有着两个重要的东西,那就是 lambda 与 stream,这两样对现在代码编程还是有很大的影响。虽然 接口 增加了 default等一些新特性,但都没有这两样重要的多。
stream 是个什么鬼呢》? 从字面意思便可以理解为 流,不过这个流 和 以前的 io、buffer流还是不一样的,这个流是针对于 集合(collection)来使用的。它的使用就很好理解了,流嘛,都有一个开始、中间、结束(终端)。如同雪川融化经过长江流入大海一样一样的。
lambda 又是个什么鬼呢》?从字面意思理解为匿名函数,它也确实没有辜负这个名字,匿名简写。这个东东是为了简化代码操作。比如声明一个方法体,需要new Runnable()啊,它可以简写为 ()->{},极大的简化了语法。
2. Stream 常用接口与操作
常用函数式接口
Supplier,主要方法:T get(),这是一个生产者,可以提供一个T对象。Consumer,主要方法:void accept(T),这是一个消费者,默认方法:andthen(),稍后执行。Predicate,主要方法:boolean test(T t),这是一个判断者,默认方法:and():且,or():或,negate():非。Function,主要方法:R apply(T t),这是一个修改者,默认方法:compose():优先执行,andThen(),稍后执行,identity():直接传自身。
Stream 常用 api 操作
| 操作 |
类型 |
返回类型 |
函数式接口 |
函数描述符 |
| filter |
中间 |
Stream |
Predicate |
T->Boolean |
| distinct |
中间-有状态 |
Stream |
|
|
| Skip |
中间-有状态 |
Stream |
Long |
|
| Limit |
中间-有状态 |
Stream |
Long |
|
| Map |
中间 |
Stream |
Function |
T->R |
| Flatmap |
中间 |
Stream |
Function |
T->Stream |
| Sorted |
中间-有状态 |
Stream |
Compartor |
(T,T)->int |
| anyMatch |
终端 |
Boolean |
Predicate |
T->Boolean |
| noneMatch |
终端 |
Boolean |
Predicate |
T->Boolean |
| allMatch |
终端 |
Boolean |
Predicate |
T->Boolean |
| findAny |
终端 |
Optional |
|
|
| findFirst |
终端 |
Optional |
|
|
| forEach |
终端 |
Void |
Consumer |
T->void |
| Collect |
终端 |
R |
Collector |
|
| Reduce |
终端-有状态 |
Optional |
BinaryOperator |
(T,T)->T |
| Count |
终端 |
Long |
|
|
想要知道更多骚操作?看看 java.util.stream 下面的 Stream 接口即可。
Stream filter(Predicate var1);
Stream map(Function var1);
IntStream mapToInt(ToIntFunction var1);
LongStream mapToLong(ToLongFunction var1);
DoubleStream mapToDouble(ToDoubleFunction var1);
Stream flatMap(Function> var1);
IntStream flatMapToInt(Function var1);
LongStream flatMapToLong(Function var1);
DoubleStream flatMapToDouble(Function var1);
Stream distinct();
Stream sorted();
Stream sorted(Comparator var1);
Stream peek(Consumer var1);
Stream limit(long var1);
Stream skip(long var1);
long count();
boolean anyMatch(Predicate var1);
boolean allMatch(Predicate var1);
boolean noneMatch(Predicate var1);
Optional findFirst();
Optional findAny();
static Stream.Builder builder() {
return new StreamBuilderImpl();
} 3.举个栗
3.1 首先准备一个数据源。
创建一个用户类。
package com.example.demo.lambda;
/**
* 用户
*
* @author wbw
* @date 2020/4/4 19:19
*/
public class User {
/**
* 姓名
*/
private String name;
/**
* id
*/
private Integer id;
/**
* 年龄
*/
private Integer age;
/**
* 地址
*/
private String address;
/**
* 手机号
*/
private String phone;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, Integer id, Integer age, String address, String phone) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
this.address = address;
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", id=" + id +
", age='" + age + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
", phone='" + phone + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
准备基础数据
package com.example.demo.lambda;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* lambda
*
* @author wbw
* @date 2020/4/4 19:21
*/
public class LambdaTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始化数据
List userList = loadInfo();
System.out.println(userList);
}
/**
* 加载十条用户信息
*
* @return userList
*/
private static List loadInfo() {
List userList = new LinkedList<>();
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
userList.add(new User(names.get(i), i, random.nextInt(),
getRandomAddress(random.nextInt(10)), String.valueOf(random.nextLong())));
}
return userList;
}
/**
* 姓名
*/
private static final List names = Stream.of("张三", "李四", "王五", "张可汗", "李白", "扁鹊", "马可波罗", "上官婉儿", "太乙真人", "东皇太一").collect(Collectors.toList());
/**
* 自动生成地址(中文)
*
* @param len 长度
* @return name
*/
public static String getRandomAddress(int len) {
Random random = new Random();
StringBuilder ret = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
String str = "";
// 定义高低位
int height = (176 + Math.abs(random.nextInt(39))); // 获取高位值
int lowPos = (161 + Math.abs(random.nextInt(93))); // 获取低位值
byte[] b = {Integer.valueOf(height).byteValue(), Integer.valueOf(lowPos).byteValue()};
try {
str = new String(b, "GBK"); // 转成中文
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
ret.append(str);
}
return ret.toString();
}
}
ok,开始正式骚操作。
3.2 如何准备一个流呢?
// 初始化数据
List userList = loadInfo();
// 得到一个流
// 1. 直接调用集合自带方法
Stream stream = userList.stream();
// 2. 使用 stream 初始化
Stream 3.3 对流进行操作
// 初始化数据
List userList = loadInfo();
// 统计数量
long count = userList.stream().count();
// 转换成 map ,key为 id,(k1, k2) -> k1) 是指 key 的主键重复时,使用新的还是旧的主键,这里使用旧的
Map userMap = userList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(user -> user.getId(), user -> user, (k1, k2) -> k1));
// lambda 简写 User::getId 等于 user -> user.getId()
userMap = userList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(User::getId, user -> user, (k1, k2) -> k1));
// 再把 map 转换成 list
Collection users = Optional.of(userMap).map(Map::values).get();
// 获取前8个用户
List collect = userList.stream().limit(8).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 去重
List collect1 = userList.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
// 获取任意一个
User user = userList.stream().findAny().get();
// 获取第一个
User user1 = userList.stream().findFirst().get();
// 匹配所有
boolean b = userList.stream().allMatch(e -> e.getId() == 1);
// 匹配任意一个
boolean b1 = userList.stream().anyMatch(e -> e.getId() == 1);
// 获取 姓名 包含张的 用户
List userList1 = userList.stream().filter(e -> e.getName().contains("张")).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 对用户名 进行拆分
List collect2 = userList.stream().map(e -> e.getName().split("")).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 流扁平化 flatMap 拆分用户名,去除重复字,得到一个list
List collect3 = userList.stream().map(e -> e.getName().split("")).flatMap(Arrays::stream).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
// 获取用户名长度为 2 的用户,直到长度不为 2 时结束
long count1 = userList.stream().takeWhile(u -> u.getName().length() == 2).count();
// 和上面相反,删除 用户名长度为 2 的用户,直到 长度不为 2 时 获取。
count1 = userList.stream().dropWhile(u -> u.getName().length() == 2).count();
// 排序
userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(User::getAge)).forEach(e -> System.out.println(e.getAge()));
// 逆序
userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(User::getAge).reversed()).forEach(e -> System.out.println(e.getAge()));
// peek 等于 foreach 返回一个流,继续操作
userList.stream().peek(us -> us.setId(1)).map(User::getId).forEach(System.out::println);
// 获取 用户 年龄 最小的
User user2 = userList.stream().min((o1, o2) -> o1.getAge() > o2.getAge() ? o2.getAge() : o1.getAge()).get();
// 获取用户年龄最大的
User user3 = userList.stream().max((o1, o2) -> o1.getAge() < o2.getAge() ? o2.getAge() : o1.getAge()).get();
// reduce 比较 用户年龄,除此之外 reduce 还可以对 数组集合进行操作计算
User user4 = userList.stream().reduce((a, w) -> a.getAge() > w.getAge() ? a: w).get();
// 跳过 前五个 元素
long count2 = userList.stream().skip(5).count();
// parallel 使用多线程处理
userList.stream().parallel().forEach(System.out::println);
// sequential 串行执行 主要和 上面多线程 结合使用
userList.stream().sequential().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
// unordered 返回一个无序流
userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(User::getName)).unordered().forEach(System.out::println); 4. 结束
到这里,想必也清楚了 流的 基本操作与使用。
返回 void 与 具体的 (int、long、list、boolean、对象)都是终端操作,返回stream 都是中间操作。
完整代码
package com.example.demo.lambda;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* lambda
*
* @author wbw
* @date 2020/4/4 19:21
*/
public class LambdaTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始化数据
List userList = loadInfo();
// 统计数量
long count = userList.stream().count();
// 转换成 map ,key为 id,(k1, k2) -> k1) 是指 key 的主键重复时,使用新的还是旧的主键,这里使用旧的
Map userMap = userList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(user -> user.getId(), user -> user, (k1, k2) -> k1));
// lambda 简写 User::getId 等于 user -> user.getId()
userMap = userList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(User::getId, user -> user, (k1, k2) -> k1));
// 再把 map 转换成 list
Collection users = Optional.of(userMap).map(Map::values).get();
// 获取前8个用户
List collect = userList.stream().limit(8).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 去重
List collect1 = userList.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
// 获取任意一个
User user = userList.stream().findAny().get();
// 获取第一个
User user1 = userList.stream().findFirst().get();
// 匹配所有
boolean b = userList.stream().allMatch(e -> e.getId() == 1);
// 匹配所有
boolean b1 = userList.stream().anyMatch(e -> e.getId() == 1);
// 获取 姓名 包含张的 用户
List userList1 = userList.stream().filter(e -> e.getName().contains("张")).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 对用户名 进行拆分
List collect2 = userList.stream().map(e -> e.getName().split("")).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 流扁平化 flatMap 拆分用户名,去除重复字,得到一个list
List collect3 = userList.stream().map(e -> e.getName().split("")).flatMap(Arrays::stream).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
// 获取用户名长度为 2 的用户,直到长度不为 2 时结束
long count1 = userList.stream().takeWhile(u -> u.getName().length() == 2).count();
// 和上面相反,删除 用户名长度为 2 的用户,直到 长度不为 2 时 获取。
count1 = userList.stream().dropWhile(u -> u.getName().length() == 2).count();
// 排序
userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(User::getAge)).forEach(e -> System.out.println(e.getAge()));
// 逆序
userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(User::getAge).reversed()).forEach(e -> System.out.println(e.getAge()));
// peek 等于 foreach 返回一个流,继续操作
userList.stream().peek(us -> us.setId(1)).map(User::getId).forEach(System.out::println);
// 获取 用户 年龄 最小的
User user2 = userList.stream().min((o1, o2) -> o1.getAge() > o2.getAge() ? o2.getAge() : o1.getAge()).get();
// 获取用户年龄最大的
User user3 = userList.stream().max((o1, o2) -> o1.getAge() < o2.getAge() ? o2.getAge() : o1.getAge()).get();
// reduce 比较 用户年龄,除此之外 reduce 还可以对 数组集合进行操作计算
User user4 = userList.stream().reduce((a, w) -> a.getAge() > w.getAge() ? a: w).get();
// 跳过 前五个 元素
long count2 = userList.stream().skip(5).count();
// parallel 使用多线程处理
userList.stream().parallel().forEach(System.out::println);
// sequential 串行执行 主要和 上面多线程 结合使用
userList.stream().sequential().forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
// unordered 返回一个无序流
userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(User::getName)).unordered().forEach(System.out::println);
}
/**
* 加载十条用户信息
*
* @return userList
*/
private static List loadInfo() {
List userList = new LinkedList<>();
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
userList.add(new User(names.get(i), i, random.nextInt(),
getRandomAddress(random.nextInt(10)), String.valueOf(random.nextLong())));
}
return userList;
}
/**
* 姓名
*/
private static final List names = Stream.of("张三", "李四", "王五", "张可汗", "李白", "扁鹊", "马可波罗", "上官婉儿", "太乙真人", "东皇太一").collect(Collectors.toList());
/**
* 自动生成地址(中文)
*
* @param len 长度
* @return name
*/
public static String getRandomAddress(int len) {
Random random = new Random();
StringBuilder ret = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
String str = "";
// 定义高低位
int height = (176 + Math.abs(random.nextInt(39))); // 获取高位值
int lowPos = (161 + Math.abs(random.nextInt(93))); // 获取低位值
byte[] b = {Integer.valueOf(height).byteValue(), Integer.valueOf(lowPos).byteValue()};
try {
str = new String(b, "GBK"); // 转成中文
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
ret.append(str);
}
return ret.toString();
}
}