基于八叉树颜色删减C++实现
基于八叉树颜色删减C++实现
一、减色处理目的
位图采用RGB颜色模型,是一个二维的像素矩阵的方法显示和存储的图象,矩阵中的每个元素代表一个像素。真彩图像为24位图,即包含多达224种颜色。真彩图片的特点:它没有调色板,直接用元素来表示像素的颜色值,每个元素(R,G,B)包含一个字节的红®色分量,一个字节的绿(G)色分量,和一个字节的蓝(B)色分量。可见真彩图片颜色细腻,但数据量巨大,一帧1024×768分辨率的真彩图片要占用空间:1024×768×3B=2.25MB。256色图为8位图,它由调色板和索引数据组成。调色板保存256种颜色的色彩分量值。索引数据的每个元素由8位组成,该8位的值为调色板的上对应颜色的索引位置。256色图的特点:只能表示256种颜色,但数据量小,一帧1024×768分辨率256色图只占用空间:1024×768+256×3=768.8kB。
二、色彩变换算法,真彩图转256色图
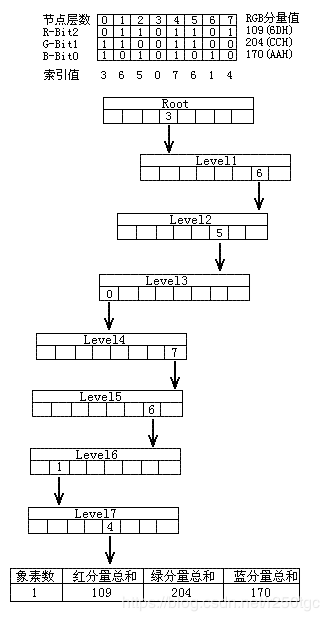
要实现色彩转换,关键如何从真彩224种颜色中选出256种颜色,又要使颜色的失真比较小八叉树颜色量化算法。算法基本思路是:将图像中使用的RGB颜色值分布到层状的八叉树中。八叉树的深度可达9层,即根节点层加上分别表示8位的R、G、B值的每一位的8层节点。较低的节点层对应于较不重要的RGB值的位(右边的位),因此,为了提高效率和节省内存,可以去掉最低部的2 ~ 3层,这样不会对结果有太大的影响。叶节点编码存储像素的个数和R、G、B颜色分量的值;而中间的节点组成了从最顶层到叶节点的路径。这是一种高效的存储方式,既可以存储图像中出现的颜色和其出现的次数,也不会浪费内存来存储图像中不出现的颜色。算法特点:效率高,效果好
三、八叉树颜色量化算法实现
颜色量化步骤:
①、扫描图像的所有像素,将它们的数据累加到相应的节点中;遇到新的颜色则创建一个叶子节点,并将此像素的颜色数据存入其中。
②、如果叶子节点数目大于目标调色板所要的颜色数,就将部分叶子节点合并到父节点中,并将父节点转化为叶子节点,在其中存放颜色分量的累加值及其像素出现的次数。同时删除原来被合并的叶子节点。
③所有像素处理结束,遍历八叉树,将叶子节点的各颜色值求平均值作为节点的颜色分量值读出并存入目标调色板。
④再次遍历所有像素,通过每个像素的颜色值与调色板中选中的256色运算,求得一个最接近像素颜色值的调色板颜色,把该像素换相应的调色板颜色索引。
三、处理结果
颜色删减之后的图像
四、代码实现C++
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_DEPRECATE
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned char uint8;
struct octNode
{
long long cnt, rSum, gSum, bSum;
bool isLeaf;
int depth;
octNode* child[8];
octNode* pre;
octNode* next;
octNode()
{
cnt = 0;
rSum = 0;
gSum = 0;
bSum = 0;
isLeaf = false;
depth = 0;
pre = NULL;
next = NULL;
memset(child, NULL, sizeof(child));
}
octNode(int d)
{
cnt = 0;
rSum = 0;
gSum = 0;
bSum = 0;
isLeaf = false;
depth = d;
pre = NULL;
next = NULL;
memset(child, NULL, sizeof(child));
};
octNode(uint8 r, uint8 g, uint8 b)
{
cnt = 1;
rSum = r;
gSum = g;
bSum = b;
isLeaf = true;
depth = 9;
pre = NULL;
next = NULL;
memset(child, NULL, sizeof(child));
};
};
class octTree
{
private:
octNode* root; //八叉树的根
int colors; //当前的颜色总数
int maxColors; //最大颜色数
octNode** head;
public:
octTree();
octTree(int maxColorNum);
~octTree() ;
void insertColor(uint8 r, uint8 g, uint8 b); //插入一个颜色
uint8 generatePalette(RGBQUAD* pal); //生成调色板
void deleteNode(octNode* p);
void newNode(int d);
};
void octTree::deleteNode(octNode* p)
{
if (p == NULL)
{
return;
}
if (p->isLeaf == true)
{
colors--;
delete p;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
deleteNode(p->child[i]);
}
delete p;
}
void octTree::newNode(int d)
{
root = new octNode();
colors = 0;
maxColors = d;
head = new octNode * [9];
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
{
if (i == 0)
{
head[i] = root;
}
else
{
head[i] = NULL;
}
}
}
octTree::octTree()
{
newNode(0);
}
octTree::octTree(int maxColorNum)
{
newNode(maxColorNum);
}
octTree::~octTree()
{
deleteNode(root);
}
void octTree::insertColor(uint8 r, uint8 g, uint8 b)
{
int* num = new int[8];
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
num[i] = 0;
uint8 m = 1 << (7 - i);
if (m & r)
num[i] += 4;
if (m & g)
num[i] += 2;
if (m & b)
num[i] += 1;
}
octNode * p = root;
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
{
if (p->isLeaf == true)
{
p->cnt = p->cnt + 1;
p->rSum = p->rSum + r;
p->gSum = p->gSum + g;
p->bSum = p->bSum + b;
}
else //p->isLeaf==false
{
if (p->child[num[i]] == NULL)
{
if (i < 7)
{
p->child[num[i]] = new octNode(i + 1);
octNode * q = p->child[num[i]];
if (head[i + 1] == NULL)
{
head[i + 1] = q;
}
else
{
head[i + 1]->pre = q;
q->next = head[i + 1];
head[i + 1] = q;
}
p = p->child[num[i]];
}
else if (i == 7)
{
p->child[num[i]] = new octNode(r, g, b);
colors++;
p = p->child[num[i]];
i++;
if (head[i] == NULL)
{
head[i] = p;
}
else
{
head[i]->pre = p;
p->next = head[i];
head[i] = p;
}
break;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
else //p->child[num[i]] != NULL
{
p = p->child[num[i]];
}
}
}
double per = 0;
int temp1 = colors - maxColors;
int temp2 = colors;
while (colors > maxColors)
{
double x= (double)(temp2 - colors) * 100 / temp1;
if (x - per >= 10)
{
per = x;
printf("\b\b\b%2d%%", per);
}
for (int u = 7; u > 0; u--)
{
if (head[u] == NULL)
{
continue;
}
octNode* p2 = head[u];
for (; p2 != NULL; p2 = p2->next)
{
if (p2->isLeaf==false)
{
break;
}
}
if (p2 == NULL)
{
continue;
}
int childNum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
if (p2->child[i] != NULL)
{
p2->cnt += p2->child[i]->cnt;
p2->rSum += p2->child[i]->rSum;
p2->gSum += p2->child[i]->gSum;
p2->bSum += p2->child[i]->bSum;
if (p2->child[i]->pre != NULL)
{
p2->child[i]->pre->next = p2->child[i]->next;
}
if (p2->child[i]->next != NULL)
{
p2->child[i]->next->pre = p2->child[i]->pre;
}
if (p2->child[i] == head[u + 1])
{
head[u + 1] = p2->child[i]->next;
}
p2->child[i] = NULL;
childNum++;
}
}
p2->isLeaf = true;
colors -= (childNum - 1);
break;
}
}
}
int func(uint8 r, uint8 g, uint8 b, RGBQUAD * pal, int i)
{
int R = (int)(r - pal[i].rgbRed) * (r - pal[i].rgbRed);
int G = (int)(g - pal[i].rgbGreen) * (g - pal[i].rgbGreen);
int B = (int)(b - pal[i].rgbBlue) * (b - pal[i].rgbBlue);
return R + G + B;
}
uint8 selectClosestColor(uint8 r, uint8 g, uint8 b, RGBQUAD * pal)
{
int I = 0;
int V = func(r, g, b, pal, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
if (func(r, g, b, pal, i) < V)
{
I = i;
V = func(r, g, b, pal, i);
}
}
return (uint8)I;
}
uint8 octTree::generatePalette(RGBQUAD * pal) //生成调色板
{
int number = 0;
for (int L = 8; L >= 0; L--)
{
for (octNode* p = head[L]; p != NULL; p = p->next)
{
if (p == NULL)
{
return number;
}
if (!p->isLeaf)
continue;
pal[number].rgbRed = p->rSum / p->cnt;
pal[number].rgbGreen = p->gSum / p->cnt;
pal[number].rgbBlue = p->bSum / p->cnt;
pal[number].rgbReserved = 0;
number++;
}
}
return number;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if (argc < 3)
{
printf("using: exe[0], input file[1], output file[2]\n");
return -1;
}
BITMAPFILEHEADER bf, * pbf;//输入、输出文件的文件头
BITMAPINFOHEADER bi, * pbi;//输入、输出文件的信息头
RGBQUAD* pRGBQuad;//待生成的调色板指针
uint8* pImage;//转换后的图象数据
DWORD bfSize;//文件大小
LONG biWidth, biHeight;//图象宽度、高度
DWORD biSizeImage;//图象的大小,以字节为单位,每行字节数必须是4的整数倍
unsigned long biFullWidth;//每行字节数必须是4的整数倍
//打开输入文件
char* inputName, * outputName;
FILE* fpIn, * fpOut;
//inputName = (char*)"source.BMP";
//outputName = (char*)"result.BMP";
inputName = argv[1];
outputName = argv[2];
printf("Opening %s ... ", inputName);
if (!(fpIn = fopen(inputName, "rb")))
{
printf("\nCan't open %s!\n", inputName);
return -1;
}
printf("Success!\n");
//创建输出文件
printf("Creating %s ... ", outputName);
if (!(fpOut = fopen(outputName, "wb")))
{
printf("\nCan't create %s!\n", outputName);
return -1;
}
printf("Success!\n");
//读取输入文件的文件头、信息头
fread(&bf, sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER), 1, fpIn);
fread(&bi, sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER), 1, fpIn);
//读取文件信息
biWidth = bi.biWidth;
biHeight = bi.biHeight;
biFullWidth = ceil(biWidth / 4.) * 4;//bmp文件每一行的字节数必须是4的整数倍
biSizeImage = biFullWidth * biHeight;
bfSize = biFullWidth * biHeight + 54 + 256 * 4;//图象文件的大小,包含文件头、信息头
//设置输出文件的BITMAPFILEHEADER
pbf = new BITMAPFILEHEADER;
pbf->bfType = 19778;
pbf->bfSize = bfSize;
pbf->bfReserved1 = 0;
pbf->bfReserved2 = 0;
pbf->bfOffBits = 54 + 256 * 4;
//写出BITMAPFILEHEADER
if (fwrite(pbf, sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER), 1, fpOut) != 1)
{
printf("\nCan't write bitmap file header!\n");
fclose(fpOut);
return -1;
}
//设置输出文件的BITMAPINFOHEADER
pbi = new BITMAPINFOHEADER;
pbi->biSize = 40;
pbi->biWidth = biWidth;
pbi->biHeight = biHeight;
pbi->biPlanes = 1;
pbi->biBitCount = 8;
pbi->biCompression = 0;
pbi->biSizeImage = biSizeImage;
pbi->biXPelsPerMeter = 0;
pbi->biYPelsPerMeter = 0;
pbi->biClrUsed = 0;
pbi->biClrImportant = 0;
//写出BITMAPFILEHEADER
if (fwrite(pbi, sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER), 1, fpOut) != 1)
{
printf("\nCan't write bitmap info header!\n");
fclose(fpOut);
return -1;
}
//构建颜色八叉树
printf("Building Color OctTree ... ");
octTree* tree;
tree = new octTree(256);
uint8 RGB[3];
//读取图像中每个像素的颜色,并将其插入颜色八叉树
for (int i = 0; i < bi.biHeight; i++)
{
fseek(fpIn, bf.bfOffBits + i * ceil(biWidth * 3 / 4.) * 4, 0);
for (int j = 0; j < bi.biWidth; j++)
{
//读取一个像素的颜色,并将其插入颜色八叉树
fread(&RGB, 3, 1, fpIn);
tree->insertColor(RGB[2], RGB[1], RGB[0]);
}
}
printf("Success!\n");
//生成并填充调色板
printf("Generating palette ... ");
pRGBQuad = new RGBQUAD[256];
tree->generatePalette(pRGBQuad);
//输出256色调色板
if (fwrite(pRGBQuad, 256 * sizeof(RGBQUAD), 1, fpOut) != 1)
{
printf("\nCan't write palette!\n");
fclose(fpOut);
return -1;
}
printf("Success!\n");
//填充图像数据
printf("Generating the output image ... ");
pImage = new uint8[biSizeImage];
memset(pImage, 0, biSizeImage);
for (int i = 0; i < bi.biHeight; i++)
{
fseek(fpIn, bf.bfOffBits + i * ceil(biWidth * 3 / 4.) * 4, 0);
for (int j = 0; j < bi.biWidth; j++)
{
//读取一个像素的颜色,并将其转换位颜色索引值
fread(&RGB, 3, 1, fpIn);
pImage[i * biFullWidth + j] = selectClosestColor(RGB[2], RGB[1], RGB[0], pRGBQuad);
}
}
//输出图象数据
if (fwrite(pImage, biSizeImage, 1, fpOut) != 1)
{
printf("\nCan't write image data!\n");
fclose(fpOut);
return -1;
}
printf("Success!\n");
delete tree;
delete pbf;
delete pbi;
delete[] pRGBQuad;
delete[] pImage;
fclose(fpIn);
fclose(fpOut);
printf("All done!\n");
return 0;
}