java-数字和字符串
java数字和字符串
- 装箱和拆箱(整型为例,其他类比即可知道)
1.封装类
所有的基本类型都有类类型,如int对应的类是Integer,这种类就叫封装类。
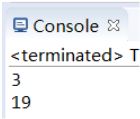
public class TestNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 5;
//把一个基本类型的变量,转换为Integer对象
Integer it = new Integer(i);
//把一个Integer对象,转换为一个基本类型的int
int i2 = it.intValue();
}
}
自动装箱:不需要调用构造方法。 Integer it =i;
自动拆箱:不需要调用Integer的intValue方法。 int i2 = it;
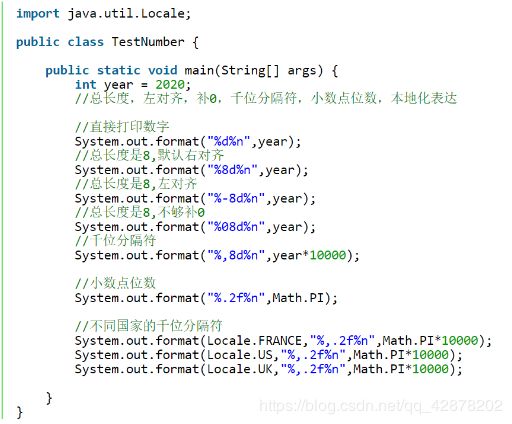
int的范围
最大值:Integer.MAX_VALUE
最小值:Integer.MIN_VALUE
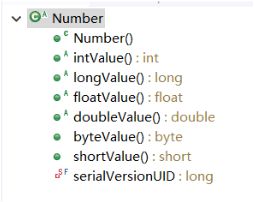
2.抽象类Number
Byte,Short,Integer,Long,Float,Double 都是封装类,且为抽象类Number的子类。
public class TestNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 5;
Integer it = new Integer(i);
//Integer是Number的子类,所以打印true
System.out.println(it instanceof Number);
}
}
其他子类都有以下这些方法
3.强制转换

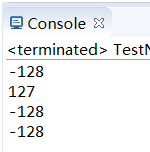
注:使用强制转换的方式进行装箱拆箱并没有多大的意义,强制转换后和原来的区别在于:可能强转的时候数据过大产生溢出,同时基本类型都继承抽象类Number,如Byte类型都有byteValue(),shortValue(),intValue()…等等方法,只是调用的时候返回不同类型的数据。
补充:对于自动拆箱,对于比自己范围大的,可以直接赋值
double e = 5;
Integer i44 = (int)e;
double d2 = i44;//double也可以是long,float
double as=i44.floatValue();
double ass=i44.doubleValue();
double asss=i44.byteValue();
int as=1111;
double ass=as;//赋值会自动类型转换
float asss=as;//赋值会自动类型转换
long assss=as;//赋值会自动类型转换
double sdddddd=(long)1111;//也是可以的,满足范围小赋值给范围大
1.定义
java.lang.Math 提供了一些常用的数学运算方法,并且都是以静态方法的形式存在。
2.四舍五入, 随机数,开方,次方,π,自然常数
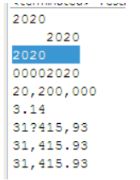
public class TestNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
float f1 = 5.4f;
float f2 = 5.5f;
//5.4四舍五入即5
System.out.println(Math.round(f1));
//5.5四舍五入即6
System.out.println(Math.round(f2));
//得到一个0-1之间的随机浮点数(取不到1),即[0,1)
System.out.println(Math.random());
//得到一个0-10之间的随机整数 (取不到10)
System.out.println((int)( Math.random()*10));
//开方
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(9));
//次方(2的4次方)
System.out.println(Math.pow(2,4));
//π
System.out.println(Math.PI);
//自然常数
System.out.println(Math.E);
}
}
- 格式化输出
public class TestNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name ="盖伦";
int kill = 8;
String title="超神";
String sentenceFormat ="%s 在进行了连续 %d 次击杀后,获得了 %s 的称号%n";
//使用printf格式化输出
System.out.printf(sentenceFormat,name,kill,title);
//使用format格式化输出
System.out.format(sentenceFormat,name,kill,title);
}
}
2.换行符
换行符就是另起一行 — ‘\n’ 换行(newline)
回车符就是回到一行的开头 — ‘\r’ 回车(return)
在eclipse里敲一个回车,实际上是回车换行符
Java是跨平台的编程语言,同样的代码,可以在不同的平台使用,比如Windows,Linux,Mac
然而在不同的操作系统,换行符是不一样的
(1)在DOS和Windows中,每行结尾是 “\r\n”;
(2)Linux系统里,每行结尾只有 “\n”;
(3)Mac系统里,每行结尾是只有 “\r”。
为了使得同一个java程序的换行符在所有的操作系统中都有一样的表现,使用%n,就可以做到平台无关的换行
public class TestNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.printf("这是换行符%n");
System.out.printf("这是换行符%n");
}
}
- 字符
1.保存一个字符的时候使用char
char c1 = 'a';
char c2 = '1';//字符1,而非数字1
char c3 = '中';//汉字字符
2.char对应的封装类:Character
char c1 = 'a';
Character c = c1; //自动装箱
c1 = c;//自动拆箱
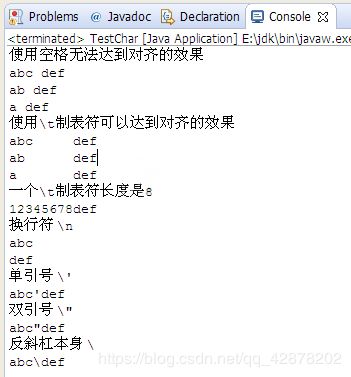
public class TestChar {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("使用空格无法达到对齐的效果");
System.out.println("abc def");
System.out.println("ab def");
System.out.println("a def");
System.out.println("使用\\t制表符可以达到对齐的效果");
System.out.println("abc\tdef");
System.out.println("ab\tdef");
System.out.println("a\tdef");
System.out.println("一个\\t制表符长度是8");
System.out.println("12345678def");
System.out.println("换行符 \\n");
System.out.println("abc\ndef");
System.out.println("单引号 \\'");
System.out.println("abc\'def");
System.out.println("双引号 \\\"");
System.out.println("abc\"def");
System.out.println("反斜杠本身 \\");
System.out.println("abc\\def");
}
}
- 字符串
1.定义
字符串即字符的组合,在Java中,字符串是一个类,所以我们见到的字符串都是对象 。
2.创建字符串
- 每当有一个字面值出现的时候,虚拟机就会创建一个字符串
- 调用String的构造方法创建一个字符串对象
- 通过+加号进行字符串拼接也会创建新的字符串对象
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String garen ="盖伦"; //字面值,虚拟机碰到字面值就会创建一个字符串对象
String teemo = new String("提莫"); //创建了两个字符串对象
char[] cs = new char[]{'崔','斯','特'};
String hero = new String(cs);// 通过字符数组创建一个字符串对象
String hero3 = garen + teemo;// 通过+加号进行字符串拼接
}
}
3.final:源代码中String 被修饰为final,所以是不能被继承的。
4.immutable
定义:String类型是Immutable的,一旦创建就不能够被改变。
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//不可改变的具体含义是指:
//不能增加长度
//不能减少长度
//不能插入字符
//不能删除字符
//不能修改字符
//一旦创建好这个字符串,里面的内容 永远 不能改变
//String 的表现就像是一个常量
String garen ="盖伦";
}
}
5.字符串长度
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name ="盖伦";
System.out.println(name.length());
String unknowHero = "";
//可以有长度为0的字符串,即空字符串
System.out.println(unknowHero.length());
}
}
6.练习-字符串数组排序
创建一个长度是8的字符串数组
使用8个长度是5的随机字符串初始化这个数组
对这个数组进行排序,按照每个字符串的首字母排序(无视大小写)
注1: 不能使用Arrays.sort() 要自己写
注2: 无视大小写,即 Axxxx 和 axxxxx 没有先后顺
public class ZifuchuanArraysSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//字符串数组排序
// 在for循环中采用StringBuilder比用String的 `+=`高效
StringBuilder str1 = new StringBuilder(); //得到字符串
String[] str3=new String[8];//存放8个长度是5的随机字符串
StringBuilder str4= new StringBuilder();
// 得到字符串
for (short i = '0'; i <= 'z'; i++) {
if (Character.isLetter((char) i) || Character.isDigit((char) i)){
str1.append((char) i);
}
}
String str2= str1.toString();
System.out.println(str2);
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++){
for(int j=0;j<5;j++){
int idx =(int) Math.floor(Math.random() * str2.length());
str4.append(str2.charAt(idx));//str2.charAt(idx);得到一个字符
str3[i]=str4.toString();
}
str4.delete(0, str4.length());//将str4清空
}
System.out.println("初始化字符串:");
for(String Str3:str3){
System.out.print(Str3+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("数组排序:");
for (int j = 0; j < str3.length; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < str3.length - j - 1; i++) {
char c1 = str3[i].charAt(0);
char c2 = str3[i + 1].charAt(0);
c1 = Character.toLowerCase(c1); //小写转换
c2 = Character.toLowerCase(c2);
//冒泡排序换位方法
if (((short)c1) >((short)c2)) {
String temp = str3[i];
str3[i] = str3[i+1];
str3[i+1] = temp;
}
}
}
for(String Str3:str3){
System.out.print(Str3+"\t");
}
}
}
- 操纵字符串
charAt(int index):获取指定位置的字符
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sentence = "盖伦,在进行了连续8次击杀后,获得了 超神 的称号";
char c = sentence.charAt(0);
System.out.println(c);
}
}
toCharArray():获取对应的字符数组,即将字符串转换字符数组
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sentence = "盖伦,在进行了连续8次击杀后,获得了超神 的称号";
char[] cs = sentence.toCharArray(); //获取对应的字符数组
System.out.println(sentence.length() == cs.length);
}
subString():截取子字符串
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sentence = "盖伦,在进行了连续8次击杀后,获得了 超神 的称号";
//截取从第3个开始的字符串 (基0)
String subString1 = sentence.substring(3);
System.out.println(subString1);
//截取从第3个开始的字符串 (基0)
//左闭右开[3,5)
String subString2 = sentence.substring(3,5);
System.out.println(subString2);
}
}
split(): 根据分隔符进行分隔
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sentence = "盖伦,在进行了连续8次击杀后,获得了 超神 的称号";
//根据,进行分割,得到3个子字符串
String subSentences[] = sentence.split(",");
for (String sub : subSentences) {
System.out.println(sub);
}
}
}
trim(): 去掉首尾空格
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sentence = " 盖伦,在进行了连续8次击杀后,获得了 超神 的称号 ";
System.out.println(sentence);
//去掉首尾空格
System.out.println(sentence.trim());
}
}
toLowerCase():全部变成小写
toUpperCase():全部变成大写
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sentence = "Garen";
//全部变成小写
System.out.println(sentence.toLowerCase());
//全部变成大写
System.out.println(sentence.toUpperCase());
}
}
定位
indexOf():判断字符或者子字符串出现的位置(首次出现)
lastIndexOf():字符串最后出现的位置
contains():是否包含子字符串
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sentence = "盖伦,在进行了连续8次击杀后,获得了超神 的称号";
System.out.println(sentence.indexOf('8')); //字符第一次出现的位置
System.out.println(sentence.indexOf("超神")); //字符串第一次出现的位置
System.out.println(sentence.lastIndexOf("了")); //字符串最后出现的位置
System.out.println(sentence.indexOf(',',5)); //从位置5开始,出现的第一次,的位置
System.out.println(sentence.contains("击杀")); //是否包含字符串"击杀"
}
}
替换
replaceAll():替换所有的
replaceFirst():只替换第一个
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sentence = "盖伦,在进行了连续8次击杀后,获得了超神 的称号";
String temp = sentence.replaceAll("击杀", "被击杀"); //替换所有的
temp = temp.replaceAll("超神", "超鬼");
System.out.println(temp);
temp = sentence.replaceFirst(",","");//只替换第一个
System.out.println(temp);
}
}
- 比较字符串
1.是否是同一个对象
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "the light";
String str2 = new String(str1);
//==用于判断是否是同一个字符串对象
System.out.println( str1 == str2);
}
}
2.是否是同一个对象-特例
在创建了一个新的字符串"the light"
之后再次创建该字符串,编译器发现已经存在现成的"the light",那么就直接拿来使用,而没有进行重复创建
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "the light";
String str3 = "the light";
System.out.println( str1 == str3);
}
}
3.内容是否相同
equals:进行字符串内容的比较,必须大小写一致
equalsIgnoreCase:忽略大小写判断内容是否一致
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "the light";
String str2 = new String(str1);
String str3 = str1.toUpperCase();
//==用于判断是否是同一个字符串对象
System.out.println( str1 == str2);
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));//完全一样返回true
System.out.println(str1.equals(str3));//大小写不一样,返回false
System.out.println(str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str3));//忽略大小写的比较,返回true
}
}
4.是否以子字符串开始或者结束
startsWith //以…开始
endsWith //以…结束
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "the light";
String start = "the";
String end = "Ight";
System.out.println(str1.startsWith(start));//以...开始
System.out.println(str1.endsWith(end));//以...结束
System.out.println(str1.endsWith("ight"));//以...结束
}
}
5.练习
比较字符串:创建一个长度是100的字符串数组
使用长度是2的随机字符填充该字符串数组
统计这个字符串数组里重复的字符串有多少种
方法一:
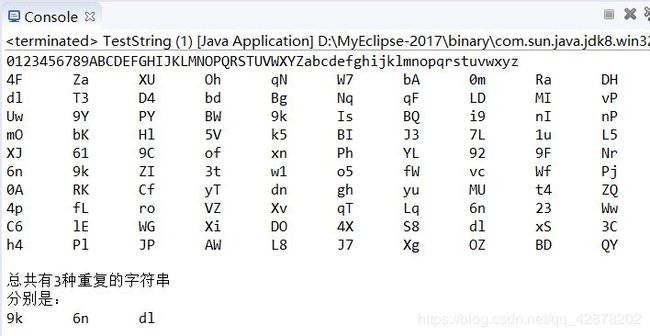
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个长度是100的字符串数组
//字符串数组排序
// 在for循环中采用StringBuilder比用String的 `+=`高效
StringBuilder str1 = new StringBuilder(); //得到字符串
String[] str3=new String[100];//存放100个长度是2的随机字符串
StringBuilder str4= new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder str5= new StringBuilder();
// 得到字符串
for (short i = '0'; i <= 'z'; i++) {
if (Character.isLetter((char) i) || Character.isDigit((char) i)){
str1.append((char) i);
}
}
String str2= str1.toString();
System.out.println(str2);
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++){
for(int j=0;j<2;j++){
int idx =(int) Math.floor(Math.random() * str2.length());
str4.append(str2.charAt(idx));//str2.charAt(idx);得到一个字符
str3[i]=str4.toString();
}
str4.delete(0, str4.length());//将str4清空
}
int i=0;
for(String Str3:str3){
System.out.print(Str3+"\t");
if(i!=0&&i%20==0){
System.out.println();
}
i++;
}
System.out.println();
int count=0;
for(i=0;i<str3.length;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<str3.length;j++){
if(str3[i].equals(str3[j])){
count++;
str5.append(str3[i]+" ");
break;
}
}
}
System.out.printf("总共有%d种重复的字符串\n",count);
System.out.println("分别是:");
System.out.println(str5);
}
}
package collection;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个长度是100的字符串数组
//字符串数组排序
// 在for循环中采用StringBuilder比用String的 `+=`高效
StringBuilder str1 = new StringBuilder(); //得到字符串
String[] str3=new String[100];//存放100个长度是2的随机字符串
StringBuilder str4= new StringBuilder();
HashSet<String> randomchar = new HashSet<String>();
HashSet<String> randomchar1 = new HashSet<String>();
// 得到字符串
for (short i = '0'; i <= 'z'; i++) {
if (Character.isLetter((char) i) || Character.isDigit((char) i)){
str1.append((char) i);
}
}
String str2= str1.toString();
System.out.println(str2);
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++){
for(int j=0;j<2;j++){
int idx =(int) Math.floor(Math.random() * str2.length());
str4.append(str2.charAt(idx));//str2.charAt(idx);得到一个字符
str3[i]=str4.toString();
}
if(randomchar.add(str3[i])==false) {//如果已经存在了str3[i],返回false,false==false
randomchar1.add(str3[i]);
}
System.out.print(str3[i]+"\t");
if(i!=0&&(i+1)%10==0){
System.out.println();
}
str4.delete(0, str4.length());//将str4清空
}
System.out.println();
System.out.printf("总共有%d种重复的字符串\n", randomchar1.size());
System.out.println("分别是:");
for(String temp:randomchar1) {
System.out.print(temp+"\t");
}
}
}
- StringBuffer
1.定义
StringBuffer是可变长的字符串(注意区分StringBuilder)
2.方法
append追加
delete 删除
insert 插入
reverse 反转
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "let there ";
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(str1); //根据str1创建一个StringBuffer对象
sb.append("be light"); //在最后追加
System.out.println(sb);
sb.delete(4, 10);//删除4-10之间的字符
System.out.println(sb);
sb.insert(4, "there ");//在4这个位置插入 there
System.out.println(sb);
sb.reverse(); //反转
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
长度 容量
package character;
public class TestString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "the";
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(str1);
System.out.println(sb.length()); //内容长度
System.out.println(sb.capacity());//总空间
}
}
package character;
public interface IStringBuffer {
public void append(String str); //追加字符串
public void append(char c); //追加字符
public void insert(int pos,char b); //指定位置插入字符
public void insert(int pos,String b); //指定位置插入字符串
public void delete(int start); //从开始位置删除剩下的
public void delete(int start,int end); //从开始位置删除结束位置-1
public void reverse(); //反转
public int length(); //返回长度
}
package character;
public class MyStringBuffer implements IStringBuffer{
int capacity = 16;
int length = 0;
char[] value; //value:用于存放字符数组
public MyStringBuffer(){
value = new char[capacity]; //capacity: 容量
}
//有参构造方法
public MyStringBuffer(String str){
this();
if(null==str)
return;
if(capacity<str.length()){
capacity = value.length*2;
value=new char[capacity];
}
if(capacity>=str.length())
System.arraycopy(str.toCharArray(), 0, value, 0, str.length());
length = str.length();
}
@Override
public void append(String str) {
insert(length,str);
}
@Override
public void append(char c) {
append(String.valueOf(c));
}
@Override
public void insert(int pos, char b) {
insert(pos,String.valueOf(b));
}
@Override
public void delete(int start) {
delete(start,length);
}
@Override
public void delete(int start, int end) {
//边界条件判断
if(start<0)
return;
if(start>length)
return;
if(end<0)
return;
if(end>length)
return;
if(start>=end)
return;
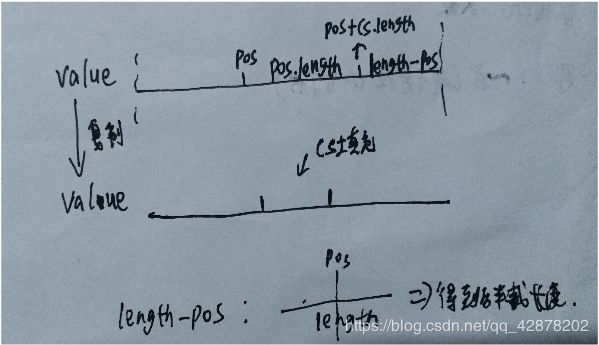
//将end后面的数据填充到从start开始(复制长度为原value的end后面的数据的长度)
System.arraycopy(value, end, value, start, length- end);
length-=end-start;
}
@Override
public void reverse() {
for (int i = 0; i < length/2; i++) {
char temp = value[i];
value[i] = value[length-i-1];
value[length-i-1] = temp;
}
}
@Override
public int length() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return length;
}
@Override
public void insert(int pos, String b) {
//边界条件判断
if(pos<0)
return;
if(pos>length)
return;
if(null==b)
return;
//扩容
while(length+b.length()>capacity){
capacity = (int) ((length+b.length())*1.5f);
char[] newValue = new char[capacity];
System.arraycopy(value, 0, newValue, 0, length);
value = newValue;
}
char[] cs = b.toCharArray();
//先把已经存在的数据往后移
System.arraycopy(value, pos, value,pos+ cs.length, length-pos);
//把要插入的数据插入到指定位置
System.arraycopy(cs, 0, value, pos, cs.length);
length = length+cs.length;
}
public String toString(){
char[] realValue = new char[length];
System.arraycopy(value, 0, realValue, 0, length);
return new String(realValue);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyStringBuffer sb = new MyStringBuffer("there light");
System.out.println(sb);
sb.insert(0, "let ");
System.out.println(sb);
sb.insert(10, "be ");
System.out.println(sb);
sb.insert(0, "God Say:");
System.out.println(sb);
sb.append("!");
System.out.println(sb);
sb.append('?');
System.out.println(sb);
sb.reverse();
System.out.println(sb);
sb.reverse();
System.out.println(sb);
sb.delete(0,4);
System.out.println(sb);
sb.delete(4);
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
- String 和 StringBuffer、StringBuilder 的区别