scrapy学习笔记(一)
scrapy学习笔记
- scrapy简介
- scrapy结构
- 各组件介绍
- window下安装方法
- 第一个scrapy项目
- 1、创建项目:
- 目录结构说明
- 创建爬虫
- items.py声明变量
- 爬虫代码
- 设置settings
- 设置piplines.py
- 爬取多个页面
- 预告
scrapy简介
Scrapy是适用于Python的一个快速、高层次的屏幕抓取和web抓取框架,用于抓取web站点并从页面中提取结构化的数据。Scrapy用途广泛,可以用于数据挖掘、监测和自动化测试。
Scrapy吸引人的地方在于它是一个框架,任何人都可以根据需求方便的修改。它也提供了多种类型爬虫的基类,如BaseSpider、sitemap爬虫等,最新版本又提供了web2.0爬虫的支持。
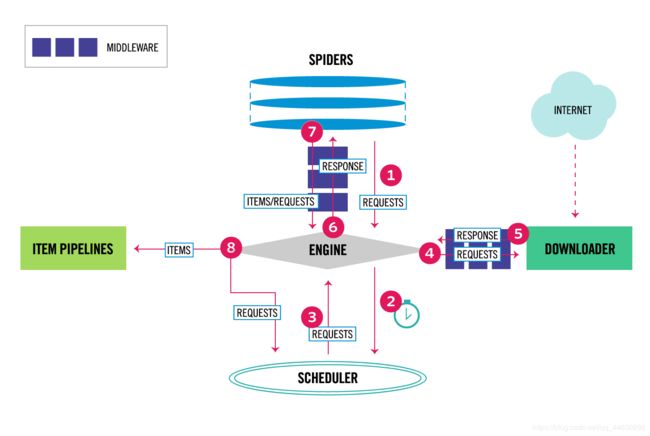
scrapy结构
各组件介绍
ENGINE
引擎(engine)控制所有部件间的数据流,并在某些事件发生时触发事件
Scheduler
调度器(scheduler)接收来自引擎的request,并对它去重,放入到请队列中;并根据队列的取出规则,把请求按顺序返回给引擎
Downloader
下载器(Downloader)获取网页数据并返回给引擎
Spiders
爬虫(Spiders)用来解析response,提取出Items和新的Requests
Item Pipeline
对Items进行进一步的清洗,并持久化
Downloader middlewares
下载中间件可以勾住下载器和引擎之间的数据流,并对它们做一些处理,比如:
在request送到下载器之前对它做一些处理,可以添加User_Agent,修改IP等
对response做一些处理
Spider middlewares
爬虫中间件可以勾住爬虫和引擎之间的数据流,并对它们做一些处理
window下安装方法
pip install scrapy
window还要安装 pipiwin32,如果不安装,那么以后运行scrapy项目时就会报错
第一个scrapy项目
1、创建项目:
scrapy startproject [爬虫项目名字]
目录结构说明

2. 项目目录结构
1、item.py
用来存放爬虫爬取下来数据的模型
2、middlewares.py
用来存放各种中间件的文件
3、pipelines.py
用来将items的模型存储到本地磁盘中
4、setting.py
爬虫的一些配置信息(请求头,多久一次请求,ip代理池等)
5、scrapy.cfg
项目的配置文件
6、spiders包:
以后所有的爬虫,都是存放到这个里面
创建爬虫
进入到项目所在的路径,执行命令:
scrapy genspider [爬虫名字] [爬虫的域名]
items.py声明变量
建议在item.py中定义好模型,以后就不要使用字典
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Define here the models for your scraped items
#
# See documentation in:
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html
import scrapy
class QsbkItem(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
author = scrapy.Field()
content = scrapy.Field()
爬虫代码
1、response是一个scrapy.http.response.html.HtmlResponse对象
可以执行xpath和css语法来提取数据
2、提取出来的数据时一个selector或者selectorlist
获取字符串,执行get()或者getall()
get():
获取selector中的第一个文本,返回的是一个str类型
getall():
获取selector中的所欲文本,返回的是一个列表类型
3、数据解析回来,要传给pipline处理
可以使用yield
或者使用return也可以,需要收集全部数据后再返回
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scrapy
from ..items import QsbkItem
from scrapy.http.response.html import HtmlResponse
from scrapy.selector.unified import SelectorList
class QsbkSpiderSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'qsbk_spider'
allowed_domains = ['qiushibaike.com']
start_urls = ['https://www.qiushibaike.com/text/page/1/']
base_domin = "https://www.qiushibaike.com"
def parse(self, response):
# selectorList
duanzidivs = response.xpath("//div[@class='col1 old-style-col1']/div")
for duanzidiv in duanzidivs:
# selector
author = duanzidiv.xpath(".//h2/text()").get().strip()
content = duanzidiv.xpath(".//div[@class='content']//text()").getall()
# 将content由list转换为string
content = "".join(content).strip()
item = QsbkItem(author=author, content=content)
# duanzi = {
# "author": author,
# "content": content,
# }
# # 将数据传输给piplines
yield item
# 相比于字典,item的好处是:可以固定参数,约束值的传递
# 在传递数据时,传递的是类,效率更高
next_url = response.xpath("//ul[@class='pagination']/li[last()]/a/@href").get()
if not next_url:
return
else:
yield scrapy.Request(self.base_domin+next_url, callback=self.parse)
设置settings
1、 无视robot协议
ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = False
2、 设置请求头
DEFAULT_REQUEST_HEADERS = {
'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8',
'Accept-Language': 'en',
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/76.0.3809.132 Safari/537.36'
}
3、设置爬取间隔
DOWNLOAD_DELAY = 1
4、设置管道运行
数值越低,优先度越高
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'qsbk.pipelines.QsbkPipeline': 1,
}
设置piplines.py
pipline:
专门用来保存数据的。其中三个方法经常使用
1、open_spider(self,spider)
当爬虫打开时使用
2、process_spider(self,item,spider)
当有item返回时当用
3、close_spider
爬虫结束后运行
4、启用pipline
在setting.py中,设置ITEM_PIPLINE如下
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
‘qsbk.pipelines.QsbkPipeline’: 1,}
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Define your item pipelines here
#
# Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting
# See: https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
from scrapy.exporters import JsonItemExporter, JsonLinesItemExporter
class QsbkPipeline(object):
def __init__(self):
# 以二进制方式打开,因为exporter使用二进制
self.fp = open("daunzi.json", 'wb')
self.exporter = JsonLinesItemExporter(self.fp, ensure_ascii=False, encoding="utf-8")
self.exporter.start_exporting()
# 爬虫开始运行时就会执行改函数
def open_spider(self, spider):
print("爬虫开始")
# 爬虫在运行过程中传递了一些item进来,就会执行该函数
# 例如yield所传回来的数据
def process_item(self, item, spider):
# # item是一个类
# # 设置ensure_ascii=False,
# item_json = json.dumps(dict(item), ensure_ascii=False)
# self.fp.write(item_json+'\n')
self.exporter.export_item(item)
return item
# 爬虫结束运行后执行该函数
def close_spider(self, spider):
# 比较耗内存,因为是先把数据保存到item,当expoter结束后再写入文件
# JsonLinesItemExporter不需要关闭exporter
# self.exporter.finish_exporting()
self.fp.close()
print("结束")
JsonItemExporter和JsonLindexItemExporter
保存json数据的时候,可以使用这两个类,让操作变得更简单
1、JsonItemExporter
每次把数据添加到内存中,最后统一写入到内存中
好处:存储的数据时一个满足json规则的数据
坏处:比较耗内存
2、JsonLindexItemExporter
每次调用export_item的时候就把这个item存储到磁盘中
好处:不耗内存 安全
坏处:每个字典是一行,不是json格式
爬取多个页面
手动获取下一个页面
# 获取下一个页面
next_url = response.xpath("//ul[@class='pagination']/li[last()]/a/@href").get()
if not next_url:
return
else:
返回的同时,将请求加入到队列当中,同时调用parse方法
yield scrapy.Request(self.base_domin+next_url, callback=self.parse)
预告
CrawSpider自动爬取多个页面