spring 整合 mybatis原理
SqlSessionFactoryBean的创建
1.SqlSessionFactoryBean这个类实现了三个接口,一个是InitializingBean,另一个是FactoryBean,还有就是ApplicationListener接口。下面说明一下实现了这三个接口的,有什么作用
InitializingBean接口:实现了这个接口,那么当bean初始化的时候,spring就会调用该接口的实现类的afterPropertiesSet方法,去实现当spring初始化该Bean 的时候所需要的逻辑。
FactoryBean接口:实现了该接口的类,在调getBean的时候会返回该工厂返回的实例对象,也就是再调一次getObject方法返回工厂的实例。
ApplicationListener接口:实现了该接口,如果注册了该监听的话,那么就可以了监听到Spring的一些事件,然后做相应的处理
SqlSessionFactoryBean的初始化
SqlSessionFactory的初始化是在Spring初始化该Bean 的时候就会初始化,实现InitializingBean接口的目的就是为了这个,让我们看看SqlSessionFactoryBean中实现InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet方法。
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
从中我们可以看到,sqlSessionFactory的实例化便在这个方法里面实例化,buildSqlSessionFactory()方法会对我们的sqlSessionFactory做定制的初始化,初始化sqlSessionFactory有两种方式,一种是我们直接通过property直接注入到改实例中,另一种是通过解析xml的方式,就是我们在configuration.xml里面的配置,根据这些配置做了相应的初始化操作,里面也是一些标签的解析属性的获取,操作,和Spring的默认标签解析有点类似,这里就不再重复说明。
获取SqlSessionFactoryBean实例
因为SqlSessionFactoryBean实现了FactoryBean接口,所以当我们通过getBean获取它的实例的时候实际是调用他的getObject方法,获取到的是sqlSessionFactory。
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception {
if (this.sqlSessionFactory == null) {
afterPropertiesSet();
}
return this.sqlSessionFactory;
}
所以我们在给dao注入sqlSessionFactory的时候,依赖填写SqlSessionFactoryBean 的实例就可以了。
MapperFactoryBean的创建
在使用mybatis的时候,我们获取dao的方式一般是这样
SqlSession session=sessionFactory.openSession();
PersonDao personDao=session.getMapper(PersonDao.class);
但在我们在spring的测试用例中使用mybatis的时候是这样使用的:
PersonDao personDao=(PersonDao) context.getBean("personDao");
为什么spring可以这样做呢,答案就在MapperFactoryBean这里
让我先来看看这个类的类层次结构图:
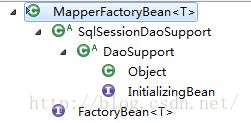
MapperFactoryBean也实现了FactoryBean和InitializingBean接口,我们也从MapperFactoryBean的初始化开始吧,看看它如何初始化。
MapperFactoryBean初始化
MapperFactoryBean继承了SqlSessionDaoSupport,SqlSessionDaoSupport继承DaoSupport,DaoSupport实现了InitializingBean接口,让我们开看看它这接口的实现:
public final void afterPropertiesSet() throws IllegalArgumentException, BeanInitializationException {
// Let abstract subclasses check their configuration.
checkDaoConfig();
// Let concrete implementations initialize themselves.
try {
initDao();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Initialization of DAO failed", ex);
}
}
该方法主要包含两个功能,一个是调用checkDaoConfig()方法,一个是调用initDao方法。checkDaoConfig方法在DaoSupport是抽象方法,让我看看它在MapperFactoryBean的实现:
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
protected void checkDaoConfig() {
super.checkDaoConfig();
notNull(this.mapperInterface, "Property 'mapperInterface' is required");
Configuration configuration = getSqlSession().getConfiguration();
if (this.addToConfig && !configuration.hasMapper(this.mapperInterface)) {
try {
configuration.addMapper(this.mapperInterface);
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("Error while adding the mapper '" + this.mapperInterface + "' to configuration.", t);
throw new IllegalArgumentException(t);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}
该方法主要是检查dao的配置,主要是检验sqlSessionFactory和mapperInterface属性不能为空,以及检测接口对于的映射文件是否存在,如果存在,那么就把它添加到configuration里面去,注册mapper。
获取MapperFactoryBean的实例
MapperFactoryBean实现了FactoryBean接口,那么在调用getBean方法获取MapperFactoryBean实例的时候,实际上调用的就是getObject方法,让我们来看看getObject的实现:
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
看到这里,我们会恍然大悟,原来在这里封装了getMapper操作,返回接口的实例,怪不得在Spring中使用MyBatis不用管理sqlSession了。
所以对于上面的测试用例,Spring怎么封装了MyBatis,如何把sqlSessionFactory和sqlSession隐藏了起来,又怎么方便的获取dao接口实例,我们大概有了一个了解。
那么让我在回到之前提到的那个问题,如果有成百上千个dao接口呢,那我们岂不是要配置添加成百上千个bean,当然不是这样,spring还为MyBatis添加了拓展的功能,可以通过扫描包目录的方式,添加dao,让我看看具体使用和实现。
MapperScannerConfigurer介绍
如果我们的dao在一个包下面又好几十个,那么我可以可以通过扫描的方式添加dao,像下面一样使用
看到上面的配置,我们会很好奇,在spring这样添加就可以扫描的方式添加dao配置,怎么做到的?让我打开类实现,具体看一下
MapperScannerConfigurer实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口,如果MapperScannerConfigurer实现了该接口,那么说明在application初始化的时候该接口会被调用,具体实现,让我先看看:
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @since 1.0.2
*/
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
if (this.processPropertyPlaceHolders) {
processPropertyPlaceHolders();
}
ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry);
scanner.setAddToConfig(this.addToConfig);
scanner.setAnnotationClass(this.annotationClass);
scanner.setMarkerInterface(this.markerInterface);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactory(this.sqlSessionFactory);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplate(this.sqlSessionTemplate);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplateBeanName(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName);
scanner.setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(this.nameGenerator);
scanner.registerFilters();
scanner.scan(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS));
}
这里我们重点关注三个主要的方法,分别是
processPropertyPlaceHolders();
scanner.registerFilters();
scanner.scan(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS));
processPropertyPlaceHolders属性处理
执行属性的处理,简单的说,就是把xml中${XXX}中的XXX替换成属性文件中的相应的值
根据配置属性生成过滤器
scanner.registerFilters();方法会根据配置的属性生成对应的过滤器,然后这些过滤器在扫描的时候会起作用。
扫描java文件
scanner.scan(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS));
该方法主要做了以下操作:
1)扫描basePackage下面的java文件
2)解析扫描到的java文件
3)调用各个在上一步骤注册的过滤器,执行相应的方法。
4)为解析后的java注册bean,注册方式采用编码的动态注册实现。
5)构造MapperFactoryBean的属性,mapperInterface,sqlSessionFactory等等,填充到BeanDefinition里面去。
做完这些,MapperFactoryBean对象也就构造完成了,扫描方式添加dao的工作也完成了。
总结
其实了解了Spring整合MyBatis的流程,我们也就大体知道Spring整合一些框架所使用的扩展方法,不过大多是都是通过继承接口的方式,然后通过spring回调该接口的方式,实现我们自己想要的扩展逻辑,所以了解spring提供的一些扩展的接口以及抽象类是扩展的关键,就像InitializingBean,BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor这些接口,知道了这些接口调用的方式,以及上面时候会调用,我们就可以知道,我们需要扩展的功能应该实现哪个接口,或者集成哪个抽象类。目前这些接口,官方没有整理出一份比较好的文档,不过在后续的博客中,我会把这些常用的拓展接口以及抽象类都提出来,介绍下,让大家熟悉下这些可以对spring进行扩展的接口以及抽象类。
作者:Fighter168
来源:CSDN
原文:link