.NET Core玩转机器学习
ML.NET 专门为.NET开发者提供了一套跨平台的开源的机器学习框架。
ML.NET支持.NET开发者不需要过度专业的机器学习开发经验,就能轻松地训练自己的模型,并且嵌入到自己的应用中。一切尽在.NET之中。ML.NET早期是由Microsoft Research开发,近十年来逐步集成到一个大体系中被众多Microsoft产品使用,如大家熟知的Windows、Bing、PowerPoint、Excel之类。
ML.NET的第一个预览版提供了分类器(如文本分类、情感分析)和回归(如价格预测)等实用的机器学习模型。第一版发布后在既有功能之上又新增了关于训练模型的.NET API,使用这些模型进行预测,就像框架中算法、转换、数据结构一类核心组件一样的开发体验。
接下来用个示例,一起进入快速上手的实践中来。
安装.NET SDK
为了创建一个.NET应用,首先下载 .NET SDK。
创建应用
使用如下命令初始化项目,创建一个控制台应用程序,目标为myApp:
dotnet new console -o myAppcd myApp安装ML.NET包
使用如下命令安装Microsoft.ML包:
dotnet add package Microsoft.ML下载数据集
假设我们使用机器学习来预测鸢尾花的类型,比如有setosa、versicolor、virginica三种,基于特征有四种:花瓣长度、花瓣宽度, 萼片长度、萼片宽度。
去UCI Machine Learning Repository: Iris Data Set下载一个现成的数据集,复制粘贴其中的数据到任何一个文本编辑器中,然后保存命名为iris-data.txt到myApp目录中。
粘贴完文本内容应该是如下格式,每一行表示不同鸢尾花的样本,数值的部分从左到右依次是萼片长度、萼片宽度、花瓣长度、花瓣宽度,最后是鸢尾花的类型。
5.1,3.5,1.4,0.2,Iris-setosa 4.9,3.0,1.4,0.2,Iris-setosa 4.7,3.2,1.3,0.2,Iris-setosa ...
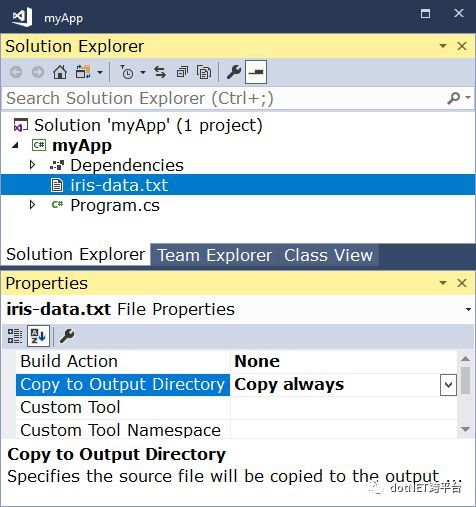
如果是使用了Visual Studio,将iris-data.txt添加至项目中,需要进行如下配置确保运行时数据集文件在输出的目录中。
编写代码
打开Program.cs文件,输入以下代码:
using Microsoft.ML;
using Microsoft.ML.Runtime.Api;
using Microsoft.ML.Trainers;
using Microsoft.ML.Transforms;
using System;
namespace myApp
{
class Program
{
// STEP 1: Define your data structures
// IrisData is used to provide training data, and as
// input for prediction operations
// - First 4 properties are inputs/features used to predict the label
// - Label is what you are predicting, and is only set when training
public class IrisData
{
[Column("0")]
public float SepalLength;
[Column("1")]
public float SepalWidth;
[Column("2")]
public float PetalLength;
[Column("3")]
public float PetalWidth;
[Column("4")]
[ColumnName("Label")]
public string Label;
}
// IrisPrediction is the result returned from prediction operations
public class IrisPrediction
{
[ColumnName("PredictedLabel")]
public string PredictedLabels;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// STEP 2: Create a pipeline and load your data
var pipeline = new LearningPipeline();
// If working in Visual Studio, make sure the 'Copy to Output Directory'
// property of iris-data.txt is set to 'Copy always'
string dataPath = "iris-data.txt";
pipeline.Add(new TextLoader
// STEP 3: Transform your data
// Assign numeric values to text in the "Label" column, because only
// numbers can be processed during model training
pipeline.Add(new Dictionarizer("Label"));
// Puts all features into a vector
pipeline.Add(new ColumnConcatenator("Features", "SepalLength", "SepalWidth", "PetalLength", "PetalWidth"));
// STEP 4: Add learner
// Add a learning algorithm to the pipeline.
// This is a classification scenario (What type of iris is this?)
pipeline.Add(new StochasticDualCoordinateAscentClassifier());
// Convert the Label back into original text (after converting to number in step 3)
pipeline.Add(new PredictedLabelColumnOriginalValueConverter() { PredictedLabelColumn = "PredictedLabel" });
// STEP 5: Train your model based on the data set
var model = pipeline.Train
// STEP 6: Use your model to make a prediction
// You can change these numbers to test different predictions
var prediction = model.Predict(new IrisData()
{
SepalLength = 3.3f,
SepalWidth = 1.6f,
PetalLength = 0.2f,
PetalWidth = 5.1f,
});
Console.WriteLine($"Predicted flower type is: {prediction.PredictedLabels}");
}
}
}
运行应用
使用如下命令行运行程序:
dotnet run在最后一行将输出对花的预测结果,你可以修改传给Predict函数各种鸢尾花的特征值看看有什么不同的结果。
恭喜,你已经跨入使用ML.NET进行机器学习的门槛了!
原文地址: https://www.cnblogs.com/Wddpct/p/9002242.html
.NET社区新闻,深度好文,欢迎访问公众号文章汇总 http://www.csharpkit.com
![]()